当前位置:网站首页>LeetCode142. Circular linked list II [two pointers, two methods for judging links in the linked list and finding ring points]
LeetCode142. Circular linked list II [two pointers, two methods for judging links in the linked list and finding ring points]
2022-07-07 22:49:00 【Qingshan's green shirt】
LeetCode142. Circular list II
List of articles
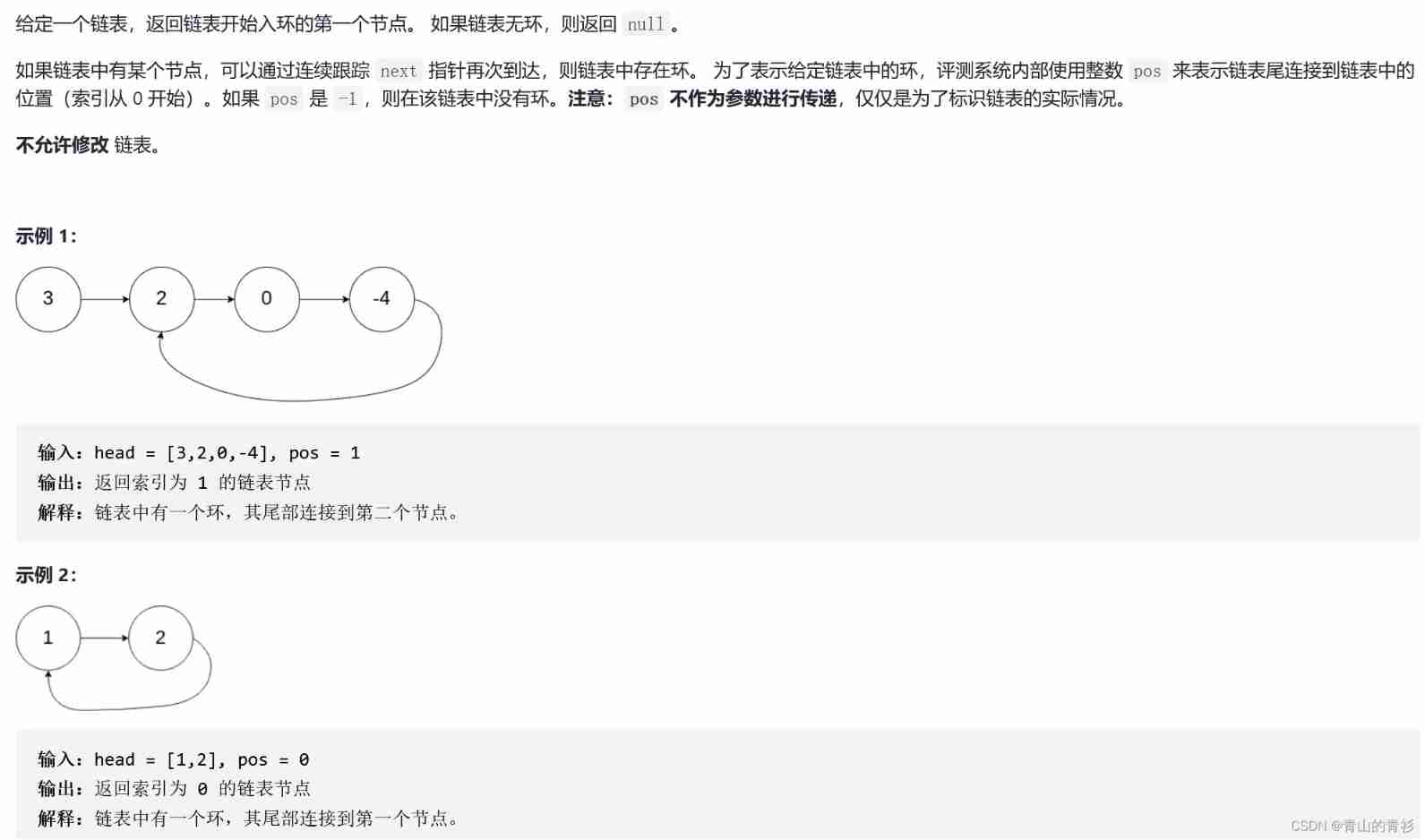
1. subject
2. Ideas
Two steps :
1. Determine whether there is a ring —— Fast and slow pointer methodIt should be noted that : We will meet , Because after entering the ring, it is equivalent to fast The pointer moves forward one chase at a time slow The pointer
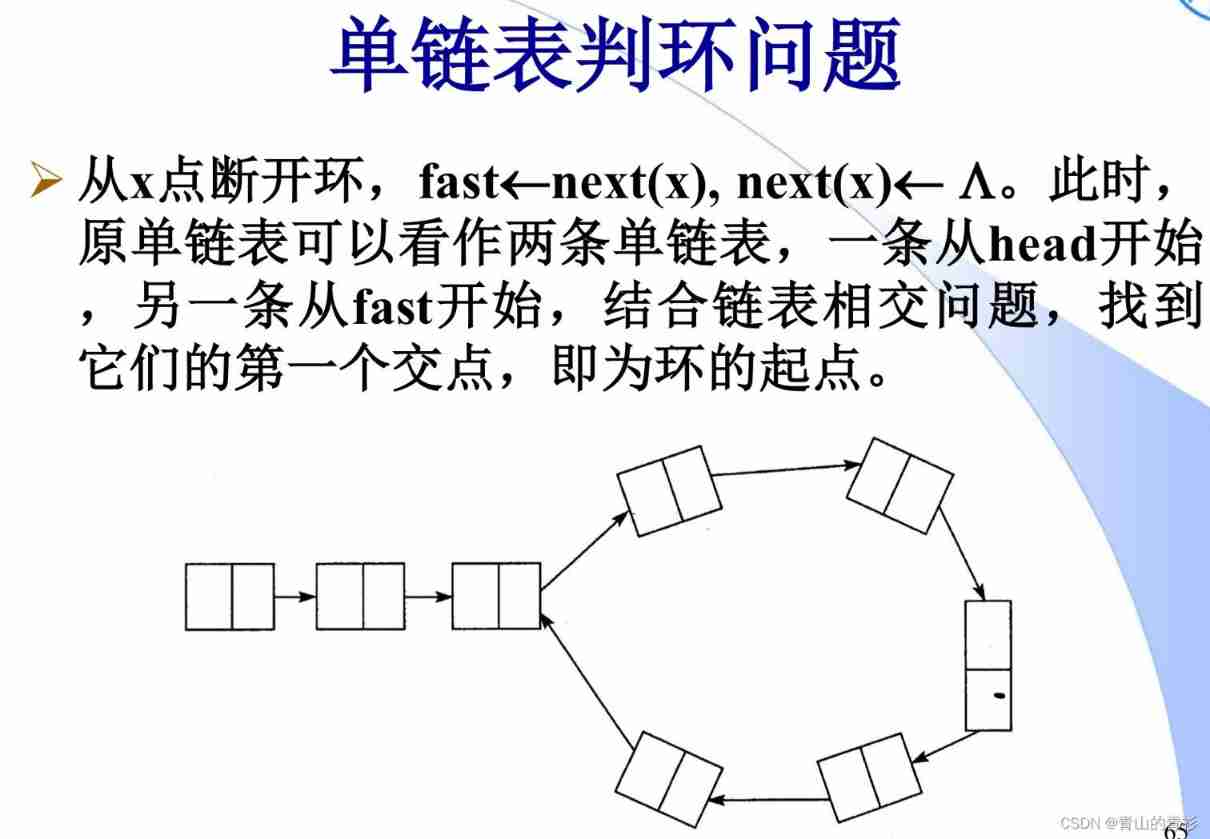
2. Look for the entrance of the ring
a. Start a pointer from the beginning node , From the meeting node Also start a pointer , These two pointers walk only one node at a time , So when these two pointers meet, it is The node of the ring entrance .
Here is the mathematical proof :n If it is greater than 1 The situation of , Namely fast The pointer turns in a circle n After the circle, I met slow The pointer . Actually sum n by 1 When The effect is the same , You can also find the circular entry node through this method , It's just ,index1 The pointer is in the ring Turn more (n-1) circle , Then meet again index2, The meeting point is still the entrance node of the ring .
b. Disconnect list , Combine the problem of linked list intersection to find the beginning
3. Code implementation
(1) Determine whether there is a ring
//1. Set the speed pointer to the header
ListNode* fast = head;
ListNode* slow = head;
//2.fast Take two steps at a time slow One step at a time
// It's not good to write like this ! If fast->next It's empty , Cannot access fast->next->next!
//while(fast->next != NULL && fast->next->next != NULL)
while(fast!=NULL && fast->next !=NULL)
{
fast = fast->next->next;
slow = slow->next;
if(fast == slow) break;// Equal to jump out
}
//3. The condition used to determine the jump is fast == slow still fast Empty finger
if(fast==NULL || fast->next == NULL)
return NULL;
matters needing attention
1. It's not good to write like this ! If fast->next It's empty , Cannot access fast->next->next!
while(fast->next != NULL && fast->next->next != NULL)
2. The cyclic condition cannot bewhile(fast != slow), In this case, the acyclic condition cannot be distinguished !
(2) Look for the entrance of the ring
a. Mathematical methods Set two more pointers
ListNode* p1 = fast;// Start a pointer from the encounter node
ListNode* p2 = head;// Start a pointer from the beginning node
while(p1 != p2)
{
p1 = p1->next;
p2 = p2->next;
}
return p1;// The encounter node is the linked list entry
b. Disconnect list , Join linked list intersection
//ListNode *x;x->next = fast;x->next = NULL That's not right !
ListNode* p = fast;
while(p->next != fast)
p = p->next;
p->next = NULL;
// Become two linked lists , One by head start A meeting point fast start
ListNode* m = head; ListNode* n = fast;
// Count the length of the two linked lists
int len1 = 0;int len2 = 0;
while(m!= NULL) {
m = m->next;len1 ++;}
while(n != NULL){
n = n->next;len2++;}
if(len1 > len2){
int n = len1 - len2;// Calculate the linked list difference
while(n--){
// The pointer of the long linked list goes backward first , Align with the pointer of the short linked list
head = head->next;
}
while( head != fast)// Step back synchronously , Until equal nodes are encountered .
{
head = head->next;
fast = fast->next;
}
return head;
}
else{
int n = len2 - len1;
while(n--){
fast = fast->next;
}
while( head != fast)
{
head = head->next;
fast = fast->next;
}
return head;
}
matters needing attention
ListNode *x;x->next = fast;x->next = NULL, Never write that ! The single linked list cannot access the node in front of it !
Complete code
Method 1 :
class Solution {
public:
ListNode *detectCycle(ListNode *head) {
ListNode* fast = head;
ListNode* slow = head;
while(fast!=NULL && fast->next !=NULL)
{
fast = fast->next->next;// Two steps at a time
slow = slow->next; // One step at a time
if(fast == slow) break;
}
if(fast==NULL || fast->next == NULL)
return NULL;
ListNode* p1 = fast;// Start a pointer from the encounter node
ListNode* p2 = head;// Start a pointer from the beginning node
while(p1 != p2)
{
p1 = p1->next;
p2 = p2->next;
}
return p1;// The encounter node is the linked list entry
}
};
Method 2 :
class Solution {
public:
ListNode *detectCycle(ListNode *head) {
ListNode* fast = head;
ListNode* slow = head;
while(fast!=NULL && fast->next !=NULL)
{
fast = fast->next->next;// Two steps at a time
slow = slow->next; // One step at a time
if(fast == slow) break;
}
if(fast==NULL || fast->next == NULL)
return NULL;
ListNode* p = fast;//ListNode *x;x->next = fast?
while(p->next != fast)
p = p->next;
p->next = NULL;
// Become two linked lists , One by head start A meeting point fast start
ListNode* m = head; ListNode* n = fast;
while(m!= NULL) {
m = m->next;len1 ++;}
while(n != NULL){
n = n->next;len2++;}
if(len1 > len2){
int n = len1 - len2;
while(n--){
head = head->next;
}
while( head != fast)
{
head = head->next;
fast = fast->next;
}
return head;
}
else{
int n = len2 - len1;
while(n--){
fast = fast->next;
}
while( head != fast)
{
head = head->next;
fast = fast->next;
}
return head;
}
}
};
边栏推荐
- Remember an experience of using selectmany
- Time convolution Network + soft threshold + attention mechanism to realize residual life prediction of mechanical equipment
- 如何选择合适的自动化测试工具?
- Xcode modifies the default background image of launchscreen and still displays the original image
- Amesim2016 and matlab2017b joint simulation environment construction
- Record a garbled code during servlet learning
- 新版代挂网站PHP源码+去除授权/支持燃鹅代抽
- 「开源摘星计划」Loki实现Harbor日志的高效管理
- Anti climbing killer
- OpenGL configure assimp
猜你喜欢
Redis集群安装

Application practice | the efficiency of the data warehouse system has been comprehensively improved! Data warehouse construction based on Apache Doris in Tongcheng digital Department
行测-图形推理-9-线条问题类
Record a garbled code during servlet learning

【Azure微服务 Service Fabric 】在SF节点中开启Performance Monitor及设置抓取进程的方式
Common verification rules of form components -2 (continuously updating ~)

行测-图形推理-5-一笔画类
Firefox browser installation impression notes clipping

如何选择合适的自动化测试工具?
OpenGL configuration vs2019
随机推荐
XMIND mind mapping software sharing
Application practice | the efficiency of the data warehouse system has been comprehensively improved! Data warehouse construction based on Apache Doris in Tongcheng digital Department
PHP records the pitfalls encountered in the complete docking of Tencent cloud live broadcast and im live group chat
Write in front -- Talking about program development
Redis官方ORM框架比RedisTemplate更优雅
Cataloger integrates lidar and IMU for 2D mapping
Record a garbled code during servlet learning
Quick sort (diagram +c code)
Debezium系列之:mysql墓碑事件
Redis official ORM framework is more elegant than redistemplate
Select sort (illustration +c code)
微服务架构开源框架详情介绍
How to close eslint related rules
Debezium series: support the use of variables in the Kill Command
Revit secondary development - modify wall thickness
C development - interprocess communication - named pipeline
vite Unrestricted file system access to
Revit secondary development - get the project file path
This experimental syntax requires enabling the parser plugin: ‘optionalChaining‘
[interview arrangement] 0211 game engine server