当前位置:网站首页>Introduction and mock implementation of list:list
Introduction and mock implementation of list:list
2022-08-02 04:52:00 【RNGWGzZs】

-----------"Don't ask if you can,Just say whether you want it or not"
(1)list是什么?
1.listcan be in the constant range,Insert anywhere、删除数据.
2.list底层是双向循环链表.
3.list相对于(vector\string)插入数据,简单高效
4.但list不支持随机访问.

(2)listfunction and its use:
①构造函数
构造函数 | 说明 |
list() | 构造空的list |
list (size_type n, const value_type& val = value_type()) | 构造的list中包含n个值为val的元素 |
list (const list& x) | 拷贝构造函数 |
list (InputIterator fifirst, InputIterator last) | 用[fifirst, last)区间中的元素构造list |

② 迭代器
迭代器 | 说明 |
begin+end | 返回第一个元素的迭代器+返回最后一个元素下一个位置的迭代器 |
rbegin + rend | 返回第一个元素的reverse_iterator,即end位置,返回最后一个元素下一个位置的reverse_iterator,即begin位置 |

③修改:
函数声明 | 说明 |
push_front | 在list首元素前插入值为val的元素 |
pop_front | 删除list中第一个元素 |
push_back | 在list尾部插入值为val的元素 |
pop_back | 删除list中最后一个元素 |
insert | 在list position 位置中插入值为val的元素 |
erase | 删除list position位置的元素 |
swap | 交换两个list中的元素 |
clear | 清空list中的有效元素 |


Most of the functions have already been introduced,Just stop here.
(3)list模拟实现:
list基本框架:

①<重>list迭代器:
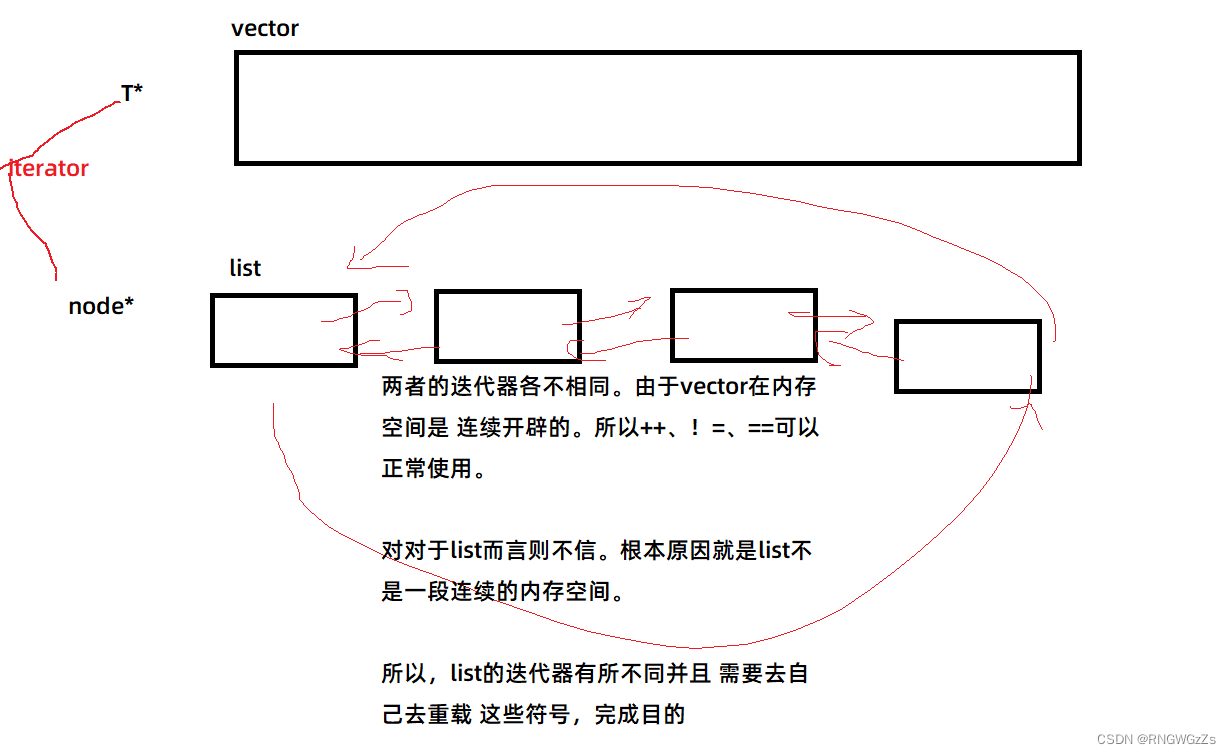
//迭代器
template<class T>
struct _list_iterator
{
//Let the node be here again Rename inside the struct
typedef _list_node<T> node;
//Some operations are involved
typedef _list_iterator<T> self;
node* _pnode; //list迭代器 本质就是个 节点指针
_list_iterator(const node* pnode)
:_pnode(pnode)
{}
//*
T& operator* ()
{
return _pnode->_val;
}
//重载!=
bool operator!=(const self& s)
{
//两个地址不一样
return _pnode != s._pnode;
}
//前置++
self& operator++()
{
_pnode = _pnode->_next;
return *this;
}
//后置++
self operator++(int)
{
node* tmp = _pnode;
_pnode = _pnode->_next;
return tmp;
}
//前置--
self& operator--()
{
_pnode = _pnode->_prev;
return *this;
}
//后置
self operator--()
{
node* tmp = _pnode;
_pnode = _pnode->_prev;
return tmp;
}
};对listThe iterator laying framework is perfect,Simply insert.

Let's start by inserting a few numbers at the end;
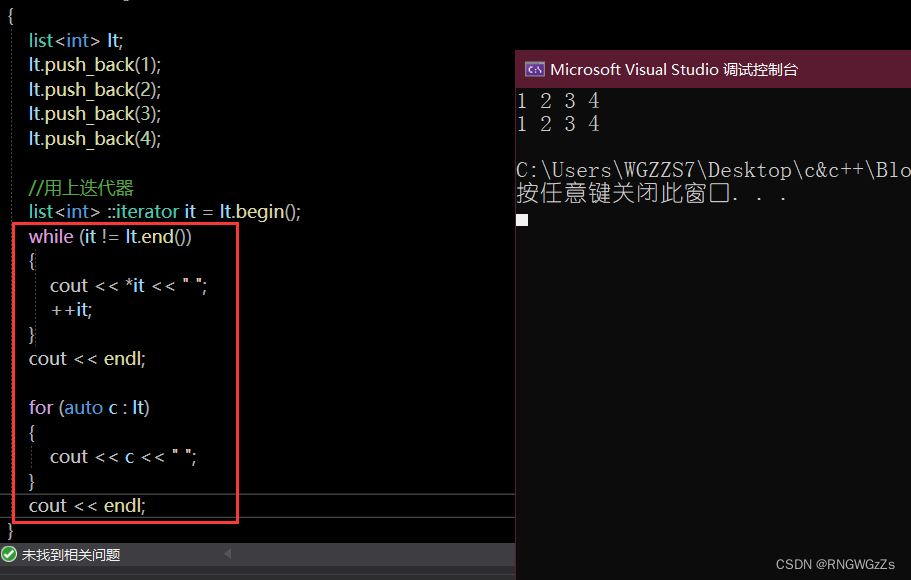
Iterators can also be used normally.
迭代器模板!!!:
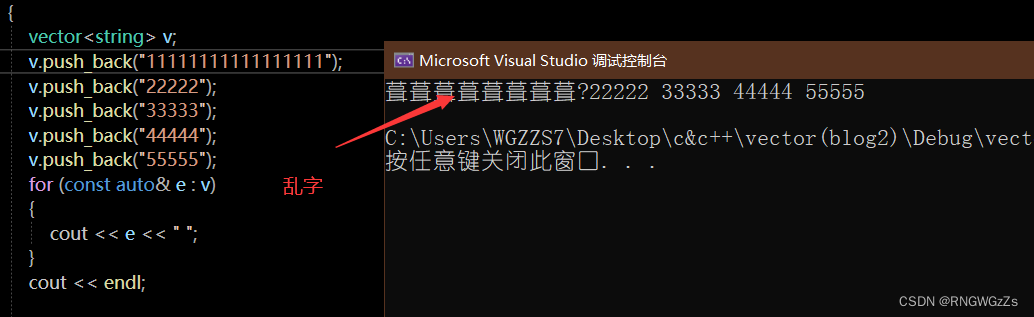
void PrintList(const list<int>& lt)
{
list<int> ::iterator it = lt.begin();
while (it != lt.end())
{
*it += 1;
cout << *it << " ";
++it;
}
cout << endl;
}At this point we encapsulate a printlist内容的函数,
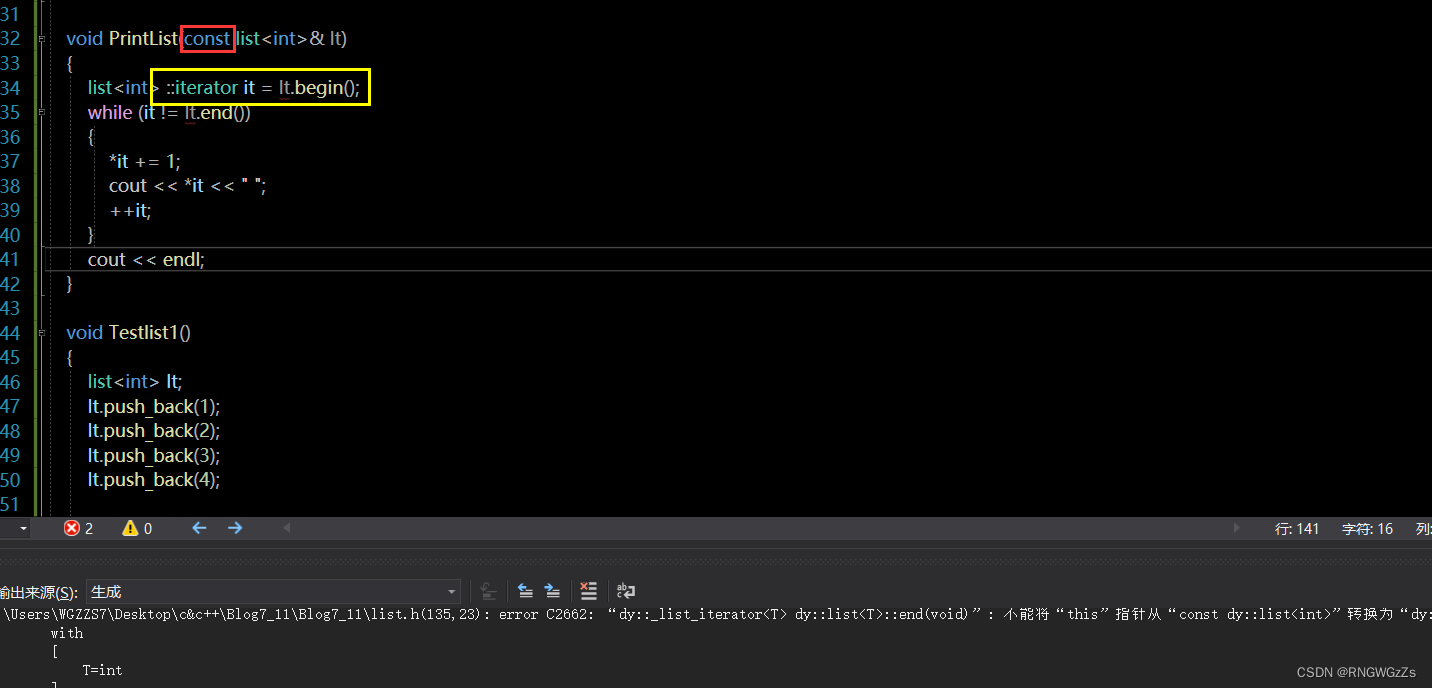
此时出现报错,The current reason may be out of useconst迭代器.
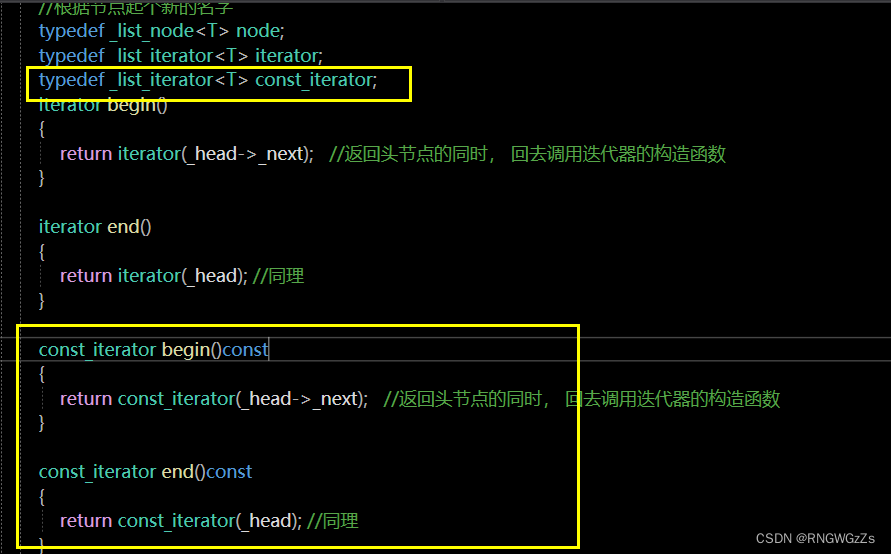
所以我们在list内 更新迭代器.
 At this point the code has changed,但问题是,Can actually be modifiedconst修饰的对象?! This is definitely more than what we want.
At this point the code has changed,但问题是,Can actually be modifiedconst修饰的对象?! This is definitely more than what we want.
问题出在:
所以,Just go and start again 单独创建一个const_iterator 才能实现.
 然而,This would be too complicated,constIterator and notconstIterators are only in one place 不同.
然而,This would be too complicated,constIterator and notconstIterators are only in one place 不同.

最后:
template<class T,class Ref,class Ptr>
struct _list_iterator
{
//Let the node be here again Rename inside the struct
typedef _list_node<T> node;
//Some operations are involved
typedef _list_iterator<T, Ref, Ptr> self;
node* _pnode; //list迭代器 本质就是个 节点指针
_list_iterator(node* pnode)
:_pnode(pnode)
{}
//*
T& operator*()
{
return _pnode->_val;
}
//重载!=
bool operator!=(const self& s)
{
//两个地址不一样
return _pnode != s._pnode;
}
//前置++
self& operator++()
{
_pnode = _pnode->_next;
return *this;
}
//后置++
self operator++(int)
{
node* tmp = _pnode;
_pnode = _pnode->_next;
return tmp;
}
//前置--
self& operator--()
{
_pnode = _pnode->_prev;
return *this;
}
//后置
self operator--(int)
{
node* tmp = _pnode;
_pnode = _pnode->_prev;
return tmp;
}
};Each will find its own corresponding part.

listThe hard part is the iterators,搞定 这部分,Subsequent operations are as easy as the palm of your hand
②属性:
size:
链表的size有两种方法:
1.计数++
size_t size()
{
size_t count = 0;
const_iterator it = begin();
while (it != end())
{
count++;
it++;
}
return count++;
}2.定义类成员变量,动态增加.
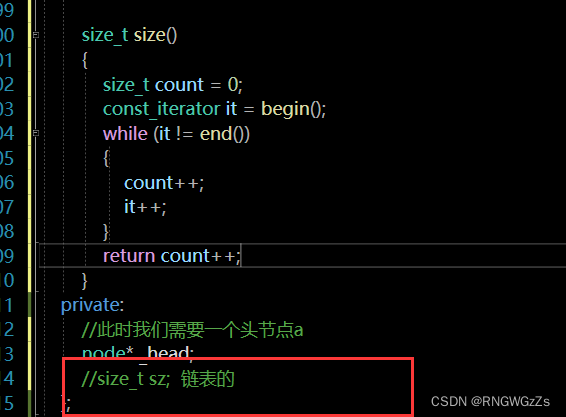
empty:
bool empty()
{
//最初 头节点 pointers point to themselves
return begin() == end();
}③修改:
push_back:
void push_back(const T& x)
{
node* newnode = new node(x); //创建节点
//尾插链接
node* tail = _head->_prev;
tail->_next = newnode;
newnode->_prev = tail;
newnode->_next = _head;
_head->_prev = newnode;
}push_front\pop_front\pop_backwill be reused(insert\erase),
Insert:
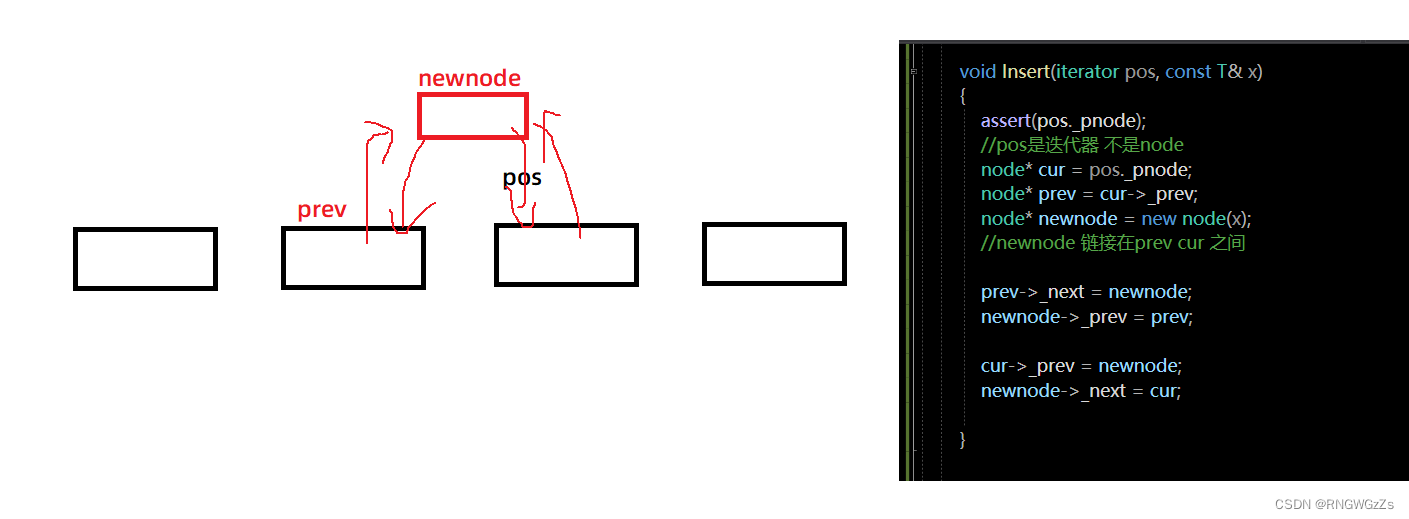
void Insert(iterator pos, const T& x)
{
assert(pos._pnode);
//pos是迭代器 不是node
node* cur = pos._pnode;
node* prev = cur->_prev;
node* newnode = new node(x);
//newnode 链接在prev cur 之间
prev->_next = newnode;
newnode->_prev = prev;
cur->_prev = newnode;
newnode->_next = cur;
}
erase:

iterator erase(iterator pos)
{
assert(pos._pnode);
node* cur = pos._pnode;
node* prev = cur->_prev;
node* next = cur->_next;
delete cur;
prev->_next = next;
next->_prev = prev;
//Returns an iterator for the next node
return iterator(next); //用next 去构造
}pop\push:
void push_back(const T& x)
{
//node* newnode = new node(x); //创建节点
尾插链接
//node* tail = _head->_prev;
//tail->_next = newnode;
//newnode->_prev = tail;
//newnode->_next = _head;
//_head->_prev = newnode;
Insert(end(),x);
}
void push_front(const T& x)
{
Insert(begin(), x);
}
void pop_back()
{
erase(--end());
}
void pop_front()
{
erase(begin());
}

④Construct and delete:
destructor cleanup:
void clear()
{
iterator it = begin();
while (it != end())
{
//erase(it++);
it=erase(it);
}
}
~list()
{
clear();
delete _head;
_head = nullptr;
}
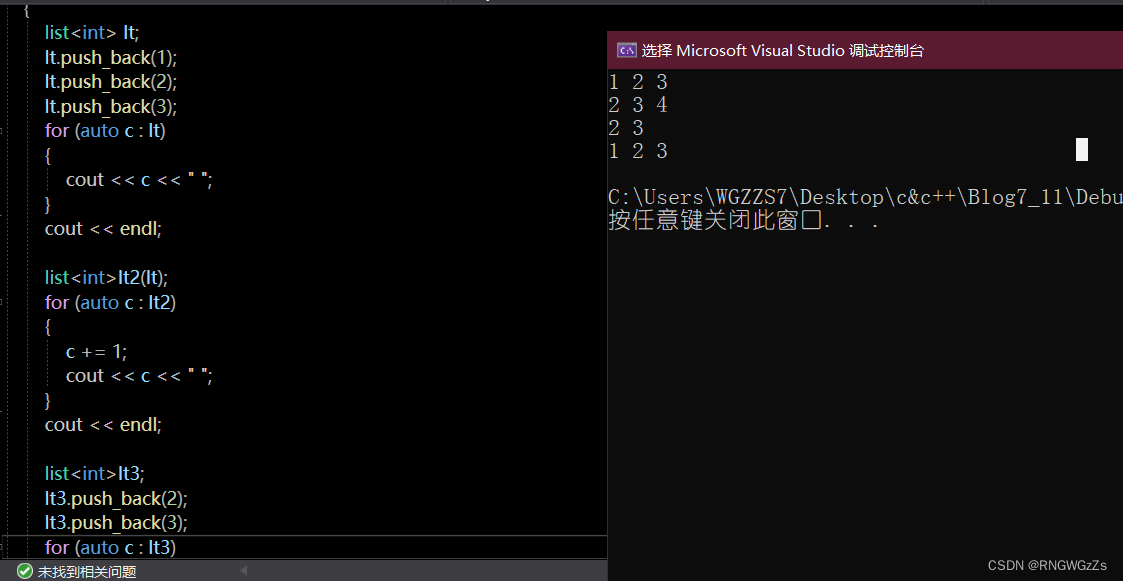
拷贝构造与赋值重载:
//拷贝构造
//l2(l1);
list(const list<T>& lt)
{
//构造头节点
_head = new node();
_head->_next = _head;
_head->_prev = _head;
//Tail in sequence
for (const auto& c : lt)
{
//Not referencing is copy construction
push_back(c);
}
}
list<T>& operator=(list<T> v)
{
swap(_head,v._head);
return *this;
}
//s1=s2;
//传统写法
list<T>& operator=(list<T>& v)
{
if (this != &v)
{
//Clean yourself first
clear();
//Insert the value again
for (const auto& c : v)
{
push_back(c);
}
}
return *this;
}
构造:
//数值构造
list(size_t n, const T& val)
{
_head = new node(); //首先创建头节点
_head->_prev = _head;
_head->_next = _head; //指针指向自己
while (n--)
{
push_back(val);
}
}
//迭代区间
list(iterator first, iterator last)
{
_head = new node(); //首先创建头节点
_head->_prev = _head;
_head->_next = _head; //指针指向自己
while (first != last)
{
push_back(*first);
first++;
}
}
这篇listThe short essay is over,希望对你有帮助
祝你好运~

边栏推荐
- 龙芯2K1000使用nfs挂载文件系统进行使用
- USB HUB USB集线器电路设计
- 2019 - ICCV - 图像修复 Image Inpainting 论文导读《StructureFlow: Image Inpainting via Structure-aware ~~》
- 兼容C51与STM32的Keil5安装方法
- bluez5.50蓝牙文件传输
- Anaconda(Jupyter)里发现不能识别自己的GPU该怎么办?
- 【plang1.4.3】语言新特性:集合
- vector的使用和模拟实现:
- 【nRF24L01 connects with Arduino to realize wireless communication】
- USB2.0一致性测试方法_高速示波器
猜你喜欢
随机推荐
Mac安装MySQL详细教程
GM8775C MIPI转LVDS调试资料分享
Compatible with C51 and STM32 Keil5 installation method
Comparative analysis of mobile cloud IoT pre-research and Alibaba Cloud development
如何用 Lightly 进行 Debug 断点调试?
如何快速搭建属于自己的物联网平台?
LT8918L LVDS转MIPI芯片技术支持资料
uniCloud use
振芯GM7123C:功能RGB转VGA芯片方案简介
向龙芯2K1000板子上烧写中标麒麟系统
VCA821可变增益放大器
HDMI转MIPI CSI东芝转换芯片-TC358743XBG/TC358749XBG
Pylon CLI 低成本的本地环境管控工具应用实例
调试九法准则
AD PCB导出Gerber文件(非常详细的步骤)
NSIS来自己设定快捷方式的图标
path 修补文件命令
使用pyqt弹出消息提示框
C语言教程 - 制作单位转换器
408-二叉树-先序中序后序层次遍历