当前位置:网站首页>Sed text processing
Sed text processing
2022-07-06 10:09:00 【wx5caecf2ed0645】
1. Basic overview
sed It's a stream editor , Non interactive editor , It processes one line at a time . When dealing with , Store the currently processed rows in a temporary buffer , call *
by “ Mode space ”(pattern space) Then use sed Command processing buffer contents , After processing , Send the contents of the buffer to the screen . Pick up
Wait for the next line , This is repeated , Until the end of the file . The contents of the document have not changed , Unless you Use redirection to store output . Sed To use from
Edit one or more files automatically ; Simplify file manipulation ; Write conversion program, etc .
2..sed Basic grammar
The first form :stdout | sed [option] "pattern command"
The second form : sed [option] "pattern command" file
3..sed Common options -i -r
sed Related sample files
[[email protected] opt]# cat file.txt
I love shell
I love SHELL
This is test file
1.sed-n、-e Examples of options
# Cancel default output
[[email protected] opt]# sed -n '/shell/p' file.txt
I love shell
# Edit multiple items
[[email protected] opt]# sed -n -e '/shell/p' -e '/SHELL/p' file.txt
I love shell
I love SHELL
2.sed -f Examples of options
# take pattern Write to file
[[email protected] opt]# cat edit.sed
/shell/p
[[email protected] opt]# sed -n -f edit.sed file.txt
3.sed -r Examples of options
[[email protected] opt]# sed -n '/shell|SHELL/p' file.txt
# Extended regular expression
[[email protected] opt]# sed -rn '/shell|SHELL/p' file.txt
I love shell
I love SHELL
4.sed -i Options
[[email protected] sed]# sed -in '/shell/d' file.txt
3.sed pattern
sed -n '10p' passwd
sed -n '10,20p' passwd
sed -n '1,+5p' passwd
sed -n '/^root/p' passwd
sed -n '/^root/,/^ftp/p' passwd
sed -n '/^\[mysql.*/,/^\[mysqld_safe\]/p' /etc/my.cnf|grep -v "^\[.*"
sed -n '2,/\/bin\/sync/p' passwd
1) Print /etc/passwd pass the civil examinations 20 That's ok
sed -n '20p' /etc/passwd
2) Print /etc/passwd From the first 8 OK, let's start , To the first 15 What's at the end of the line
sed -n '8,15p' /etc/passwd
3) Print /etc/passwd From the first 8 OK, let's start , then +5 What's at the end of the line
sed -n '8,+5p' /etc/passwd
4) Print /etc/passwd Match at the beginning of bin The contents of a string
sed -n '/^bin/p' /etc/passwd
5) Print /etc/passwd The middle begins with root Start of line for , To start with ftp The end of the line
sed -n '/^root/,/^ftp/p' /etc/passwd
6) Print /etc/passwd pass the civil examinations 8 OK, let's start , To contain /sbin/nologin The end of the content line
sed -n '8,/\/sbin\/nologin/p' /etc/passwd
4.sed Additional orders
[[email protected] sed]# sed -i '/^root/i server {\n\tlisten 80;\n\tserver_name oldxu.com;\n\tindex index.html;\n\troot /code;\n}' passwd
server {
listen 80;
server_name oldxu.com;
index index.html;
root /code;
}
Examples of exercises in this chapter :
1) passwd Document No 10 Add “Add Line”
sed -i '10a "Add Line"' passwd
2)passwd Document No 10 Go to the first place 20 That's ok , No line is followed by "Test Line"
sed -i '10,20a "Test Line"' passwd
3)passwd The file matches to /bin/bash Add "Insert Line"
sed -i '/\/bin\/bash/a "Insert Line"' passwd
4)passwd The file matches to bin Beginning line , Append "Add Line Before"
sed -i '/^bin/i "Add Line Before"' passwd
5)passwd Every line of the file is preceded by "Insert Line Before"
sed -i 'i "Insert Line Before"' passwd
6) take /etc/fstab The contents of the document are appended to passwd File first 10 After line
sed -i '10r /etc/fstab' passwd
7) take /etc/inittab The contents of the document are appended to passwd File matching /bin/sync The back of the line
sed -i '/\/bin\/sync/r /etc/inittab' passwd
8) take /etc/hosts The contents of the document are appended to passwd In file 10 The back of the line
sed -i '10r /etc/hosts' passwd
9) take passwd The file matches to /bin/bash The line of is appended to /tmp/sed.txt In file
sed -i '/\/bin\/bash/w /tmp/sed.txt' passwd
10) take passwd Document cluster 10 OK, let's start , To match to nfsnobody All lines at the beginning are appended to /tmp/sed-1.txt
sed -i '10,/^nfsnobody/w /tmp/sed-1.txt' passwd
5.sed The delete command
Examples of exercises in this chapter :
1) Delete passwd No 15 That's ok
sed -i '15d' passwd
2) Delete passwd No 8 Go to the first place 14 All the content of the line
sed -i '8,14d' passwd
3) Delete passwd China and Israel /sbin/nologin The line at the end
sed -i '/\/sbin\/nologin$/d' passwd
4) Delete passwd China and Israel bin Beginning line , To ntp All the contents of the first line
sed -i '/^bin/,/^ntp/d' passwd
5) Delete passwd pass the civil examinations 3 So far as ftp All lines at the beginning
sed '3,/^ftp/d' passwd
6) Typical demand : Delete Nginx All comments and blank lines in the configuration file
sed -ri '/^#|^$| #/d' nginx.conf
6.sed Modify the order s///g <-- Replace c modify
sed '/^SELINUX=/c SELINUX=disabled'
1. modify passwd Document No 1 The first one in the line root by ROOT
sed -i '1s/root/ROOT/' passwd
2. modify passwd Document No. 5 Go to the first place 10 All in row /sbin/nologin by /bin/bash
sed -i '5,10s/\/sbin\/nologin/\/bin\/bash/' passwd
sed -i '5,10s#/sbin/nologin#/bin/bash#' passwd
3. modify passwd The file matches with /sbin/nologin The line of , Match to login
It is capitalized LOGIN
sed -i '/\/sbin\/nologin/s#login#LOGIN#g' passwd
sed -i '/\/sbin\/nologin/s/login/LOGIN#g' passwd
4. modify passwd The file matches from to with root Beginning line , To match to bin Start line , modify bin by BIN
sed -i '/^root/,/^bin/s/bin/BIN/g' passwd
5. modify SELINUX=enforcing It is amended as follows SELINUX=disabled.( have access to c Alternative )
sed -i '/^SELINUX=/c SELINUX=disabled' selinux
6. take nginx.conf Add comments to the configuration file . ^ $
sed -i 's/^/# /' nginx.conf
7. Use sed extract eth0 NIC IP Address
ifconfig eth0 | sed -rn '2s/^.*et //p' | sed -rn 's/ ne.*//p'
ifconfig eth0 |sed -nr '2s/(^.*et) (.*) (net.*)/\2/p'
7.sed Script exercises
Requirements describe : Deal with a similar MySQL Profile's my.cnf file .
1. There are several paragraphs in the input file , a pair [ ] For a paragraph .
2. Configure file parameters for each segment , Count the total number .
[[email protected] opt]# sh example.sh
1: client 2
2: server 12
3: mysqld 12
4: mysqld_safe 7
5: embedded 8
6: mysqld-5.5 10
1. Print the contents of each paragraph
sed -n -e '/^\[.*\]/p' sed.txt | sed 's/\[//' | sed 's/\]//'
2. Count the total number of parameters in each section
sed -n '/^\[server\]/,/^\[.*\]/p' sed.txt | sed -r '/^\[|^#|^$/d'|wc -l
The script is
[[email protected] sed]# cat sed.sh
#!/bin/bash
#Author: rzq
#QQ: 0123456789
#Date: 2019-11-06
#FileName: sed.sh
#URL: https://www.jianshu.com
#Description: The test script
#Copyright (C): 2019 All rights reserved
HS () {
num=$(sed -n '/^\[.*]/p' kl.txt|sed 's/\[//'|sed 's/\]//')
}
GS () {
gs=$(sed -n '/^\['$i']/,/^\[.*]/p' kl.txt|sed -r '/^\[|^#|^$/d'|wc -l)
}
HS
b=0
for i in $num
do
let b++
GS
echo "$b $i $gs"
done
Requirements describe : Deal with one ansible Of invtory Host list .
1. Output host group , a pair [ ] For a host group .
2. Output the total number of hosts under each host group .
[[email protected] opt]# sh example.sh
1: web01: Yes 2 Console host
2: web02: Yes 12 Console host
[[email protected] sed]# cat ansible.sh
#!/bin/bash
#Author: rzq
#QQ: 0123456789
#Date: 2019-11-07
#FileName: ansible.sh
#URL: https://www.jianshu.com
#Description: The test script
#Copyright (C): 2019 All rights reserved
fu () {
FW=$(sed -n '/^\[.*]/p' lp.txt|sed 's/\[//' | sed 's/\]//')
}
ip () {
IP=$(sed -n '/^\['$i'/,/^\[.*]/p' lp.txt|sed -r '/^\[|^$/d'|wc -l)
}
fu
num=0
for i in $FW
do
let num++
ip
echo "$num $i $IP"
done
sed
Two kinds of grammar :
sed options '/pattern1/command' file
1、 Options options:
-i Change the document directly
-r Support for extended regular expressions
-f Write the processing command to the file , And then call
-e You can edit multiple operations
-n Cancel the output of default text
2. Pattern matching
string matching
Regular Expression Matching
From where -> Where to go? '/pattern1/,/pattern2/'
3. command command
increase
a # Add
i # Add
r # Read the contents of a file , Added to the /pattern1/ The back of the line
w # Write the contents of a file to a file . >
Delete
d # Delete the matching content , But it needs cooperation -i Option to manipulate the file .
Change
s/// # Replace , Replace what with what , Need to cooperate with -i Option to manipulate the file
s///g # Replace , Global replacement ( Replace all the contents that meet the conditions in a row )
c # modify , You can use regular expressions to match , And then modify Need to cooperate with -i Option to manipulate the file
check
p # The effect of printout . The default action , You have to add . Usually cooperate -n Use it together
__EOF__
边栏推荐
- Hugo blog graphical writing tool -- QT practice
- 宝塔的安装和flask项目部署
- MySQL combat optimization expert 03 uses a data update process to preliminarily understand the architecture design of InnoDB storage engine
- MySQL combat optimization expert 06 production experience: how does the production environment database of Internet companies conduct performance testing?
- MySQL的存储引擎
- MySQL实战优化高手03 用一次数据更新流程,初步了解InnoDB存储引擎的架构设计
- C杂讲 浅拷贝 与 深拷贝
- Canoe cannot automatically identify serial port number? Then encapsulate a DLL so that it must work
- MySQL實戰優化高手08 生產經驗:在數據庫的壓測過程中,如何360度無死角觀察機器性能?
- MySQL Real Time Optimization Master 04 discute de ce qu'est binlog en mettant à jour le processus d'exécution des déclarations dans le moteur de stockage InnoDB.
猜你喜欢

Keep these four requirements in mind when learning single chip microcomputer with zero foundation and avoid detours
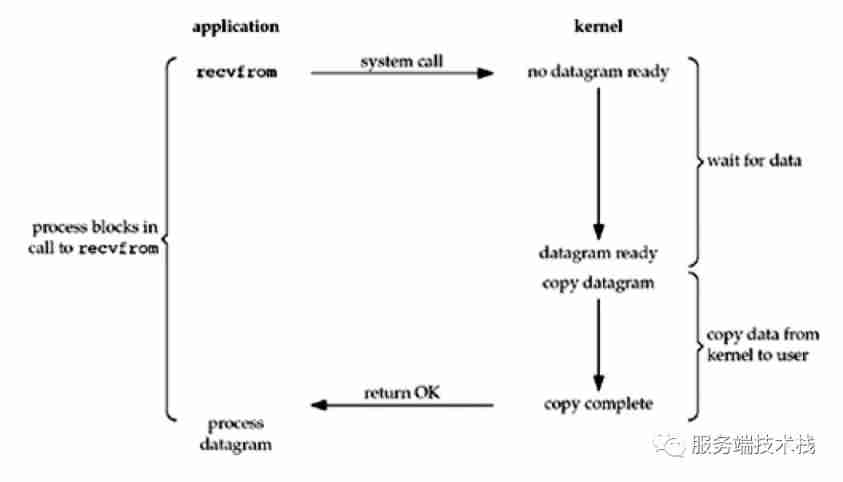
What you have to know about network IO model
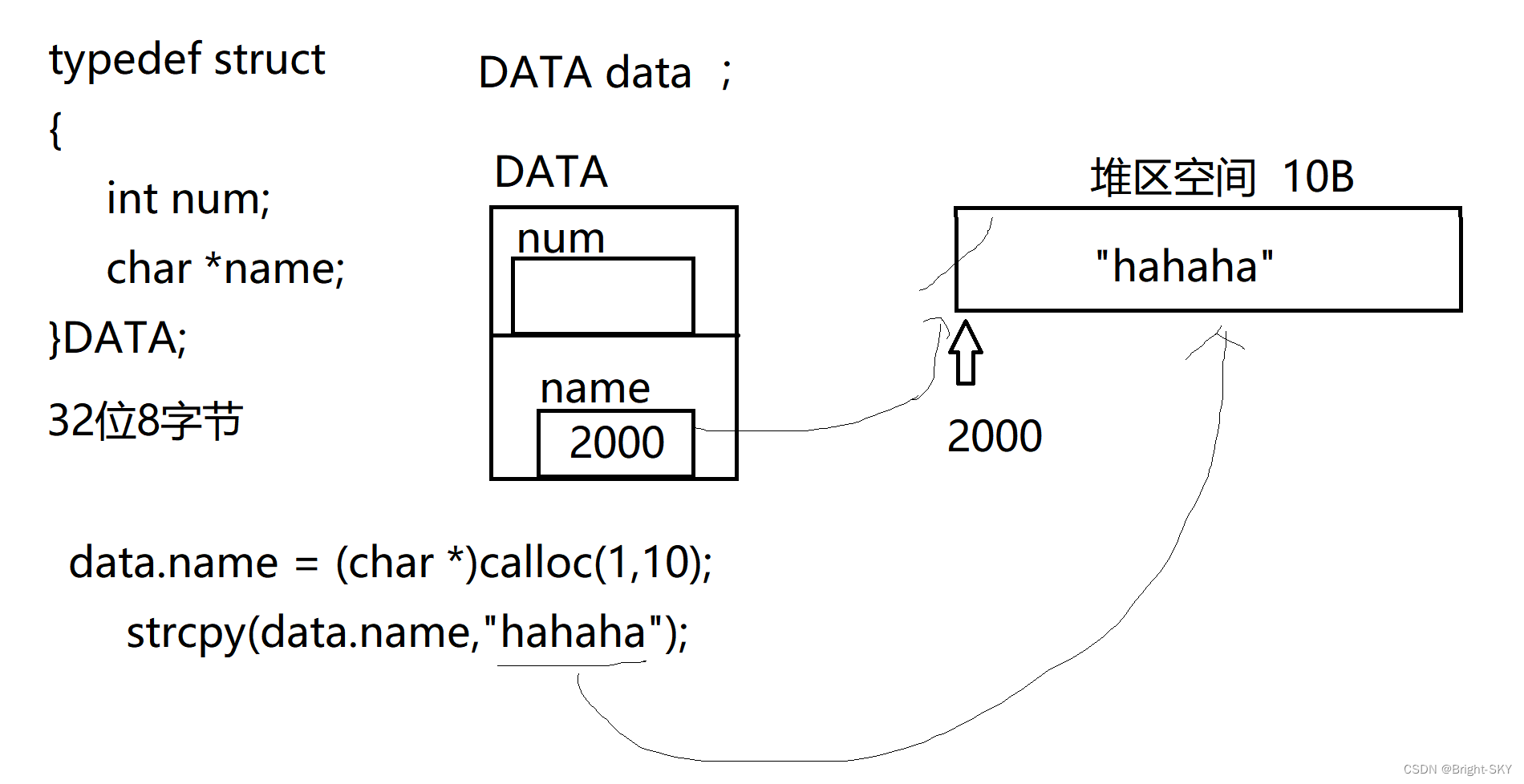
C杂讲 浅拷贝 与 深拷贝

Preliminary introduction to C miscellaneous lecture document
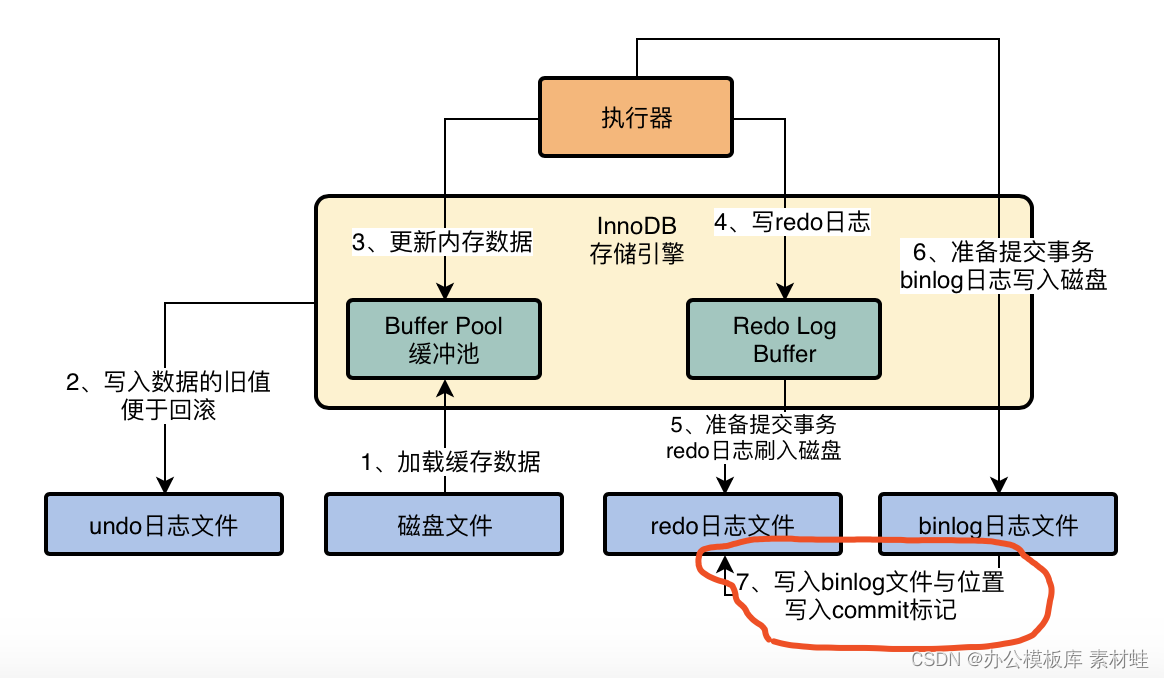
MySQL實戰優化高手04 借著更新語句在InnoDB存儲引擎中的執行流程,聊聊binlog是什麼?
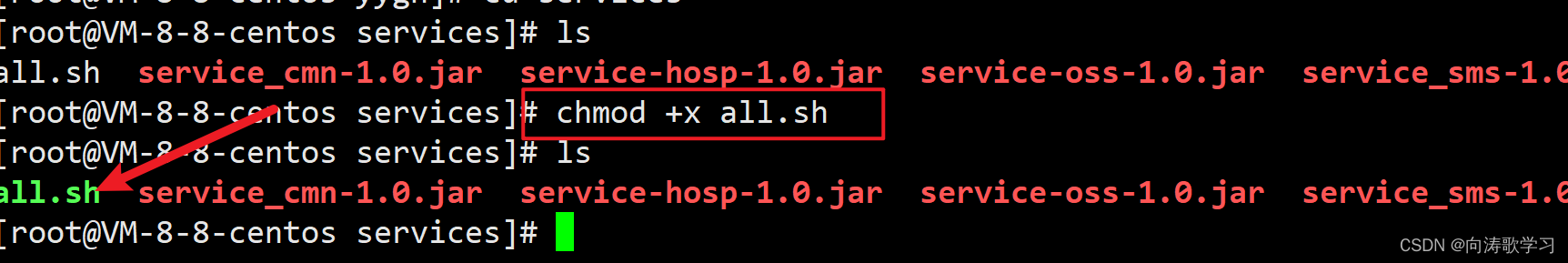
How to make shell script executable

MySQL Real Time Optimization Master 04 discute de ce qu'est binlog en mettant à jour le processus d'exécution des déclarations dans le moteur de stockage InnoDB.

The 32-year-old fitness coach turned to a programmer and got an offer of 760000 a year. The experience of this older coder caused heated discussion
Docker MySQL solves time zone problems
Installation of pagoda and deployment of flask project
随机推荐
Mexican SQL manual injection vulnerability test (mongodb database) problem solution
Routes and resources of AI
C miscellaneous dynamic linked list operation
MySQL实战优化高手07 生产经验:如何对生产环境中的数据库进行360度无死角压测?
51单片机进修的一些感悟
jar运行报错no main manifest attribute
Regular expressions are actually very simple
MySQL实战优化高手05 生产经验:真实生产环境下的数据库机器配置如何规划?
MySQL combat optimization expert 03 uses a data update process to preliminarily understand the architecture design of InnoDB storage engine
MySQL的存储引擎
Contrôle de l'exécution du module d'essai par panneau dans Canoe (primaire)
CAPL 脚本打印函数 write ,writeEx ,writeLineEx ,writeToLog ,writeToLogEx ,writeDbgLevel 你真的分的清楚什么情况下用哪个吗?
单片机如何从上电复位执行到main函数?
17 医疗挂号系统_【微信支付】
Random notes
Pointer learning
MySQL實戰優化高手04 借著更新語句在InnoDB存儲引擎中的執行流程,聊聊binlog是什麼?
The programming ranking list came out in February. Is the result as you expected?
MySQL real battle optimization expert 08 production experience: how to observe the machine performance 360 degrees without dead angle in the process of database pressure test?
安装OpenCV时遇到的几种错误