当前位置:网站首页>max-flow min-cut
max-flow min-cut
2022-07-06 09:46:00 【C_ eeking】
Max flow min cut
Algorithmic thought
The maximum flow minimum cut mainly uses its theorem to calculate the capacity of the minimum cut , Maximum flow minimum cut theorem : The flow of the largest flow in any network is equal to the capacity of the smallest cut , No detailed proof is given here , Only discuss relevant concepts
cut : Network node division , All nodes are divided into S , T S,T S,T Two sets , Source point s ∈ S s∈S s∈S, Confluence t ∈ T t∈T t∈T, Cut is recorded as C U T ( S , T ) CUT(S,T) CUT(S,T), Like a knife, the node is divided into two parts
Net flow cut : aggregate S S S And collection T T T Between the connected edges , from S S S To T T T The edge of Of Sum of capacity , The minimum cut is the cut with the minimum capacity
if f f f For a stream of the network , C U T ( S , T ) CUT(S,T) CUT(S,T) For any cut of the network , that f f f The flow value of is equal to the net flow of the cut f ( S , T ) f(S,T) f(S,T) And f f f The flow value of does not exceed the capacity of the cut c ( S , T ) c(S,T) c(S,T), All flow values are less than or equal to the cut flow
Maximum flow minimum cut theorem : if f f f Is the largest flow of the network , C U T ( S , T ) CUT(S,T) CUT(S,T) Is the minimum cut of the network , Then the maximum flow value is equal to the minimum cutting capacity
Training
POJ3469
The main idea of the topic : Yes A,B Two core CPU function N A module , Each module has the cost of running on the corresponding core , And there are M Modules need data exchange , If the module is running on the same core , Then the data exchange cost can be ignored , Otherwise, it will cost the given cost , Find the minimum total cost
Ideas : Each module is either in A On , Either in B On , in other words , Last All points will be divided into two sets , This is somewhat similar to a bipartite graph , But these two sets have edges inside , Does not conform to the definition of bipartite graph , So we can consider the minimum cut , Divide all points into two sets , Running on the A The module on is seen as S S S aggregate , stay B See on T T T aggregate , As shown in the figure , The edges cut by the cutting line include S S S The modules in the collection are A Operating costs on a 1 , a 2 , … , a n a_1,a_2,\dots,a_n a1,a2,…,an,T Assemble in B Operating costs on b 1 , b 2 , … b n b_1,b_2,\dots b_n b1,b2,…bn And the cost of data exchange between modules , The original problem is transformed into the problem of finding the minimum cut , Then it is transformed into the problem of finding the maximum flow 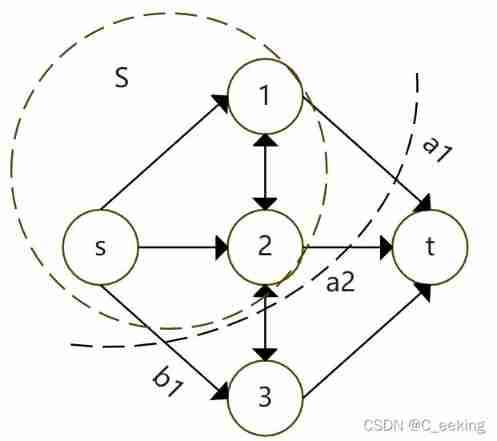
Code
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstring>
#include <queue>
using namespace std;
const int maxn=2e4+10;
const int inf=0x3f3f3f3f;
int n,m,head[maxn],cnt,d[maxn];
struct node {
int next,to,cap,flow;
} e[maxn*60];
void Add(int from,int to,int cap,int flow) {
e[cnt].next=head[from];
e[cnt].to=to;
e[cnt].cap=cap;
e[cnt].flow=flow;
head[from]=cnt++;
}
bool BFS(int s,int t) {
// layered
memset(d,0,sizeof(d));
queue<int>q;
q.push(s);
d[s]=1;
while(!q.empty()) {
int u=q.front();
q.pop();
for(int i=head[u]; ~i; i=e[i].next) {
int v=e[i].to;
if(!d[v]&&e[i].cap>e[i].flow) {
// If the current can be increased
d[v]=d[u]+1;
q.push(v);
if(v==t)return 1;
}
}
}
return 0;
}
int DFS(int u,int flow,int t) {
if(u==t)return flow;
int res=flow;//res Store the current increment value of the current node
for(int i=head[u]; ~i&&res; i=e[i].next) {
// Traverse the adjacent edges satisfying the conditions and increase the current
int v=e[i].to;
if(d[v]==d[u]+1&&e[i].cap>e[i].flow) {
int k=DFS(v,min(res,e[i].cap-e[i].flow),t);// Get the smallest backtracking flow
if(!k)d[v]=0;
e[i].flow+=k;// Increase the flow after obtaining the minimum backtracking flow
e[i^1].flow-=k;
res-=k;// The current increment value decreases , Because the adjacent side has increased the current
}
}
return flow-res;// Return the actual total current increase value
}
int Dinic(int s,int t) {
int ans=0;// Store maximum stream
while(BFS(s,t))ans+=DFS(s,inf,t);
return ans;
}
int main() {
scanf("%d%d",&n,&m);
int s=0,t=n+1;
memset(head,-1,sizeof(head));
for(int i=1; i<=n; i++) {
int a,b;
scanf("%d%d",&a,&b);
Add(s,i,a,0);// Drawing
Add(i,s,0,0);// Residual network edge building
Add(i,t,b,0);
Add(t,i,0,0);
}
while(m--) {
int a,b,w;
scanf("%d%d%d",&a,&b,&w);
Add(a,b,w,0);// Drawing
Add(b,a,0,0);// Residual network edge building
Add(b,a,w,0);
Add(a,b,0,0);
}
printf("%d",Dinic(s,t));
return 0;
}
LuoguP2762
The main idea of the topic : A little
Ideas : Obviously , Instruments and experiments form a bipartite diagram , You can try to solve it with network flow correlation algorithm , Add source connection experiment , Instrument connection junction , There is no capacity constraint between experiment and instrument , The capacity constraint is set to infinity , Pictured , Take the selected experiments and instruments as S aggregate , The rest of the composition T aggregate
Net profit = Selected experimental benefits - The cost of the selected instrument = ∑ E i ∈ S p i − ∑ I k ∈ S c k \sum_{E_i∈S}p_i-\sum_{I_k∈S}c_k ∑Ei∈Spi−∑Ik∈Sck
And the selected experimental income = All experimental benefits - Experimental income is not selected , Then the original formula can be changed to
∑ E i ∈ S p i − ∑ I k ∈ S c k \sum_{E_i∈S}p_i-\sum_{I_k∈S}c_k ∑Ei∈Spi−∑Ik∈Sck
= ∑ i = 1 m p i − ∑ E i ∈ T p i − ∑ I k ∈ S c k =\sum_{i=1}^mp_i-\sum_{E_i∈T}p_i-\sum_{I_k∈S}c_k =∑i=1mpi−∑Ei∈Tpi−∑Ik∈Sck
= ∑ i = 1 m p i − ( ∑ E i ∈ T p i + ∑ I k ∈ S c k ) =\sum_{i=1}^mp_i-(\sum_{E_i∈T}p_i+\sum_{I_k∈S}c_k) =∑i=1mpi−(∑Ei∈Tpi+∑Ik∈Sck)
and ∑ E i ∈ T p i + ∑ I k ∈ S c k \sum_{E_i∈T}p_i+\sum_{I_k∈S}c_k ∑Ei∈Tpi+∑Ik∈Sck Is the sum of the edge capacities on the cutting line , Immediate cut , In order to maximize the total income , Then the minimum cut is required , Then find the maximum flow
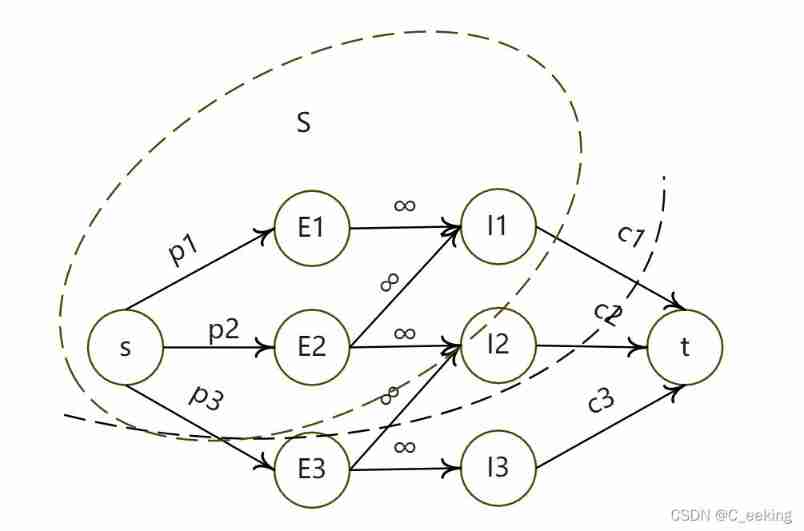
Code
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
const int inf=0x3f3f3f3f;
const int maxn=1e4;
int n,m,head[maxn],cnt,ve,vi,sum,d[maxn];
struct node {
int to,next,cap,flow;
} e[maxn];
void Add(int from,int to,int cap,int flow) {
e[cnt].cap=cap;
e[cnt].flow=flow;
e[cnt].to=to;
e[cnt].next=head[from];
head[from]=cnt++;
}
bool BFS(int s,int t) {
// layered
memset(d,0,sizeof(d));
queue<int>q;
q.push(s);
d[s]=1;
while(!q.empty()) {
int u=q.front();
q.pop();
for(int i=head[u]; ~i; i=e[i].next) {
int v=e[i].to;
if(!d[v]&&e[i].cap>e[i].flow) {
// If the current can be increased
d[v]=d[u]+1;
q.push(v);
if(v==t)return 1;
}
}
}
return 0;
}
int DFS(int u,int flow,int t) {
if(u==t)return flow;
int res=flow;//res Store the current increment value of the current node
for(int i=head[u]; ~i&&res; i=e[i].next) {
// Traverse the adjacent edges satisfying the conditions and increase the current
int v=e[i].to;
if(d[v]==d[u]+1&&e[i].cap>e[i].flow) {
int k=DFS(v,min(res,e[i].cap-e[i].flow),t);// Get the smallest backtracking flow
if(!k)d[v]=0;
e[i].flow+=k;// Increase the flow after obtaining the minimum backtracking flow
e[i^1].flow-=k;
res-=k;// The current increment value decreases , Because the adjacent side has increased the current
}
}
return flow-res;// Return the actual total current increase value
}
int Dinic(int s,int t) {
int ans=0;// Store maximum stream
while(BFS(s,t))
ans+=DFS(s,inf,t);
return ans;
}
int main() {
scanf("%d%d",&m,&n);
int s=0,t=n+m+1;
memset(head,-1,sizeof(head));
for(int i=1; i<=m; i++ ) {
scanf("%d",&ve);
Add(s,i,ve,0);
Add(i,s,0,0);
sum+=ve;
char tools[10000];
memset(tools,0,sizeof tools);
cin.getline(tools,10000);
int ulen=0,tool;
while (sscanf(tools+ulen,"%d",&tool)==1) {
// It has been used before scanf After reading, the sponsor agrees to pay for the experiment
//tool It is one of the instruments required for this experiment
// This business , You can save the number read in 、 Handle , Such as connecting sides .
Add(i,tool+m,inf,0);
Add(tool+m,i,0,0);
if (tool==0)
ulen++;
else
while (tool) {
tool/=10;
ulen++;
}
ulen++;
}
}
for(int i=1; i<=n; i++) {
int w;
scanf("%d",&w);
Add(i+m,t,w,0);
Add(t,i+m,0,0);
}
int mx=Dinic(s,t);
for(int i=1; i<=m; i++)
if(d[i])printf("%d ",i);
putchar('\n');
for(int i=m+1; i<=m+n; i++)
if(d[i])printf("%d ",i-m);
putchar('\n');
printf("%d",sum-mx);
return 0;
}
LuoguP4210
The main idea of the topic : A little
Ideas : First of all , Why is the minimum cut , Why the minimum cut is required
According to the meaning , Divide all points into A,B Two large sets , Then the total income is ∑ i ∈ A V a i + ∑ i ∈ B V b i − ∑ i ∈ A V b i − ∑ i ∈ B V a i − ∑ i ∈ A , j ∈ B E i , j + ∑ i ∈ A , j ∈ A E i , j + ∑ i ∈ B , j ∈ B E i , j \sum_{i∈A} V_{a_i}+\sum_{i∈B} V_{b_i}-\sum_{i∈A} V_{b_i}-\sum_{i∈B} V_{a_i}-\sum_{i∈A,j∈B}E_{i,j}+\sum_{i∈A,j∈A}E_{i,j}+\sum_{i∈B,j∈B}E_{i,j} ∑i∈AVai+∑i∈BVbi−∑i∈AVbi−∑i∈BVai−∑i∈A,j∈BEi,j+∑i∈A,j∈AEi,j+∑i∈B,j∈BEi,j, That is to say , All points are in A Medium income + All points are in B Medium income - stay A In the middle of B earnings - stay B In the middle of A earnings - Connect A,B Edge income of set + Connect A Edge income of set + Connect B Edge income of set , Pictured , and ∑ i ∈ A V b i + ∑ i ∈ B V a i + ∑ i ∈ A , j ∈ B E i , j \sum_{i∈A} V_{b_i}+\sum_{i∈B} V_{a_i}+\sum_{i∈A,j∈B}E_{i,j} ∑i∈AVbi+∑i∈BVai+∑i∈A,j∈BEi,j It just corresponds to the edge of the cutting line in the figure , Just the cutting capacity , Then for the best interests of the whole , You need the minimum cut , Then find the maximum flow 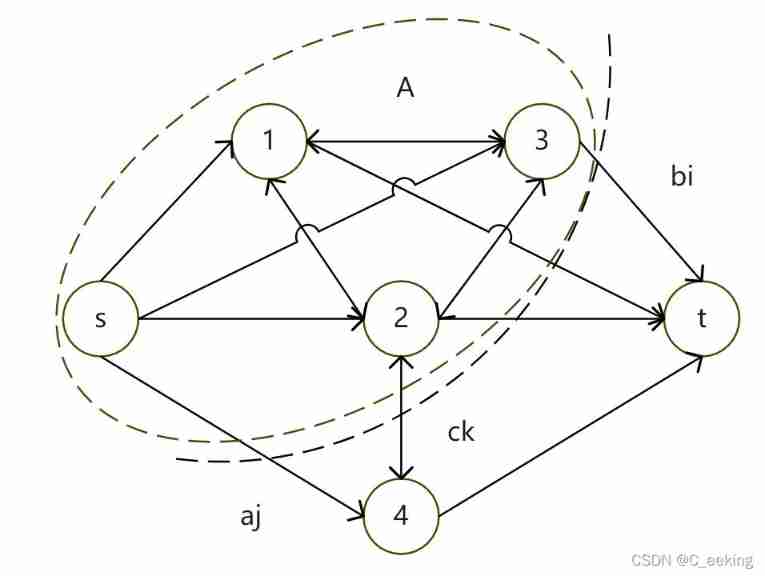 The next step is drawing , Divide points into A,B Two parts , Let's make A As S aggregate ,T As B aggregate , Point revenue can be directly connected with the corresponding source point and sink point , What is difficult to deal with is the side benefit of the problem ,
The next step is drawing , Divide points into A,B Two parts , Let's make A As S aggregate ,T As B aggregate , Point revenue can be directly connected with the corresponding source point and sink point , What is difficult to deal with is the side benefit of the problem ,
For a given edge , If the side Must belong to A, Then you will lose B Revenue , Then the minimum cut must include This is the edge B The benefits on , For the sake of representation , Put this side on B The income on the market is divided into two , Give two endpoints , That is, there are two more endpoints and two more flows to the sink , The minimum cut either passes through these two flows at the same time , Or don't go through ( On behalf of side return B 了 ), Yes, it must belong to B So is the point of
Next, consider another case of edges , Both belong to A, Also belong to B, If the minimum cut must pass through this edge , Then it must include this side A,B Income and negative income C, That is to connect the two ends , Flow is ABC The benefits and ( Repeat here , Finally, divide the result by 2 that will do )
Because the data may be odd, it cannot be divided into two , Multiply the data by 2 Divide the result by 2
Code
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
const int inf=0x3f3f3f3f;
const int maxn=1e4+10;
int n,m,cnt,head[maxn],d[maxn];
struct node {
int to,next,cap,flow;
} e[maxn*80];
void Add(int from,int to,int cap,int flow) {
e[cnt].to=to;
e[cnt].next=head[from];
e[cnt].flow=flow;
e[cnt].cap=cap;
head[from]=cnt++;
}
bool BFS(int s,int t) {
// layered
memset(d,0,sizeof(d));
queue<int>q;
q.push(s);
d[s]=1;
while(!q.empty()) {
int u=q.front();
q.pop();
for(int i=head[u]; ~i; i=e[i].next) {
int v=e[i].to;
if(!d[v]&&e[i].cap>e[i].flow) {
// If the current can be increased
d[v]=d[u]+1;
q.push(v);
if(v==t)return 1;
}
}
}
return 0;
}
int DFS(int u,int flow,int t) {
if(u==t)return flow;
int res=flow;//res Store the current increment value of the current node
for(int i=head[u]; ~i&&res; i=e[i].next) {
// Traverse the adjacent edges satisfying the conditions and increase the current
int v=e[i].to;
if(d[v]==d[u]+1&&e[i].cap>e[i].flow) {
int k=DFS(v,min(res,e[i].cap-e[i].flow),t);// Get the smallest backtracking flow
if(!k)d[v]=0;
e[i].flow+=k;// Increase the flow after obtaining the minimum backtracking flow
e[i^1].flow-=k;
res-=k;// The current increment value decreases , Because the adjacent side has increased the current
}
}
return flow-res;// Return the actual total current increase value
}
int Dinic(int s,int t) {
int ans=0;// Store maximum stream
while(BFS(s,t))
ans+=DFS(s,inf,t);
return ans;
}
int main() {
scanf("%d%d",&n,&m);
int s=0,t=n+1,sum=0;
memset(head,-1,sizeof(head));
Add(s,1,inf,0),Add(1,s,0,0);
Add(n,t,inf,0),Add(t,n,0,0);
for(int i=2; i<=n-1; i++) {
int v;
scanf("%d",&v);
v*=2;
sum+=v;
Add(s,i,v,0),Add(i,s,0,0);
}
for(int i=2; i<=n-1; i++) {
int v;
scanf("%d",&v);
v*=2;
sum+=v;
Add(i,t,v,0),Add(t,i,0,0);
}
while(m--) {
int x,y,ea,eb,ec;
scanf("%d%d%d%d%d",&x,&y,&ea,&eb,&ec);
ea*=2;
eb*=2;
ec*=2;
sum+=ea+eb;
Add(x,y,(ea/2+eb/2+ec),0),Add(y,x,(ea/2+eb/2+ec),0);
Add(s,x,ea/2,0),Add(x,s,0,0);
Add(s,y,ea/2,0),Add(y,s,0,0);
Add(x,t,eb/2,0),Add(t,x,0,0);
Add(y,t,eb/2,0),Add(t,y,0,0);
}
printf("%d",(sum-Dinic(s,t))/2);
return 0;
}
LuoguP4177
The main idea of the topic : A little
Ideas : If there is no rent / Buy this operation , Then this topic is the classic topic of maximal weighted closed subgraph , The ordinary maximum weight closed subgraph connects the source point with the work , Edge right is income , The machine is connected to the sink , At the expense of edge power , The correspondence between work and machine is infinite , And there is one more rental in this topic , Then there is a kind of edge right that needs to be changed , You can replace infinity with the corresponding leased edge , From the perspective of correctness , When solving the optimal solution , If the total rental cost is lower than the cost of purchasing the machine , The edge weight of the machine and the meeting point will not be full , Prevent the purchase of machines from increasing costs , On the contrary, the edge weight of the machine and the meeting point will be full , Limit costs and prevent multiple rentals
Code
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define int long long
using namespace std;
const int maxn=3e6;
const int inf=0x3f3f3f3f;
int n,m,cnt,head[2424],d[2424];// Don't open the memory too much
struct node {
int next,to,cap,flow;
} e[maxn];
void Add(int from,int to,int cap,int flow) {
e[cnt].to=to;
e[cnt].next=head[from];
e[cnt].cap=cap;
e[cnt].flow=flow;
head[from]=cnt++;
}
bool BFS(int s,int t) {
// layered
memset(d,0,sizeof(d));
queue<int>q;
q.push(s);
d[s]=1;
while(!q.empty()) {
int u=q.front();
q.pop();
for(int i=head[u]; ~i; i=e[i].next) {
int v=e[i].to;
if(!d[v]&&e[i].cap>e[i].flow) {
// If the current can be increased
d[v]=d[u]+1;
q.push(v);
if(v==t)return 1;
}
}
}
return 0;
}
int DFS(int u,int flow,int t) {
if(u==t)return flow;
int res=flow;//res Store the current increment value of the current node
for(int i=head[u]; ~i&&res; i=e[i].next) {
// Traverse the adjacent edges satisfying the conditions and increase the current
int v=e[i].to;
if(d[v]==d[u]+1&&e[i].cap>e[i].flow) {
int k=DFS(v,min(res,e[i].cap-e[i].flow),t);// Get the smallest backtracking flow
if(!k)d[v]=0;
e[i].flow+=k;// Increase the flow after obtaining the minimum backtracking flow
e[i^1].flow-=k;
res-=k;// The current increment value decreases , Because the adjacent side has increased the current
}
}
return flow-res;// Return the actual total current increase value
}
int Dinic(int s,int t) {
int ans=0;// Store maximum stream
while(BFS(s,t))
ans+=DFS(s,inf,t);
return ans;
}
signed main() {
scanf("%lld%lld",&n,&m);
int s=0,t=n+m+1,sum=0;
memset(head,-1,sizeof(head));
for(int i=1; i<=n; i++) {
int x,k;
scanf("%lld%lld",&x,&k);
sum+=x;
Add(s,i,x,0);
Add(i,s,0,0);
while(k--) {
int a,b;
scanf("%lld%lld",&a,&b);
Add(i,a+n,b,0);
Add(a+n,i,0,0);
}
}
for(int i=1; i<=m; i++) {
int y;
scanf("%lld",&y);
Add(i+n,t,y,0);
Add(t,i+n,0,0);
}
printf("%lld",sum-Dinic(s,t));
return 0;
}
summary
The minimum cut model is generally used to solve The most value of multiple constraints under single set of points and double attribution and The maximum value of multiple constraints under two sets of points and multiple matching , It is similar to bipartite graph , But the minimal cut can have edges in the inner set , This is different from the bipartite graph , It also determines that it cannot use the algorithm of bipartite graph in most cases , For the minimum cut problem , You need to find the conditions for dividing the set , Understand why the set should be divided like this , Beyond the basic point weight and edge weight conditions , How to convert other conditions of the problem into flow and construct in the graph , Mapping is always the most critical step , The next steps are actually fixed
reference
边栏推荐
- 嵌入式開發中的防禦性C語言編程
- 在CANoe中通过Panel面板控制Test Module 运行(高级)
- Programmation défensive en langage C dans le développement intégré
- 《ASP.NET Core 6框架揭秘》样章发布[200页/5章]
- [Chongqing Guangdong education] reference materials for nine lectures on the essence of Marxist Philosophy in Wuhan University
- Processes of libuv
- CANoe的数据回放(Replay Block),还是要结合CAPL脚本才能说的明白
- Solve the problem of too many small files
- Full stack development of quartz distributed timed task scheduling cluster
- 068. Find the insertion position -- binary search
猜你喜欢

MapReduce instance (VI): inverted index
大学想要选择学习自动化专业,可以看什么书去提前了解?

五月集训总结——来自阿光
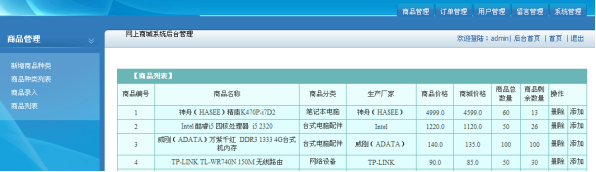
Design and implementation of online shopping system based on Web (attached: source code paper SQL file)
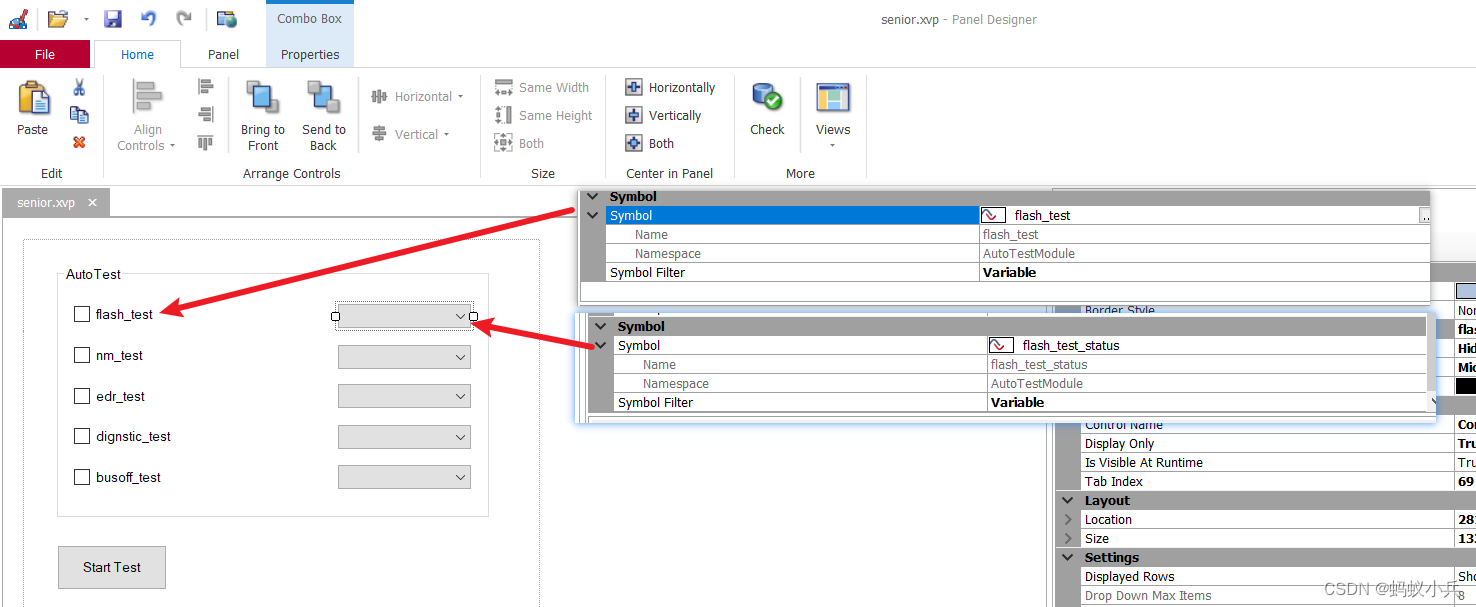
在CANoe中通过Panel面板控制Test Module 运行(高级)

Regular expressions are actually very simple
![《ASP.NET Core 6框架揭秘》样章发布[200页/5章]](/img/4f/5688c391dd19129d912a3557732047.jpg)
《ASP.NET Core 6框架揭秘》样章发布[200页/5章]
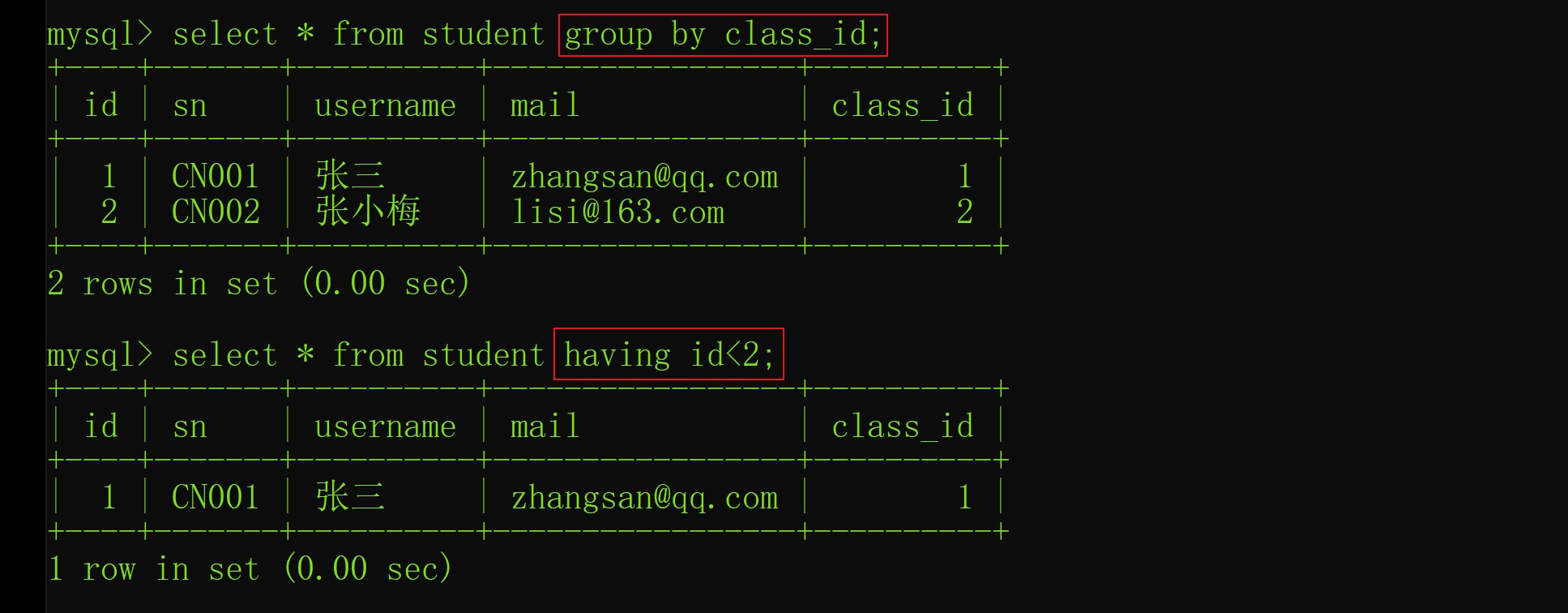
面试突击62:group by 有哪些注意事项?
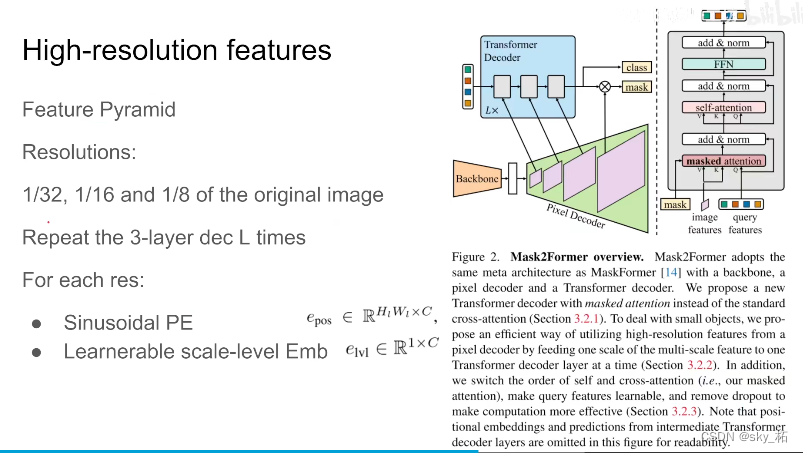
【深度学习】语义分割:论文阅读:(2021-12)Mask2Former
CANoe的数据回放(Replay Block),还是要结合CAPL脚本才能说的明白
随机推荐
嵌入式开发中的防御性C语言编程
CANoe不能自动识别串口号?那就封装个DLL让它必须行
《ASP.NET Core 6框架揭秘》样章发布[200页/5章]
【深度学习】语义分割-源代码汇总
为什么要数据分层
手把手教您怎么编写第一个单片机程序
运维,放过监控-也放过自己吧
六月刷题02——字符串
VH6501学习系列文章
Design and implementation of online shopping system based on Web (attached: source code paper SQL file)
Interview shock 62: what are the precautions for group by?
YARN组织架构
018. Valid palindromes
June brush question 02 - string
Redis distributed lock implementation redison 15 questions
Counter attack of noodles: redis asked 52 questions in a series, with detailed pictures and pictures. Now the interview is stable
Regular expressions are actually very simple
Sqlmap installation tutorial and problem explanation under Windows Environment -- "sqlmap installation | CSDN creation punch in"
Global and Chinese markets for modular storage area network (SAN) solutions 2022-2028: Research Report on technology, participants, trends, market size and share
Une grande vague d'attaques à la source ouverte