当前位置:网站首页>[CV-Learning] Semantic Segmentation
[CV-Learning] Semantic Segmentation
2022-08-04 06:06:00 【Xiao Liang has to work hard】
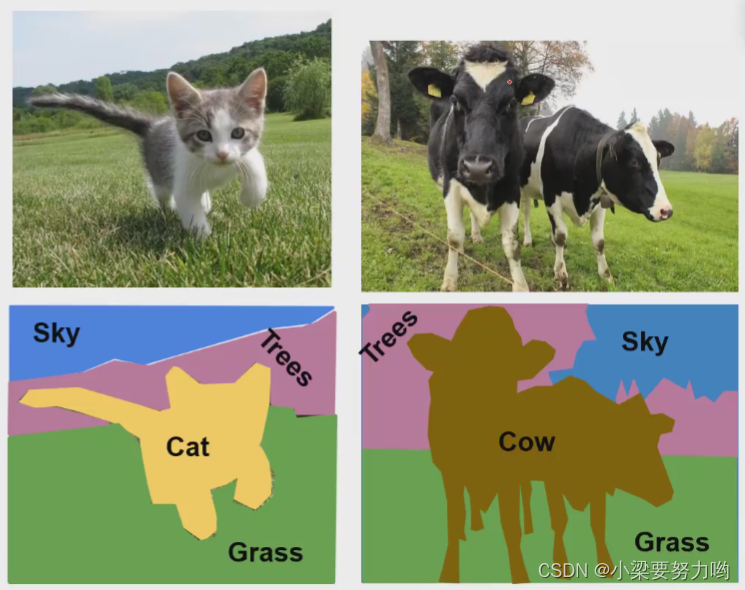
Semantic segmentation
Definition: Assign a class label to each pixel of an image, regardless of instance, only consider pixel class.
Old ideas (sliding window)
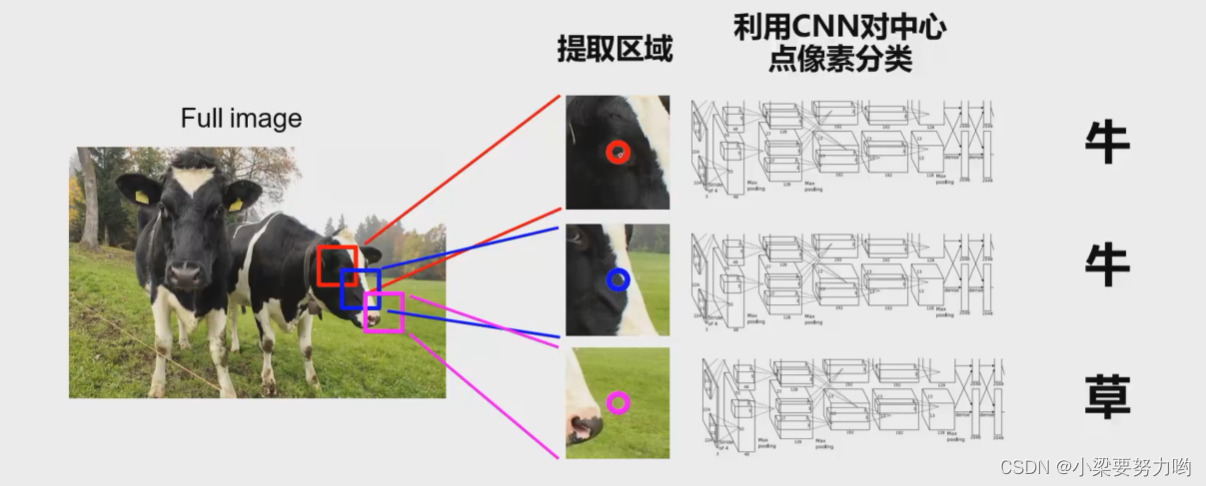
Ideas: Take a certain pixel as the center, select an area, and classify the area.
Problem: The efficiency is too low, and the overlapping area features are calculated repeatedly.
New idea (full convolution)
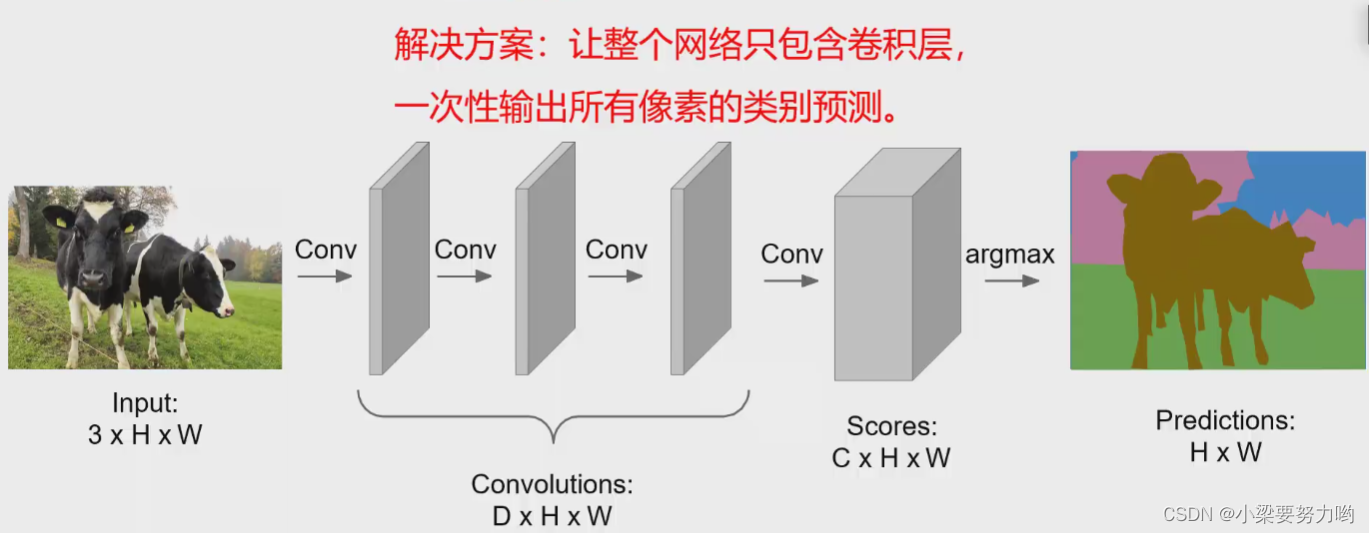
Idea: Perform pooling during Convolutions to keep the image size and depth unchanged, and then obtain Scores with a depth of C, where each depth represents a category, and each pixel can be judged by category.Finally, by judging the sum of the cross-entropy loss of each pixel, the total loss is controlled by feedback, and the lower the better.
Problem: The original resolution of the image is maintained during the Convolutions process, which requires a huge amount of video memory.Therefore, the Convolutions process can be optimized to improve performance.
Performance improvements
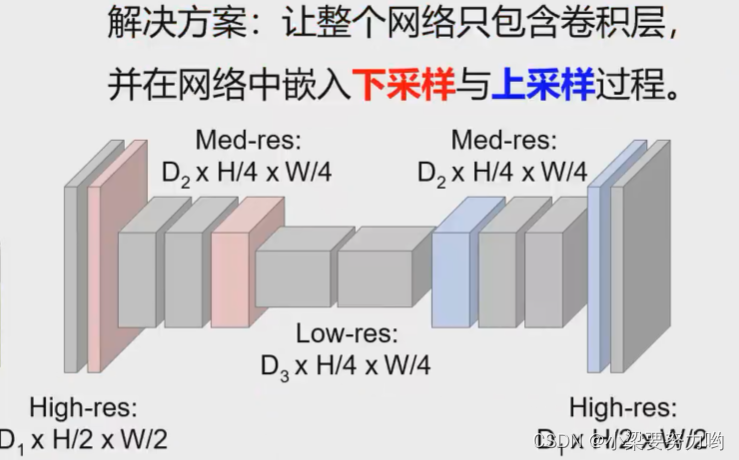
Ideas: In the process of Convolutions, first down-sampling is performed to extract high-level semantic features, and then the original learning is returned through up-sampling to establish a high-level semantic-to-classmark mapping.
Downsampling
pooling, strided convolution
Upsample t
unpooling or strided transpose convolution
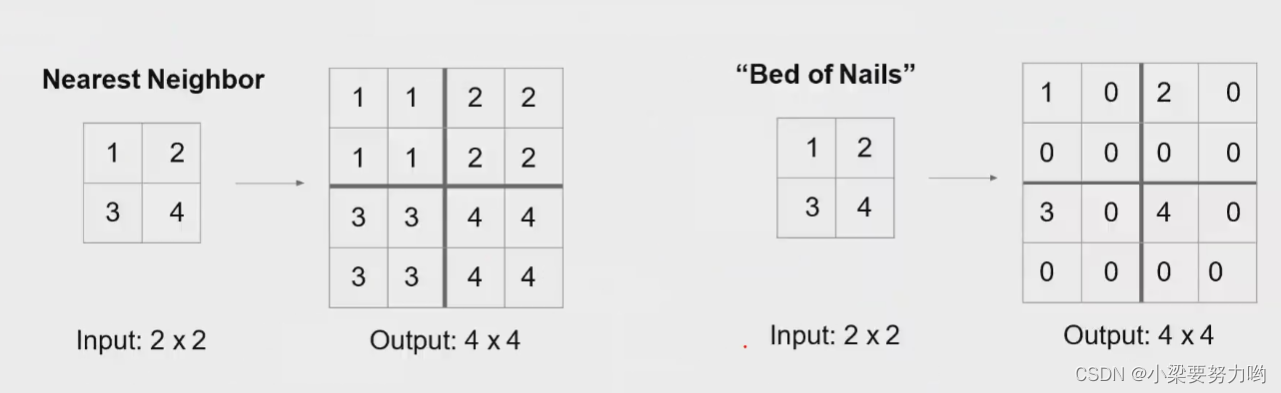
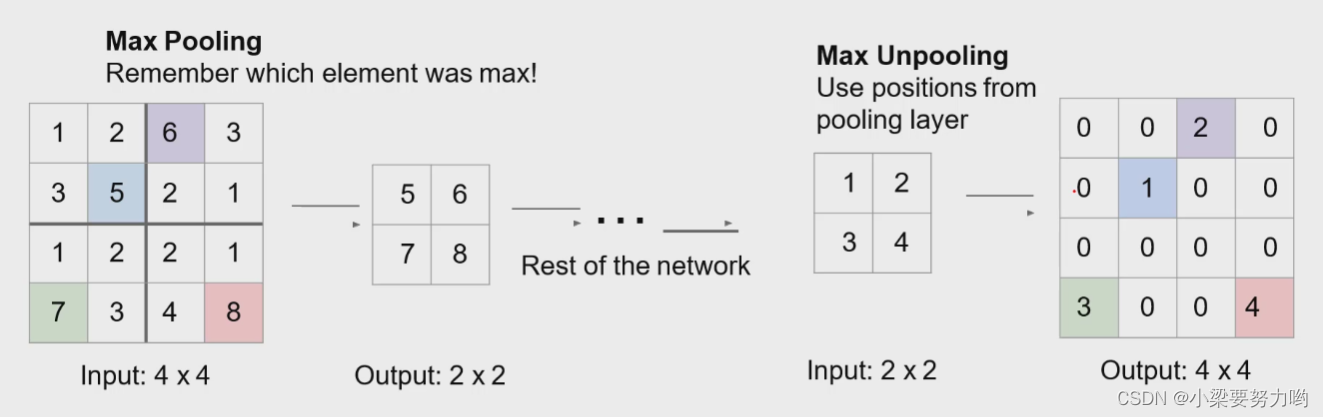
Hard-coded upsampling
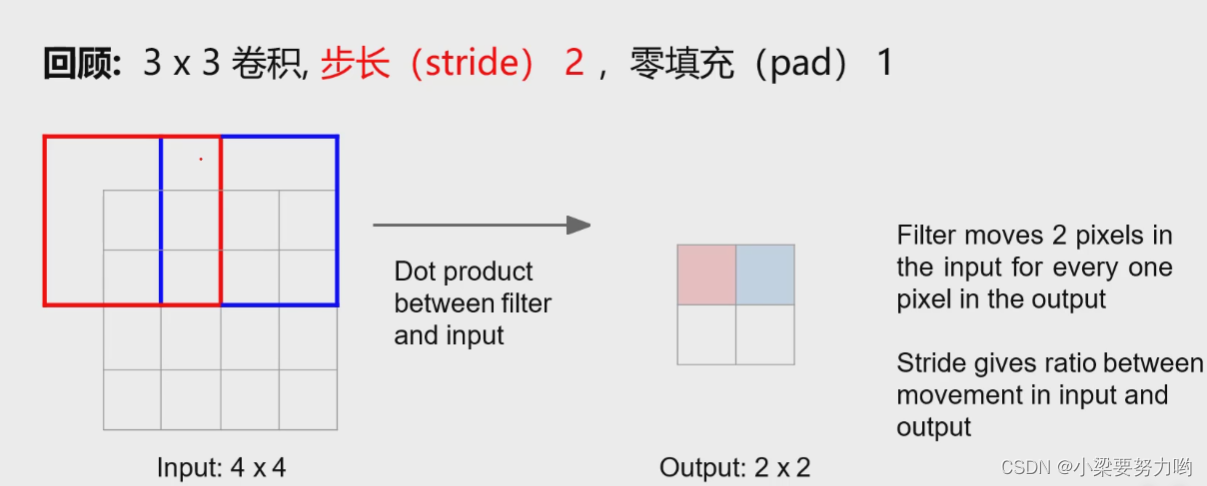
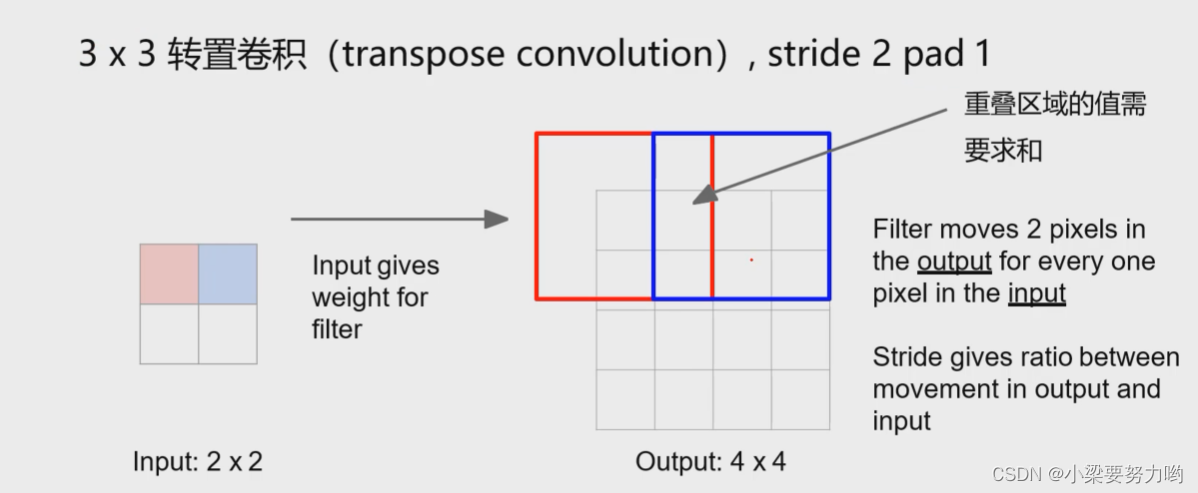
Learnable Upsampling (Transpose convolution)
Downsampling
Upsampling
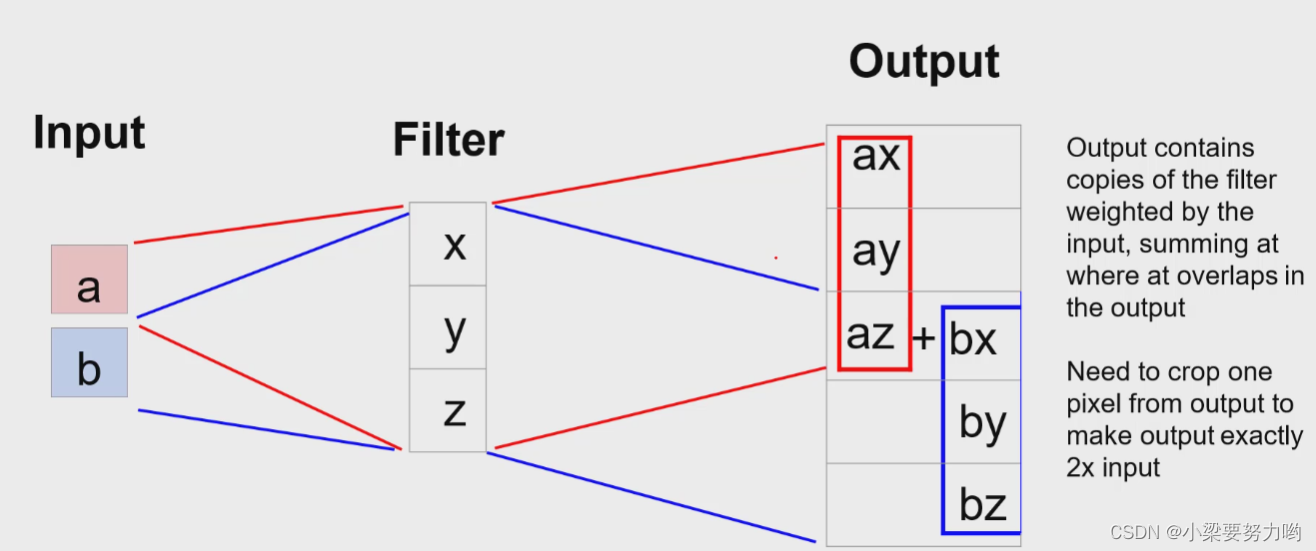
One-dimensional upsampling example
Filter is a filter kernel, which is a matrix that can be learned.
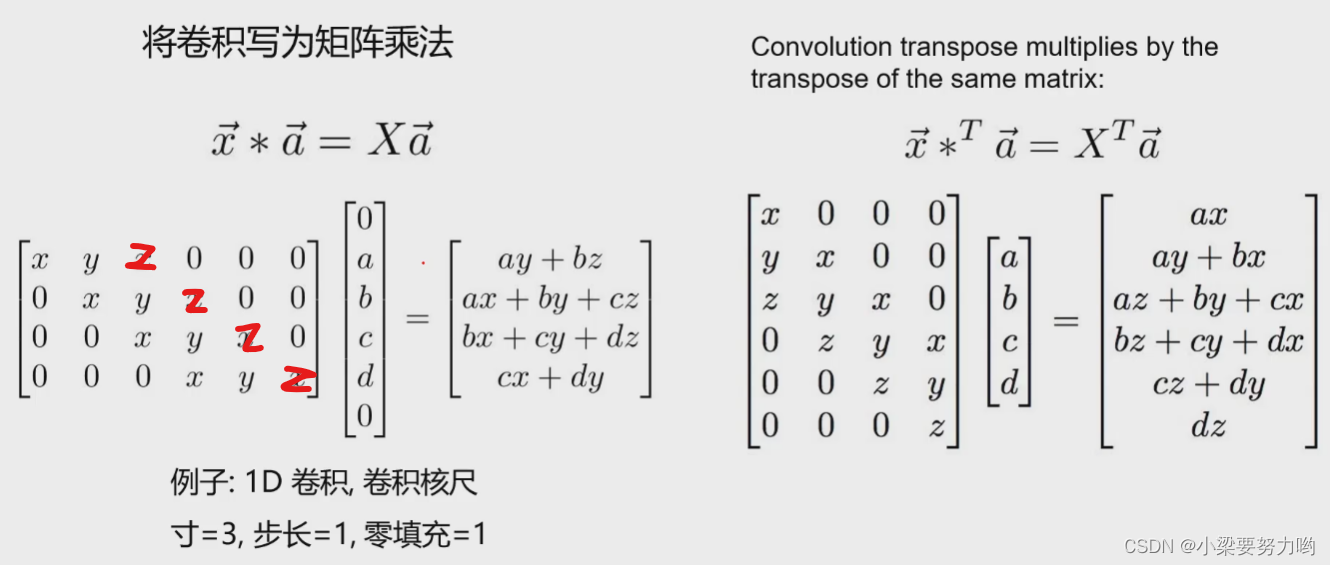
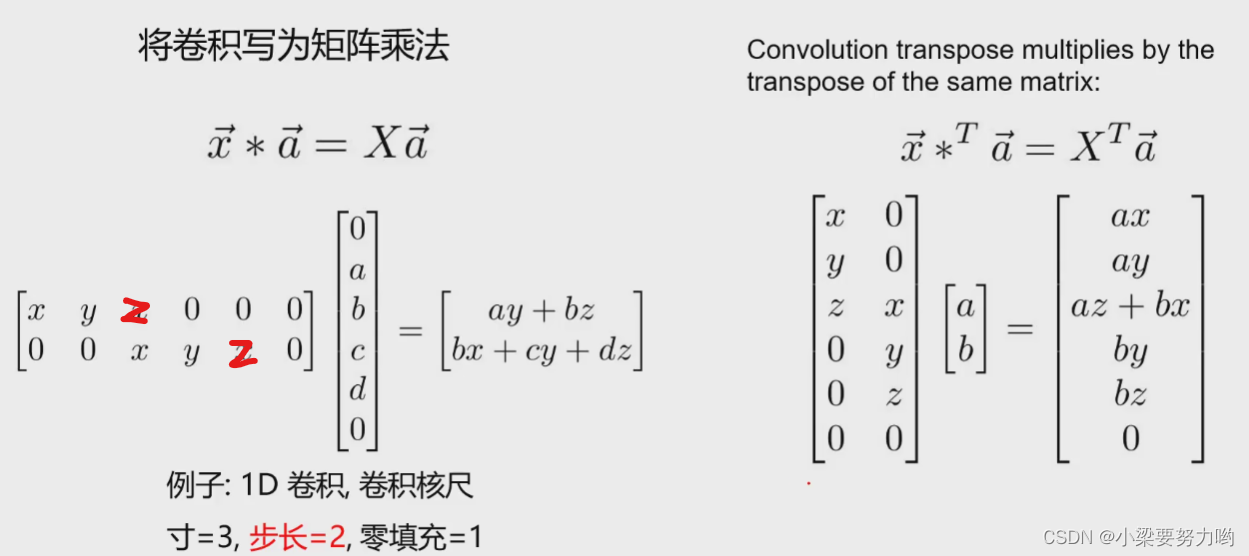
Convolution and matrix multiplication (one-dimensional)
The following legends are down-sampling first, and then up-sampling restoration.
Example 1: Step 1
Example2: Step size is 2
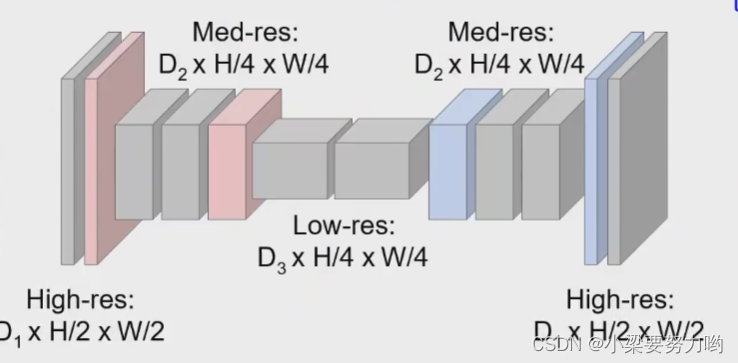
UNET
Upsampling is obtained based on the high-level semantics obtained by downsampling, but sometimes the high-level semantics do not work well, and low-level semantics need to be used.
In response to this problem, UNET is proposed, which integrates the low-level semantics in the downsampling process into the upsampling process, resulting in better results.
Integration ideas:
1. Copy the red feature channel on the left and combine it with the upsampled feature channel.
2. After the red feature channel on the left is processed by convolution, it is combined with the up-sampled feature channel.
边栏推荐
- 剑指 Offer 2022/7/4
- TensorFlow2学习笔记:8、tf.keras实现线性回归,Income数据集:受教育年限与收入数据集
- Kubernetes基本入门-概念介绍(一)
- SQL练习 2022/7/2
- WARNING: sql version 9.2, server version 11.0. Some psql features might not work.
- (五)栈及其应用
- MAE 论文《Masked Autoencoders Are Scalable Vision Learners》
- yolov3中数据读入(一)
- Polynomial Regression (PolynomialFeatures)
- Upload靶场搭建&&第一二关
猜你喜欢
随机推荐
剑指 Offer 20226/30
两个APP进行AIDL通信
Th in thymeleaf: href use notes
yolov3中数据读入(一)
Install dlib step pit record, error: WARNING: pip is configured with locations that require TLS/SSL
Jupyter Notebook installed library;ModuleNotFoundError: No module named 'plotly' solution.
【CV-Learning】Image Classification
TensorFlow2学习笔记:6、过拟合和欠拟合,及其缓解方案
Postgresql 快照
WARNING: sql version 9.2, server version 11.0. Some psql features might not work.
postgresql 游标(cursor)的使用
TensorFlow2 study notes: 8. tf.keras implements linear regression, Income dataset: years of education and income dataset
Learning curve learning_curve function in sklearn
PostgreSQL模式(Schema)
TensorFlow2 study notes: 5. Common activation functions
SQL练习 2022/7/3
MySql--存储引擎以及索引
flink on yarn任务迁移
Linear Regression 02---Boston Housing Price Prediction
[Deep Learning 21 Days Learning Challenge] Memo: What does our neural network model look like? - detailed explanation of model.summary()