当前位置:网站首页>OpenGL Chapter 10 illuminant
OpenGL Chapter 10 illuminant
2022-06-11 03:34:00 【Carefree young heart】
An object that projects a light source is a projector
Parallel light (Directional Light)
Point source (Point Light)
Spotlight (Spotlight)
Parallel light
Because all the light sources of the directional light are parallel " The relative position of the light source and the object " It's not that important ,
We just need to define one " The direction of the vector direction" To simulate directional light 
//directionLight.fs
#version 330 core
out vec4 FragColor;
struct Material {
sampler2D diffuse;
sampler2D specular;
float shininess;
};
struct Light {
//vec3 position;
vec3 direction;// Define a " The direction of the vector direction" To simulate directional light
vec3 ambient;// Ambient light component of light
vec3 diffuse;// Diffuse reflection component of light
vec3 specular;// The specular reflection component of light
};
in vec3 FragPos;
in vec3 Normal;
in vec2 TexCoords;
uniform vec3 viewPos;
uniform Material material;// Create structure objects
uniform Light light;// Create structure objects
void main()
{
// ambient
vec3 ambient = light.ambient * texture(material.diffuse, TexCoords).rgb;
// Ambient light component = The initial ambient light component of light * Diffuse material texture This is equivalent to telling the shader that the ambient light will be affected material.diffuse The influence of material
// The material is represented in the main function by set Pass in
// diffuse
vec3 norm = normalize(Normal);// Normalized normal vector
// vec3 lightDir = normalize(light.position - FragPos);
vec3 lightDir = normalize(-light.direction); // The direction of the vector direction" To simulate directional light Yes light.direction Reverse vector .
// The lighting calculation we currently use requires a light direction from the segment to the light source , But people are more used to defining directional light as a global direction starting from the light source .
float diff = max(dot(norm, lightDir), 0.0);// Point multiplication calculates the angle between the normal and the reflected ray
vec3 diffuse = light.diffuse * diff * texture(material.diffuse, TexCoords).rgb;
// Tell the shader that diffuse will be affected by material.diffuse The influence of material
// specular
vec3 viewDir = normalize(viewPos - FragPos);// The direction of human perspective From the object to the observer
vec3 reflectDir = reflect(-lightDir, norm);// Tell the incident light and normal reflect Calculate the vector of reflected light
float spec = pow(max(dot(viewDir, reflectDir), 0.0), material.shininess);//material.shininess Highlight level 2 4 8 16 32 64 128 The lower the level, the more blurred the aperture
vec3 specular = light.specular * spec * texture(material.specular, TexCoords).rgb;
// Tell the shader that highlights will be affected by material.diffuse The influence of material
vec3 result = ambient + diffuse + specular;
FragColor = vec4(result, 1.0);
}
//directionLight.vs
#version 330 core
layout (location = 0) in vec3 aPos;// The initial position is 0 The attribute of is vertex position
layout (location = 1) in vec3 aNormal;// The initial position is 1 The attribute of is normal position
layout (location = 2) in vec2 aTexCoords;// The initial position is 2 The attribute of is mapping coordinates
out vec3 FragPos;// Output the position of the object
out vec3 Normal;// Output normals
out vec2 TexCoords;// Output map
uniform mat4 model;// Define global variables model Set... In the main function
uniform mat4 view;// Define global variables view Set... In the main function
uniform mat4 projection;// Define global variables projection Set... In the main function
void main()
{
FragPos = vec3(model * vec4(aPos, 1.0));
// The position of an object in world coordinates after model transformation
Normal = mat3(transpose(inverse(model))) * aNormal;
// Normal transformation matrix = Transpose of inverse matrix * Normal matrix
TexCoords = aTexCoords;
// UVW Map
gl_Position = projection * view * vec4(FragPos, 1.0);// The last position you see in the cone
}
//LightingMaps
#include "Shader.h"
#define STB_IMAGE_IMPLEMENTATION
#include "stb_image.h"
#include <glad/glad.h>
#include <GLFW/glfw3.h>
#include <glm/glm.hpp>
#include <glm/gtc/matrix_transform.hpp>
#include <glm/gtc/type_ptr.hpp>
#include <iostream>
void mouse_callback(GLFWwindow* window, double xpos, double ypos);
void scroll_callback(GLFWwindow* window, double xoffset, double yoffset);
void processInput(GLFWwindow* window);
// settings
const unsigned int SCR_WIDTH = 800; // Define the size of screen space
const unsigned int SCR_HEIGHT = 600;
// camera
glm::vec3 cameraPos = glm::vec3(0.0f, 0.0f, 3.0f);
glm::vec3 cameraFront = glm::vec3(0.0f, 0.0f, -1.0f);
glm::vec3 cameraUp = glm::vec3(0.0f, 1.0f, 0.0f);
bool firstMouse = true;
float yaw = -90.0f; // Yaw is initialized to -90.0 degree , Because the yaw is 0.0 Will result in a direction vector pointing to the right , So we initially rotated a little to the left .
float pitch = 0.0f; // Initialize pitch angle
float lastX = 800.0f / 2.0;// In order to set the initial position as the center of the screen, take half the size of the screen space
float lastY = 600.0 / 2.0;
float fov = 45.0f;// Initial field angle
// timing
float deltaTime = 0.0f; // time between current frame and last frame
float lastFrame = 0.0f;
glm::vec3 lightPos(1.2f, 1.0f, 2.0f);
//glm::vec3 lightPos(1.2f, 1.0f, 2.0f);
void processInput(GLFWwindow* window);
float vertices[] = {
// positions // normals // texture coords
-0.5f, -0.5f, -0.5f, 0.0f, 0.0f, -1.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f,
0.5f, -0.5f, -0.5f, 0.0f, 0.0f, -1.0f, 1.0f, 0.0f,
0.5f, 0.5f, -0.5f, 0.0f, 0.0f, -1.0f, 1.0f, 1.0f,
0.5f, 0.5f, -0.5f, 0.0f, 0.0f, -1.0f, 1.0f, 1.0f,
-0.5f, 0.5f, -0.5f, 0.0f, 0.0f, -1.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f,
-0.5f, -0.5f, -0.5f, 0.0f, 0.0f, -1.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f,
-0.5f, -0.5f, 0.5f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f,
0.5f, -0.5f, 0.5f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f, 1.0f, 0.0f,
0.5f, 0.5f, 0.5f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f, 1.0f, 1.0f,
0.5f, 0.5f, 0.5f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f, 1.0f, 1.0f,
-0.5f, 0.5f, 0.5f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f,
-0.5f, -0.5f, 0.5f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f,
-0.5f, 0.5f, 0.5f, -1.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f, 0.0f,
-0.5f, 0.5f, -0.5f, -1.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f, 1.0f,
-0.5f, -0.5f, -0.5f, -1.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f,
-0.5f, -0.5f, -0.5f, -1.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f,
-0.5f, -0.5f, 0.5f, -1.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f,
-0.5f, 0.5f, 0.5f, -1.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f, 0.0f,
0.5f, 0.5f, 0.5f, 1.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f, 0.0f,
0.5f, 0.5f, -0.5f, 1.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f, 1.0f,
0.5f, -0.5f, -0.5f, 1.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f,
0.5f, -0.5f, -0.5f, 1.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f,
0.5f, -0.5f, 0.5f, 1.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f,
0.5f, 0.5f, 0.5f, 1.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f, 0.0f,
-0.5f, -0.5f, -0.5f, 0.0f, -1.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f,
0.5f, -0.5f, -0.5f, 0.0f, -1.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f, 1.0f,
0.5f, -0.5f, 0.5f, 0.0f, -1.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f, 0.0f,
0.5f, -0.5f, 0.5f, 0.0f, -1.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f, 0.0f,
-0.5f, -0.5f, 0.5f, 0.0f, -1.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f,
-0.5f, -0.5f, -0.5f, 0.0f, -1.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f,
-0.5f, 0.5f, -0.5f, 0.0f, 1.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f,
0.5f, 0.5f, -0.5f, 0.0f, 1.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f, 1.0f,
0.5f, 0.5f, 0.5f, 0.0f, 1.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f, 0.0f,
0.5f, 0.5f, 0.5f, 0.0f, 1.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f, 0.0f,
-0.5f, 0.5f, 0.5f, 0.0f, 1.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f,
-0.5f, 0.5f, -0.5f, 0.0f, 1.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f
};
// Define a vec3 Type array to store the displacement matrix
glm::vec3 cubePositions[] = {
glm::vec3(0.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f),
glm::vec3(2.0f, 5.0f, -15.0f),
glm::vec3(-1.5f, -2.2f, -2.5f),
glm::vec3(-3.8f, -2.0f, -12.3f),
glm::vec3(2.4f, -0.4f, -3.5f),
glm::vec3(-1.7f, 3.0f, -7.5f),
glm::vec3(1.3f, -2.0f, -2.5f),
glm::vec3(1.5f, 2.0f, -2.5f),
glm::vec3(1.5f, 0.2f, -1.5f),
glm::vec3(-1.3f, 1.0f, -1.5f),
};
int main()
{
//Glfw: Initialization and configuration
// ------------------------------
glfwInit();
glfwWindowHint(GLFW_CONTEXT_VERSION_MAJOR, 3);
glfwWindowHint(GLFW_CONTEXT_VERSION_MINOR, 3);
glfwWindowHint(GLFW_OPENGL_PROFILE, GLFW_OPENGL_CORE_PROFILE);
#ifdef __APPLE__
glfwWindowHint(GLFW_OPENGL_FORWARD_COMPAT, GL_TRUE);
#endif
//glfw Window creation
// --------------------
GLFWwindow* window = glfwCreateWindow(SCR_WIDTH, SCR_HEIGHT, "LearnOpenGL", NULL, NULL);// Use the size of the defined screen space
if (window == NULL)
{
std::cout << "Failed to create GLFW window" << std::endl;
glfwTerminate();
return -1;
}
glfwMakeContextCurrent(window);
glfwSetCursorPosCallback(window, mouse_callback);
glfwSetScrollCallback(window, scroll_callback);
// First we have to tell GLFW, It should hide the cursor , And capture (Capture) it .
glfwSetInputMode(window, GLFW_CURSOR, GLFW_CURSOR_DISABLED);
// Load all OpenGL A function pointer
// ---------------------------------------
if (!gladLoadGLLoader((GLADloadproc)glfwGetProcAddress))
{
std::cout << "Failed to initialize GLAD" << std::endl;
return -1;
}
// Configure global opengl state
// -----------------------------
glEnable(GL_DEPTH_TEST);
// Build and compile our shader Program
// ------------------------------------
Shader ourShader("shaderSampler.vs", "shaderSampler.fs");
Shader modelShader("directionLight.vs", "directionLight.fs");
Shader lightShader("lightShader.vs", "lightShader.fs");
// Create and compile vertex data ( And buffer ), Configure vertex attributes
// ------------------------------------------------------------------
unsigned int VBO, VAO, VAO2;
glGenVertexArrays(1, &VAO);
glGenBuffers(1, &VBO);
glBindBuffer(GL_ARRAY_BUFFER, VBO);
glBufferData(GL_ARRAY_BUFFER, sizeof(vertices), vertices, GL_STATIC_DRAW);
glBindVertexArray(VAO);
// Location properties
glVertexAttribPointer(0, 3, GL_FLOAT, GL_FALSE, 8 * sizeof(float), (void*)0);
glEnableVertexAttribArray(0);
// Then in the vertex shader layout (location = 1) in vec3 aNormal;// tell GPU Location 1 Properties of
glGenVertexArrays(1, &VAO2);
glBindVertexArray(VAO2);
//glBindBuffer(GL_ARRAY_BUFFER, VBO);
// Location properties
glVertexAttribPointer(0, 3, GL_FLOAT, GL_FALSE, 8 * sizeof(float), (void*)0);
glEnableVertexAttribArray(0);
// Normal attributes
glVertexAttribPointer(1, 3, GL_FLOAT, GL_FALSE, 8 * sizeof(float), (void*)(3 * sizeof(float)));
glEnableVertexAttribArray(1);
glVertexAttribPointer(2, 2, GL_FLOAT, GL_FALSE, 8 * sizeof(float), (void*)(6 * sizeof(float)));
glEnableVertexAttribArray(2);
// Load and create a texture
// -------------------------
unsigned int texture1, texture2;
// texture 1
// ---------
glGenTextures(1, &texture1);
glBindTexture(GL_TEXTURE_2D, texture1);
// Set the texture wrapping Parameters
glTexParameteri(GL_TEXTURE_2D, GL_TEXTURE_WRAP_S, GL_REPEAT);
glTexParameteri(GL_TEXTURE_2D, GL_TEXTURE_WRAP_T, GL_REPEAT);
// Set the texture filtering Parameters
glTexParameteri(GL_TEXTURE_2D, GL_TEXTURE_MIN_FILTER, GL_LINEAR);
glTexParameteri(GL_TEXTURE_2D, GL_TEXTURE_MAG_FILTER, GL_LINEAR);
// Load image , Create textures and generate mipmaps // Multi level principle texture
int width, height, nrChannels;
stbi_set_flip_vertically_on_load(true); // tell stb_image.h stay y Flip the loaded texture on the axis .
// Why do you need to flip Y The axis is because the starting position of the texture image is the upper right and the coordinates of our vertices (0,0) The point is lower left
unsigned char* data = stbi_load("container2.png", &width, &height, &nrChannels, 0);
if (data)
{
glTexImage2D(GL_TEXTURE_2D, 0, GL_RGBA, width, height, 0, GL_RGBA, GL_UNSIGNED_BYTE, data);
glGenerateMipmap(GL_TEXTURE_2D);
}
else
{
std::cout << "Failed to load texture" << std::endl;
}
stbi_image_free(data);
// texture 2
// ---------
glGenTextures(1, &texture2);
glBindTexture(GL_TEXTURE_2D, texture2);
// Set the texture wrapping Parameters
glTexParameteri(GL_TEXTURE_2D, GL_TEXTURE_WRAP_S, GL_REPEAT);
glTexParameteri(GL_TEXTURE_2D, GL_TEXTURE_WRAP_T, GL_REPEAT);
// Set the texture filtering Parameters
glTexParameteri(GL_TEXTURE_2D, GL_TEXTURE_MIN_FILTER, GL_LINEAR);
glTexParameteri(GL_TEXTURE_2D, GL_TEXTURE_MAG_FILTER, GL_LINEAR);
// load image, create texture and generate mipmaps
//data = stbi_load(("aotu.jpg"), &width, &height, &nrChannels, 0);
//data = stbi_load(("shanshui.jpg"), &width, &height, &nrChannels, 0);
data = stbi_load(("container2_specular.png"), &width, &height, &nrChannels, 0);
if (data)
{
// If there is no map, please give priority to this RGBA Medium alpha(A) passageway If your map has alpha Please be sure to use RGBA Otherwise, the map cannot be displayed
glTexImage2D(GL_TEXTURE_2D, 0, GL_RGBA, width, height, 0, GL_RGBA, GL_UNSIGNED_BYTE, data);
glGenerateMipmap(GL_TEXTURE_2D);
}
else
{
std::cout << "Failed to load texture" << std::endl;
}
stbi_image_free(data);
// Tell... For each sampler opengl Which texture unit does it belong to ( Just do it once )
// -------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
modelShader.use();
modelShader.setInt("material.diffuse", 0);
modelShader.setInt("material.specular", 1);
// ourShader.setVec3("lightPos", lightPos);
// Render loop
// -----------
while (!glfwWindowShouldClose(window))
{
float currentFrame = glfwGetTime();
deltaTime = currentFrame - lastFrame;
lastFrame = currentFrame;
// -----
processInput(window);
// Rendering
// ------
glClearColor(0.2f, 0.3f, 0.3f, 1.0f);
glClear(GL_COLOR_BUFFER_BIT | GL_DEPTH_BUFFER_BIT); // Clears the color buffer of the previous frame as well as Depth test buffer
// Activate shader
float angle = 20.0f * 0 * (float)glfwGetTime();// Give me a glfwGetTime Let the model rotate
glm::mat4 projection = glm::mat4(1.0f);
glm::mat4 view = glm::mat4(1.0f);
glm::mat4 model = glm::mat4(1.0f);
//glm::vec3 lightPos = glm::vec3(cubePositions[10]);// Light source location
projection = glm::perspective(glm::radians(fov), 800.0f / 600.0f, 0.1f, 100.0f);// Projection matrix Parameters : Viewport size , Screen aspect ratio , as well as near and far
view = glm::lookAt(cameraPos, cameraPos + cameraFront, cameraUp);//lookAt matrix Parameters : Camera position , Observe the position of the target , A vertical upward direction
model = glm::translate(model, cubePositions[0]);// Pass in the array to each new model, which has different displacement in world coordinates
model = glm::rotate(model, glm::radians(angle), glm::vec3(1.0f, 0.3f, 0.5f));
//lightShader.use();
lightPos.x = 1.0f + sin(glfwGetTime()) * 2.0f;
lightPos.y = sin(glfwGetTime() / 2.0f) * 1.0f;
//model = glm::mat4(1.0f);
//model = glm::translate(model, lightPos);// Pass in the array to each new model, which has different displacement in world coordinates
//angle = 20.0f * 2 * (float)glfwGetTime();// Give me a glfwGetTime Let the model rotate
//model = glm::rotate(model, glm::radians(angle) , glm::vec3(1.0f, 0.3f, 0.5f));// Rotating objects
//model = glm::scale(model, glm::vec3(0.2f));// Reduce the object on each axis to 0.2 times
//lightShader.setMat4("model", model);
//lightShader.setMat4("projection", projection);
//lightShader.setMat4("view", view);
//glBindVertexArray(VAO);
//glDrawArrays(GL_TRIANGLES, 0, 36);
modelShader.use();
model = glm::mat4(1.0f);
model = glm::translate(model, cubePositions[0]);// Pass in the array to each new model, which has different displacement in world coordinates
angle = 20.0f * 1 * (float)glfwGetTime();// Give me a glfwGetTime Let the model rotate
model = glm::rotate(model, glm::radians(angle) * 0, glm::vec3(1.0f, 0.5f, 0.5f));//rotate Model location Rotation angle Rotation axis
modelShader.setMat4("model", model);// Set the model transformation matrix
modelShader.setMat4("projection", projection);// Set the projection change matrix
modelShader.setMat4("view", view);// Set the view change matrix
modelShader.setVec3("objectColor", 1, 0.5, 0.5);// Set the color of the object
modelShader.setVec3("lightColor", 1, 1, 1);// Set the color of the light source. Of course, you can also set a uniform To set variables
//modelShader.setVec3("lightPos", lightPos);// Set the light source position
modelShader.setVec3("viewPos", cameraPos);// Set the position of the camera to the viewing position
// Set each of the materials uniform component
modelShader.setVec3("material.ambient", 1.0f, 1.0f, 1.0f);
/*modelShader.setVec3("material.diffuse", 1.0f, 0.5f, 0.31f); modelShader.setVec3("material.specular", 0.5f, 0.5f, 0.5f);*/
modelShader.setFloat("material.shininess", 32.0f);
// Set up the light uniform component
modelShader.setVec3("light.ambient", 0.2f, 0.2f, 0.2f);
modelShader.setVec3("light.diffuse", 0.5f, 0.5f, 0.5f);
modelShader.setVec3("light.specular", 1.0f, 1.0f, 1.0f);
modelShader.setVec3("light.direction", -0.2f, -1.0f, -0.3f);// Set the directional light
modelShader.setVec3("light.position", lightPos);
// Set the object color to change over time
//glm::vec3 lightColor;
//lightColor.x = sin(glfwGetTime() * 2.0f);
//lightColor.y = sin(glfwGetTime() * 0.7f);
//lightColor.z = sin(glfwGetTime() * 1.3f);
//glm::vec3 diffuseColor = lightColor * glm::vec3(0.5f); // Reduce the impact
//glm::vec3 ambientColor = diffuseColor * glm::vec3(0.2f); // Very low impact
//modelShader.setVec3("light.ambient", ambientColor);
//modelShader.setVec3("light.diffuse", diffuseColor);
// Light attenuation coefficient of point light source
modelShader.setFloat("light.constant", 1.0f);
modelShader.setFloat("light.linear", 0.14f);
modelShader.setFloat("light.quadratic", 0.07f);
// Activate texture
glActiveTexture(GL_TEXTURE0);
glBindTexture(GL_TEXTURE_2D, texture1);
glActiveTexture(GL_TEXTURE1);
glBindTexture(GL_TEXTURE_2D, texture2);
for (unsigned int i = 0; i < 10; i++)
{
glm::mat4 model;
model = glm::translate(model, cubePositions[i]);
float angle = 20.0f * i;
model = glm::rotate(model, glm::radians(angle), glm::vec3(1.0f, 0.3f, 0.5f));
modelShader.setMat4("model", model);
glBindVertexArray(VAO2);
glDrawArrays(GL_TRIANGLES, 0, 36);
}
glfwSwapBuffers(window);
glfwPollEvents();
}
glDeleteVertexArrays(1, &VAO);
glDeleteBuffers(1, &VBO);
glfwTerminate();
return 0;
}
void processInput(GLFWwindow* window)
{
if (glfwGetKey(window, GLFW_KEY_ESCAPE) == GLFW_PRESS)
glfwSetWindowShouldClose(window, true);
float cameraSpeed = 5.5f * deltaTime;; // adjust accordingly
if (glfwGetKey(window, GLFW_KEY_W) == GLFW_PRESS)
cameraPos += cameraSpeed * cameraFront;
if (glfwGetKey(window, GLFW_KEY_S) == GLFW_PRESS)
cameraPos -= cameraSpeed * cameraFront;
if (glfwGetKey(window, GLFW_KEY_A) == GLFW_PRESS)
cameraPos -= glm::normalize(glm::cross(cameraFront, cameraUp)) * cameraSpeed;
if (glfwGetKey(window, GLFW_KEY_D) == GLFW_PRESS)
cameraPos += glm::normalize(glm::cross(cameraFront, cameraUp)) * cameraSpeed;
if (glfwGetKey(window, GLFW_KEY_SPACE) == GLFW_PRESS)// Here is a space bar so that we can Y Move on the axis
cameraPos += cameraUp * cameraSpeed;
//cameraPos.y = 0.0f;
// You can do this by Y The vector in the direction is set to 0 Make him FPS This type of camera can only be used in XZ Move on the plane
}
void mouse_callback(GLFWwindow* window, double xposIn, double yposIn)
{
float xpos = static_cast<float>(xposIn);
float ypos = static_cast<float>(yposIn);
// This bool The variable is initially set to true Of
// We need to set it as the center of the screen at the beginning
// If you don't do this At the beginning of the program, it will call the callback function to point to the position of the screen when you enter the mouse
// So it's far from the center
if (firstMouse)
{
lastX = xpos;
lastY = ypos;
firstMouse = false;
}
// Then, in the mouse callback function, we calculate the offset of the mouse position between the current frame and the previous frame :
float xoffset = xpos - lastX;
float yoffset = lastY - ypos; // y The coordinates are from bottom to top
lastX = xpos;
lastY = ypos;
float sensitivity = 0.1f; // sensitivity This value can be set arbitrarily
xoffset *= sensitivity;
yoffset *= sensitivity;
yaw += xoffset;
pitch += yoffset;
// To make sure the camera doesn't roll over
if (pitch > 89.0f)
pitch = 89.0f;
if (pitch < -89.0f)
pitch = -89.0f;
// stay xz Look at... On the plane Y Axis
// Here we only update y value , Observe carefully x and z The component is also affected . From the triangles, we can see that their value is equal to :
//direction.x = cos(glm::radians(pitch));
//direction.y = sin(glm::radians(pitch)); // Notice that we first turn the angle into radians
//direction.z = cos(glm::radians(pitch));// here Y Axis updates do affect Z But I don't quite understand why it's directly equal to cos(pitch)
//
//
//
// Here we only update y value , Observe carefully x and z The component is also affected . From the triangles, we can see that their value is equal to :
//direction.x = cos(glm::radians(yaw));
//direction.y =1 // Y unchanged
//direction.z = sin(glm::radians(yaw));
//
// The following equation is equivalent to first completing the rotation transformation of the pitch angle and then multiplying it by the yaw angle
// Combine the above two steps
glm::vec3 front;
front.x = cos(glm::radians(yaw)) * cos(glm::radians(pitch));
front.y = sin(glm::radians(pitch));
front.z = sin(glm::radians(yaw)) * cos(glm::radians(pitch));
cameraFront = glm::normalize(front);
}
// glfw: whenever the mouse scroll wheel scrolls, this callback is called
// ----------------------------------------------------------------------
void scroll_callback(GLFWwindow* window, double xoffset, double yoffset)
{
//yoffset Is the direction in which our roller rolls vertically
if (fov >= 1.0f && fov <= 45.0f)
fov -= yoffset;
// Set a boundary for him stay 1 To 45 Between
if (fov < 1.0f)
fov = 1.0f;
if (fov > 45.0f)
fov = 45.0f;
}

Point source
The attenuation formula looks scary, but we just need to use that formula Then adjust the parameters according to the attenuation meter A point light is a light source that can be configured with position and attenuation 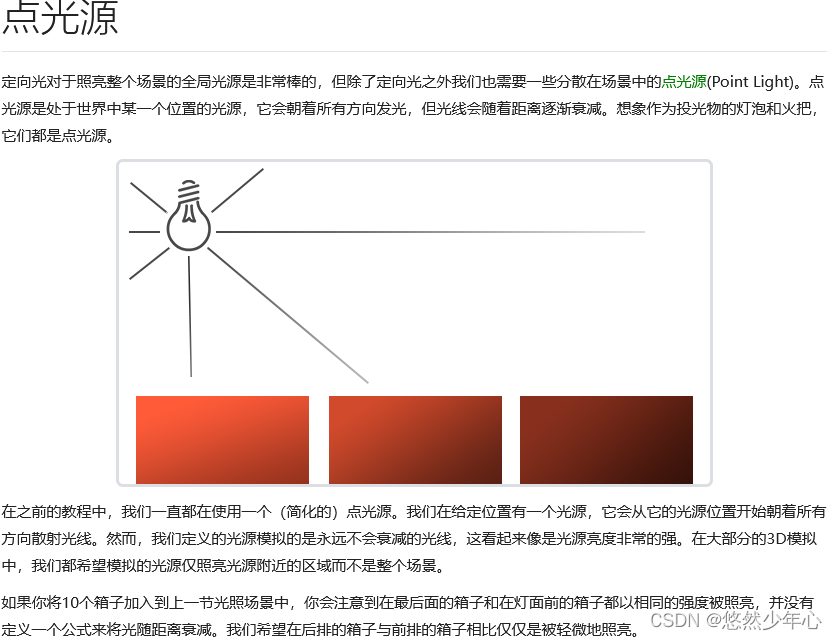 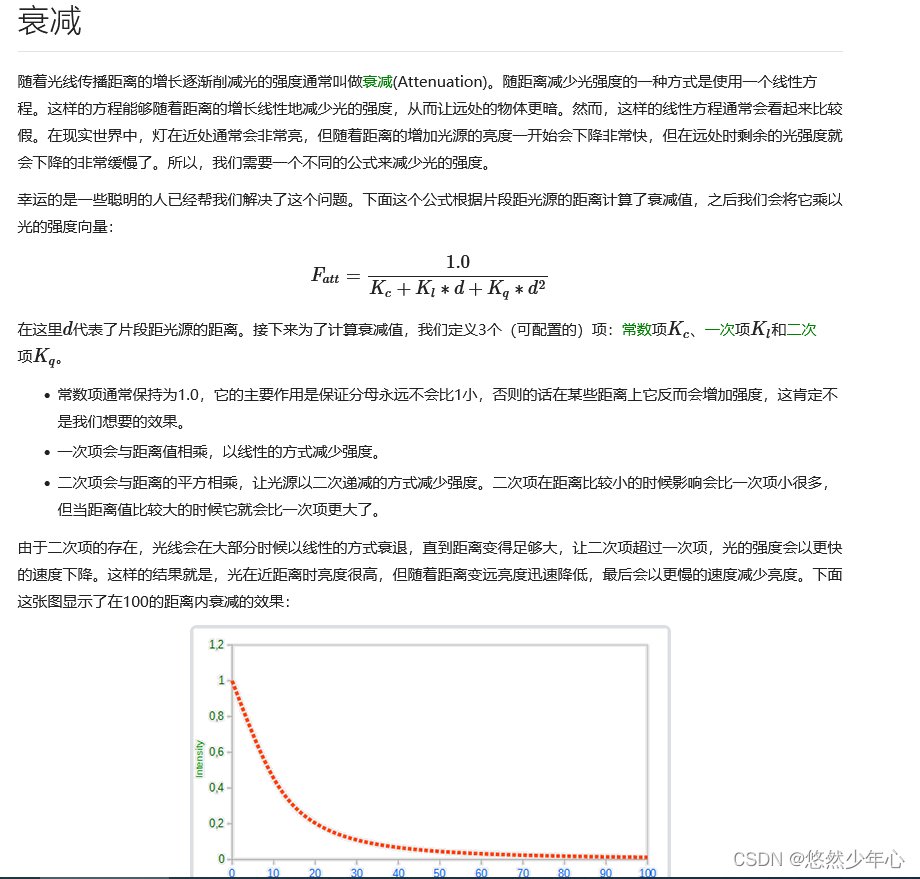 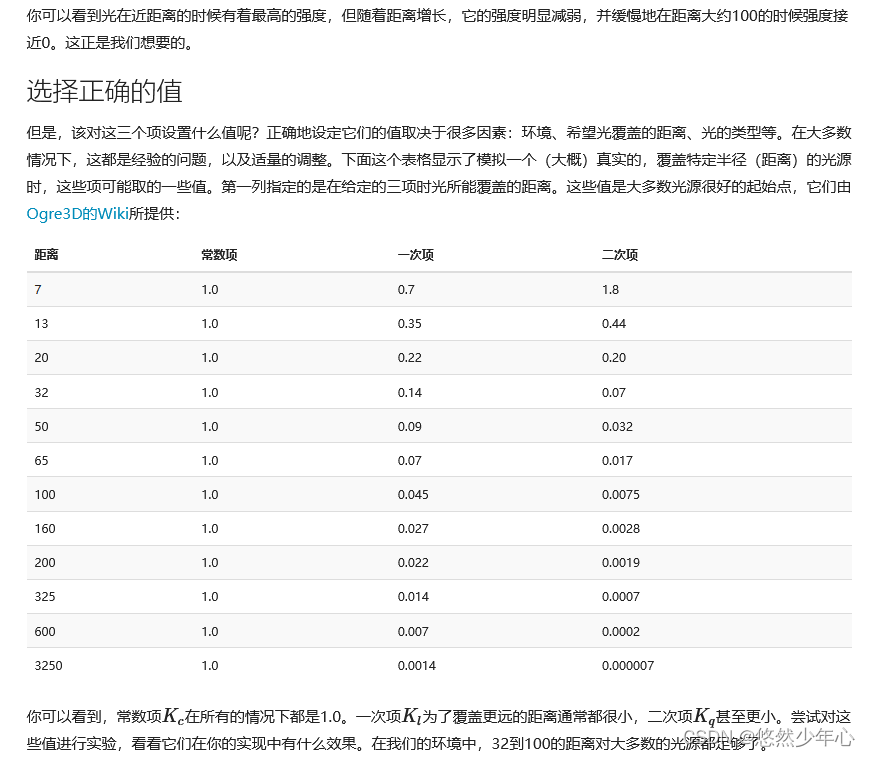 //PointLight.fs Get the first 1 The effect of seed map
#version 330 core
out vec4 FragColor;
struct Material {
sampler2D diffuse;
sampler2D specular;
float shininess;
};
struct Light {
vec3 position;
vec3 ambient;
vec3 diffuse;
vec3 specular;
float constant;// Constant term
float linear;// One time
float quadratic;// Second term
float cutOff;//SpotDir( The spotlight points to ) The direction and LightDir( The vector from the clip to the light source ) Cosine of the included angle
};
in vec3 FragPos;
in vec3 Normal;
in vec2 TexCoords;
uniform vec3 viewPos;
uniform Material material;
uniform Light light;
void main()
{
// ambient
vec3 ambient = texture(material.diffuse, TexCoords).rgb;
// Ambient light component = The initial ambient light component of light * Diffuse material texture This is equivalent to telling the shader that the ambient light will be affected material.diffuse The influence of material
// The material is represented in the main function by set Pass in
// diffuse
vec3 norm = normalize(Normal);// Normalized normal vector
vec3 lightDir = normalize(light.position - FragPos);
//vec3 lightDir = normalize(-light.direction); // The direction of the vector direction" To simulate directional light Yes light.direction Reverse vector .
// The lighting calculation we currently use requires a light direction from the segment to the light source , But people are more used to defining directional light as a global direction starting from the light source .
float diff = max(dot(norm, lightDir), 0.0);// Point multiplication calculates the angle between the normal and the reflected ray
vec3 diffuse = light.diffuse * diff * texture(material.diffuse, TexCoords).rgb;
// Tell the shader that diffuse will be affected by material.diffuse The influence of material
// specular
vec3 viewDir = normalize(viewPos - FragPos);// The direction of human perspective From the object to the observer
vec3 reflectDir = reflect(-lightDir, norm);// Tell the incident light and normal reflect Calculate the vector of reflected light
float spec = pow(max(dot(viewDir, reflectDir), 0.0), material.shininess);//material.shininess Highlight level 2 4 8 16 32 64 128 The lower the level, the more blurred the aperture
vec3 specular = light.specular * spec * texture(material.specular, TexCoords).rgb;
// Tell the shader that highlights will be affected by material.diffuse The influence of material
float distance = length(light.position - FragPos);// Attenuation distance
float attenuation = 1.0 / (light.constant + light.linear * distance + light.quadratic * (distance * distance));// Illumination attenuation formula
// The denominator : The linear attenuation in the front is required to be faster The latter is the quadratic term. The more it decays, the slower it decays constant + One time + Second term The greater the distance, the greater the influence of the quadratic term on this function
ambient *= attenuation;
diffuse *= attenuation;
specular *= attenuation;
vec3 result = ambient + diffuse + specular;
FragColor = vec4(result, 1.0);
}
//PointLight.fs2 Get the first 2 The effect of seed map
#version 330 core
out vec4 FragColor;
struct Material {
sampler2D diffuse;
sampler2D specular;
float shininess;
};
struct Light {
vec3 position;
vec3 ambient;
vec3 diffuse;
vec3 specular;
float constant;// Constant term
float linear;// One time
float quadratic;// Second term
float cutOff;//SpotDir( The spotlight points to ) The direction and LightDir( The vector from the clip to the light source ) Cosine of the included angle
};
in vec3 FragPos;
in vec3 Normal;
in vec2 TexCoords;
uniform vec3 viewPos;
uniform Material material;
uniform Light light;
void main()
{
// ambient
vec3 ambient = light.ambient * texture(material.diffuse, TexCoords).rgb;
// Ambient light component = The initial ambient light component of light * Diffuse material texture This is equivalent to telling the shader that the ambient light will be affected material.diffuse The influence of material
// The material is represented in the main function by set Pass in
// diffuse
vec3 norm = normalize(Normal);// Normalized normal vector
vec3 lightDir = normalize(light.position - FragPos);
//vec3 lightDir = normalize(-light.direction); // The direction of the vector direction" To simulate directional light Yes light.direction Reverse vector .
// The lighting calculation we currently use requires a light direction from the segment to the light source , But people are more used to defining directional light as a global direction starting from the light source .
float diff = max(dot(norm, lightDir), 0.0);// Point multiplication calculates the angle between the normal and the reflected ray
vec3 diffuse = light.diffuse * diff * texture(material.diffuse, TexCoords).rgb;
// Tell the shader that diffuse will be affected by material.diffuse The influence of material
// specular
vec3 viewDir = normalize(viewPos - FragPos);// The direction of human perspective From the object to the observer
vec3 reflectDir = reflect(-lightDir, norm);// Tell the incident light and normal reflect Calculate the vector of reflected light
float spec = pow(max(dot(viewDir, reflectDir), 0.0), material.shininess);//material.shininess Highlight level 2 4 8 16 32 64 128 The lower the level, the more blurred the aperture
vec3 specular = light.specular * spec * texture(material.specular, TexCoords).rgb;
// Tell the shader that highlights will be affected by material.diffuse The influence of material
float distance = length(light.position - FragPos);// Attenuation distance
float attenuation = 1.0 / (light.constant + light.linear * distance + light.quadratic * (distance * distance));// Illumination attenuation formula
// The denominator : The linear attenuation in the front is required to be faster The latter is the quadratic term. The more it decays, the slower it decays constant + One time + Second term The greater the distance, the greater the influence of the quadratic term on this function
ambient *= attenuation;
diffuse *= attenuation;
specular *= attenuation;
vec3 result = ambient + diffuse + specular;
FragColor = vec4(result, 1.0);
}


//LightingMaps
#include "Shader.h"
#define STB_IMAGE_IMPLEMENTATION
#include "stb_image.h"
#include <glad/glad.h>
#include <GLFW/glfw3.h>
#include <glm/glm.hpp>
#include <glm/gtc/matrix_transform.hpp>
#include <glm/gtc/type_ptr.hpp>
#include <iostream>
void mouse_callback(GLFWwindow* window, double xpos, double ypos);
void scroll_callback(GLFWwindow* window, double xoffset, double yoffset);
void processInput(GLFWwindow* window);
// settings
const unsigned int SCR_WIDTH = 800; // Define the size of screen space
const unsigned int SCR_HEIGHT = 600;
// camera
glm::vec3 cameraPos = glm::vec3(0.0f, 0.0f, 3.0f);
glm::vec3 cameraFront = glm::vec3(0.0f, 0.0f, -1.0f);
glm::vec3 cameraUp = glm::vec3(0.0f, 1.0f, 0.0f);
bool firstMouse = true;
float yaw = -90.0f; // Yaw is initialized to -90.0 degree , Because the yaw is 0.0 Will result in a direction vector pointing to the right , So we initially rotated a little to the left .
float pitch = 0.0f; // Initialize pitch angle
float lastX = 800.0f / 2.0;// In order to set the initial position as the center of the screen, take half the size of the screen space
float lastY = 600.0 / 2.0;
float fov = 45.0f;// Initial field angle
// timing
float deltaTime = 0.0f; // time between current frame and last frame
float lastFrame = 0.0f;
glm::vec3 lightPos(1.2f, 1.0f, 2.0f);
//glm::vec3 lightPos(1.2f, 1.0f, 2.0f);
void processInput(GLFWwindow* window);
float vertices[] = {
// positions // normals // texture coords
-0.5f, -0.5f, -0.5f, 0.0f, 0.0f, -1.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f,
0.5f, -0.5f, -0.5f, 0.0f, 0.0f, -1.0f, 1.0f, 0.0f,
0.5f, 0.5f, -0.5f, 0.0f, 0.0f, -1.0f, 1.0f, 1.0f,
0.5f, 0.5f, -0.5f, 0.0f, 0.0f, -1.0f, 1.0f, 1.0f,
-0.5f, 0.5f, -0.5f, 0.0f, 0.0f, -1.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f,
-0.5f, -0.5f, -0.5f, 0.0f, 0.0f, -1.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f,
-0.5f, -0.5f, 0.5f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f,
0.5f, -0.5f, 0.5f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f, 1.0f, 0.0f,
0.5f, 0.5f, 0.5f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f, 1.0f, 1.0f,
0.5f, 0.5f, 0.5f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f, 1.0f, 1.0f,
-0.5f, 0.5f, 0.5f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f,
-0.5f, -0.5f, 0.5f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f,
-0.5f, 0.5f, 0.5f, -1.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f, 0.0f,
-0.5f, 0.5f, -0.5f, -1.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f, 1.0f,
-0.5f, -0.5f, -0.5f, -1.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f,
-0.5f, -0.5f, -0.5f, -1.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f,
-0.5f, -0.5f, 0.5f, -1.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f,
-0.5f, 0.5f, 0.5f, -1.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f, 0.0f,
0.5f, 0.5f, 0.5f, 1.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f, 0.0f,
0.5f, 0.5f, -0.5f, 1.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f, 1.0f,
0.5f, -0.5f, -0.5f, 1.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f,
0.5f, -0.5f, -0.5f, 1.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f,
0.5f, -0.5f, 0.5f, 1.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f,
0.5f, 0.5f, 0.5f, 1.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f, 0.0f,
-0.5f, -0.5f, -0.5f, 0.0f, -1.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f,
0.5f, -0.5f, -0.5f, 0.0f, -1.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f, 1.0f,
0.5f, -0.5f, 0.5f, 0.0f, -1.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f, 0.0f,
0.5f, -0.5f, 0.5f, 0.0f, -1.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f, 0.0f,
-0.5f, -0.5f, 0.5f, 0.0f, -1.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f,
-0.5f, -0.5f, -0.5f, 0.0f, -1.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f,
-0.5f, 0.5f, -0.5f, 0.0f, 1.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f,
0.5f, 0.5f, -0.5f, 0.0f, 1.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f, 1.0f,
0.5f, 0.5f, 0.5f, 0.0f, 1.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f, 0.0f,
0.5f, 0.5f, 0.5f, 0.0f, 1.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f, 0.0f,
-0.5f, 0.5f, 0.5f, 0.0f, 1.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f,
-0.5f, 0.5f, -0.5f, 0.0f, 1.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f
};
// Define a vec3 Type array to store the displacement matrix
glm::vec3 cubePositions[] = {
glm::vec3(0.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f),
glm::vec3(2.0f, 5.0f, -15.0f),
glm::vec3(-1.5f, -2.2f, -2.5f),
glm::vec3(-3.8f, -2.0f, -12.3f),
glm::vec3(2.4f, -0.4f, -3.5f),
glm::vec3(-1.7f, 3.0f, -7.5f),
glm::vec3(1.3f, -2.0f, -2.5f),
glm::vec3(1.5f, 2.0f, -2.5f),
glm::vec3(1.5f, 0.2f, -1.5f),
glm::vec3(-1.3f, 1.0f, -1.5f),
};
int main()
{
//Glfw: Initialization and configuration
// ------------------------------
glfwInit();
glfwWindowHint(GLFW_CONTEXT_VERSION_MAJOR, 3);
glfwWindowHint(GLFW_CONTEXT_VERSION_MINOR, 3);
glfwWindowHint(GLFW_OPENGL_PROFILE, GLFW_OPENGL_CORE_PROFILE);
#ifdef __APPLE__
glfwWindowHint(GLFW_OPENGL_FORWARD_COMPAT, GL_TRUE);
#endif
//glfw Window creation
// --------------------
GLFWwindow* window = glfwCreateWindow(SCR_WIDTH, SCR_HEIGHT, "LearnOpenGL", NULL, NULL);// Use the size of the defined screen space
if (window == NULL)
{
std::cout << "Failed to create GLFW window" << std::endl;
glfwTerminate();
return -1;
}
glfwMakeContextCurrent(window);
glfwSetCursorPosCallback(window, mouse_callback);
glfwSetScrollCallback(window, scroll_callback);
// First we have to tell GLFW, It should hide the cursor , And capture (Capture) it .
glfwSetInputMode(window, GLFW_CURSOR, GLFW_CURSOR_DISABLED);
// Load all OpenGL A function pointer
// ---------------------------------------
if (!gladLoadGLLoader((GLADloadproc)glfwGetProcAddress))
{
std::cout << "Failed to initialize GLAD" << std::endl;
return -1;
}
// Configure global opengl state
// -----------------------------
glEnable(GL_DEPTH_TEST);
// Build and compile our shader Program
// ------------------------------------
Shader ourShader("shaderSampler.vs", "shaderSampler.fs");
Shader modelShader("PointLight.vs", "PointLight.fs");
Shader lightShader("lightShader.vs", "lightShader.fs");
// Create and compile vertex data ( And buffer ), Configure vertex attributes
// ------------------------------------------------------------------
unsigned int VBO, VAO, VAO2;
glGenVertexArrays(1, &VAO);
glGenBuffers(1, &VBO);
glBindBuffer(GL_ARRAY_BUFFER, VBO);
glBufferData(GL_ARRAY_BUFFER, sizeof(vertices), vertices, GL_STATIC_DRAW);
glBindVertexArray(VAO);
// Location properties
glVertexAttribPointer(0, 3, GL_FLOAT, GL_FALSE, 8 * sizeof(float), (void*)0);
glEnableVertexAttribArray(0);
// Then in the vertex shader layout (location = 1) in vec3 aNormal;// tell GPU Location 1 Properties of
glGenVertexArrays(1, &VAO2);
glBindVertexArray(VAO2);
//glBindBuffer(GL_ARRAY_BUFFER, VBO);
// Location properties
glVertexAttribPointer(0, 3, GL_FLOAT, GL_FALSE, 8 * sizeof(float), (void*)0);
glEnableVertexAttribArray(0);
// Normal attributes
glVertexAttribPointer(1, 3, GL_FLOAT, GL_FALSE, 8 * sizeof(float), (void*)(3 * sizeof(float)));
glEnableVertexAttribArray(1);
glVertexAttribPointer(2, 2, GL_FLOAT, GL_FALSE, 8 * sizeof(float), (void*)(6 * sizeof(float)));
glEnableVertexAttribArray(2);
// Load and create a texture
// -------------------------
unsigned int texture1, texture2;
// texture 1
// ---------
glGenTextures(1, &texture1);
glBindTexture(GL_TEXTURE_2D, texture1);
// Set the texture wrapping Parameters
glTexParameteri(GL_TEXTURE_2D, GL_TEXTURE_WRAP_S, GL_REPEAT);
glTexParameteri(GL_TEXTURE_2D, GL_TEXTURE_WRAP_T, GL_REPEAT);
// Set the texture filtering Parameters
glTexParameteri(GL_TEXTURE_2D, GL_TEXTURE_MIN_FILTER, GL_LINEAR);
glTexParameteri(GL_TEXTURE_2D, GL_TEXTURE_MAG_FILTER, GL_LINEAR);
// Load image , Create textures and generate mipmaps // Multi level principle texture
int width, height, nrChannels;
stbi_set_flip_vertically_on_load(true); // tell stb_image.h stay y Flip the loaded texture on the axis .
// Why do you need to flip Y The axis is because the starting position of the texture image is the upper right and the coordinates of our vertices (0,0) The point is lower left
unsigned char* data = stbi_load("container2.png", &width, &height, &nrChannels, 0);
if (data)
{
glTexImage2D(GL_TEXTURE_2D, 0, GL_RGBA, width, height, 0, GL_RGBA, GL_UNSIGNED_BYTE, data);
glGenerateMipmap(GL_TEXTURE_2D);
}
else
{
std::cout << "Failed to load texture" << std::endl;
}
stbi_image_free(data);
// texture 2
// ---------
glGenTextures(1, &texture2);
glBindTexture(GL_TEXTURE_2D, texture2);
// Set the texture wrapping Parameters
glTexParameteri(GL_TEXTURE_2D, GL_TEXTURE_WRAP_S, GL_REPEAT);
glTexParameteri(GL_TEXTURE_2D, GL_TEXTURE_WRAP_T, GL_REPEAT);
// Set the texture filtering Parameters
glTexParameteri(GL_TEXTURE_2D, GL_TEXTURE_MIN_FILTER, GL_LINEAR);
glTexParameteri(GL_TEXTURE_2D, GL_TEXTURE_MAG_FILTER, GL_LINEAR);
// load image, create texture and generate mipmaps
//data = stbi_load(("aotu.jpg"), &width, &height, &nrChannels, 0);
//data = stbi_load(("shanshui.jpg"), &width, &height, &nrChannels, 0);
data = stbi_load(("container2_specular.png"), &width, &height, &nrChannels, 0);
if (data)
{
// If there is no map, please give priority to this RGBA Medium alpha(A) passageway If your map has alpha Please be sure to use RGBA Otherwise, the map cannot be displayed
glTexImage2D(GL_TEXTURE_2D, 0, GL_RGBA, width, height, 0, GL_RGBA, GL_UNSIGNED_BYTE, data);
glGenerateMipmap(GL_TEXTURE_2D);
}
else
{
std::cout << "Failed to load texture" << std::endl;
}
stbi_image_free(data);
// Tell... For each sampler opengl Which texture unit does it belong to ( Just do it once )
// -------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
modelShader.use();
modelShader.setInt("material.diffuse", 0);
modelShader.setInt("material.specular", 1);
// ourShader.setVec3("lightPos", lightPos);
// Render loop
// -----------
while (!glfwWindowShouldClose(window))
{
float currentFrame = glfwGetTime();
deltaTime = currentFrame - lastFrame;
lastFrame = currentFrame;
// -----
processInput(window);
// Rendering
// ------
glClearColor(0.2f, 0.3f, 0.3f, 1.0f);
glClear(GL_COLOR_BUFFER_BIT | GL_DEPTH_BUFFER_BIT); // Clears the color buffer of the previous frame as well as Depth test buffer
// Activate shader
float angle = 20.0f * 0 * (float)glfwGetTime();// Give me a glfwGetTime Let the model rotate
glm::mat4 projection = glm::mat4(1.0f);
glm::mat4 view = glm::mat4(1.0f);
glm::mat4 model = glm::mat4(1.0f);
//glm::vec3 lightPos = glm::vec3(cubePositions[10]);// Light source location
projection = glm::perspective(glm::radians(fov), 800.0f / 600.0f, 0.1f, 100.0f);// Projection matrix Parameters : Viewport size , Screen aspect ratio , as well as near and far
view = glm::lookAt(cameraPos, cameraPos + cameraFront, cameraUp);//lookAt matrix Parameters : Camera position , Observe the position of the target , A vertical upward direction
model = glm::translate(model, cubePositions[0]);// Pass in the array to each new model, which has different displacement in world coordinates
model = glm::rotate(model, glm::radians(angle), glm::vec3(1.0f, 0.3f, 0.5f));
lightShader.use();
//lightPos.x = 1.0f + sin(glfwGetTime()) * 2.0f;
//lightPos.y = sin(glfwGetTime() / 2.0f) * 1.0f;
model = glm::mat4(1.0f);
model = glm::translate(model, lightPos);// Pass in the array to each new model, which has different displacement in world coordinates
angle = 20.0f * 2 * (float)glfwGetTime();// Give me a glfwGetTime Let the model rotate
model = glm::rotate(model, glm::radians(angle) , glm::vec3(1.0f, 0.3f, 0.5f));// Rotating objects
model = glm::scale(model, glm::vec3(0.2f));// Reduce the object on each axis to 0.2 times
lightShader.setMat4("model", model);
lightShader.setMat4("projection", projection);
lightShader.setMat4("view", view);
glBindVertexArray(VAO);
glDrawArrays(GL_TRIANGLES, 0, 36);
modelShader.use();
model = glm::mat4(1.0f);
model = glm::translate(model, cubePositions[0]);// Pass in the array to each new model, which has different displacement in world coordinates
angle = 20.0f * 1 * (float)glfwGetTime();// Give me a glfwGetTime Let the model rotate
model = glm::rotate(model, glm::radians(angle) * 0, glm::vec3(1.0f, 0.5f, 0.5f));//rotate Model location Rotation angle Rotation axis
modelShader.setMat4("model", model);// Set the model transformation matrix
modelShader.setMat4("projection", projection);// Set the projection change matrix
modelShader.setMat4("view", view);// Set the view change matrix
modelShader.setVec3("objectColor", 1, 0.5, 0.5);// Set the color of the object
modelShader.setVec3("lightColor", 1, 1, 1);// Set the color of the light source. Of course, you can also set a uniform To set variables
//modelShader.setVec3("lightPos", lightPos);// Set the light source position
modelShader.setVec3("viewPos", cameraPos);// Set the position of the camera to the viewing position
// Set each of the materials uniform component
modelShader.setVec3("material.ambient", 1.0f, 1.0f, 1.0f);
/*modelShader.setVec3("material.diffuse", 1.0f, 0.5f, 0.31f); modelShader.setVec3("material.specular", 0.5f, 0.5f, 0.5f);*/
modelShader.setFloat("material.shininess", 32.0f);
// Set up the light uniform component
modelShader.setVec3("light.ambient", 0.2f, 0.2f, 0.2f);
modelShader.setVec3("light.diffuse", 0.5f, 0.5f, 0.5f);
modelShader.setVec3("light.specular", 1.0f, 1.0f, 1.0f);
modelShader.setVec3("light.direction", -0.2f, -1.0f, -0.3f);// Set the directional light
modelShader.setVec3("light.position", lightPos);
// Set the object color to change over time
//glm::vec3 lightColor;
//lightColor.x = sin(glfwGetTime() * 2.0f);
//lightColor.y = sin(glfwGetTime() * 0.7f);
//lightColor.z = sin(glfwGetTime() * 1.3f);
//glm::vec3 diffuseColor = lightColor * glm::vec3(0.5f); // Reduce the impact
//glm::vec3 ambientColor = diffuseColor * glm::vec3(0.2f); // Very low impact
//modelShader.setVec3("light.ambient", ambientColor);
//modelShader.setVec3("light.diffuse", diffuseColor);
// Light attenuation coefficient of point light source
modelShader.setFloat("light.constant", 1.0f);
modelShader.setFloat("light.linear", 0.14f);
modelShader.setFloat("light.quadratic", 0.07f);
// Activate texture
glActiveTexture(GL_TEXTURE0);
glBindTexture(GL_TEXTURE_2D, texture1);
glActiveTexture(GL_TEXTURE1);
glBindTexture(GL_TEXTURE_2D, texture2);
for (unsigned int i = 0; i < 10; i++)
{
glm::mat4 model;
model = glm::translate(model, cubePositions[i]);
float angle = 20.0f * i;
model = glm::rotate(model, glm::radians(angle), glm::vec3(1.0f, 0.3f, 0.5f));
modelShader.setMat4("model", model);
glBindVertexArray(VAO2);
glDrawArrays(GL_TRIANGLES, 0, 36);
}
glfwSwapBuffers(window);
glfwPollEvents();
}
glDeleteVertexArrays(1, &VAO);
glDeleteBuffers(1, &VBO);
glfwTerminate();
return 0;
}
void processInput(GLFWwindow* window)
{
if (glfwGetKey(window, GLFW_KEY_ESCAPE) == GLFW_PRESS)
glfwSetWindowShouldClose(window, true);
float cameraSpeed = 5.5f * deltaTime;; // adjust accordingly
if (glfwGetKey(window, GLFW_KEY_W) == GLFW_PRESS)
cameraPos += cameraSpeed * cameraFront;
if (glfwGetKey(window, GLFW_KEY_S) == GLFW_PRESS)
cameraPos -= cameraSpeed * cameraFront;
if (glfwGetKey(window, GLFW_KEY_A) == GLFW_PRESS)
cameraPos -= glm::normalize(glm::cross(cameraFront, cameraUp)) * cameraSpeed;
if (glfwGetKey(window, GLFW_KEY_D) == GLFW_PRESS)
cameraPos += glm::normalize(glm::cross(cameraFront, cameraUp)) * cameraSpeed;
if (glfwGetKey(window, GLFW_KEY_SPACE) == GLFW_PRESS)// Here is a space bar so that we can Y Move on the axis
cameraPos += cameraUp * cameraSpeed;
//cameraPos.y = 0.0f;
// You can do this by Y The vector in the direction is set to 0 Make him FPS This type of camera can only be used in XZ Move on the plane
}
void mouse_callback(GLFWwindow* window, double xposIn, double yposIn)
{
float xpos = static_cast<float>(xposIn);
float ypos = static_cast<float>(yposIn);
// This bool The variable is initially set to true Of
// We need to set it as the center of the screen at the beginning
// If you don't do this At the beginning of the program, it will call the callback function to point to the position of the screen when you enter the mouse
// So it's far from the center
if (firstMouse)
{
lastX = xpos;
lastY = ypos;
firstMouse = false;
}
// Then, in the mouse callback function, we calculate the offset of the mouse position between the current frame and the previous frame :
float xoffset = xpos - lastX;
float yoffset = lastY - ypos; // y The coordinates are from bottom to top
lastX = xpos;
lastY = ypos;
float sensitivity = 0.1f; // sensitivity This value can be set arbitrarily
xoffset *= sensitivity;
yoffset *= sensitivity;
yaw += xoffset;
pitch += yoffset;
// To make sure the camera doesn't roll over
if (pitch > 89.0f)
pitch = 89.0f;
if (pitch < -89.0f)
pitch = -89.0f;
// stay xz Look at... On the plane Y Axis
// Here we only update y value , Observe carefully x and z The component is also affected . From the triangles, we can see that their value is equal to :
//direction.x = cos(glm::radians(pitch));
//direction.y = sin(glm::radians(pitch)); // Notice that we first turn the angle into radians
//direction.z = cos(glm::radians(pitch));// here Y Axis updates do affect Z But I don't quite understand why it's directly equal to cos(pitch)
//
//
//
// Here we only update y value , Observe carefully x and z The component is also affected . From the triangles, we can see that their value is equal to :
//direction.x = cos(glm::radians(yaw));
//direction.y =1 // Y unchanged
//direction.z = sin(glm::radians(yaw));
//
// The following equation is equivalent to first completing the rotation transformation of the pitch angle and then multiplying it by the yaw angle
// Combine the above two steps
glm::vec3 front;
front.x = cos(glm::radians(yaw)) * cos(glm::radians(pitch));
front.y = sin(glm::radians(pitch));
front.z = sin(glm::radians(yaw)) * cos(glm::radians(pitch));
cameraFront = glm::normalize(front);
}
// glfw: whenever the mouse scroll wheel scrolls, this callback is called
// ----------------------------------------------------------------------
void scroll_callback(GLFWwindow* window, double xoffset, double yoffset)
{
//yoffset Is the direction in which our roller rolls vertically
if (fov >= 1.0f && fov <= 45.0f)
fov -= yoffset;
// Set a boundary for him stay 1 To 45 Between
if (fov < 1.0f)
fov = 1.0f;
if (fov > 45.0f)
fov = 45.0f;
}
Spotlight (Spotlight)


//Spotlight.vs
#version 330 core
layout (location = 0) in vec3 aPos;// The initial position is 0 The attribute of is vertex position
layout (location = 1) in vec3 aNormal;// The initial position is 1 The attribute of is normal position
layout (location = 2) in vec2 aTexCoords;// The initial position is 2 The attribute of is mapping coordinates
out vec3 FragPos;// Output the position of the object
out vec3 Normal;// Output normals
out vec2 TexCoords;// Output map
uniform mat4 model;// Define global variables model Set... In the main function
uniform mat4 view;// Define global variables view Set... In the main function
uniform mat4 projection;// Define global variables projection Set... In the main function
void main()
{
FragPos = vec3(model * vec4(aPos, 1.0));
// The position of an object in world coordinates after model transformation
Normal = mat3(transpose(inverse(model))) * aNormal;
// Normal transformation matrix = Transpose of inverse matrix * Normal matrix
TexCoords = aTexCoords;
// UVW Map
gl_Position = projection * view * vec4(FragPos, 1.0);// The last position you see in the cone
}
//Spotlight.fs
#version 330 core
out vec4 FragColor;
struct Material {
sampler2D diffuse;
sampler2D specular;
float shininess;
};
struct Light {
vec3 position;
vec3 direction;
float cutOff;// Define an inner cone
float outerCutOff;// Define an outer cone
vec3 ambient;
vec3 diffuse;
vec3 specular;
float constant;// Constant term
float linear;// One time
float quadratic;// Second term
};
in vec3 FragPos;
in vec3 Normal;
in vec2 TexCoords;
uniform vec3 viewPos;
uniform Material material;
uniform Light light;
void main()
{
vec3 lightDir = normalize(light.position - FragPos);// Calculation lightDir The vector of the object pointing to the light source
// Then use this vector to calculate theta horn
// check if lighting is inside the spotlight cone
float theta = dot(lightDir, normalize(-light.direction)); // Click it out theta Cosine value
if(theta > light.cutOff) // Here, we compare the cosine values at the angle of 0-90 The greater the degree, the smaller the cosine, so here is > Symbol
{
// The next one is the same as the previous one
// ambient
vec3 ambient = light.ambient * texture(material.diffuse, TexCoords).rgb;
// diffuse
vec3 norm = normalize(Normal);
float diff = max(dot(norm, lightDir), 0.0);
vec3 diffuse = light.diffuse * diff * texture(material.diffuse, TexCoords).rgb;
// specular
vec3 viewDir = normalize(viewPos - FragPos);
vec3 reflectDir = reflect(-lightDir, norm);
float spec = pow(max(dot(viewDir, reflectDir), 0.0), material.shininess);
vec3 specular = light.specular * spec * texture(material.specular, TexCoords).rgb;
// attenuation Attenuation term
float distance = length(light.position - FragPos);
float attenuation = 1.0 / (light.constant + light.linear * distance + light.quadratic * (distance * distance));
// ambient *= attenuation;
// Remove attenuation from the environment , Otherwise, at a large distance , Because in else Environment items in the branch , The light will be darker than the inside of the spotlight
diffuse *= attenuation;
specular *= attenuation;
vec3 result = ambient + diffuse + specular;
FragColor = vec4(result, 1.0);
}
else
{
// If you use ambient light outside the cone
FragColor = vec4(light.ambient * texture(material.diffuse, TexCoords).rgb, 1.0);
}
}
//LightingMaps
#include "Shader.h"
#define STB_IMAGE_IMPLEMENTATION
#include "stb_image.h"
#include <glad/glad.h>
#include <GLFW/glfw3.h>
#include <glm/glm.hpp>
#include <glm/gtc/matrix_transform.hpp>
#include <glm/gtc/type_ptr.hpp>
#include <iostream>
void mouse_callback(GLFWwindow* window, double xpos, double ypos);
void scroll_callback(GLFWwindow* window, double xoffset, double yoffset);
void processInput(GLFWwindow* window);
// settings
const unsigned int SCR_WIDTH = 800; // Define the size of screen space
const unsigned int SCR_HEIGHT = 600;
// camera
glm::vec3 cameraPos = glm::vec3(0.0f, 0.0f, 3.0f);
glm::vec3 cameraFront = glm::vec3(0.0f, 0.0f, -1.0f);
glm::vec3 cameraUp = glm::vec3(0.0f, 1.0f, 0.0f);
bool firstMouse = true;
float yaw = -90.0f; // Yaw is initialized to -90.0 degree , Because the yaw is 0.0 Will result in a direction vector pointing to the right , So we initially rotated a little to the left .
float pitch = 0.0f; // Initialize pitch angle
float lastX = 800.0f / 2.0;// In order to set the initial position as the center of the screen, take half the size of the screen space
float lastY = 600.0 / 2.0;
float fov = 45.0f;// Initial field angle
// timing
float deltaTime = 0.0f; // time between current frame and last frame
float lastFrame = 0.0f;
glm::vec3 lightPos(1.2f, 1.0f, 2.0f);
//glm::vec3 lightPos(1.2f, 1.0f, 2.0f);
void processInput(GLFWwindow* window);
float vertices[] = {
// positions // normals // texture coords
-0.5f, -0.5f, -0.5f, 0.0f, 0.0f, -1.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f,
0.5f, -0.5f, -0.5f, 0.0f, 0.0f, -1.0f, 1.0f, 0.0f,
0.5f, 0.5f, -0.5f, 0.0f, 0.0f, -1.0f, 1.0f, 1.0f,
0.5f, 0.5f, -0.5f, 0.0f, 0.0f, -1.0f, 1.0f, 1.0f,
-0.5f, 0.5f, -0.5f, 0.0f, 0.0f, -1.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f,
-0.5f, -0.5f, -0.5f, 0.0f, 0.0f, -1.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f,
-0.5f, -0.5f, 0.5f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f,
0.5f, -0.5f, 0.5f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f, 1.0f, 0.0f,
0.5f, 0.5f, 0.5f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f, 1.0f, 1.0f,
0.5f, 0.5f, 0.5f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f, 1.0f, 1.0f,
-0.5f, 0.5f, 0.5f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f,
-0.5f, -0.5f, 0.5f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f,
-0.5f, 0.5f, 0.5f, -1.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f, 0.0f,
-0.5f, 0.5f, -0.5f, -1.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f, 1.0f,
-0.5f, -0.5f, -0.5f, -1.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f,
-0.5f, -0.5f, -0.5f, -1.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f,
-0.5f, -0.5f, 0.5f, -1.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f,
-0.5f, 0.5f, 0.5f, -1.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f, 0.0f,
0.5f, 0.5f, 0.5f, 1.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f, 0.0f,
0.5f, 0.5f, -0.5f, 1.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f, 1.0f,
0.5f, -0.5f, -0.5f, 1.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f,
0.5f, -0.5f, -0.5f, 1.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f,
0.5f, -0.5f, 0.5f, 1.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f,
0.5f, 0.5f, 0.5f, 1.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f, 0.0f,
-0.5f, -0.5f, -0.5f, 0.0f, -1.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f,
0.5f, -0.5f, -0.5f, 0.0f, -1.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f, 1.0f,
0.5f, -0.5f, 0.5f, 0.0f, -1.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f, 0.0f,
0.5f, -0.5f, 0.5f, 0.0f, -1.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f, 0.0f,
-0.5f, -0.5f, 0.5f, 0.0f, -1.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f,
-0.5f, -0.5f, -0.5f, 0.0f, -1.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f,
-0.5f, 0.5f, -0.5f, 0.0f, 1.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f,
0.5f, 0.5f, -0.5f, 0.0f, 1.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f, 1.0f,
0.5f, 0.5f, 0.5f, 0.0f, 1.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f, 0.0f,
0.5f, 0.5f, 0.5f, 0.0f, 1.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f, 0.0f,
-0.5f, 0.5f, 0.5f, 0.0f, 1.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f,
-0.5f, 0.5f, -0.5f, 0.0f, 1.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f
};
// Define a vec3 Type array to store the displacement matrix
glm::vec3 cubePositions[] = {
glm::vec3(0.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f),
glm::vec3(2.0f, 5.0f, -15.0f),
glm::vec3(-1.5f, -2.2f, -2.5f),
glm::vec3(-3.8f, -2.0f, -12.3f),
glm::vec3(2.4f, -0.4f, -3.5f),
glm::vec3(-1.7f, 3.0f, -7.5f),
glm::vec3(1.3f, -2.0f, -2.5f),
glm::vec3(1.5f, 2.0f, -2.5f),
glm::vec3(1.5f, 0.2f, -1.5f),
glm::vec3(-1.3f, 1.0f, -1.5f),
};
int main()
{
//Glfw: Initialization and configuration
// ------------------------------
glfwInit();
glfwWindowHint(GLFW_CONTEXT_VERSION_MAJOR, 3);
glfwWindowHint(GLFW_CONTEXT_VERSION_MINOR, 3);
glfwWindowHint(GLFW_OPENGL_PROFILE, GLFW_OPENGL_CORE_PROFILE);
#ifdef __APPLE__
glfwWindowHint(GLFW_OPENGL_FORWARD_COMPAT, GL_TRUE);
#endif
//glfw Window creation
// --------------------
GLFWwindow* window = glfwCreateWindow(SCR_WIDTH, SCR_HEIGHT, "LearnOpenGL", NULL, NULL);// Use the size of the defined screen space
if (window == NULL)
{
std::cout << "Failed to create GLFW window" << std::endl;
glfwTerminate();
return -1;
}
glfwMakeContextCurrent(window);
glfwSetCursorPosCallback(window, mouse_callback);
glfwSetScrollCallback(window, scroll_callback);
// First we have to tell GLFW, It should hide the cursor , And capture (Capture) it .
glfwSetInputMode(window, GLFW_CURSOR, GLFW_CURSOR_DISABLED);
// Load all OpenGL A function pointer
// ---------------------------------------
if (!gladLoadGLLoader((GLADloadproc)glfwGetProcAddress))
{
std::cout << "Failed to initialize GLAD" << std::endl;
return -1;
}
// Configure global opengl state
// -----------------------------
glEnable(GL_DEPTH_TEST);
// Build and compile our shader Program
// ------------------------------------
Shader ourShader("shaderSampler.vs", "shaderSampler.fs");
Shader modelShader("Spotlight.vs", "Spotlight.fs");
Shader lightShader("lightShader.vs", "lightShader.fs");
// Create and compile vertex data ( And buffer ), Configure vertex attributes
// ------------------------------------------------------------------
unsigned int VBO, VAO, VAO2;
glGenVertexArrays(1, &VAO);
glGenBuffers(1, &VBO);
glBindBuffer(GL_ARRAY_BUFFER, VBO);
glBufferData(GL_ARRAY_BUFFER, sizeof(vertices), vertices, GL_STATIC_DRAW);
glBindVertexArray(VAO);
// Location properties
glVertexAttribPointer(0, 3, GL_FLOAT, GL_FALSE, 8 * sizeof(float), (void*)0);
glEnableVertexAttribArray(0);
// Then in the vertex shader layout (location = 1) in vec3 aNormal;// tell GPU Location 1 Properties of
glGenVertexArrays(1, &VAO2);
glBindVertexArray(VAO2);
//glBindBuffer(GL_ARRAY_BUFFER, VBO);
// Location properties
glVertexAttribPointer(0, 3, GL_FLOAT, GL_FALSE, 8 * sizeof(float), (void*)0);
glEnableVertexAttribArray(0);
// Normal attributes
glVertexAttribPointer(1, 3, GL_FLOAT, GL_FALSE, 8 * sizeof(float), (void*)(3 * sizeof(float)));
glEnableVertexAttribArray(1);
glVertexAttribPointer(2, 2, GL_FLOAT, GL_FALSE, 8 * sizeof(float), (void*)(6 * sizeof(float)));
glEnableVertexAttribArray(2);
// Load and create a texture
// -------------------------
unsigned int texture1, texture2;
// texture 1
// ---------
glGenTextures(1, &texture1);
glBindTexture(GL_TEXTURE_2D, texture1);
// Set the texture wrapping Parameters
glTexParameteri(GL_TEXTURE_2D, GL_TEXTURE_WRAP_S, GL_REPEAT);
glTexParameteri(GL_TEXTURE_2D, GL_TEXTURE_WRAP_T, GL_REPEAT);
// Set the texture filtering Parameters
glTexParameteri(GL_TEXTURE_2D, GL_TEXTURE_MIN_FILTER, GL_LINEAR);
glTexParameteri(GL_TEXTURE_2D, GL_TEXTURE_MAG_FILTER, GL_LINEAR);
// Load image , Create textures and generate mipmaps // Multi level principle texture
int width, height, nrChannels;
stbi_set_flip_vertically_on_load(true); // tell stb_image.h stay y Flip the loaded texture on the axis .
// Why do you need to flip Y The axis is because the starting position of the texture image is the upper right and the coordinates of our vertices (0,0) The point is lower left
unsigned char* data = stbi_load("container2.png", &width, &height, &nrChannels, 0);
if (data)
{
glTexImage2D(GL_TEXTURE_2D, 0, GL_RGBA, width, height, 0, GL_RGBA, GL_UNSIGNED_BYTE, data);
glGenerateMipmap(GL_TEXTURE_2D);
}
else
{
std::cout << "Failed to load texture" << std::endl;
}
stbi_image_free(data);
// texture 2
// ---------
glGenTextures(1, &texture2);
glBindTexture(GL_TEXTURE_2D, texture2);
// Set the texture wrapping Parameters
glTexParameteri(GL_TEXTURE_2D, GL_TEXTURE_WRAP_S, GL_REPEAT);
glTexParameteri(GL_TEXTURE_2D, GL_TEXTURE_WRAP_T, GL_REPEAT);
// Set the texture filtering Parameters
glTexParameteri(GL_TEXTURE_2D, GL_TEXTURE_MIN_FILTER, GL_LINEAR);
glTexParameteri(GL_TEXTURE_2D, GL_TEXTURE_MAG_FILTER, GL_LINEAR);
// load image, create texture and generate mipmaps
//data = stbi_load(("aotu.jpg"), &width, &height, &nrChannels, 0);
//data = stbi_load(("shanshui.jpg"), &width, &height, &nrChannels, 0);
data = stbi_load(("container2_specular.png"), &width, &height, &nrChannels, 0);
if (data)
{
// If there is no map, please give priority to this RGBA Medium alpha(A) passageway If your map has alpha Please be sure to use RGBA Otherwise, the map cannot be displayed
glTexImage2D(GL_TEXTURE_2D, 0, GL_RGBA, width, height, 0, GL_RGBA, GL_UNSIGNED_BYTE, data);
glGenerateMipmap(GL_TEXTURE_2D);
}
else
{
std::cout << "Failed to load texture" << std::endl;
}
stbi_image_free(data);
// Tell... For each sampler opengl Which texture unit does it belong to ( Just do it once )
// -------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
modelShader.use();
modelShader.setInt("material.diffuse", 0);
modelShader.setInt("material.specular", 1);
// ourShader.setVec3("lightPos", lightPos);
// Render loop
// -----------
while (!glfwWindowShouldClose(window))
{
float currentFrame = glfwGetTime();
deltaTime = currentFrame - lastFrame;
lastFrame = currentFrame;
// -----
processInput(window);
// Rendering
// ------
glClearColor(0.2f, 0.3f, 0.3f, 1.0f);
glClear(GL_COLOR_BUFFER_BIT | GL_DEPTH_BUFFER_BIT); // Clears the color buffer of the previous frame as well as Depth test buffer
// Activate shader
float angle = 20.0f * 0 * (float)glfwGetTime();// Give me a glfwGetTime Let the model rotate
glm::mat4 projection = glm::mat4(1.0f);
glm::mat4 view = glm::mat4(1.0f);
glm::mat4 model = glm::mat4(1.0f);
//glm::vec3 lightPos = glm::vec3(cubePositions[10]);// Light source location
projection = glm::perspective(glm::radians(fov), 800.0f / 600.0f, 0.1f, 100.0f);// Projection matrix Parameters : Viewport size , Screen aspect ratio , as well as near and far
view = glm::lookAt(cameraPos, cameraPos + cameraFront, cameraUp);//lookAt matrix Parameters : Camera position , Observe the position of the target , A vertical upward direction
model = glm::translate(model, cubePositions[0]);// Pass in the array to each new model, which has different displacement in world coordinates
model = glm::rotate(model, glm::radians(angle), glm::vec3(1.0f, 0.3f, 0.5f));
//lightShader.use();
lightPos.x = 1.0f + sin(glfwGetTime()) * 2.0f;
lightPos.y = sin(glfwGetTime() / 2.0f) * 1.0f;
//model = glm::mat4(1.0f);
//model = glm::translate(model, lightPos);// Pass in the array to each new model, which has different displacement in world coordinates
//angle = 20.0f * 2 * (float)glfwGetTime();// Give me a glfwGetTime Let the model rotate
//model = glm::rotate(model, glm::radians(angle), glm::vec3(1.0f, 0.3f, 0.5f));// Rotating objects
//model = glm::scale(model, glm::vec3(0.2f));// Reduce the object on each axis to 0.2 times
//lightShader.setMat4("model", model);
//lightShader.setMat4("projection", projection);
//lightShader.setMat4("view", view);
//glBindVertexArray(VAO);
//glDrawArrays(GL_TRIANGLES, 0, 36);
modelShader.use();
model = glm::mat4(1.0f);
model = glm::translate(model, cubePositions[0]);// Pass in the array to each new model, which has different displacement in world coordinates
angle = 20.0f * 1 * (float)glfwGetTime();// Give me a glfwGetTime Let the model rotate
model = glm::rotate(model, glm::radians(angle) * 0, glm::vec3(1.0f, 0.5f, 0.5f));//rotate Model location Rotation angle Rotation axis
modelShader.setMat4("model", model);// Set the model transformation matrix
modelShader.setMat4("projection", projection);// Set the projection change matrix
modelShader.setMat4("view", view);// Set the view change matrix
modelShader.setVec3("objectColor", 1, 0.5, 0.5);// Set the color of the object
modelShader.setVec3("lightColor", 1, 1, 1);// Set the color of the light source. Of course, you can also set a uniform To set variables
//modelShader.setVec3("lightPos", lightPos);// Set the light source position
modelShader.setVec3("viewPos", cameraPos);// Set the position of the camera to the viewing position
// Set each of the materials uniform component
modelShader.setVec3("material.ambient", 1.0f, 1.0f, 1.0f);
/*modelShader.setVec3("material.diffuse", 1.0f, 0.5f, 0.31f); modelShader.setVec3("material.specular", 0.5f, 0.5f, 0.5f);*/
modelShader.setFloat("material.shininess", 32.0f);
// Set up the light uniform component
modelShader.setVec3("light.ambient", 0.1f, 0.1f, 0.1f);
modelShader.setVec3("light.diffuse", 0.8f, 0.8f, 0.8f);
modelShader.setVec3("light.specular", 1.0f, 1.0f, 1.0f);
modelShader.setVec3("light.direction", 0.0f, 0.0f, -1.0f);// Set the directional light
modelShader.setVec3("light.position", 0.0f,0.0f,5.0f);// You can adjust the position of the light to adjust the range of the cone
modelShader.setFloat("light.cutOff", glm::cos(glm::radians(12.5f)));// Set inner cone
modelShader.setFloat("light.outerCutOff", glm::cos(glm::radians(17.5f)));// Set the outer cone
// Set the object color to change over time
//glm::vec3 lightColor;
//lightColor.x = sin(glfwGetTime() * 2.0f);
//lightColor.y = sin(glfwGetTime() * 0.7f);
//lightColor.z = sin(glfwGetTime() * 1.3f);
//glm::vec3 diffuseColor = lightColor * glm::vec3(0.5f); // Reduce the impact
//glm::vec3 ambientColor = diffuseColor * glm::vec3(0.2f); // Very low impact
//modelShader.setVec3("light.ambient", ambientColor);
//modelShader.setVec3("light.diffuse", diffuseColor);
// Light attenuation coefficient of point light source
modelShader.setFloat("light.constant", 1.0f);
modelShader.setFloat("light.linear", 0.09f);
modelShader.setFloat("light.quadratic", 0.032f);
// Activate texture
glActiveTexture(GL_TEXTURE0);
glBindTexture(GL_TEXTURE_2D, texture1);
glActiveTexture(GL_TEXTURE1);
glBindTexture(GL_TEXTURE_2D, texture2);
for (unsigned int i = 0; i < 10; i++)
{
glm::mat4 model;
model = glm::translate(model, cubePositions[i]);
float angle = 20.0f * i;
model = glm::rotate(model, glm::radians(angle), glm::vec3(1.0f, 0.3f, 0.5f));
modelShader.setMat4("model", model);
glBindVertexArray(VAO2);
glDrawArrays(GL_TRIANGLES, 0, 36);
}
glfwSwapBuffers(window);
glfwPollEvents();
}
glDeleteVertexArrays(1, &VAO);
glDeleteBuffers(1, &VBO);
glfwTerminate();
return 0;
}
void processInput(GLFWwindow* window)
{
if (glfwGetKey(window, GLFW_KEY_ESCAPE) == GLFW_PRESS)
glfwSetWindowShouldClose(window, true);
float cameraSpeed = 5.5f * deltaTime;; // adjust accordingly
if (glfwGetKey(window, GLFW_KEY_W) == GLFW_PRESS)
cameraPos += cameraSpeed * cameraFront;
if (glfwGetKey(window, GLFW_KEY_S) == GLFW_PRESS)
cameraPos -= cameraSpeed * cameraFront;
if (glfwGetKey(window, GLFW_KEY_A) == GLFW_PRESS)
cameraPos -= glm::normalize(glm::cross(cameraFront, cameraUp)) * cameraSpeed;
if (glfwGetKey(window, GLFW_KEY_D) == GLFW_PRESS)
cameraPos += glm::normalize(glm::cross(cameraFront, cameraUp)) * cameraSpeed;
if (glfwGetKey(window, GLFW_KEY_SPACE) == GLFW_PRESS)// Here is a space bar so that we can Y Move on the axis
cameraPos += cameraUp * cameraSpeed;
//cameraPos.y = 0.0f;
// You can do this by Y The vector in the direction is set to 0 Make him FPS This type of camera can only be used in XZ Move on the plane
}
void mouse_callback(GLFWwindow* window, double xposIn, double yposIn)
{
float xpos = static_cast<float>(xposIn);
float ypos = static_cast<float>(yposIn);
// This bool The variable is initially set to true Of
// We need to set it as the center of the screen at the beginning
// If you don't do this At the beginning of the program, it will call the callback function to point to the position of the screen when you enter the mouse
// So it's far from the center
if (firstMouse)
{
lastX = xpos;
lastY = ypos;
firstMouse = false;
}
// Then, in the mouse callback function, we calculate the offset of the mouse position between the current frame and the previous frame :
float xoffset = xpos - lastX;
float yoffset = lastY - ypos; // y The coordinates are from bottom to top
lastX = xpos;
lastY = ypos;
float sensitivity = 0.1f; // sensitivity This value can be set arbitrarily
xoffset *= sensitivity;
yoffset *= sensitivity;
yaw += xoffset;
pitch += yoffset;
// To make sure the camera doesn't roll over
if (pitch > 89.0f)
pitch = 89.0f;
if (pitch < -89.0f)
pitch = -89.0f;
// stay xz Look at... On the plane Y Axis
// Here we only update y value , Observe carefully x and z The component is also affected . From the triangles, we can see that their value is equal to :
//direction.x = cos(glm::radians(pitch));
//direction.y = sin(glm::radians(pitch)); // Notice that we first turn the angle into radians
//direction.z = cos(glm::radians(pitch));// here Y Axis updates do affect Z But I don't quite understand why it's directly equal to cos(pitch)
//
//
//
// Here we only update y value , Observe carefully x and z The component is also affected . From the triangles, we can see that their value is equal to :
//direction.x = cos(glm::radians(yaw));
//direction.y =1 // Y unchanged
//direction.z = sin(glm::radians(yaw));
//
// The following equation is equivalent to first completing the rotation transformation of the pitch angle and then multiplying it by the yaw angle
// Combine the above two steps
glm::vec3 front;
front.x = cos(glm::radians(yaw)) * cos(glm::radians(pitch));
front.y = sin(glm::radians(pitch));
front.z = sin(glm::radians(yaw)) * cos(glm::radians(pitch));
cameraFront = glm::normalize(front);
}
// glfw: whenever the mouse scroll wheel scrolls, this callback is called
// ----------------------------------------------------------------------
void scroll_callback(GLFWwindow* window, double xoffset, double yoffset)
{
//yoffset Is the direction in which our roller rolls vertically
if (fov >= 1.0f && fov <= 45.0f)
fov -= yoffset;
// Set a boundary for him stay 1 To 45 Between
if (fov < 1.0f)
fov = 1.0f;
if (fov > 45.0f)
fov = 45.0f;
}

Edge blur processing 

Just use this formula change fs
//Spotlight.fs
#version 330 core
out vec4 FragColor;
struct Material {
sampler2D diffuse;
sampler2D specular;
float shininess;
};
struct Light {
vec3 position;
vec3 direction;
float cutOff;
float outerCutOff;
vec3 ambient;
vec3 diffuse;
vec3 specular;
float constant;
float linear;
float quadratic;
};
in vec3 FragPos;
in vec3 Normal;
in vec2 TexCoords;
uniform vec3 viewPos;
uniform Material material;
uniform Light light;
void main()
{
// ambient
vec3 ambient = light.ambient * texture(material.diffuse, TexCoords).rgb;
// diffuse
vec3 norm = normalize(Normal);
vec3 lightDir = normalize(light.position - FragPos);
float diff = max(dot(norm, lightDir), 0.0);
vec3 diffuse = light.diffuse * diff * texture(material.diffuse, TexCoords).rgb;
// specular
vec3 viewDir = normalize(viewPos - FragPos);
vec3 reflectDir = reflect(-lightDir, norm);
float spec = pow(max(dot(viewDir, reflectDir), 0.0), material.shininess);
vec3 specular = light.specular * spec * texture(material.specular, TexCoords).rgb;
// spotlight (soft edges)
// Directly multiply by this influence formula Use the calculated theta and epsilon
float theta = dot(lightDir, normalize(-light.direction));
float epsilon = (light.cutOff - light.outerCutOff);
float intensity = clamp((theta - light.outerCutOff) / epsilon, 0.0, 1.0);
diffuse *= intensity;
specular *= intensity;
// attenuation
float distance = length(light.position - FragPos);
float attenuation = 1.0 / (light.constant + light.linear * distance + light.quadratic * (distance * distance));
ambient *= attenuation;
diffuse *= attenuation;
specular *= attenuation;
vec3 result = ambient + diffuse + specular;
FragColor = vec4(result, 1.0);
}

边栏推荐
- Logical deletion_ Swagger2 framework integration
- RHEL7 切换字符编码为GBK
- R analysis visual practical data (flight \u education \u restaurant \u tenant \u change \u life \u safety)
- LaTex环境下在TexStudio中使用minted插入高亮代码
- openssl enc 加解密
- {dataSource-1} closing ... {dataSource-1} closed
- UML series articles (28) architecture modeling - collaboration
- 單片機通信數據延遲問題排查
- C. Jump and Treasure(dp + 单调队列优化)
- C. Jump and treat (DP + monotonic queue optimization)
猜你喜欢

Free flying animation of paper plane based on SVG

If not, use the code generator to generate a set of addition, deletion, modification and query (2)

thinkphp3.2.3反序列化利用链分析

js顶部图标菜单点击切换背景色js特效

B_ QuRT_ User_ Guide(18)

ThoughtWorks. QRcode full-featured generator

OpenGL第十一章 多光源

Artalk | how to build a domestic hyperfusion evolutionary base with minimum investment?

單片機通信數據延遲問題排查

/The world of 10 recommended websites for learning programming has entered the era of the Internet. According to a recently released Internet trends 2016 report, China has become a leader in the Inter
随机推荐
Mavros controls UAV to conduct binocular slam in gazebo environment
Artalk | how to build a domestic hyperfusion evolutionary base with minimum investment?
OpenGL第八章 材质material
Logical deletion_ Swagger2 framework integration
Path count 2 (DP + number of combinations)
Dépannage du problème de retard des données de communication du micro - ordinateur à puce unique
Vocabulary Construction -- code completion fast food tutorial (3) - word segmentation
Lecturer paging query_ Instructor condition query with page
B_ QuRT_ User_ Guide(18)
Reasons why Chinese comments cannot be written in XML
JLINK latest version download
The tide play power is really firepower! The first big screen cinema for young people? Cool open TV Max 86 "sudden attack
用Fragment实现图片简易浏览
被“内卷”酸翻的OPPO Reno6
【ELT.ZIP】OpenHarmony啃论文俱乐部——数据高通量无损压缩方案
OpenGL第七章 基础光照
Rhel7 switch character encoding to GBK
多线程交替输出AB
Why is vfly, a high-end brand of Yadi that does not live up to its name, not high-end?
Arm development board scheme and manufacturer analysis