当前位置:网站首页>How PHP uses redis
How PHP uses redis
2022-06-23 02:20:00 【User 1349575】
- Redis Is an open source use ANSI C Language writing 、 Support network 、 Log type that can be memory based or persistent 、Key- Value database , And provide multilingual API.
- Redis The supported data types are String( character string ), List( list ), Hash( Dictionaries ), Set( aggregate ), Sorted Set( Ordered set );
- Redis Default port 6379
1. Connect
$redis = new Redis(); // Instantiation
$redis->connect('127.0.0.1', 6379); // Connect
$redis->auth('redis password '); // No password redis This step can be ignored 2. data type
2-1 string character string
// Store or change
$redis->set('test', 'aaa');
// Get value
$redis->get('test'); // aaa2-2 list list
Methods l representative list operation
- Storage
$redis->lpush('list', 'a'); // Add... From the left
$redis->lpush('list', 'b');
$redis->lpush('list', 'c');
$redis->rpush('list', 'd'); // Join from the right
$redis->lset('list', 2, 'e');// Set or change the value of the specified position in the list , Successfully returns 1, Failure returns error message - Delete
$redis->lpop('list'); // Delete the first one on the left
$redis->rpop('list'); // Delete the first one on the right
// $redis->lrem('list name ', ' value ', num);
// Delete elements... Based on values , The second parameter is the value to delete ( The element with this value is deleted ),
// The third parameter num Express : Where to start deleting 、 Delete a few ,
//num>0 Delete from the header to the footer , Delete num End ;
//num<0 Delete from the footer to the header , Delete |num| individual ;
//num=0 Remove all values in the table as 'b' The elements of
$redis->lrem('list', 'b', 2);- obtain , Returns an array of
$redis->lrange('list', 0, -1); // Returns an array . Stored in key The elements of the specified range in the list in ,
// The first parameter is the list name
// The second parameter is the starting bit subscript ,
// The third is the ending subscript ( Contains the end bit element ).
// Negative numbers represent the reciprocal ,-1 For the last one ;
// If the start is greater than the end, null is returned , The end is longer than the actual length , Return to the last element .
$redis->lgetrange('list', 0, 2);// Get the value of the specified interval in the list , ditto
$redis->ltrim('list', 0, 3); // Intercepts and retains the values of the specified interval in the list , Delete the remaining values .
// Successfully returns 1, Failure returns error message . Negative numbers represent the reciprocal
$redis->lsize('list'); // Get the length of the list
$redis->lget('list', 2) // Get the value of the specified position in the list
$redis->lindex('list', 2); // Get the value of the specified position in the list 2-3 hash Dictionaries
One string Type of field and value Mapping table , Ideal for storing objects . Every hash Can be stored 2 Of 32 Power - 1 Key value pair (40 More than ) hash The table is equivalent to redis Storage key => value Medium key, The contents of the table are equivalent to value
In the method h representative hash operation
- Storage
// $redis->hset('hash surface ', key, value);
// If hash Table does not exist , Create a should hash surface , If it doesn't exist key The setting is successful , return true,
// If there is , Replace the original value , return false, Failure to return false
// The first parameter is the dictionary name
$redis->hset('hashtest', 'a', 'aaa'); // return true
$redis->hset('hashtest', 'a', 'bbb'); // return false,a To change the value of bbb
$redis->hset('hashtest', 'b', 'bbb'); // return true, increase b, The value is bb
$redis->hmset('hashtest', [1 => 1, 2 => 2, 3 => 3]); // Batch assignment ,
$redis->hincrby('hashtest', '1', 1); // hash In the table key The corresponding value increases by itself 1( Integers ),
// The first parameter dictionary name
// The second parameter is key name ,
// The third parameter is the amplitude of self increment . If the... Does not exist in the table key, The... Is automatically added key, And set the value as self increasing amplitude
$redis->hincrbyfloat('hashtest', '2', 1.5); // hash In the table key Self increasing - obtain
$redis->hget('hash surface ', key); // Get a key Corresponding value
$redis->hget('hashtest', 'a'); // obtain hashtest in a Value
$redis->hkeys('hashtest'); // obtain hash All of the... In the table keys( Key name ), Returns an array
$redis->hvals('hashtest'); // obtain hash All of the... In the table values( value ), The order is random , Returns an array
$redis->hgetall('hashtest'); // obtain hash All key value pairs in the table , The order is random , Returns an array
$redis->hlen('hashtest'); // obtain hash In the table key The number of
$redis->hmget('hashtest', [1, 2, 3]); // Get more than one in batch key Corresponding value, The second parameter is keyArr
$redis->hexists('hashtest', 'b'); // Judge hash Whether the key- Delete
$redis->hdel('hashtest', 'a');
// Delete hash One of the tables key, Successfully returns true,
// If the table does not exist or key There is no return false2-4 set aggregate
Redis Of Set yes String Unordered collection of type . Collection members are unique , This means that duplicate data cannot appear in the collection .
The maximum number of members in the collection is 2 Of 32 Power - 1 (4294967295, Each collection can store 40 More than 100 million members ).
Methods s representative set operation
- add to
// $redis->sadd('set aggregate ', ' value ');
// Go to settest Add a value to the , success , Returns the number of additions , Failure to return 0.
// The first parameter is set Collection name
// The second parameter is to insert new values into the set , namely : Go to value Insert new value in
$redis->sadd('settest', 'a'); // 1
$redis->sadd('settest', 'b'); // 1
$redis->sadd('settest', 'a'); // 0
$redis->sadd('settest', ['c', 'd', 'e']); // Add more than one value at a time - obtain
$redis->smembers('settest');
// Get all the elements in the collection
$redis->sismember('settest', 'b');
// Determine if the element is set member
$redis->scard('settest');
// View the number of elements in the collection
$redis->sinter('settest', 'settest2');
// Returns the intersection of two sets
$redis->sinterstore('settest3', 'settest', 'settest2');
// take settest and settest2 Put the intersection of into the set settest3 in
$redis->sunion('settest', 'settest2');
// Returns the union of two sets
$redis->sunionstore('settest4', 'settest', 'settest2');
// take settest and settest2 Put the union of into the set settest4 in
$redis->sdiff('settest', 'settest2');
// Returns the difference set of two sets
$redis->sdiffstore('settest5', 'settest', 'settest2');
// take settest and settest2 Put the difference set of into the set settest5 in - Delete
$redis->srem('settest', 'a'); // Delete a value in the set ,
$redis->srem('settest', 'a', 'b'); // Delete multiple values
$redis->spop('settest'); // Remove a random element from the collection , And return the element 2-5. sorted set Ordered set
Redis An ordered set is the same as a set string Collection of type elements , And duplicate members are not allowed .
The difference is that each element is associated with a double Score of type .redis It's the scores that sort the members of a collection from small to large .
Members of an ordered set are unique , But fractions (score) But it can be repeated .
The maximum number of members in the collection is 2 Of 32 Power - 1 (4294967295, Each collection can store 40 More than 100 million members ).
Methods z Represents an ordered set operation
- Add or update
// $redis->zadd(' An ordered collection name ', fraction , value );
// Assemble in order ztest One of the values , Fractional values can be integer values or double precision floating-point numbers .
// perform zadd when , If it doesn't exist , Create a new ordered set ;
// If ztest When there is but not an ordered set type , Return an error .
$redis->zadd('ztest', 1, 'a');
$redis->zadd('ztest', 2, 'a');
// When an element exists , Update the score of this element , And reinsert the element , Make sure the elements are in the right place .
// But it is not a new addition
$redis->zadd('ztest', fraction 1, value 1, fraction 2, value 2); // Insert multiple values into an ordered set
$redis->zadd('ztest', 2, 'b', 3, 'c', 4, 'd');
$redis->zincrby('set', 2, 'c'); // The specified value c increase 2 - obtain
// $redis->zrange('z aggregate ', Start bit , End bit , Boolean value );
// Get the ordered set of the specified interval . Returns an array of . Score from small to large .
// The first parameter : An ordered collection name
// The second parameter : The starting position ,
// The third parameter : End position ( Include this location ), A negative number represents the penultimate ,
// Fourth parameter : Optional parameters , Boolean value , With or without scores , Default false
$redis->zrange('ztest', 0, 1);
// ['a', 'b'] Sort by score , But no score
$redis->zrange('ztest', 0, 1, true);
// ['a' => 2, 'b' => 2] Sort by score , And carry the score [' Elements ' => ' fraction ']
$redis->zrevrange('zset', 1, 2);
// Get the ordered set of the specified interval . Returns an array of . Scores range from big to small .
$redis->zscore('ztest', 'a');
// Get the score of the specified element
$redis->zcard('zset');
// Get the number of storage elements
$redis->zcount('zset', 2, 5);
// Score between 2~5 The number of elements of
$redis->zrangebyscore('zset', 2, 3);
// Returns a score between 2~3 The elements of , No score , The display mode is the same as zrange
$redis->zrangebyscore('zset', 2, 3, ['withscores' => true]);
// Returns a score between 2~3 The elements of , And display with scores , The display mode is the same as zrange- Delete
$redis->zrem('zset', 'c'); // Delete the specified member
$redis->zremrangebyscore('set', 2, 3); // Remove scores between 2~3 The elements of , Return the number of deletions 3. Other common methods
3-1 Find out about key
// Find out the corresponding according to the conditions key( key ), Support string splicing ( The return value is an array , An empty array will be returned even if no data is found )
// * Represents any character of any length , ? Any character of a length
$redis->keys('A'); // Find out what is equal to A the key
$redis->keys('a*'); // Find out to a start , Followed by any value key ,
$redis->keys('*b*'); // Find out if the link contains b Of key
$redis->keys('c??'); // Find the length of 3, And the first character is c Of key
$a = a;
$redis->keys($a . '*');
// Use keys Can be used after for Cycle plus get() To get relevant keys Corresponding value 3-2 Expiration time
- View expiration time
// $redis->ttl('key name ');
// View a certain key Remaining time of validity , Return seconds .
// When No expiration date when , return :-1;
// When No key value when , return -2;
$redis->ttl('ttltest'); // see ttltest Expiration time remaining 2. Set expiration time
Redis::expire('key', second); // Expire in seconds
Redis::expireAt('key', timeStemp); // To a certain Time stamp ( second ) Expire when 边栏推荐
- //1.15 putchar function
- 【CodeWars】What is between?
- await is only valid in async function
- 1. introduction to MySQL database connection pool function technology points
- C language game minesweeping [simple implementation]
- Digital integrated circuit design process
- Targeted and ready to go
- 9. class and object practice and initialization list
- Operate attribute chestnut through reflection
- This monitoring tool is enough for the operation and maintenance of small and medium-sized enterprises - wgcloud
猜你喜欢

1.3-1.4 web page data capture

Li Mu's notes on machine learning -1.2

Information theory and coding

Docker installs mysql5.7 and mounts the configuration file

Unity official case nightmare shooter development summary < I > realization of the role's attack function
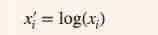
II Data preprocessing

1. Mx6u image burning principle (no specific process)

Spark broadcast variables and accumulators (cases attached)

Cmake simple usage

Branch and loop statements (including goto statements) -part1
随机推荐
5g access network and base station evolution
1. Mx6u bare metal program (1) - Lighting master
Epoll introduction and principle explanation
5g spectrum
JS request path console reports an error failed to launch 'xxx' because the scheme does not have a registered handler
Branch and loop statements (including goto statements) -part1
Unity official case nightmare shooter development summary < I > realization of the role's attack function
pd. read_ CSV and np Differences between loadtext
Error C2061 syntax error: identifier ‘PreparedStatement‘
Mobile communication Overview - Architecture
Small knowledge points of asset
what the fuck! If you can't grab it, write it yourself. Use code to realize a Bing Dwen Dwen. It's so beautiful ~!
Exercise analysis summary
Quick sorting C language code + auxiliary diagram + Notes
Single chip microcomputer (STC series 8051 core single chip microcomputer)
Source code analysis | activity setcontentview I don't flash
EDI project cases of customers in medical device industry
Dynamic address book in C language (add, delete, modify, check (duplicate), delete, sort and export)
Pywebio to quickly build web applications
Detailed explanation of makefile usage