当前位置:网站首页>Operation and application of stack and queue
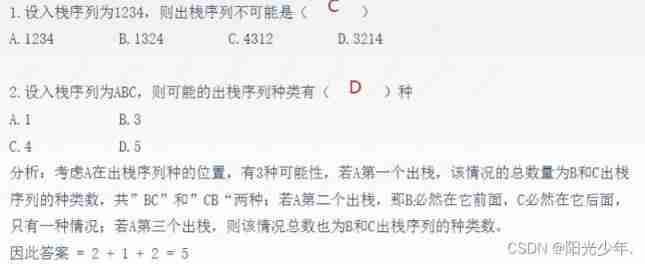
Operation and application of stack and queue
2022-07-02 09:27:00 【Sunshine Youth】
Content of this section
、
1. Stack and queue characteristics

Stack : after In first out
• Stack : Restricted linear table , Operations are only allowed from one end of the table . This end is called To the top of the stack , The other end is Stack At the end of
• Press in elements (push): Add an element to the top of the stack , The new element becomes the top of the new stack .
• Pop up elements (pop): Remove the top element , The elements of the original stack top become the new stack top / Or the stack becomes empty
• The picture shows the result of entering and leaving the stack :

*key1: Stack is an advanced and backward data structure ,pop and push The operation is only carried out at the top of the stack

queue : First In first out
• queue : Restricted linear table , Only operations from both ends of the table are allowed , One end is the head of the team , At one end is the tail of the team .
• The team (enqueue): Add an element to the end of the team , The new element becomes the new team tail
• Out of the team (dequeue): Remove the head element , The next element becomes the new team leader / Or the queue becomes empty
• Graphic demonstration process :

2. Stack and recursion

• Stack Last in, first out Its characteristics naturally coincide with the function call relationship in the program
• When the program is executed , In function A To call another function B When you say , What's going to happen ?
Immediately enter the called function B Execute its code , When finished, return to A Continue on the next line of A The rest of the code
• So when the operating system executes code , Calls between functions - The return relationship is maintained through the call stack
• The recursive call of a function is essentially a stack call , Therefore, a recursive function can be rewritten into a completely equivalent non recursive function by using stack , Avoid the call stack overhead at the operating system level .

3. Stack and queue applications
 、
、
The application of the stack : Parentheses matching
• Purpose : Judge whether your brackets in a string —— matching
•![]()
• Why can stack be used to solve this problem ?
• When you have an open parenthesis , I hope to meet the other half of it immediately , But if you encounter another left parenthesis , Then its demand is more urgent than mine , I need it First Handle after The left parenthesis
• Later needs are met first -> LIFO problem -> Solve with stack
The application of the stack
• Expression evaluation , Such as 1+2*3
• Hexadecimal conversion
• Non recursive depth first traversal (DFS)
Application of queues : Circular queue ( Circular queues are based on sequential sequences )
• How would you implement a sequential sequence ?
![]()
•' False spillover ' The phenomenon : The available space in the front of the underlying sequence table can no longer be used
• resolvent : Circular queue

4. Code implementation
Sequential stack implementation
• At the bottom of the sequence stack is an array , The low address is at the bottom of the stack , The high address is the top of the stack , Can only operate at the top of the stack
![]()
/*( The order ) Stack */
// Stack data structure definition
#define MAX_SIZE 10
typedef struct{
Student *data;
int size;
}Stack;// Push an element into the top of the stack
bool Push(Stack &stk,const Student &s){
if (stk.size==MAX_SIZE){
return false;
}
int newTop=stk.size;
stk.data[newTop]=s;
stk.size++;
return true;
}// Pop up top element
bool Pop(Stack &stk){
if(stk.size==0){
return false;}
stk.size--;
return true;
}*key1: At the bottom of the sequence stack is an array space , And realize stack by maintaining the current stack size
*key2: The current top element subscript and stack size of the sequential stack are top=size-1 The relationship between
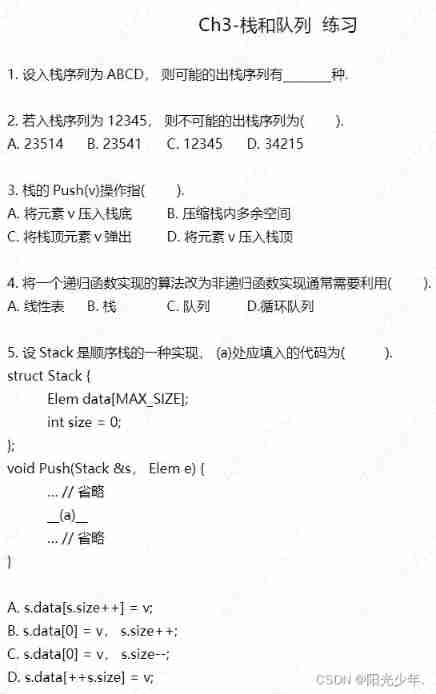
1. set up Stack Is an implementation of sequence stack , stay (a) The code to be filled in is :___________.(stk.size--)
struct Stack{
Elem data[MAX_SIZE];
int size=0;
};
bool Pop(Stack &s){
if (stk.size==0)return false;
___(a)____;
return true;
}
Loop queue implementation
• At the bottom of the circular queue is an array , By maintaining the subscripts of the head and tail of the team in this array
/* Circular queue */
// Circular queue data structure
#define M 10
typedef struct{
Student data[M];
int front;
int back;//bcak Indicates the next vacancy at the end of the team
}CQueue;//c=Circulative// Find the number of elements in the circular queue
int GetSize(CQueue &queue){
int size=(queue.back-queue.front+M)%M;
return size;
}*key1: The capacity of the circular queue is MAX_SIZE-1
*key2: Calculate the current number of elements in the circular queue
1. Suppose the bottom array of a circular queue is array[M], We have an agreement f Expressed as the first element of the current team ,b It is the last of the current tail element
An element , Then the number of elements in the current queue is ()
A.b-f B.(b-f+M)%M
C.b-f+M D.(f-b+M)%M
analysis : To do the circular queue problem, we must draw the bottom array to simulate !
Case one :
The second case :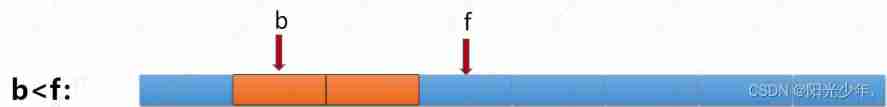
M=8, Blue indicates queue elements .
analysis : For the first case, direct =b-f, The second case is equal to b-f+M
Unify the answer : because b-f>0, So add M Right again M The remainder just disappears M. The second reason is b-f<0,b-f+M<M
So for M The remainder does not work . The summary answer is B Options
Loop queue implementation
• At the bottom of the circular queue is an array , By maintaining the subscripts of the head and tail of the team in this array
// Loop queue listing
bool Enqueue_CQ(CQueue &queue,const Student &s){
int newBack=(queue.back+1)%M;
if(newBack==queue.front){
return false;// Head to tail means the queue is full }
queue.data[queue.back]=s;// Put it at the end of the line
queue.back=newBack;
return true;
}// Cyclic queue dequeue
bool Dequeue_CQ(CQueue &queue){
if (queue.front==queue.back){
return false;// The coincidence of head and tail indicates that the queue is empty
} queue.front=(queue.front+1)%M;
return true;
}*key3: The full condition of the circular queue is (back+1)%MAX_SIZE==front '' Head to tail ''
*key4: The empty condition of the circular queue is back==front '' Head tail coincidence ''
1.(a) The code to be filled in is :______________.(queue.front ==queue.back)
bool Dequeue_CQ(CQueue &queue){
if (___(a)____){
return false;// The coincidence of head and tail indicates that the queue is empty
}queue.front=(queue.front +1)%queue.capacity;
return true;
}
practice :



Complete code :
/*
Ch3 Stacks and queues
*/
// Instance data elements : Student
typedef struct {
char id[10];
int age;
double score;
} Student;
/* ( The order ) Stack */
// Stack data structure definition
#define MAX_SIZE 10
typedef struct {
Student *data;
int size;
} Stack;
// Initialization stack
Stack Create() {
Stack stk;
stk.data = new Student[MAX_SIZE];
stk.size = 0;
return stk;
}
// Get stack top element
bool Top(Stack &stk, Student &res) {
if (stk.size == 0) {
return false;
}
int top = stk.size - 1;
res = stk.data[top];
return true;
}
// Pop up top element
bool Pop(Stack &stk) {
if (stk.size == 0) {
return false;
}
stk.size--;
return true;
}
// Push an element into the top of the stack
bool Push(Stack &stk, const Student &s) {
if (stk.size == MAX_SIZE) {
return false;
}
int newTop = stk.size;
stk.data[newTop] = s;
stk.size++;
return true;
}
/* The application of the stack : Parentheses matching */
#include <stack>
#include <string>
bool IsParenthesesMatch(std::string s) {
std::stack<char> stk;
for (int i = 0; i < s.length(); ++i) {
switch (s[i]) {
case '(':
case '[':
case '{':
stk.push(s[i]);
break;
case ')':
if (stk.empty() || stk.top() != '(') {
return false;
}
stk.pop();
break;
case ']':
if (stk.empty() || stk.top() != '[') {
return false;
}
stk.pop();
break;
case '}':
if (stk.empty() || stk.top() != '}') {
return false;
}
stk.pop();
break;
}
}
return stk.empty();
}
/* Circular queue */
// Circular queue data structure
#define M 10
typedef struct {
Student data[M];
int front;
int back; // back Indicates the next vacancy at the end of the team
} CQueue; // C = Circulative
// Loop queue in
bool Enqueue_CQ(CQueue &queue, const Student &s) {
int newBack = (queue.back + 1) % M;
if (newBack == queue.front) {
return false; // Head to tail means the queue is full
}
queue.data[queue.back] = s; // Put it at the end of the line
queue.back = newBack; // Move back
return true;
}
// Loop queue out
bool Dequeue_CQ(CQueue &queue) {
if (queue.front == queue.back) {
return false; // The coincidence of head and tail indicates that the queue is empty
}
queue.front = (queue.front + 1) % M;
return true;
}
// Find the number of elements in the circular queue
int GetSize(CQueue &queue) {
int size = (queue.back - queue.front + M) % M;
return size;
}边栏推荐
- Matplotlib swordsman - a stylist who can draw without tools and code
- 机器学习之数据类型案例——基于朴素贝叶斯法,用数据辩男女
- Watermelon book -- Chapter 6 Support vector machine (SVM)
- 京东面试官问:LEFT JOIN关联表中用ON还是WHERE跟条件有什么区别
- Talk about the secret of high performance of message queue -- zero copy technology
- [go practical basis] gin efficient artifact, how to bind parameters to structures
- Knife4j 2. Solution to the problem of file control without selection when uploading x version files
- Statistical learning methods - Chapter 5, decision tree model and learning (Part 1)
- 微服务实战|原生态实现服务的发现与调用
- 【Go实战基础】gin 如何绑定与使用 url 参数
猜你喜欢
Matplotlib swordsman line - layout guide and multi map implementation (Updated)
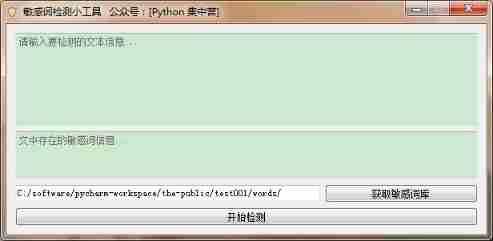
How to use pyqt5 to make a sensitive word detection tool
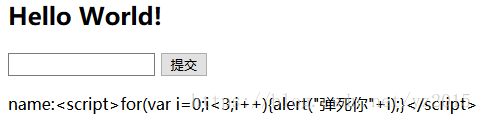
web安全与防御

Supplier selection and prequalification of Oracle project management system
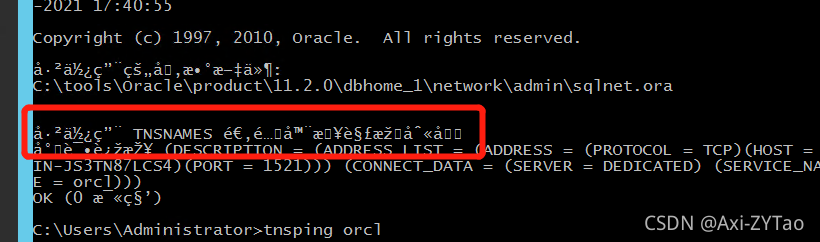
Solutions to Chinese garbled code in CMD window

Watermelon book -- Chapter 6 Support vector machine (SVM)
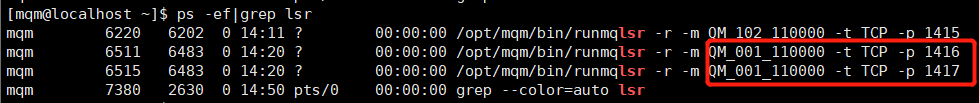
队列管理器running状态下无法查看通道
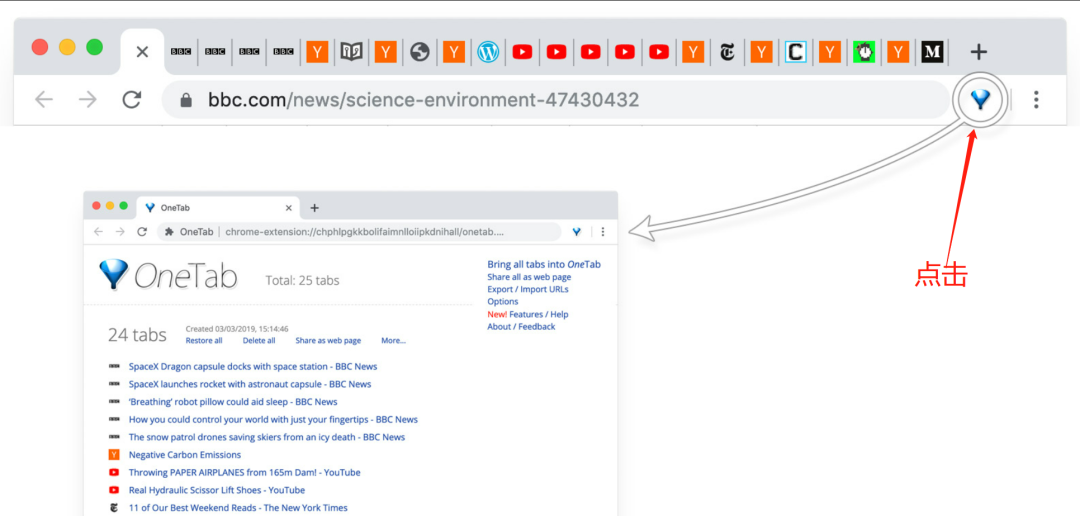
Chrome browser tag management plug-in – onetab
Troubleshooting and handling of an online problem caused by redis zadd
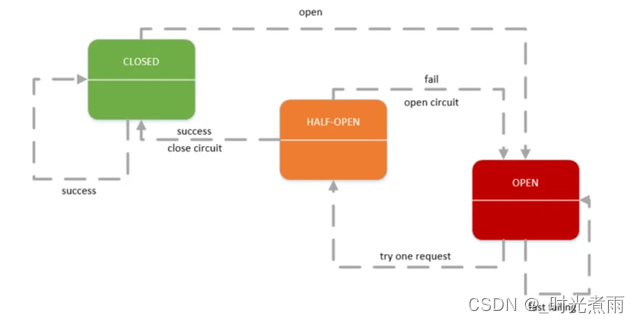
微服务实战|熔断器Hystrix初体验
随机推荐
Don't look for it. All the necessary plug-ins for Chrome browser are here
盘点典型错误之TypeError: X() got multiple values for argument ‘Y‘
Chrome user script manager tempermonkey monkey
微服务实战|原生态实现服务的发现与调用
Matplotlib swordsman Tour - an artist tutorial to accommodate all rivers
Learn combinelatest through a practical example
Matplotlib swordsman line - layout guide and multi map implementation (Updated)
长篇总结(代码有注释)数构(C语言)——第四章、串(上)
Required request body is missing:(跨域问题)
Knowledge points are very detailed (code is annotated) number structure (C language) -- Chapter 3, stack and queue
What are the differences between TP5 and laravel
[go practical basis] how to customize and use a middleware in gin
【Go实战基础】gin 如何自定义和使用一个中间件
Micro service practice | introduction and practice of zuul, a micro service gateway
Redis installation and deployment (windows/linux)
分布式服务架构精讲pdf文档:原理+设计+实战,(收藏再看)
企业级SaaS CRM实现
Chrome浏览器标签管理插件–OneTab
I've taken it. MySQL table 500W rows, but someone doesn't partition it?
机器学习之数据类型案例——基于朴素贝叶斯法,用数据辩男女