当前位置:网站首页>Is the operation of assigning values to int variables atomic?
Is the operation of assigning values to int variables atomic?
2022-07-27 09:00:00 【Li Xiaoyao】
Focus on 、 Official account of star standard , Straight to the highlights
source :https://www.windsings.com/posts/2a85d31f/
Preface
This is the problem encountered during the interview , Didn't answer . After returning home, I checked , Sort it out and write it down .
The original question : What instruction set supports atomic operations ? What is the principle ? If you consider the entire instruction set , The problem is too big , Simplify here . With X86 and ARM For example .
Atomic operations are inseparable operations , At the end of execution, it will not be interrupted by any event . On a single processor system (UniProcessor, abbreviation UP) in , Any operation that can be completed in a single instruction can be considered an atomic operation , Because interrupts can only occur between instructions .
such as ,C The language code

If not optimized , It is possible to generate the following assembly :

So when there are multiple processes executing this code , There may be concurrency problems :

There will be problems .
In a single processor , The solution to this problem is , take count++ Statements are translated into single instruction operations

X86 Instruction set support inc operation , such count The operation can be completed in one finger .
The context switching of a process is always completed after an instruction is executed , Therefore, the above concurrency problems will not occur . For a single processor , A processor instruction is an atomic operation .
Again ,ARM Inside SWP and X86 Inside XCHG For single processors , It's atomic manipulation .
however , In multiprocessor systems (Symmetric Multi-Processor, abbreviation SMP) It's different in , Because there are multiple processors running independently in the system , Even operations that can be completed in a single instruction may be disturbed . Because at this time, the topic of concurrency is no longer the process , It's the processor .
X86 framework
Intel X86 Instruction set provides instruction prefix lock Used to lock the front-end serial bus FSB, It ensures that the instruction execution will not receive interference from other processors .
such as :

Use lock After the instruction prefix , During processing count Concurrent access to memory (Read/Write) Forbidden , Thus ensuring the atomicity of instructions .
As shown in the figure :
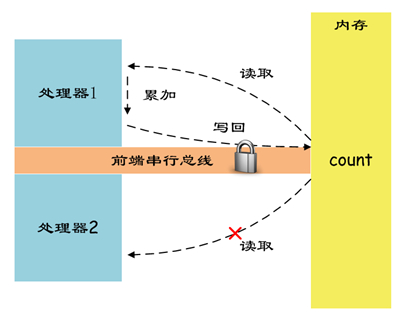
X86LOCK
The principle is Intel Development Manual It is explained as follows :
Description
Causes the processor’s LOCK# signal to be asserted during execution of the accompanying instruction (turns the instruction into an atomic instruction). In a multiprocessor environment, the LOCK# signal ensures that the processor has exclusive use of any shared memory while the signal is asserted.
The LOCK prefix can be prepended only to the following instructions and only to those forms of the instructions where the destination operand is a memory operand: ADD, ADC, AND, BTC, BTR, BTS, CMPXCHG, CMPXCH8B, CMPXCHG16B, DEC, INC, NEG, NOT, OR, SBB, SUB, XOR, XADD, and XCHG. If the LOCK prefix is used with one of these instructions and the source operand is a memory operand, an undefined opcode exception (#UD) may be generated. An undefined opcode exception will also be generated if the LOCK prefix is used with any instruction not in the above list. The XCHG instruction always asserts the LOCK# signal regardless of the presence or absence of the LOCK prefix.
The LOCK prefix is typically used with the BTS instruction to perform a read-modify-write operation on a memory location in shared memory environment.
The integrity of the LOCK prefix is not affected by the alignment of the memory field. Memory locking is observed for arbitrarily misaligned fields.
Make the processor's LOCK# Signal valid ( Change instructions into atomic instructions ). In a multiprocessor environment ,LOCK# The signal ensures that the processor has exclusive use of any shared memory when the signal is valid .
LOCK Prefix It can only be attached before the following instructions , And it only applies to those instruction formats where the target operand is a memory operand :ADD,ADC,AND,BTC,BTR,BTS,CMPXCHG,CMPXCH8B,CMPXCHG16B,DEC,INC, NEG,NOT,OR,SBB,SUB,XOR,XADD and XCHG.
If LOCK The prefix is used with one of these instructions , And the source operand is a memory operand , Undefined opcode exceptions may be generated (#UD). If LOCK The prefix is used with any instruction that is not in the above list , Undefined opcode exceptions will also occur . Whether it exists or not LOCK Prefix ,XCHG Instructions always state LOCK# The signal .
LOCK Prefixes are usually associated with BTS Instructions used together , To perform a read at a memory location in a shared memory environment – modify – Write operation .
LOCK The integrity of the prefix is not affected by memory field alignment . Memory locking is for any misaligned fields .
Implementation in the operating system
Linux Source code The definition of atomic self increment one in is as follows :

LOCK_PREFIX Is defined as follows :

so : In the case of symmetric multiprocessor architecture ,LOCK_PREFIX Is interpreted as an instruction prefix lock. For single processor architecture ,LOCK_PREFIX It doesn't contain anything .
in addition , about CAS, Yes cmpxchg Command to operate . The code is as follows :
static __always_inline int atomic_cmpxchg(atomic_t *v, int old, int new)
{
return cmpxchg(&v->counter, old, new);
}
#define cmpxchg(ptr, old, new) \
__cmpxchg(ptr, old, new, sizeof(*(ptr)))
#define __cmpxchg(ptr, old, new, size) \
__raw_cmpxchg((ptr), (old), (new), (size), LOCK_PREFIX)
#define __raw_cmpxchg(ptr, old, new, size, lock) \
({ \
__typeof__(*(ptr)) __ret; \
__typeof__(*(ptr)) __old = (old); \
__typeof__(*(ptr)) __new = (new); \
switch (size) { \
case __X86_CASE_B: \
{ \
volatile u8 *__ptr = (volatile u8 *)(ptr); \
asm volatile(lock "cmpxchgb %2,%1" \
: "=a" (__ret), "+m" (*__ptr) \
: "q" (__new), "0" (__old) \
: "memory"); \
break; \
} \
case __X86_CASE_W: \
{ \
volatile u16 *__ptr = (volatile u16 *)(ptr); \
asm volatile(lock "cmpxchgw %2,%1" \
: "=a" (__ret), "+m" (*__ptr) \
: "r" (__new), "0" (__old) \
: "memory"); \
break; \
} \
case __X86_CASE_L: \
{ \
volatile u32 *__ptr = (volatile u32 *)(ptr); \
asm volatile(lock "cmpxchgl %2,%1" \
: "=a" (__ret), "+m" (*__ptr) \
: "r" (__new), "0" (__old) \
: "memory"); \
break; \
} \
case __X86_CASE_Q: \
{ \
volatile u64 *__ptr = (volatile u64 *)(ptr); \
asm volatile(lock "cmpxchgq %2,%1" \
: "=a" (__ret), "+m" (*__ptr) \
: "r" (__new), "0" (__old) \
: "memory"); \
break; \
} \
default: \
__cmpxchg_wrong_size(); \
} \
__ret; \
})ARM framework
stay ARM Under the architecture , No, LOCK# Instructions , Its concrete realization is as follows :## ARMv6 Before In the early ARM Architecture is not supported SMP Of , These single core architectures CPU The way to realize atomic operation is by closing CPU Interrupt to complete .
stay Linux about ARM Architecture code
There are the following :

This is a set of code shared by many operations .
about cmpxchg:
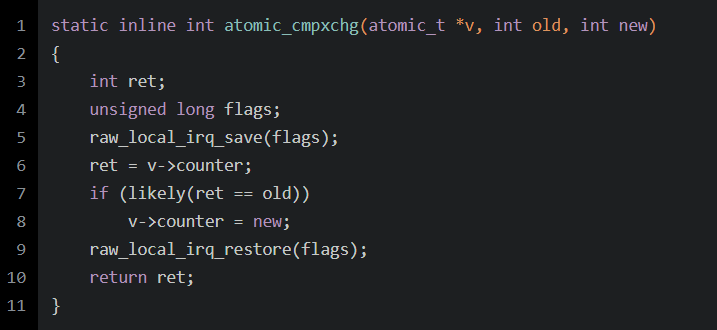
You can see , Yes v->counter The operation of is a critical area , The execution of instructions cannot be interrupted , Memory access also needs to be kept undisturbed .
ARMv6 Previous versions Protect this critical area by turning off local interrupts , It looks quite simple , The secret lies in ARMv6 Previous versions did not support SMP.
Like the classic read-modify-write problem , Its essence is to keep a pair of memory read and write Atomicity of access , That is to say, the read and write access of memory cannot be interrupted . This problem can be solved through hardware 、 Software or a combination of software and hardware .
In the early ARM CPU The solution given is to rely on hardware :SWP This assembly instruction performs a read memory operation 、 Memory write once , But from a programmer's point of view ,SWP This instruction is atomic , Reading and writing will not be interrupted by any asynchronous events . How is the specific underlying hardware done ? Now , The hardware will provide a lock signal, It's going on memory Set during operation lock The signal , Tell the bus that this is a non interruptible memory access , Until it's done SWP Two memory accesses are required before clear lock The signal .
Say more about SWP and SWPB The content of
These two instructions are used for synchronization , Not used to perform atomic operations . Introducing exclusive access ARM Before the architecture ,SWP and SWPB Instructions are often used to synchronize .
Its limitation is : If the interrupt is triggered when the exchange operation is triggered , Then the processor must complete the loading and storage of instructions before executing the interrupt , This increases the interrupt delay . Because independent loading and exclusive storage are separate instructions , Therefore, this effect will be reduced when using new synchronization primitives .
But in multi-core systems , Preventing all processors from accessing main memory during instruction exchange will reduce system performance . In a multi-core system with processors operating at different frequencies but sharing the same main memory , This is especially the case .
So in ARMv6 And later , Abandoned SWP, ARMv6 Architecture introduces the concept of exclusive access to memory , Provides more flexible atomic memory updates .
ARMv6 The architecture is based on Load-Exclusive and Store-Exclusive Synchronization primitives LDREX and STREX In the form of Introduced Load Link and Store Conditional Instructions . from ARMv6T2 Start , These instructions are in ARM and Thumb Available in the instruction set . Independent loading and proprietary storage provide flexible and scalable synchronization , Replaced the abandoned SWP and SWPB Instructions .
Later, we used LDREX and STREX Instructions , stay armv7 Then I used ldrex and strex:

Access instructions LDREX/STREX And ordinary LDR/STR The access instructions are different , It is “ Monopoly ” Access instructions . This pair of instruction memory access processes is called “exclusive monitor” To monitor whether exclusive access is possible .
Exclusive memory access instruction :
(1)LDREX R1 ,[R0] Instructions are exclusive from R0 Take a word from the address referred to and store it in R0 in ;
(2)STREX R2,R1,[R0] Instructions are used exclusively R1 To update memory , If exclusive access conditions allow , Then the update succeeds and returns 0 To R2, Otherwise, failure returns 1 To R2.
Last , Do you know the answer ?
Copyright notice : Source network of this paper , Free delivery of knowledge , The copyright belongs to the original author . If involves the work copyright question , Please contact me to delete .
‧‧‧‧‧‧‧‧‧‧‧‧‧‧‧‧ END ‧‧‧‧‧‧‧‧‧‧‧‧‧‧‧
Pay attention to my WeChat official account , reply “ Add group ” Join the technical exchange group according to the rules . Click on “ Read the original ” See more sharing , Welcome to share 、 Collection 、 give the thumbs-up 、 Looking at .边栏推荐
- 杭州电子商务研究院发布“数字化存在”新名词解释
- Matlab求解微分代数方程 (DAE)
- The wechat installation package has soared from 0.5m to 260m. Why are our programs getting bigger and bigger?
- vscod
- Digital intelligence innovation
- 接口测试工具-Jmeter压力测试使用
- The execution sequence of async/await, macro tasks and micro tasks
- flex布局 (实战小米官网)
- Huawei machine test question: Martian computing JS
- 低成本、低门槛、易部署,4800+万户中小企业数字化转型新选择
猜你喜欢

08_ Service fusing hystrix

Unity3d 2021 software installation package download and installation tutorial

Flink1.15 source code reading Flink clients client execution process (reading is boring)
How to permanently set source

4276. 擅长C

CUDA programming-01: build CUDA Programming Environment

被三星和台积电挤压的Intel终放下身段,为中国芯片定制芯片工艺

The following license SolidWorks Standard cannot be obtained, and the use license file cannot be found. (-1,359,2)。

redis 网络IO

一些实用、常用、效率越来越高的 Kubernetes 别名
随机推荐
[interprocess communication IPC] - semaphore learning
【微服务~Sentinel】Sentinel之dashboard控制面板
New year's goals! The code is more standardized!
Storage and computing engine
693. 行程排序
Matlab画图技巧与实例:堆叠图stackedplot
苹果降价600元,对本就溃败的国产旗舰手机几乎是毁灭性打击
3311. Longest arithmetic
【进程间通信IPC】- 信号量的学习
PyQt5快速开发与实战 4.1 QMainWindow
redis的string类型及bitmap
3311. 最长算术
Pytorch custom CUDA operator tutorial and runtime analysis
Mmrotate trains its dataset from scratch
Primary function t1744963 character writing
A survey of robust lidar based 3D object detection methods for autonomous driving paper notes
Some practical, commonly used and increasingly efficient kubernetes aliases
How to optimize the deep learning model to improve the reasoning speed
Horse walking oblique sun (backtracking method)
【每日算法Day 94】经典面试题:机器人的运动范围
