当前位置:网站首页>C. Jump and treat (DP + monotonic queue optimization)
C. Jump and treat (DP + monotonic queue optimization)
2022-06-11 03:29:00 【to cling】
Problem
Give an example from 0 Start , The length is n+1 A sequence , from 1 To n Each point has a certain value of gold coins a[i]( Positive but negative ). from 0 Start at node , You can jump no more than each time p Nodes , Jump to the node i Go up ( Assuming that the i Node No. jumps to j Node No , i < j , j − i ≤ p i < j, j - i\leq p i<j,j−i≤p ). Yes q A asked , One at a time x( 1 ≤ x ≤ n 1 \leq x \leq n 1≤x≤n), You can only jump to x On the node of multiples ( If the node number is less than n Words , Can only jump to x On the integer multiple node of . When jumping to less than or equal to n The last x On the integer multiple node of , Just take the last step out n, And this step does not exceed p that will do ), meanwhile , Each jump cannot exceed p, And must eventually jump to greater than n On the node of : Ask how much gold coins you can collect . If you can't jump to greater than n On the node of , The output "Noob".
Solution
- State means :dp[i] It means to jump to the node i The most valuable gold coin that can be collected on the .
- State shift : d p [ i ] = m a x ( d p [ j ] ) + a [ i ] ( i % x = 0 , j % x = 0 , i − j ≤ p ) dp[i] = max(dp[j]) + a[i]~~~~~~(i \% x = 0, j \% x = 0,i - j \leq p) dp[i]=max(dp[j])+a[i] (i%x=0,j%x=0,i−j≤p)
Can be maintained with monotonic queues that can be transferred to state i Several states of . - Be careful : Finally, you must jump to greater than n Node , The last state should be
n + 1, Not the last x On the integer multiple node of (n / x * x + x). And the two states are not equivalent .
for example : n = 10,p = 5, x = 2.
When the last state isn + 1when (11), Can be dp[6],dp[8],dp[10] The biggest one in the transfer .
and , The last state isn / x * x + xwhen (12), Can be dp[8],dp[10] The biggest one in the transfer .
obviously , The two cases are not equivalent , Pay special attention to .
Code
const int N = 2e6 + 6;
ll dp[N];
ll a[N];
unordered_map<ll, ll>mp;
int main()
{
IOS;
int n, q, p; cin >> n >> q >> p;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
cin >> a[i];
while (q--)
{
deque<int> q;
int x; cin >> x;
if (mp.count(x))
{
cout << mp[x] << endl;
continue;
}
if (x > p) cout << "Noob\n";
else
{
dp[0] = 0;
q.push_back(0);
vector<int>b;
b.push_back(0);
for (int i = x; i <= n; i += x)
b.push_back(i);
b.push_back(n + 1);// Be careful : In this question n You can only jump within x Multiple ,n It can not be x Multiple , So it can't be written n / x * x + x
for (int i = 1; i < sz(b); i++)
{
while (q.empty() == 0 && b[i] - b[q.front()] > p) q.pop_front();
dp[i] = dp[q.front()] + a[b[i]];
while (q.empty() == 0 && dp[q.back()] <= dp[i]) q.pop_back();
q.push_back(i);
}
mp[x] = dp[sz(b) - 1];
cout << mp[x] << endl;
}
}
return 0;
}
Tips
Be careful : Read the questions carefully , The last state of this question is especially detailed .. It's also crucial
边栏推荐
- JS top icon menu click to switch background color JS special effect
- R analysis visual practical data (flight \u education \u restaurant \u tenant \u change \u life \u safety)
- J. Balanced Tree
- ThoughtWorks.QRCode功能齐全的生成器
- Xu Li 618, how can Suning fight this hard battle?
- B_ QuRT_ User_ Guide(17)
- B_ QuRT_ User_ Guide(16)
- Lombok use
- 用Fragment实现图片简易浏览
- TimeHelper
猜你喜欢

单片机通信数据延迟问题排查

Azure Kubernates Service 更新|提升开发体验和效率
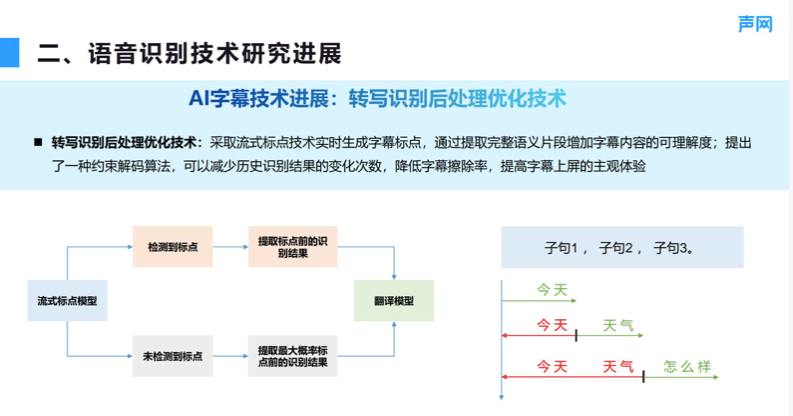
Mazhiqiang: research progress and application of speech recognition technology -- RTC dev Meetup
JS click the sun and moon to switch between day and night JS special effect
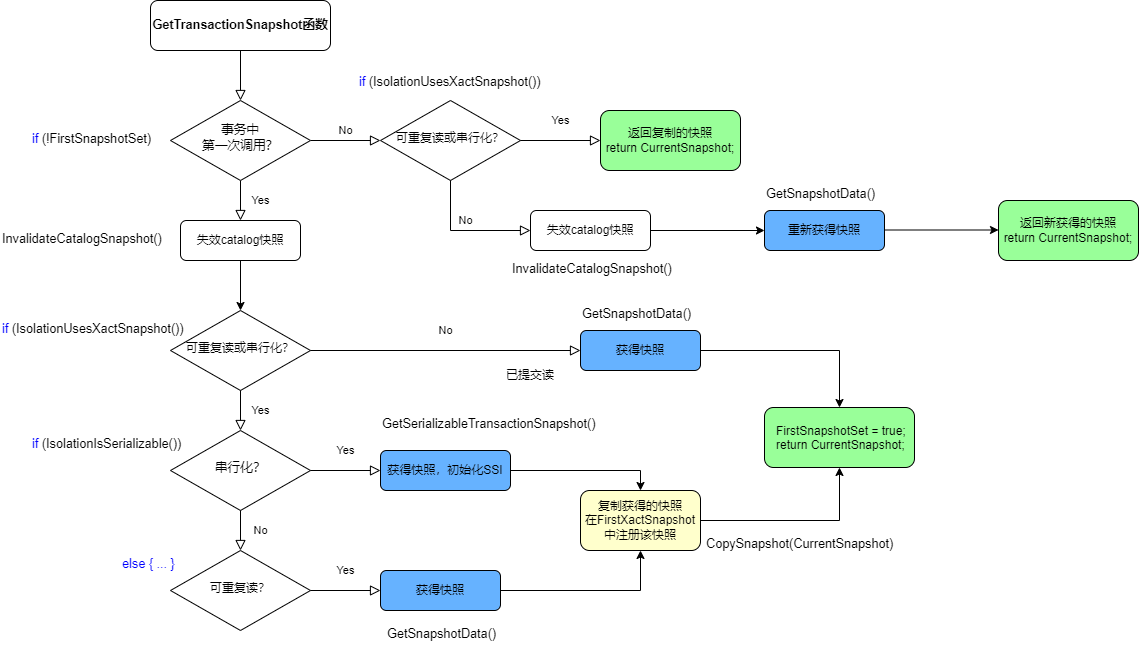
PostgreSQL source code learning (18) -- mvcc ③ - creating (obtaining) snapshots

canvas+svg线条粒子动画网页背景

Configuring the command line compiled environment -msvc

PostgreSQL source code learning (XX) -- fault recovery ① - transaction log format

B_ QuRT_ User_ Guide(17)

What has TCL done right to break through the technological strength of Chinese brand innovation?
随机推荐
OpenGl第十章 投光物
js点击太阳月亮切换白天黑夜js特效
Oppo K9 tests "bundling sales" and consumers "earn" or "lose"?
Vocabulary Construction -- code completion fast food tutorial (3) - word segmentation
postgresql copy语句
Unity's data persistence -- Jason
Unity之数据持久化——Json
Technology Pro strength evaluation: comprehensive PK of high-end massage chair market, who is worthy of the machine king?
C. Jump and Treasure(dp + 单调队列优化)
js实现柯里化
rt-thread测试
【ELT.ZIP】OpenHarmony啃论文俱乐部——快速随机访问字符串压缩
RequestContextHolder
iQOO 8实测上手体验:王者归来,从不高调
摘桃子(双指针)
实现发布订阅模式-----手撕js系列
Opencv实现纵横比保持的图像缩放
一文搞懂单片机驱动8080LCD
Multi thread alternate output ab
被“内卷”酸翻的OPPO Reno6