当前位置:网站首页>Mapreduce实例(五):二次排序
Mapreduce实例(五):二次排序
2022-07-06 09:01:00 【笑看风云路】
大家好,我是风云,欢迎大家关注我的博客 或者 微信公众号【笑看风云路】,在未来的日子里我们一起来学习大数据相关的技术,一起努力奋斗,遇见更好的自己!
实现思路
在Map阶段,使用job.setInputFormatClass定义的InputFormat将输入的数据集分割成小数据块splites,同时InputFormat提供一个RecordReader的实现。本实验中使用的是TextInputFormat,他提供的RecordReader会将文本的字节偏移量作为key,这一行的文本作为value。这就是自定义Map的输入是<LongWritable, Text>的原因。然后调用自定义Map的map方法,将一个个<LongWritable, Text>键值对输入给Map的map方法。注意输出应该符合自定义Map中定义的输出<IntPair, IntWritable>。最终生成一个List<IntPair, IntWritable>。在map阶段的最后,会先调用job.setPartitionerClass对这个List进行分区,每个分区映射到一个reducer。每个分区内又调用job.setSortComparatorClass设置的key比较函数类排序。可以看到,这本身就是一个二次排序。 如果没有通过job.setSortComparatorClass设置key比较函数类,则可以使用key实现的compareTo方法进行排序。 在本实验中,就使用了IntPair实现的compareTo方法。
在Reduce阶段,reducer接收到所有映射到这个reducer的map输出后,也是会调用job.setSortComparatorClass设置的key比较函数类对所有数据对排序。然后开始构造一个key对应的value迭代器。这时就要用到分组,使用job.setGroupingComparatorClass设置的分组函数类。只要这个比较器比较的两个key相同,他们就属于同一个组,它们的value放在一个value迭代器,而这个迭代器的key使用属于同一个组的所有key的第一个key。最后就是进入Reducer的reduce方法,reduce方法的输入是所有的(key和它的value迭代器)。同样注意输入与输出的类型必须与自定义的Reducer中声明的一致。
代码实现
二次排序:在mapreduce中,所有的key是需要被比较和排序的,并且是二次,先根据partitioner,再根据大小。而本例中也是要比较两次。先按照第一字段排序,然后在第一字段相同时按照第二字段排序。根据这一点,我们可以构造一个复合类IntPair,他有两个字段,先利用分区对第一字段排序,再利用分区内的比较对第二字段排序。Java代码主要分为四部分:自定义key,自定义分区函数类,map部分,reduce部分。
自定义key的代码:
public static class IntPair implements WritableComparable<IntPair>
{
int first; //第一个成员变量
int second; //第二个成员变量
public void set(int left, int right)
{
first = left;
second = right;
}
public int getFirst()
{
return first;
}
public int getSecond()
{
return second;
}
@Override
//反序列化,从流中的二进制转换成IntPair
public void readFields(DataInput in) throws IOException
{
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
first = in.readInt();
second = in.readInt();
}
@Override
//序列化,将IntPair转化成使用流传送的二进制
public void write(DataOutput out) throws IOException
{
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
out.writeInt(first);
out.writeInt(second);
}
@Override
//key的比较
public int compareTo(IntPair o)
{
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
if (first != o.first)
{
return first < o.first ? 1 : -1;
}
else if (second != o.second)
{
return second < o.second ? -1 : 1;
}
else
{
return 0;
}
}
@Override
public int hashCode()
{
return first * 157 + second;
}
@Override
public boolean equals(Object right)
{
if (right == null)
return false;
if (this == right)
return true;
if (right instanceof IntPair)
{
IntPair r = (IntPair) right;
return r.first == first && r.second == second;
}
else
{
return false;
}
}
}
所有自定义的key应该实现接口WritableComparable,因为是可序列的并且可比较的,并重载方法。该类中包含以下几种方法:
1.反序列化,从流中的二进制转换成IntPair 方法为public void readFields(DataInput in) throws IOException
2.序列化,将IntPair转化成使用流传送的二进制 方法为public void write(DataOutput out)
3. key的比较 public int compareTo(IntPair o) 另外新定义的类应该重写的两个方法 public int hashCode() 和public boolean equals(Object right) 。
分区函数类代码
public static class FirstPartitioner extends Partitioner<IntPair, IntWritable>
{
@Override
public int getPartition(IntPair key, IntWritable value,int numPartitions)
{
return Math.abs(key.getFirst() * 127) % numPartitions;
}
}
对key进行分区,根据自定义key中first乘以127取绝对值再对numPartions取余来进行分区。这主要是为实现第一次排序。
分组函数类代码
public static class GroupingComparator extends WritableComparator
{
protected GroupingComparator()
{
super(IntPair.class, true);
}
@Override
//Compare two WritableComparables.
public int compare(WritableComparable w1, WritableComparable w2)
{
IntPair ip1 = (IntPair) w1;
IntPair ip2 = (IntPair) w2;
int l = ip1.getFirst();
int r = ip2.getFirst();
return l == r ? 0 : (l < r ? -1 : 1);
}
}
分组函数类。在reduce阶段,构造一个key对应的value迭代器的时候,只要first相同就属于同一个组,放在一个value迭代器。这是一个比较器,需要继承WritableComparator。
Map代码:
public static class Map extends Mapper<LongWritable, Text, IntPair, IntWritable>
{
//自定义map
private final IntPair intkey = new IntPair();
private final IntWritable intvalue = new IntWritable();
public void map(LongWritable key, Text value, Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException
{
String line = value.toString();
StringTokenizer tokenizer = new StringTokenizer(line);
int left = 0;
int right = 0;
if (tokenizer.hasMoreTokens())
{
left = Integer.parseInt(tokenizer.nextToken());
if (tokenizer.hasMoreTokens())
right = Integer.parseInt(tokenizer.nextToken());
intkey.set(right, left);
intvalue.set(left);
context.write(intkey, intvalue);
}
}
}
Reduce代码:
public static class Reduce extends Reducer<IntPair, IntWritable, Text, IntWritable>
{
private final Text left = new Text();
private static final Text SEPARATOR = new Text("------------------------------------------------");
public void reduce(IntPair key, Iterable<IntWritable> values,Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException
{
context.write(SEPARATOR, null);
left.set(Integer.toString(key.getFirst()));
System.out.println(left);
for (IntWritable val : values)
{
context.write(left, val);
//System.out.println(val);
}
}
}
完整代码:
package mapreduce;
import java.io.DataInput;
import java.io.DataOutput;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.StringTokenizer;
import org.apache.hadoop.conf.Configuration;
import org.apache.hadoop.fs.Path;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.IntWritable;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.LongWritable;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.Text;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.WritableComparable;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.WritableComparator;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Job;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Mapper;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Partitioner;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Reducer;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.input.FileInputFormat;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.input.TextInputFormat;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.output.FileOutputFormat;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.output.TextOutputFormat;
public class SecondarySort
{
public static class IntPair implements WritableComparable<IntPair>
{
int first;
int second;
public void set(int left, int right)
{
first = left;
second = right;
}
public int getFirst()
{
return first;
}
public int getSecond()
{
return second;
}
@Override
public void readFields(DataInput in) throws IOException
{
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
first = in.readInt();
second = in.readInt();
}
@Override
public void write(DataOutput out) throws IOException
{
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
out.writeInt(first);
out.writeInt(second);
}
@Override
public int compareTo(IntPair o)
{
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
if (first != o.first)
{
return first < o.first ? 1 : -1;
}
else if (second != o.second)
{
return second < o.second ? -1 : 1;
}
else
{
return 0;
}
}
@Override
public int hashCode()
{
return first * 157 + second;
}
@Override
public boolean equals(Object right)
{
if (right == null)
return false;
if (this == right)
return true;
if (right instanceof IntPair)
{
IntPair r = (IntPair) right;
return r.first == first && r.second == second;
}
else
{
return false;
}
}
}
public static class FirstPartitioner extends Partitioner<IntPair, IntWritable>
{
@Override
public int getPartition(IntPair key, IntWritable value,int numPartitions)
{
return Math.abs(key.getFirst() * 127) % numPartitions;
}
}
public static class GroupingComparator extends WritableComparator
{
protected GroupingComparator()
{
super(IntPair.class, true);
}
@Override
//Compare two WritableComparables.
public int compare(WritableComparable w1, WritableComparable w2)
{
IntPair ip1 = (IntPair) w1;
IntPair ip2 = (IntPair) w2;
int l = ip1.getFirst();
int r = ip2.getFirst();
return l == r ? 0 : (l < r ? -1 : 1);
}
}
public static class Map extends Mapper<LongWritable, Text, IntPair, IntWritable>
{
private final IntPair intkey = new IntPair();
private final IntWritable intvalue = new IntWritable();
public void map(LongWritable key, Text value, Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException
{
String line = value.toString();
StringTokenizer tokenizer = new StringTokenizer(line);
int left = 0;
int right = 0;
if (tokenizer.hasMoreTokens())
{
left = Integer.parseInt(tokenizer.nextToken());
if (tokenizer.hasMoreTokens())
right = Integer.parseInt(tokenizer.nextToken());
intkey.set(right, left);
intvalue.set(left);
context.write(intkey, intvalue);
}
}
}
public static class Reduce extends Reducer<IntPair, IntWritable, Text, IntWritable>
{
private final Text left = new Text();
private static final Text SEPARATOR = new Text("------------------------------------------------");
public void reduce(IntPair key, Iterable<IntWritable> values,Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException
{
context.write(SEPARATOR, null);
left.set(Integer.toString(key.getFirst()));
System.out.println(left);
for (IntWritable val : values)
{
context.write(left, val);
//System.out.println(val);
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, InterruptedException, ClassNotFoundException
{
Configuration conf = new Configuration();
Job job = new Job(conf, "secondarysort");
job.setJarByClass(SecondarySort.class);
job.setMapperClass(Map.class);
job.setReducerClass(Reduce.class);
job.setPartitionerClass(FirstPartitioner.class);
job.setGroupingComparatorClass(GroupingComparator.class);
job.setMapOutputKeyClass(IntPair.class);
job.setMapOutputValueClass(IntWritable.class);
job.setOutputKeyClass(Text.class);
job.setOutputValueClass(IntWritable.class);
job.setInputFormatClass(TextInputFormat.class);
job.setOutputFormatClass(TextOutputFormat.class);
String[] otherArgs=new String[2];
otherArgs[0]="hdfs://localhost:9000/mymapreduce8/in/goods_visit2";
otherArgs[1]="hdfs://localhost:9000/mymapreduce8/out";
FileInputFormat.setInputPaths(job, new Path(otherArgs[0]));
FileOutputFormat.setOutputPath(job, new Path(otherArgs[1]));
System.exit(job.waitForCompletion(true) ? 0 : 1);
}
}
-------------- end ----------------
微信公众号:扫描下方二维码或 搜索 笑看风云路 关注
边栏推荐
- Post training quantification of bminf
- Meituan Er Mian: why does redis have sentinels?
- [shell script] use menu commands to build scripts for creating folders in the cluster
- Redis之cluster集群
- Different data-driven code executes the same test scenario
- Mysql database recovery (using mysqlbinlog command)
- Multivariate cluster analysis
- Detailed explanation of cookies and sessions
- Sqlmap installation tutorial and problem explanation under Windows Environment -- "sqlmap installation | CSDN creation punch in"
- Intel distiller Toolkit - Quantitative implementation 1
猜你喜欢

Pytest parameterization some tips you don't know / pytest you don't know
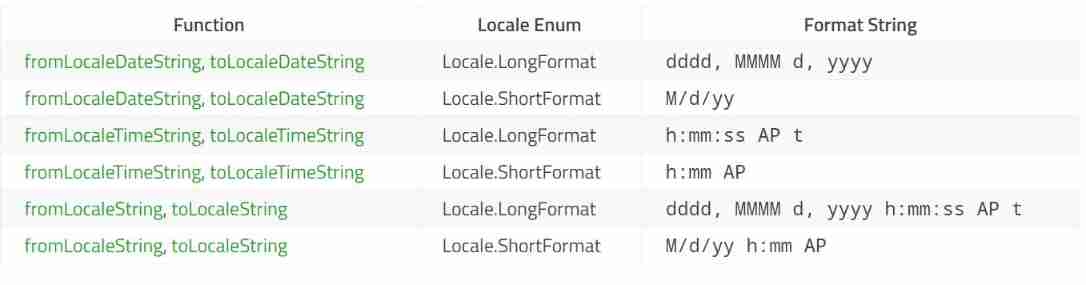
QML type: locale, date

In depth analysis and encapsulation call of requests
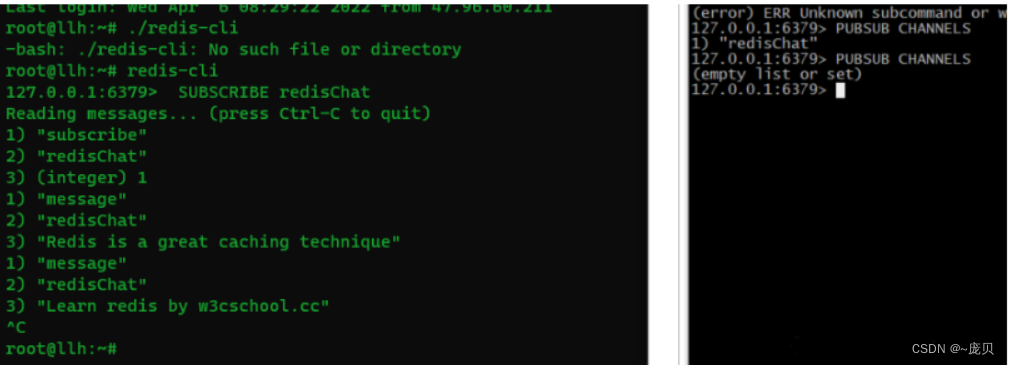
Redis之发布订阅
![[shell script] - archive file script](/img/50/1bef6576902890dfd5771500414876.png)
[shell script] - archive file script
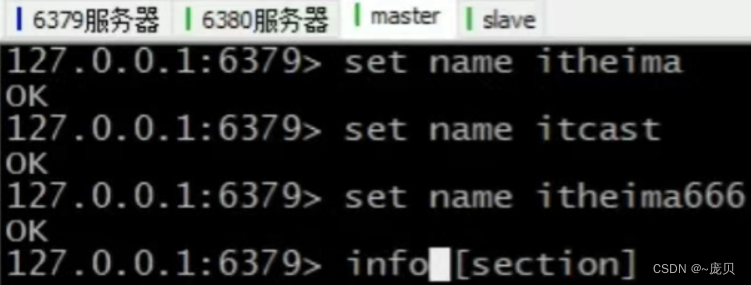
Master slave replication of redis
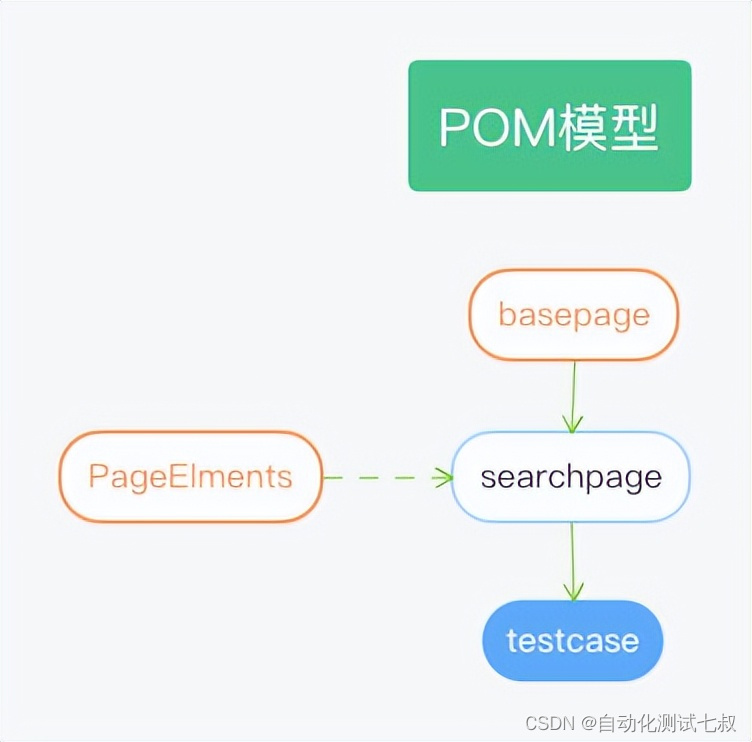
Selenium+Pytest自动化测试框架实战
Simclr: comparative learning in NLP

IDS' deletion policy

KDD 2022 paper collection (under continuous update)
随机推荐
leetcode-14. Longest common prefix JS longitudinal scanning method
CUDA realizes focal_ loss
CSP student queue
【shell脚本】使用菜单命令构建在集群内创建文件夹的脚本
What is MySQL? What is the learning path of MySQL
requests的深入刨析及封装调用
[oc]- < getting started with UI> -- learning common controls
Implement window blocking on QWidget
Advanced Computer Network Review(4)——Congestion Control of MPTCP
One article read, DDD landing database design practice
Kratos战神微服务框架(三)
Kratos ares microservice framework (II)
工作流—activiti7环境搭建
五层网络体系结构
英雄联盟轮播图自动轮播
Seven layer network architecture
Servlet learning diary 7 -- servlet forwarding and redirection
Digital people anchor 618 sign language with goods, convenient for 27.8 million people with hearing impairment
Design and implementation of online snack sales system based on b/s (attached: source code paper SQL file)
Redis之连接redis服务命令