当前位置:网站首页>Analysis of the problems of the 7th Blue Bridge Cup single chip microcomputer provincial competition
Analysis of the problems of the 7th Blue Bridge Cup single chip microcomputer provincial competition
2022-07-03 07:30:00 【start field】
Today brings you the seventh (2016) Analysis of the provincial competition topic , The topic is not difficult on the whole , Let's have a look .
subject 

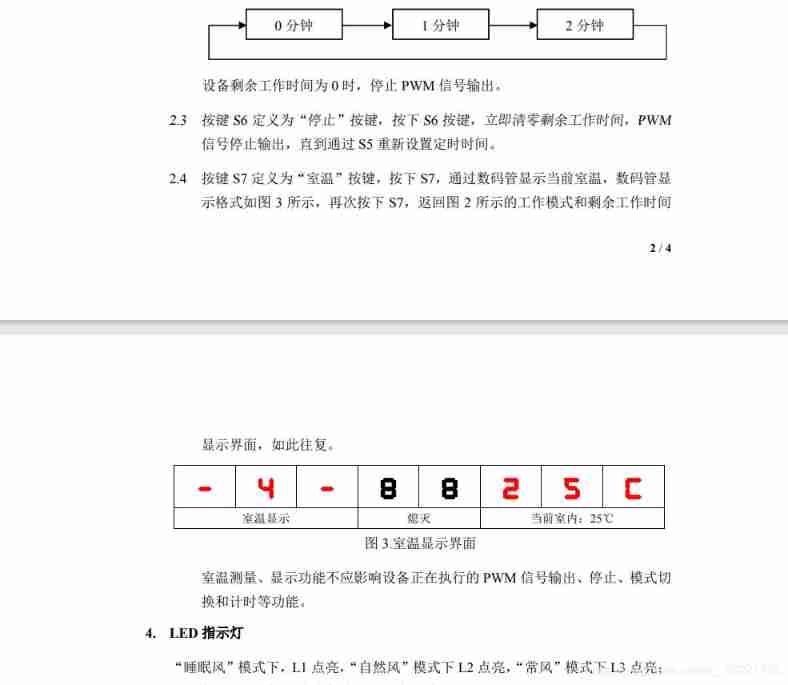

The overall problem of this provincial competition is not difficult , In addition to PWM It's not easy to understand , Others are easy to understand , The most important thing is the logic of programming . Topic investigated LED Show 、 Key 、 The nixie tube shows ( These three modules will be tested for each set of questions , We should be familiar with )、PWM、DS18B20.
1 The nixie tube shows
There are two modes of nixie tube , One is the working mode , One is room temperature mode . We can write two interface functions , One is used to display the working mode , Another shows room temperature mode , Press the key to select which mode to display .
2 LED Show
Define a variable mode, Control by pressing the key mode The value of makes it in 1-3 In between .mode by 1 when L1 bright ,mode by 2 when L2 bright ,mode by 3 when L3 bright .
3 Key module
The title is used s4,s5,s6,s7 Four buttons , It's a stand-alone keyboard .s4 Used to control mode Value .s5 Used to control the countdown , Also define a countdown_mode Variable in 1-3 In between ,countdown_mode by 1 The countdown is 0,countdown_mode by 2 The countdown is 60,countdown_mode by 3 The countdown is 120.s6 Is to put countdown_mode Set to 1.s7 There are two states , Define a temp_m Variable to control , by 1 Display room temperature mode , by 0 Display the working mode .
4 pwm
because pwm The signal frequency of is 1KHz, Namely 1ms.P34 The pin has a connection timer 0, We use it 1ms Timer for 0 To control pwm Duty cycle of , For example, when pwm The duty cycle of is 20% when , You can use a timer 0 Control makes L1 bright 0.2ms, destroy 0.8ms To display pwm Duty cycle of . See code for details .
5 DS18B20
Is to rewrite the underlying driver code (onewire), Then put it in the timer , Measure every once in a while .
onewire.c
#include"onewire.h"
#define u8 unsigned char
#define u16 unsigned int
bit initflag;
sbit DQ=P1^4;
void Delay1us()
{
_nop_();
_nop_();
_nop_();
}
void delay_us(unsigned int us)
{
while(us--)
{
Delay1us();
}
}
bit init_ds18b20()
{
DQ=0;
delay_us(500);
DQ=1;
delay_us(20);
initflag=DQ;
delay_us(50);
return initflag;
}
unsigned int get_temp()
{
unsigned char low,high;
unsigned int result;
float i;
init_ds18b20();//³õʼ»¯
ds18b20_wirteByte(0xcc);
ds18b20_wirteByte(0x44);
init_ds18b20();
ds18b20_wirteByte(0xcc);
ds18b20_wirteByte(0xbe);
low=ds18b20_readByte();
high=ds18b20_readByte();
result=high&0x0f;
result<<=8;
result=result|low;
i=result*0.0625;
result=i*100;
return result;
}
void ds18b20_wirteByte(unsigned char dat)
{
unsigned char i=0;
for(i;i<8;i++)
{
DQ=0;
DQ=dat&0x01;
delay_us(65);
DQ=1;
dat=dat>>1;
}
}
u8 ds18b20_readByte()
{
unsigned char i=0;
unsigned char dat;
for (i;i<8;i++)
{
DQ=0;
dat=dat>>1;
DQ=1;
if(DQ)
{
dat|=0x80;
}
delay_us(15);
}
return dat;
}
onewire.h
#ifndef _ONEWIRE_H_
#define _ONEWIRE_H_
#define u8 unsigned char
#define u16 unsigned int
#include<STC15F2K60S2.h>
#include"intrins.h"
void Delay1us();
void delay_us(u16 us);
bit init_ds18b20();
u16 get_temp();
void ds18b20_wirteByte(u8 dat);
u8 ds18b20_readByte();
#endifINIT.c
I like to initialize 、 Timer 、 The nixie tube shows 、 The keyboard is placed in a module .
#include"INIT.h"
#define u8 unsigned char
#define u16 unsigned int
#define state P3
#define state_0 0
#define state_1 1
#define state_2 2
u8 tab[]={0xc0,0xf9,0xa4,0xb0,0x99,0x92,0x82,0xf8,0x80,0x90,0xbf,0xff,0xc6};
u8 seg[]={11,11,11,11,11,11,11,11};
static u8 key_state=0;
static u8 segadder=0;
u8 row=0,key_press=0,key_num=0;
void all_init() // Turn off irrelevant peripherals
{
P2=(P2&0x1f)|0x80;
P0=0xff;
P2&=0x1f;
P2=(P2&0x1f)|0xa0;
P04=0;
P06=0;
P2&=0x1f;
P2=(P2&0x1f)|0xc0;
P0=0x00;
P2&=0x1f;
P2=(P2&0x1f)|0xe0;
P0=0xff;
P2&=0x1f;
}
void display() // Nixie tube display function
{
P2=(P2&0x1f)|0xe0; // Blanking
P0=0xff;
P2&=0x1f;
P2=(P2&0x1f)|0xc0; // Biting
P0=1<<segadder;
P2&=0x1f;
P2=(P2&0x1f)|0xe0; // Segment selection
P0=tab[seg[segadder]];
P2&=0x1f;
if(++segadder==8)
segadder=0;
}
u8 read_key() // Independent keyboard
{
switch(key_state)
{
case state_0:
state=0x0f;
key_press=state;
if(key_press!=0x0f)
key_state=state_1;
break;
case state_1:
key_press=state;
if(key_press!=0x0f)
{
if((key_press & 0x08)==0) row=4;
if((key_press & 0x04)==0) row=5;
if((key_press & 0x02)==0) row=6;
if((key_press & 0x01)==0) row=7;
key_state=state_2;
}
else
key_state=state_0;
break;
case state_2:
state=0x0f;
key_press=state;
if(key_press==0x0f)
key_state=state_0;
break;
}
key_num=row;
row=0;
return key_num;
}
void Timer0Init(void) //100us
{
AUXR |= 0x80;
TMOD &= 0xF0;
TL0 = 0xAE;
TH0 = 0xFB;
TF0 = 0;
TR0 = 1;
EA = 1;
}
void Timer1Init(void) //1ms
{
AUXR |= 0x40;
TMOD &= 0x0F;
TL1 = 0xCD;
TH1 = 0xD4;
TF1 = 0;
TR1 = 1;
ET1 = 1;
EA = 1;
}
INIT.h
#ifndef _INIT_H_
#define _INIT_H_
#define u8 unsigned char
#define u16 unsigned int
#include<STC15F2K60S2.h>
#include"intrins.h"
void all_init();
void display();
u8 read_key();
void Timer0Init(void);
void Timer1Init(void);
#endifjm.c
This module is the function controlled by each key .
#include"jm.h"
#include"onewire.h"
#define u8 unsigned char
#define u16 unsigned int
extern u8 seg[],countdown,moude,temp_flag; // extern Indicates that this variable is defined elsewhere , To quote... Here
u16 temp;
void jm4() //s4 Functions controlled
{
seg[0]=10;
seg[1]=moude;
seg[2]=10;
seg[3]=11;
}
void jm5() //s5 Functions controlled
{
seg[4]=countdown/1000;
seg[5]=countdown/100%10;
seg[6]=countdown/10%10;
seg[7]=countdown%10;
}
void jm6() //s6 Functions controlled
{
seg[4]=countdown/1000;
seg[5]=countdown/100%10;
seg[6]=countdown/10%10;
seg[7]=countdown%10;
}
void jm7() //s7 Functions controlled
{
if(temp_flag==1)
{
temp_flag=0;
temp=get_temp();
}
seg[0]=10;
seg[1]=4;
seg[2]=10;
seg[3]=11;
seg[4]=11;
seg[5]=temp/1000;
seg[6]=temp/100%10;
seg[7]=12;
}
jm.h
#ifndef _JM_H_
#define _JM_H_
#define u8 unsigned char
#define u16 unsigned int
#include<STC15F2K60S2.h>
#include"intrins.h"
void jm4();
void jm5();
void jm6();
void jm7();
#endifmain.c
#include"INIT.h"
#include"jm.h"
#include"onewire.h"
#define u8 unsigned char
#define u16 unsigned int
static u16 moude_count=0,pwm;
u8 num=0,moude=1,countdown=0,temp_m=0,countdown_moude=1;
u8 temp_flag=0;
u8 jma,jmb;
u16 countdown_count=0,temp_count=0;
extern seg[];
void main()
{
all_init();
Timer0Init();
Timer1Init();
while(1)
{
if(countdown>0) ET0 = 1; // The countdown is greater than 0 Turn on timer 0
else ET0 = 0;
num=read_key();
switch(num)
{
case 4:
if(++moude==4) moude=1; // Three working modes
if(moude==1) pwm=2;
if(moude==2) pwm=3;
if(moude==3) pwm=7;
jma=0,jmb=0;
break;
case 5:
if(++countdown_moude==4) countdown_moude=1; // Set the countdown
if(countdown_moude==1) countdown=0;
if(countdown_moude==2) countdown=60;
if(countdown_moude==3) countdown=120;
jma=0,jmb=1;
break;
case 6: // stop it , Zero clearing
countdown=0;
jma=1,jmb=0;
break;
case 7: // Working or room temperature interface
temp_m^=1;
if(temp_m==1)
{
jma=1,jmb=1;
}
else
{
jma=0,jmb=0;
}
break;
}
num=0;
if(jma==0&&jmb==0)
{
jm4();
jm5();
}
if(jma==0&&jmb==1) jm5();
if(jma==1&&jmb==0) jm6();
if(jma==1&&jmb==1) jm7();
}
}
void Timer1() interrupt 3
{
display();
countdown_count++;
temp_count++;
if(countdown_count==1000) // Every second counts down by one
{
if(countdown>0) countdown--;
countdown_count=0;
}
if(temp_count==200) // Every time 200ms Get the room temperature once
{
temp_flag=1;
temp_count=0;
}
}
void Timer0() interrupt 1
{
if(moude_count<pwm) pwm The larger the duty cycle ,led The brighter the light .
{
if(moude==1&&countdown!=0)
{
P2=(P2&0x1f)|0x80;P0=0xfe;P2&=0x1f;
}
if(moude==2&&countdown!=0)
{
P2=(P2&0x1f)|0x80;P0=0xfd;P2&=0x1f;
}
if(moude==3&&countdown!=0)
{
P2=(P2&0x1f)|0x80;P0=0xfb;P2&=0x1f;
}
}
else
{
P2=(P2&0x1f)|0x80;P0=0xff;P2&=0x1f;
}
if(++moude_count>=10) moude_count=0;
}
Last , This is my first time to write a blog , Where the writing is not good , I hope you will correct me . I will also write later , I plan to finish writing a question , Just discuss with you .
边栏推荐
- Inverted chain disk storage in Lucene (pfordelta)
- Deep learning parameter initialization (I) Xavier initialization with code
- [solved] win10 cannot find a solution to the local group policy editor
- lucene scorer
- New stills of Lord of the rings: the ring of strength: the caster of the ring of strength appears
- The embodiment of generics in inheritance and wildcards
- PdfWriter. GetInstance throws system Nullreferenceexception [en] pdfwriter GetInstance throws System. NullRef
- 【已解决】win10找不到本地组策略编辑器解决方法
- VMware network mode - bridge, host only, NAT network
- Leetcode 213: 打家劫舍 II
猜你喜欢

Leetcode 213: looting II

VMware network mode - bridge, host only, NAT network

【CoppeliaSim4.3】C#调用 remoteApi控制场景中UR5
【开发笔记】基于机智云4G转接板GC211的设备上云APP控制

项目经验分享:实现一个昇思MindSpore 图层 IR 融合优化 pass

VMWare网络模式-桥接,Host-Only,NAT网络

New stills of Lord of the rings: the ring of strength: the caster of the ring of strength appears

Common APIs
![[solved] unknown error 1146](/img/f1/b8dd3ca8359ac9eb19e1911bd3790a.png)
[solved] unknown error 1146

Understanding of class
随机推荐
PdfWriter. GetInstance throws system Nullreferenceexception [en] pdfwriter GetInstance throws System. NullRef
JS monitors empty objects and empty references
Some experiences of Arduino soft serial port communication
Common operations of JSP
[coppeliasim4.3] C calls UR5 in the remoteapi control scenario
I. D3.js hello world
docker建立mysql:5.7版本指定路径挂载不上。
Store WordPress media content on 4everland to complete decentralized storage
不出网上线CS的各种姿势
Docker builds MySQL: the specified path of version 5.7 cannot be mounted.
TypeScript let与var的区别
HISAT2 - StringTie - DESeq2 pipeline 进行bulk RNA-seq
Warehouse database fields_ Summary of SQL problems in kingbase8 migration of Jincang database
Industrial resilience
Jeecg request URL signature
Vertx's responsive MySQL template
树莓派更新工具链
Common problems in io streams
IO stream system and FileReader, filewriter
[solved] win10 cannot find a solution to the local group policy editor