Express frame
1.1 Express What is the frame
Express It's based on Node Platform web Application development framework , It offers a range of powerful features , Help you create a variety of Web application . We can use npm install express Command to download .
1.2Express Frame features
-
It provides a convenient and concise route definition (router Third party modules are from express Extracted from the framework )
-
Access to HTTP The request parameters are simplified
-
High support for template engine , Easy to render dynamic HTML page
-
It provides middleware mechanism to effectively control HTTP request
-
It has a large number of third-party middleware to extend the function
1.3 Native Node.js And Express Framework versus routing
app.on('request', (req, res) => {
// Get the request path of the client
let { pathname } = url.parse(req.url);
// Judge the request path Different path addresses respond to different content
if (pathname == '/' || pathname == 'index') {
res.end(' Welcome to the home page ');
} else if (pathname == '/list') {
res.end(' Welcome to the list page ');
} else if (pathname == '/about') {
res.end(' Welcome to our page ')
} else {
res.end(' I'm sorry , The page you visited went on a trip ');
}
});
// When the client uses get Access to / when
app.get('/', (req, res) => {
// Respond to the client
res.send('Hello Express');
});
// When the client uses post Access to /add When routing
app.post('/add', (req, res) => {
res.send(' Use post The way requested /add route ');
});
1.4 Native Node.js And Express Get request parameters by framework comparison
app.on('request', (req, res) => {
// obtain GET Parameters
let {query} = url.parse(req.url, true);
// obtain POST Parameters
let postData = '';
req.on('data', (chunk) => {
postData += chunk;
});
req.on('end', () => {
console.log(querystring.parse(postData)
}));
});
app.get('/', (req, res) => {
// obtain GET Parameters
console.log(req.query);
});
app.post('/', (req, res) => {
// obtain POST Parameters
console.log(req.body);
})
1.5 Express First experience
Use Express Framework creation web The server is so simple , call express The function returned by the module can be .
// introduce Express frame
const express = require('express');
// Use the framework to create web The server
const app = express();
// When the client uses get Access to / When routing
app.get('/', (req, res) => {
// 1.send The type of response content is detected inside the method
// 2.send Method will automatically set http Status code
// 3.send Method will help us set the content type and encoding of the response automatically
// Respond to the client send Method automatically sets the request header based on the type of content
res.send('Hello Express'); // <h2>Hello Express</h2> {say: 'hello'}
});
// Program monitoring 3000 port
app.listen(3000);
2. middleware
2.1 What is Middleware
Middleware is a bunch of methods , Can receive requests from clients 、 Can respond to requests , The request can also be passed on to the next middleware for processing .
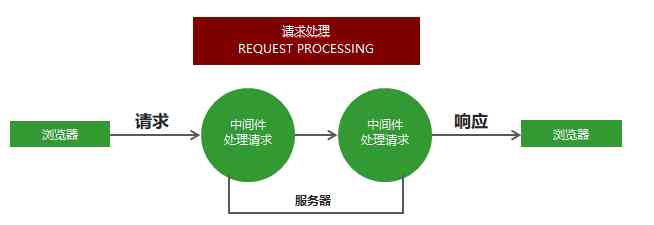
Middleware is mainly composed of two parts , Middleware method and request processing function .
app.get(' Request path ',' Processing function ') // Receive and process get request app.post(' Request path ',' Processing function ') // Receive and process post request
Multiple middleware can be set up for the same request , Multiple processing of the same request . By default , Requests match middleware from top to bottom , Once the match is successful , Terminate match .
You can call next Method gives control of the request to the next middleware , Until the middleware that ends the request .
next, Permission control function
app.get('/request', (req,res,next) => {
req.name = " Zhang San ";
next() ;
};
app.get('/request',(req,res) => {
res.send(req.name) ;
}) ;
2.2 app.use Middleware usage
app.use Match all request methods , You can pass in the request handler directly , The representative receives all requests .
app.use((req, res, next) => {
console.log(req.url);
next();
});
app.use The first parameter can also pass in the request address , No matter what kind of request , As long as it is the request address, it receives the request .
app.use('/admin', (req, res, next) => {
console.log(req.url);
next();
});
2.3 Middleware applications
-
Route protection , When the client accesses the page that needs to log in , You can use middleware to determine the user login status first , If the user is not logged in , Block the request , Direct response , Prohibit users from entering the page that needs to log in .
-
Website maintenance notice , Define the middleware that receives all requests at the top of all routes , Respond directly to the client , The website is under maintenance .
-
Customize 404 page
// introduce express frame
const express = require('express');
// Create a web server
const app = express();
// app.use((req, res, next) => {
// res.send(' Website maintenance ');
// })
app.use('/admin', (req, res, next) => {
let isLogin = false;
if (isLogin) {
next();
} else {
res.send(' Please log in ');
}
});
app.get('/admin', (req, res) => {
res.send(' You have logged in ');
});
app.use((req, res, next) => {
// Respond for the client 404 Status code and prompt information
res.status(404).send(' The page you visited does not exist ');
});
// Listening port
app.listen(3000);
console.log(' Website server started successfully ');
2.4 Error handling middleware
In the process of program execution , Inevitably, there will be some mistakes that can't be prepared , For example, file read failure , Database connection failed . Error handling middleware is a place where errors are handled centrally . Can only handle synchronization code errors
app.use((err, req, res, next) => {
res.status(500).send(' An unknown error has occurred on the server ');
})
When a program goes wrong , call next() Method , And the error message is passed to next() Method , The error handling middleware can be triggered .
app.get("/", (req, res, next) => {
// Read a nonexistent file
fs.readFile("/file-does-not-exist", (err, data) => {
if (err) {
next(err);
}
});
});
// introduce express frame
const express = require('express');
const fs = require('fs');
// Create a web server
const app = express();
app.get('/index', (req, res, next) => {
// throw Throw out
// Error() Error object
// throw new Error(' The program has a location error ');
fs.readFile('./01.js', (err, result) => {
if (err != null) {
next(err);
} else {
res.send(result);
}
});
});
// Error handling middleware
app.use((err, req, res, next) => {
res.status(500).send(err.message);
})
// Listening port
app.listen(3000);
console.log(' Website server started successfully ');
2.5 Capture the error
stay node.js in , asynchronous API The error messages are obtained through the callback function , Support Promise Yes The asynchrony of the elephant API Mistakes can be made by catch Methods to capture .
If an error occurs in asynchronous function execution, how to catch the error ? try catch You can catch errors that occur during the execution of asynchronous functions and other synchronous code , But no other type of API What happened .
// introduce express frame
const express = require('express');
const fs = require('fs');
const promisify = require('util').promisify;
const readFile = promisify(fs.readFile);
// Create a web server
const app = express();
app.get('/index', async (req, res, next) => {
try {
await readFile('./aa.js');
} catch (err) {
next(err);
}
});
// Error handling middleware
app.use((err, req, res, next) => {
res.status(500).send(err.message);
})
// Listening port
app.listen(3000);
console.log(' Website server started successfully ');
3.Express Request processing
3.1 Building modular routing
// introduce express frame
const express = require('express');
// Create routing objects
const home = express.Router();
// Create a server
const app = express();
// Match the route to the request path
app.use('/home', home);
// Create a secondary route
home.get('/index', (req, res) => {
// localhost:3000/home/index visit
res.send(' Welcome to the home page of the blog ');
})
// Listening port
app.listen(3000);
console.log(' Server started successfully ');
3.2 GET Parameter acquisition
Express Use... In the framework req.query Can get GET Parameters , Inside the framework will be GET Parameters are converted to objects and return .
// Receive the parameters after the question mark in the address bar
// for example : http://localhost:3000/?name=zhangsan&age=30
app.get('/', (req, res) => {
console.log(req.query); // {"name": "zhangsan", "age": "30"}
});
3.3POST Parameter acquisition
Express In the receiving post Request parameters need to use third-party packages body-parser.
// introduce body-parser modular
const bodyParser = require('body-parser');
// To configure body-parser modular
// When extended Parameter values for false when , Methods use querystring This system module processes the parameter format
// When the parameter is true Use a name called qs The third-party module processes the request parameters ,qs Module can also convert request parameter format to object type ,
And it's more functional than querystring Powerful , But for now querystring To meet the needs , So the parameter is set to false
app.use(bodyParser.urlencoded({ extended: false }));
// Receiving request
app.post('/add', (req, res) => {
// Receive request parameters
console.log(req.body);
})
3.4express Routing parameters
// introduce express frame
const express = require('express');
// Create a web server
const app = express();
// http://localhost:3000/index/123/zhangsan/20
app.get('/index/:id/:name/:age', (req, res) => {
res.send(req.params); //{"id":"123","name":"zhangsan","age":"20"}
})
// Listening port
app.listen(3000);
console.log(' Server started successfully ');
3.5 Processing of static resources
adopt express Built in express.satic You can easily host static files . for example img,css,Javascript Documents, etc. .
app.use (express. static('public'));
Now? ,public The files under the directory can be accessed .
4.express-art-template template engine
template engine
-
In order to make art-template Template engine can be better and Express Frame fit , Template engine official in the original art-template template engine On the basis of encapsulation express- art-template.
-
Use npm install art-template express-art-template Command to install .
// introduce express frame
const express = require('express');
const path = require('path');
// Create a web server
const app = express();
// 1. tell express What template engine does the framework use to render template files with what suffix
// 1 Template suffix
// 2 The template engine used
app.engine('art', require('express-art-template'));
// 2. tell express What is the location of the frame template
// Pay attention to the first views It's a fixed parameter yes express Configuration item name of the framework tell express The storage location of the frame template
// the second views It's the folder name
app.set('views', path.join(__dirname, 'views'));
// 3. tell express What is the default suffix for framework templates
app.set('view engine', 'art');
app.get('/index', (req, res) => {
//1. Splicing template path
//2. Splice template suffix
//3. Which template and which data are spliced
//4. The splicing result is responded to the client
res.render('index', {
msg: 'message'
});
});
app.get('/list', (req, res) => {
res.render('list', {
msg: 'list page'
});
});
// Listening port
app.listen(3000);
app.locals object
Set the variable to app.locals Under the object , This data is available in all templates .
app.locals.users = [{
name: ' Zhang San ',
age: 20
},{
name: ' Li Si ',
age: 20
}]