当前位置:网站首页>Talking about JVM 4: class loading mechanism
Talking about JVM 4: class loading mechanism
2022-07-05 00:49:00 【QinGeneral】

In the previous article, we learned how to read the bytecode and the runtime stack frame structure in the bytecode execution engine , The method calls in bytecode execution engine have not been covered .Java The polymorphic characteristics of Chinese are inseparable JVM Dynamic binding of , Dynamic binding technology is the key to method dynamic invocation . And if you want to introduce the method calling mechanism , You need to know the bytecode in JVM The life cycle process from load to unload .
The bytecode is JVM From load to unload , Through the following process .
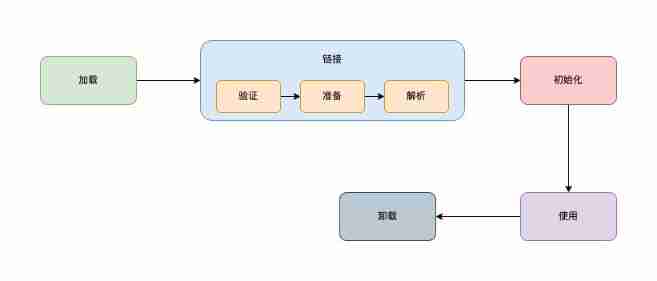
We now know how to read outside class The structure of bytecode , And part of the runtime . The former belongs to “ load ” Previous content , The latter belongs to “ Use ” Stage . This time we will take a look at the process from loading to using , This is it. JVM Class loading mechanism of .
There are many ways to input external bytecode , For example, local class file 、 Network byte stream 、 Bytecode content generated by the program .
Java Virtual machine will be external class Bytecode loaded into memory , It needs to be loaded 、 link 、 Three phases of initialization .
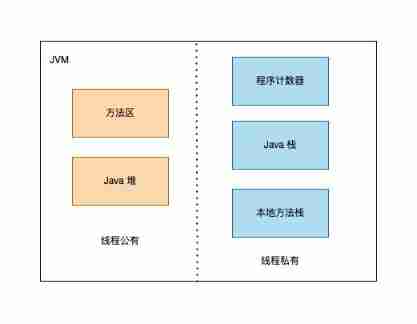
Before you understand the class loading mechanism , Let's start with a brief review JVM Division of logical areas . Include 5 part :
- Method area
- Java Pile up
- Program counter
- Java Stack
- Native Method Stack
load
The loading phase is mainly responsible for reading the external byte stream , Convert the storage structure of byte stream into runtime data structure , Store in method area . At the same time Java Create corresponding classes in the heap java.lang.Class object , As the access to method area data . At this time, the runtime data structure in the method area is implemented by virtual machines .
Except that the byte stream of array class is directly generated by the virtual machine , Other classes are loaded mainly by ClassLoader complete .ClassLoader There is a boot class loader 、 Extend the classloader 、 Apply the class loader , Its structure conforms to the parental delegation model , It means that the subclass loader needs to be loaded by the parent class loader before loading the class , Such layers of transmission , If the parent class does not handle it, it will be handed over to the child class .
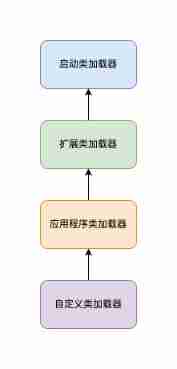
The boot class loader consists of C++ To write , No, Java object . Extend the classloader 、 Application class loaders are java.lang.ClassLoader Subclass , Need to be loaded by other classes , Such as starting class loader , Loading in .
The boot class loader is mainly responsible for loading the most basic 、 Important classes , Such as JRE Next lib In the directory jar package . The extension class loader is responsible for loading JRE Next lib/ext General in the directory 、 The extension class . The application class loader mainly loads the classes under the application path .
The parental delegation model ensures the security and uniqueness of the class loading process , Because any subclass loader ( Including the class loader implemented by the developer ) Before loading the class , You need to hand over the class to the parent class loader first . On the one hand, this ensures the division of loading functions of different attribute classes , such as Object Classes are always loaded by the boot class loader , This allows no matter which class loader is loaded Object, This class can guarantee the same and unique . On the other hand , This ensures the security of class loading , Developers cannot forge things like java.lang.Object Wait for basic classes to cheat JVM, Because of the built-in ClassLoader Relevant safety verification work has been done .
It should be noted that , If the same bytecode is loaded by different class loading instances , You get two different classes .
Java 9 Modular support for ClassLoader Some modifications have been made , I will not go into details here .
link
The link phase is divided into verification 、 Get ready 、 Analyze three stages .
Validation phase
The verification phase is mainly responsible for verifying whether the bytecode loaded in the previous step conforms to the specification , Ensure that it will not harm JVM The safety of the . This step is an important guarantee for program safety , The work at this stage also accounts for a considerable proportion in the whole class loading process , Mainly including byte code format 、 grammar 、 Semantic verification .
Preparation stage
The preparation phase is mainly responsible for allocating memory for static fields in the class , And initialized to zero . At this time, only memory will be allocated to class variables , stay JDK 8 And after , Class variables will be stored in Class Where the object is located Java Allocate in the heap . The memory allocation of instance variables should wait until the object is instantiated .
Analytic stage
The parsing phase is the process of converting symbolic references in the constant pool into direct references .
When we learned to read bytecode , Constants of the constant pool are represented by indexes , The reference relationship between constants 、 Method bytecode obtains variables and other operations through reference index , These indexes are called symbolic references . Symbolic reference only expresses the logical reference relationship between variables , And the actual runtime variables 、 The memory location of the method is not fixed , So before running bytecode , These symbolic references need to be resolved into pointers to the target 、 Offset or handle , This is related to the specific memory layout of the runtime .
Of course , The parsing phase did not complete the parsing process of all symbol references , For classes or interfaces 、 Field 、 Class method 、 The parsing of interface methods can be completed at this stage . But for method types 、 The resolution of method handles and call point qualifiers is closely related to the feature support of dynamic languages , It will not be completed at this stage . This is because the specific method corresponding to the method call has not been determined at this time , It can't be determined until it is actually implemented .
initialization
The initialization phase is the beginning when the virtual machine starts executing the application code , It's the execution class constructor <clinit> Method process . The method by Javac Compile time , By collecting class variable assignment statements and static Code blocks are merged to produce .
As follows Java Code and its corresponding <clinit> Bytecode as an example , It can be found that class constructors only deal with class variables and content in static code blocks , Ignore instance variables .
// java
private static int a = 100;
static {
a = 1000;
}
private int mThisIsInt = 1024;
// bytecode
bipush 100
putstatic #28 <Demo.a : I>
sipush 1000
putstatic #28 <Demo.a : I>
return
Here we can mention the implementation of static inner class singleton pattern .
public class Singleton {
private Singleton() {
}
private static class Holder {
static final Singleton INSTANCE = new Singleton();
}
public static Singleton getInstance() {
return Holder.INSTANCE;
}
}
Inner class Holder The initialization time of is when the static field of this class is called , Now trigger <clinit> Method call , Then create a singleton object .JVM When this method is called, it will be locked , Ensure that the method will be called only once . This feature ensures the delayed loading of singletons and the safety of multithreading .
summary
This time we have mastered JVM The three stages of the class loading process : load 、 link 、 initialization .JVM Logically, it is divided into method areas 、Java Pile up 、 Program counter 、Java Stack 、 Native Method Stack . Method area and Java Heap is mainly used to store data , Including byte code corresponding data structure and runtime object . Other parts are mainly responsible for runtime method calls 、 Computing and other functions .
After understanding the class loading mechanism 、JVM After logical region division and execution of runtime stack frame and method bytecode , Next time we have time to talk about how calls between methods happen .
边栏推荐
猜你喜欢
JS how to realize array to tree
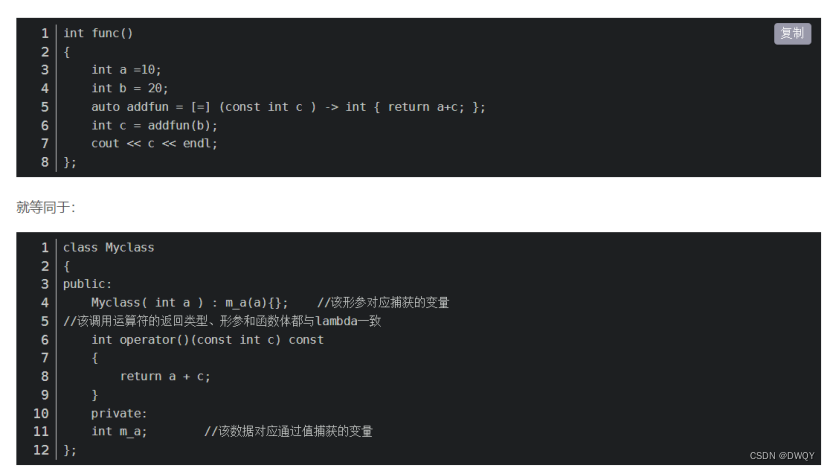
lambda expressions

abc 258 G - Triangle(bitset)

Summer challenge brings you to play harmoniyos multi terminal piano performance
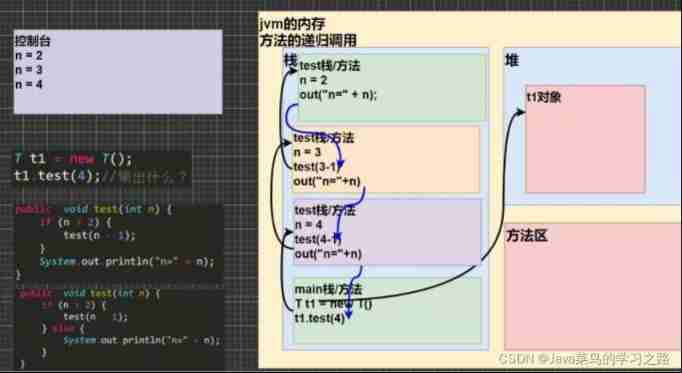
Recursive execution mechanism
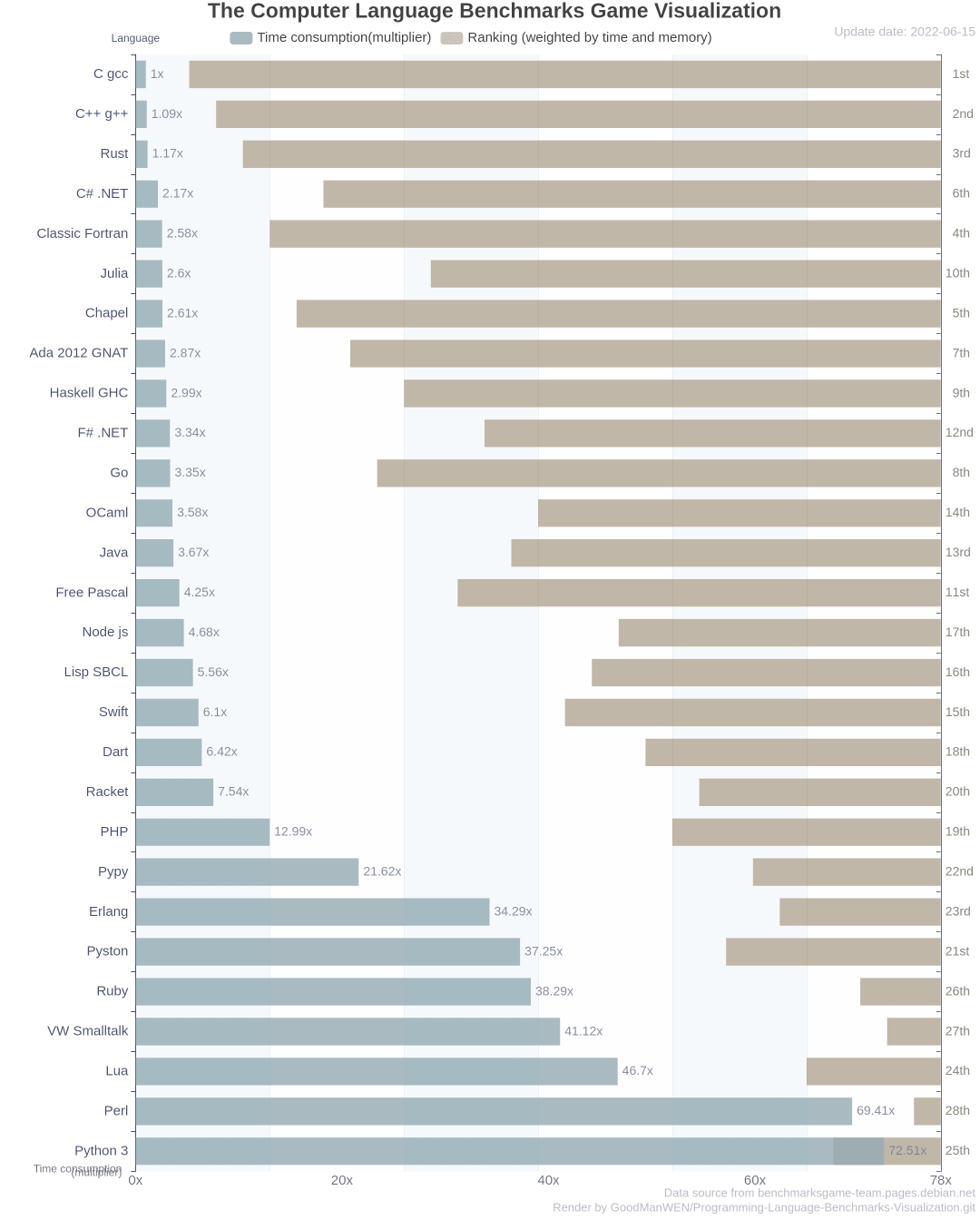
各大主流编程语言性能PK,结果出乎意料
![P3304 [SDOI2013]直径(树的直径)](/img/5c/984675bf4517481f80f54657c6c7ad.png)
P3304 [SDOI2013]直径(树的直径)

Complete knapsack problem (template)
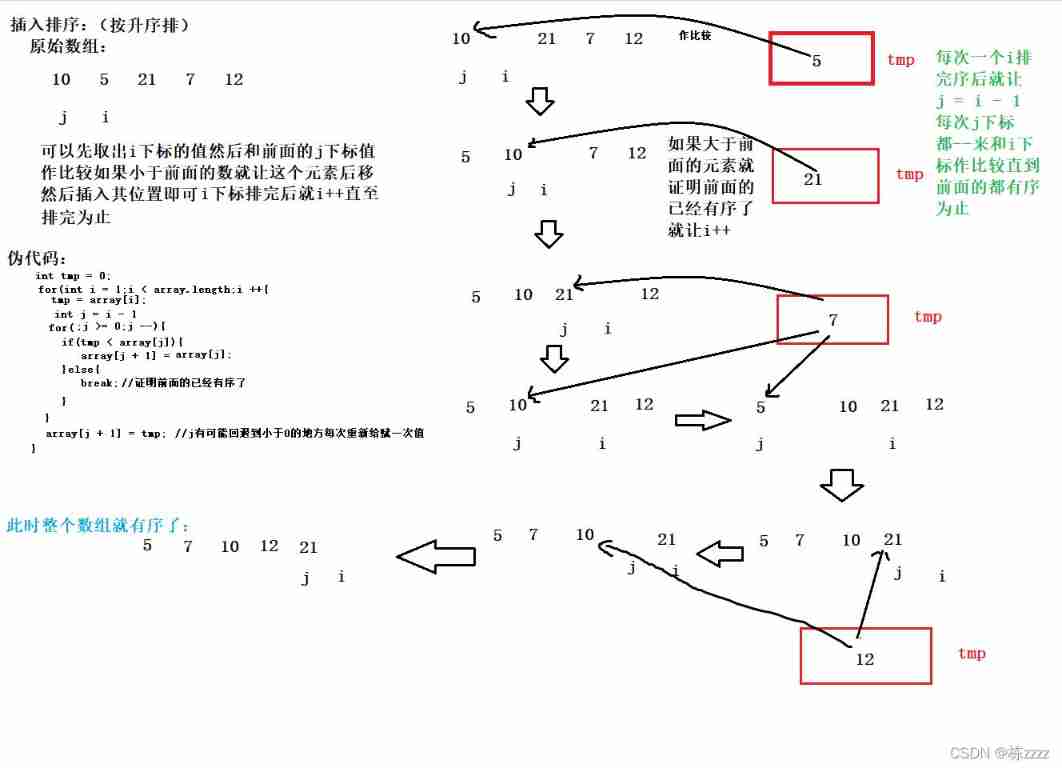
Insert sort of sort
What you learned in the eleventh week
随机推荐
Relationship between classes and objects
2022.07.03(LC_6111_统计放置房子的方式数)
Hologres Query管理及超时处理
IT转测试岗,从迷茫到坚定我究竟付出了什么?
Learning of basic amplification circuit
Several simplified forms of lambda expression
Continuous modification of business scenario functions
Distributed base theory
Multilingual Wikipedia website source code development part II
leetcode518,377
Ap8022 switching power supply small household appliances ACDC chip offline switching power supply IC
大专学历,33岁宝妈又怎样?我照样销售转测试,月入13k+
SAP UI5 应用开发教程之一百零六 - 如何提高 SAP UI5 应用路由 url 的可读性试读版
《论文笔记》Multi-UAV Collaborative Monocular SLAM
MongoDB系列之学习笔记教程汇总
skimage: imread & imsave & imshow
【Unity】InputSystem
Open3d uses GICP to register point clouds
Pycharm professional download and installation tutorial
全栈开发提效神器——ApiFox(Postman + Swagger + Mock + JMeter)