当前位置:网站首页>MSE (mean square error) calculation package function
MSE (mean square error) calculation package function
2022-06-12 07:46:00 【Jace Lee】
List of articles
background
I need to write several simulations recently , Need a lot of MSE( Mean square error ) Calculation , So I'll just MSE Operations are encapsulated as functions , The subsequent use can be called directly .
function code
%Project: Mean square error function
%Author: Jace
%Data: 2021/11/01
%==================== The body of the function ====================
function [MSE]=MSE(Dim,Step,N,xkf,x)
%==================== Allocate space ========================
MSE=zeros(Dim,N);
MSEC=zeros(1,Dim);
%==================== iterative process ====================
for n=1:Dim
%-------- Dimension cycle --------
for k=Step:N
%-------- Time cycle --------
MSEC(n)=0;% The square sum of error variable is cleared
for i = k-(Step-1):k
%-------- Add and cycle --------
MSEC(n)=MSEC(n)+(xkf(n,i)-x(n,i))^2;% The sum of the squares of the errors
end
MSE(n,k)=MSEC(n)/Step;% Take the average
end
end
end
Calling method
[MSE]=MSE(Dim,Step,N,xkf,x)
Corresponding
[MSE matrix ]=MSE( The state dimension Dim,MSE length Step, Total duration N, Estimation matrix xkf, State matrix x)
Be careful :
- The default dimension is the status dimension , Each state value estimate can be directly calculated with the real MSE, Got MSE The matrix of the Dim_nN dimension . If you don't need a complete calculation , You can customize Dim The number . Such as Dim=1, Then only the first state value is calculated MSE, It is calculated accordingly MSE There is only a 1N dimension ;
- Input estimation matrix xkf And state matrix x It is the result matrix of the iterative calculation of the estimation algorithm , The dimension should be Dim_n*N dimension ;
- Because before Step Insufficient length for calculation , Therefore, the value obtained is 0.
Call the test function
%Project: Basic 2D Kalman Test functions
%Author: Jace
%Data: 2021/11/02
%==================== Get ready ====================
close all;
clear all;
clc;
%==================== Set global parameters ====================
%-------- Global parameter --------
N=100;% Set the number of sampling points , That is, the duration
%-------- Set dimension --------
Dim_n=2;% The state dimension
Dim_m=2;% Measurement dimension
%-------- System model parameters --------
A=[1.002,0;0,0.998];% State transition matrix
H=[1,0;0,1];% Local measurement 1 Measurement matrix
Gamma=1;
%-------- Noise related parameters --------
P0=0.01;% Initial state noise covariance
Q=0.01*eye(Dim_n);% Set the system noise
R=0.1*eye(Dim_m);% Set observation noise
w=sqrt(Q)*randn(Dim_n,N);
v=sqrt(R)*randn(Dim_m,N);
%==================== Allocate space ========================
%-------- system parameter --------
x=zeros(Dim_n,N);
z=zeros(Dim_m,N);% Measured value
%--------Kalman Process parameters --------
p=zeros(Dim_n,Dim_n,N);
xkf=zeros(Dim_n,N);% Estimated state
%==================== initialization ====================
%-------- System parameter initialization --------
x(:,1)=[10+P0*randn(1);20+P0*randn(1)];% The initial true state value of the object
z(:,1)=H*x(:,1)+v(:,1);% Initial value of observed true value
%-------- Estimate parameter initialization --------
p(:,:,1)=0.1*eye(Dim_n);% Initial value of error covariance
xkf(:,1)=x(:,1);% Global estimation state initialization
%-------- Specific matrix initialization --------
In=eye(Dim_n);%2*2 Unit matrix
%==================== iterative process ====================
for k=2:N
% System model
x(:,k)=A*x(:,k-1)+w(:,k);
% Measurement model , Scalar
z(:,k)=H*x(:,k)+v(:,k);
%==================== standard Kalman The process ====================
[p(:,:,k),xkf(:,k)]=Lkf(2,A,H,Gamma,Q,R,p(:,:,k-1),xkf(:,k-1),z(:,k));
end
%====================MSE Calculation ====================
Step=10;
[MSE]=MSE(Dim_n,Step,N,xkf,x);
%==================== mapping ====================
%MSE
figure;
hold on,box on;
plot(MSE(1,:),'-r.');
plot(MSE(2,:),'-g.');
legend('MSE1','MSE2');
xlabel(' Sampling time ');ylabel(' The number ');
title('MSE');
边栏推荐
- Chapter 2 - cyber threats and attacks
- Fcpx plug-in: simple line outgoing text title introduction animation call outs with photo placeholders for fcpx
- R语言caTools包进行数据划分、scale函数进行数据缩放、class包的knn函数构建K近邻分类器、比较不同K值超参数下模型准确率(accuracy)
- Leetcode notes: biweekly contest 79
- R语言将dataframe数据中指定数据列的数据从小数转化为百分比表示、数据转换为百分数
- Scoring prediction problem
- Topic 1 Single_Cell_analysis(4)
- GD32F4(5):GD32F450时钟配置为200M过程分析
- Voice assistant - Qu - single entity recall
- Voice assistant - Qu - ner and intention slot model
猜你喜欢

Scoring prediction problem

Voice assistant -- vertical class perpetual motion machine -- automated iteration framework

Golang 快速生成数据库表的 model 和 queryset
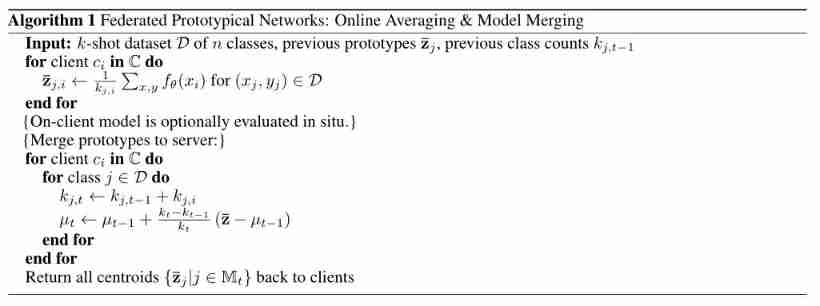
Federated reconnaissance: efficient, distributed, class incremental learning paper reading + code analysis

Voice assistant - Introduction and interaction process

最新hbuilderX编辑uni-app项目运行于夜神模拟器

Personalized federated learning with Moreau envelopes

Voice assistant - Qu - single entity recall
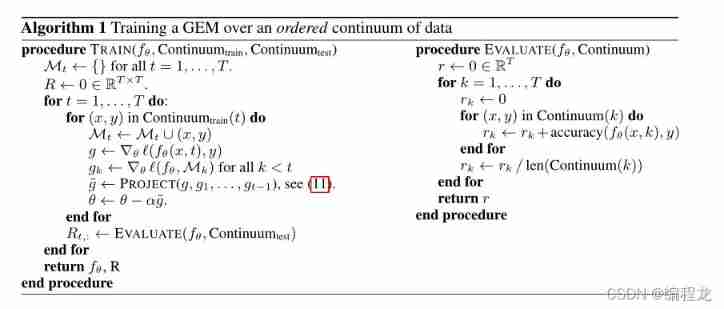
Gradient epic memory for continuous learning

Thyristor, it is a very important AC control device
随机推荐
LeetCode34. 在排序数组中查找元素的第一个和最后一个位置
Gradient epic memory for continuous learning
20220526 yolov1-v5
Modelarts培训任务1
Personalized federated learning with Moreau envelopes
Voice assistant - future trends
Shortcut key modification of TMUX and VIM
R语言使用neuralnet包构建神经网络回归模型(前馈神经网络回归模型),计算模型在测试集上的MSE值(均方误差)
Non IID data and continuous learning processes in federated learning: a long road ahead
Question bank and answers of special operation certificate examination for safety management personnel of hazardous chemical business units in 2022
20220525 RCNN--->Faster RCNN
R language uses rstudio to save visualization results as PDF files (export--save as PDF)
Cold start problem of recommended system
Continuous local training for better initialization of Federated models
Voice assistant - Introduction and interaction process
Topic 1 Single_Cell_analysis(3)
In depth learning - overview of image classification related models
LeetCode笔记:Biweekly Contest 79
Summary of machine learning + pattern recognition learning (I) -- k-nearest neighbor method
Hongmeng OS first training