当前位置:网站首页>IO流及其操作
IO流及其操作
2022-08-03 05:09:00 【*super】
IO操作
内存-->磁盘:输出output
磁盘-->内存:输入input
C盘,admin 下 test文件夹下有一个文件hello.txt .编写程序获取文件大小(提示利用File类型)
import java.io.File;
public class test01 {
public static long getFileSize(String filename) {
File file = new File(filename);
return file.length();
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
long size = getFileSize("c:/test/hello.txt");
System.out.println("hello.txt文件大小为: " + size);
}
}一、File类(详情见JDK)
public static void main(String[] args) {
File file =new File("d:/1/a.txt");
System.out.println(file);
File file1=new File("d:/1","a.txt");
System.out.println(file1);
File file2=new File("d:/1");
File file3=new File(file2,"a.txt");
System.out.println(file3);
}二、常见方法
public static void main(String[] args) {
File file =new File("a.txt");
System.out.println(file.getAbsolutePath());//获取到文件的绝对路径
System.out.println(file.getName());//获取文件名
System.out.println(file.getPath());//获取封装路径
System.out.println(file.length());//获取文件长度
}
三、文件和目录的操作
package IOdemo;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.IOException;
/**
* @Author:张金贺
* @Date:2022/7/6 17:14
* @Version 1.0
*/
public class demo4 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
File f =new File("d:/1");
boolean b = f.createNewFile();//创建文件
System.out.println(b);
System.out.println(f.delete());//删除文件
System.out.println(f.exists());//判断文件是否存在
System.out.println(f.isFile());//判断是否是文件
System.out.println(f.isDirectory());//判断是否是文件夹
String[] fs= f.list();//获取到该文件夹下所有文件和文件夹的名字
for (String s:fs) {
System.out.println(s);
}
File[] sf=f.listFiles();///获取到该文件夹下所有文件和文件夹的文件对象
for (File file:sf) {
System.out.println(file);
}
}
}
四、递归
public class demo3 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
test();
}
public static void test(){
System.out.println("递归");
test();
}
}案例1
利用递归,计算1-n之间的和。
package IOdemo;
import java.util.Scanner;
/**
* @Author:张金贺
* @Date:2022/7/6 17:36
* @Version 1.0
*/
public class demo5 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc =new Scanner(System.in);
int a= sc.nextInt();
System.out.println(sum(a));
}
public static int sum(int n){
if (n==1){
return 1;
}
return n+sum(n-1);
}
}
案例2
递归打印文件目录
package IOdemo;
import java.io.File;
/**
* @Author:张金贺
* @Date:2022/7/6 17:46
* @Version 1.0
*/
public class demo6 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
File f=new File("d:/1");
print(f);
}
public static void print(File f){
File[] fs= f.listFiles();//获取该目录下所有的文件和目录
for (File file : fs) {
if (file.isDirectory()){//如果是目录
print(file);
}else {
System.out.println(file.getName());
}
}
}
}
五、字节
1.字节输出流
package IOdemo;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.nio.charset.StandardCharsets;
/**
* @Author:张金贺
* @Date:2022/7/6 17:54
* @Version 1.0
*/
public class demo07 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
FileOutputStream fo=new FileOutputStream("d:/1/b.txt",true);//true表示不覆盖原内容
byte[] bs= "abc".getBytes();//将abc转换为字节
try {
fo.write(bs);
}catch (IOException ex){
System.out.println(ex.getMessage());
}finally {
if (fo!=null){
fo.close();
}
}
}
}
2.字节输入流
public class demo08 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
FileInputStream input =new FileInputStream("d:/1/a.txt");
// int ch=input.read();//读取a.txt中的数据 一次读取一个字节
// int ch1=input.read();
// int ch2=input.read();
// System.out.println((char) ch2);
int re=0;//读取出来的内容
while ((re=input.read())!=-1){
System.out.println((char) re);
}
input.close();
}
}
3.高效读取
public class demo08 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
FileInputStream input =new FileInputStream("d:/1/a.txt");
byte[] bs=new byte[1024];
int len=0;//读取的数据的长度
// input.read(bs);//读取内容并且放入bs
while((len= input.read(bs))!=-1){//读取txt中的内容并且放入bs
System.out.println(new String(bs,0,len));
}
input.close();
}
}4.字节流复制文件
public class demo09 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
FileInputStream input =new FileInputStream("d:/1/a.txt");
FileOutputStream out =new FileOutputStream("d:/1/2/c.txt");
int ch=0;//接收读取的数据的int变量
while ((ch=input.read())!=-1){
out.write(ch);
}
input.close();
out.close();
}
}5.高效复制
public class demo10 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
FileInputStream input =new FileInputStream("d:/1/b.txt");
FileOutputStream output =new FileOutputStream("d:/1/2/h.txt");
byte[] bs =new byte[1024];
int len =0;
while ((len=input.read(bs))!=-1){
output.write(bs);
}
input.close();
output.close();
}
}六、字符
字符编码表参考学习(字符编码表_weixin_45577832的博客-CSDN博客_字符编码表)
1.字符输出流
public class demo2 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
FileWriter writer =new FileWriter("d:/1/a.txt",true);
writer.write("大家好");
writer.flush();//刷新缓冲区
writer.close();//关闭输出流
}
}2.字符输入流
public class demo1 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
FileReader reader =new FileReader("d:/1/a.txt");
int ch=0;//接收读取数据
while ((ch=reader.read())!=-1){
System.out.println(ch);
System.out.println((char) ch);
}
reader.close();
}
}
3.字符流复制文件
public class fuzhi {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
FileReader reader=new FileReader("d:/1/a.txt");
FileWriter writer=new FileWriter("d:/1/l.txt");
char[] ch=new char[1024];//创建缓冲区
int len =0;//记录每次读取的长度
while ((reader.read(ch))!=-1){
writer.write(ch);
}
reader.close();
writer.close();
}
}七、缓冲流(大量处理数据)
1.高效的字节缓冲输出流
public class demo01 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
FileOutputStream out=new FileOutputStream("d:/1/b.txt",true);
BufferedOutputStream bout =new BufferedOutputStream(out);
bout.write("hello".getBytes());
bout.close();
}
}2.高效的字节缓冲输入流
public class demo01 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
FileInputStream input=new FileInputStream("d:/1/b.txt");
BufferedInputStream bout =new BufferedInputStream(input);
int ch=0;
while ((ch= bout.read())!=-1){
System.out.println((char) ch);
}
bout.close();
}
}3.字符缓冲流
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
//输出流
FileWriter writer = new FileWriter("d:/1/a.txt");
BufferedWriter bw = new BufferedWriter(writer); //创建字符缓冲输出流
bw.write("abc"); //写入abc
bw.newLine();//换行
bw.write( "xyz");bw.close();
//输入流
FileReader reader = new FileReader( "d:/1/a.txt") ;
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(reader);
String str=null;
while((str=br.readLine()) !=null) {
System.out.println(str);
}
br.close() ;
}4.字符缓冲流复制文件
public class fuzhi {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new FileReader("d:/1/a.txt"));
BufferedWriter bw = new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter("d:/1/b.txt"));
String line =null;//记录读取到的字符串
while((line=br.readLine()) !=null) {
bw.write(line);
bw.newLine();
}
bw.close() ;
br.close();
}
}八、IO流案例
1.使用基本的流与高效的流完成复制文件
需求:将d:\\test.avi文件进行复制
采用4种方式复制
方式1:采用基本的流,一次一个字节的方式复制 共耗时224613毫秒
方式2:采用基本的流,一个多个字节的方式复制 共耗时327豪秒
方式3:采用高效的流,一次一个字节的方式复制 共耗时2047毫秒
方式4:采用高效的流,一个多个字节的方式复制 共耗时96毫秒
数据源:d:\\test.avi
目的地1: d:\\ copy1.avi
目的地2:d:\\ copy2.avi
目的地3: d:\\copy3.avi
目的地4: d:\\ copy4.avi
实现的步骤:
1,指定数据源
2,指定目的地
3,读数据
4,写数据
5,关闭流
package IOdemo.lianxi;
import java.io.*;
/**
* @Author:张金贺
* @Date:2022/7/6 19:01
* @Version 1.0
*/
public class test {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
long start =System.currentTimeMillis();
method1("d/1/a.txt","d/1/b.txt");
long end =System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println(end-start);
}
// 基本的流一次读取一个字节 复制文件
public static void method1(String src,String desc) throws IOException {
FileInputStream input = new FileInputStream(src);
FileOutputStream output = new FileOutputStream(desc);
int ch=0;
while((ch=input.read()) !=-1){
output.write(ch);
}
input.close() ;
output.close() ;
}
// 基本的流一次读取一个字节数组 复制文件
public static void method2(String src,String desc) throws IOException {
FileInputStream input = new FileInputStream(src);
FileOutputStream output = new FileOutputStream(desc);
int ch=0;
byte[] b=new byte[1024];
while((ch=input.read(b)) !=-1){
output.write(b);
}
input.close() ;
output.close() ;
}
// 采用高效的流,一次一个字节的方式 复制文件
public static void method3(String src,String desc) throws IOException {
FileInputStream input = new FileInputStream(src);
FileOutputStream output = new FileOutputStream(desc);
BufferedInputStream bi =new BufferedInputStream(input);
BufferedOutputStream bu= new BufferedOutputStream(output);
int ch=0;
while((ch=bi.read()) !=-1){
output.write(ch);
}
input.close() ;
output.close() ;
}
// 采用高效的流,一个多个字节的方式 复制文件
public static void method4(String src,String desc) throws IOException {
FileInputStream input = new FileInputStream(src);
FileOutputStream output = new FileOutputStream(desc);
BufferedInputStream bi =new BufferedInputStream(input);
BufferedOutputStream bu= new BufferedOutputStream(output);
int ch=0;
byte[] b=new byte[1024];
while((ch=bi.read(b)) !=-1){
output.write(b);
}
input.close() ;
output.close() ;
}
}
九、序列化和反序列化
1.定义
序列化是将对象的状态写入到特定的流中的过程。
反序列化则是从特定的流中获取数据重新构建对象的过程。
用于从流中读取对象的操作流ObjectInputStream称为反序列化流。
用于向流中写入对象的操作流ObjectOutputStream称为序列化流。
2.案例
package IOdemo.xuliehua;
import java.io.Serializable;
/**
* @Author:张金贺
* @Date:2022/7/6 19:44
* @Version 1.0
*/
public class Person implements Serializable {
private String name;
private Integer age;
public Person(String name, Integer age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public Integer getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(Integer age) {
this.age = age;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Person{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
", age=" + age +
'}';
}
}
序列化:
public class demo01 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
Person p =new Person("张三",23);
FileOutputStream out =new FileOutputStream("template/p.txt");
ObjectOutputStream os =new ObjectOutputStream(out);//用来序列化的对象
os.writeObject(p);//序列化p对象
out.close();
os.close();
}
}反序列化:
public class demo01 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException {
FileInputStream inputStream =new FileInputStream("template/p.txt");
ObjectInputStream oi =new ObjectInputStream(inputStream);
Person p= (Person) oi.readObject();//反序列化
System.out.println(p.toString());
oi.close();
}
}3.序列化的接口
public class Person implements Serializable
private static final 1ong serialVersionUID=1L;//序列化的版本号
private transient Integer age;//表示age不会被序列化
4.Properties集合
Properties 类表示了一个持久的属性集。Properties 可保存在流中或从流中加载。属性列表中每个
键及其对应值都是一个字符串。
特点:
(1)、Hashtable的子类,map集合中的方法都可以用。
(2)、该集合没有泛型。键值都是字符串。
(3)、它是一个可以持久化的属性集。键值可以存储到集合中,也可以存储到持久化的设备(硬盘、
U盘、光盘)上。键值的来源也可以是持久化的设备。
(4)、有和流技术相结合的方法。
public class demo011 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Properties p =new Properties();
p.setProperty("张三","23");//键和值都是String
p.setProperty("李四","23");
Set<String> keys= p.stringPropertyNames();//获取到所有键
for (String key:keys) {
String value =p.getProperty(key);
System.out.println("key="+key+"value+"+value);
}
}
}5.Properties和IO流的交互
需求:使用Properties集合,完成把集合内容存储到IO流所对应文件中的操作
分析:
1,创建Properties集合
2,添加元素到集合
3,创建流
4,把集合中的数据存储到流所对应的文件中
stroe(Writer,comments)
store(OutputStream,commonts)
把集合中的数据,保存到指定的流所对应的文件中,参数commonts 代表对描述信息
5,关闭流保存数据:
public class demo1 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
Properties pro =new Properties();
pro.setProperty("张三","23");//键和值都是String
pro.setProperty("李四","23");
FileOutputStream out =new FileOutputStream("template/pro.properties");
pro.store(out,"sava data");//保存数据
out.close();
}
}加载数据:
public class demo1 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
Properties pro =new Properties();
FileInputStream input =new FileInputStream("template/pro.properties");
pro.load(input);//加载数据
System.out.println(pro);
}
}边栏推荐
- Interface testing framework combat (3) | JSON request and response assertion
- Shell conditional statement judgment
- typescript46-函数之间的类型兼容性
- idea使用@Autowired注解爆红原因及解决方法
- 【HMS core】【Ads Kit】华为广告——海外应用在国内测试正式广告无法展示
- 【Harmony OS】【ArkUI】ets开发 基础页面布局与数据连接
- 数字孪生园区场景中的坐标知识
- typescript40-class类的保护修饰符
- 2022/08/02 Study Notes (day22) Multithreading
- UV decomposition of biotin - PEG2 - azide | CAS: 1192802-98-4 biotin connectors
猜你喜欢
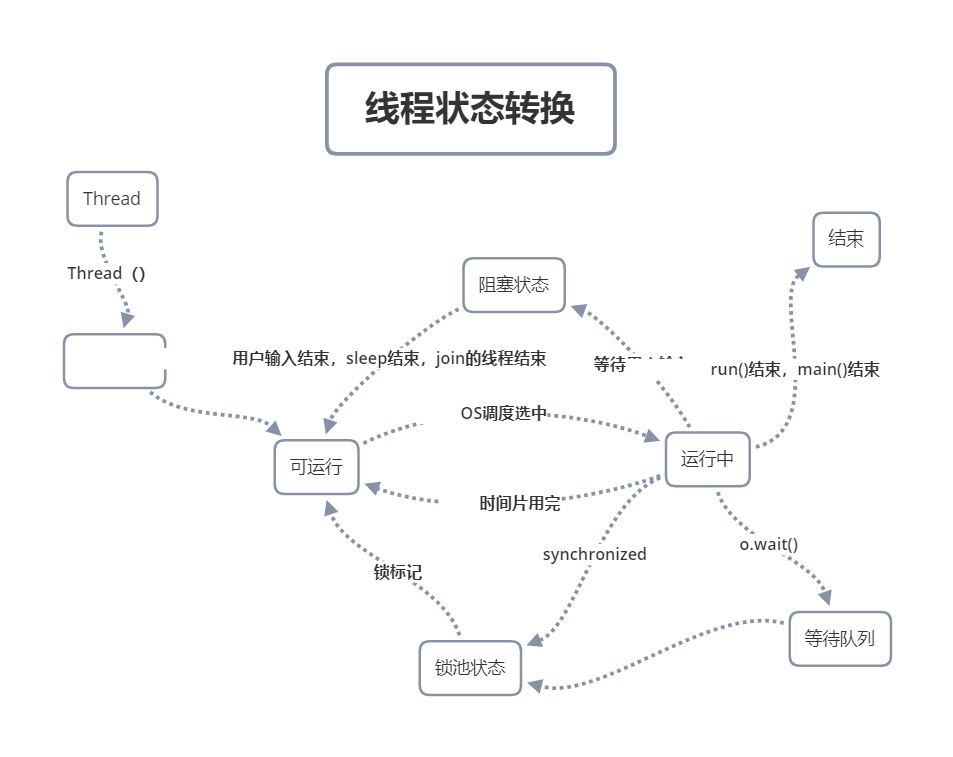
2022/08/02 学习笔记 (day22) 多线程
Interface Test Framework Practice (4) | Get Schema Assertion
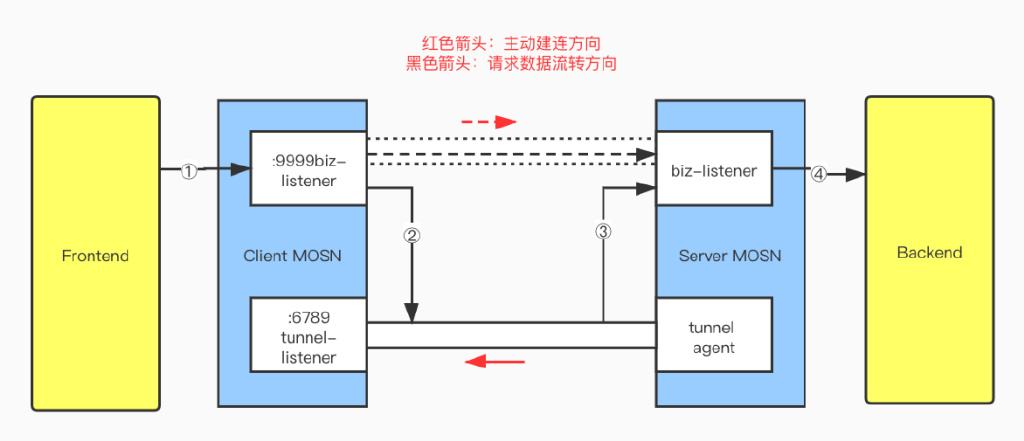
MOSN 反向通道详解

社交电商如何做粉丝运营?云平台怎么选择商业模式?
unity2D横板游戏教程6-敌人AI以及受击动画

Concepts and Methods of Exploratory Testing

js implements a bind function

Online password generator tool recommendation
在树莓派上搭建属于自己的网页(2)

13.< tag-动态规划和回文字串>lt.647. 回文子串 + lt.516.最长回文子序列
随机推荐
typescript45-接口之间的兼容性
Common lipophilic cell membrane dyes DiO, Dil, DiR, Did spectrograms and experimental procedures
Odps temporary query can write SQL, turned out to a named?
Tributyl-mercaptophosphane "tBuBrettPhos Pd(allyl)" OTf), 1798782-17-8
typescript39-class类的可见修饰符
三丁基-巯基膦烷「tBuBrettPhos Pd(allyl)」OTf),1798782-17-8
【Harmony OS】【ArkUI】ets开发 基础页面布局与数据连接
【Harmony OS】【ARK UI】Date 基本操作
unity2D横板游戏教程6-敌人AI以及受击动画
Flink state
刚上线就狂吸70W粉,新型商业模式“分享购”来了,你知道吗?
软件开发的最大的区别是什么?
Shell之条件语句
Talking about GIS Data (6) - Projected Coordinate System
odps的临时查询能在写sql的时候就给结果一个命名不?
User password encryption tool
shell脚本循环语句
Build your own web page on the Raspberry Pi (2)
Practical application of WebSocket
Common fluorescent dyes to modify a variety of groups and its excitation and emission wavelength data in the data