当前位置:网站首页>Learning notes 5 - high precision map solution
Learning notes 5 - high precision map solution
2022-07-05 10:21:00 【FUXI_ Willard】
This blog series includes 6 A column , Respectively :《 Overview of autopilot Technology 》、《 Technical foundation of autopilot vehicle platform 》、《 Autopilot positioning technology 》、《 Self driving vehicle environment perception 》、《 Decision and control of autonomous driving vehicle 》、《 Design and application of automatic driving system 》.
This column is about 《 Autopilot positioning technology 》 Book notes .
3. High precision map solution
3.1 High precision map acquisition
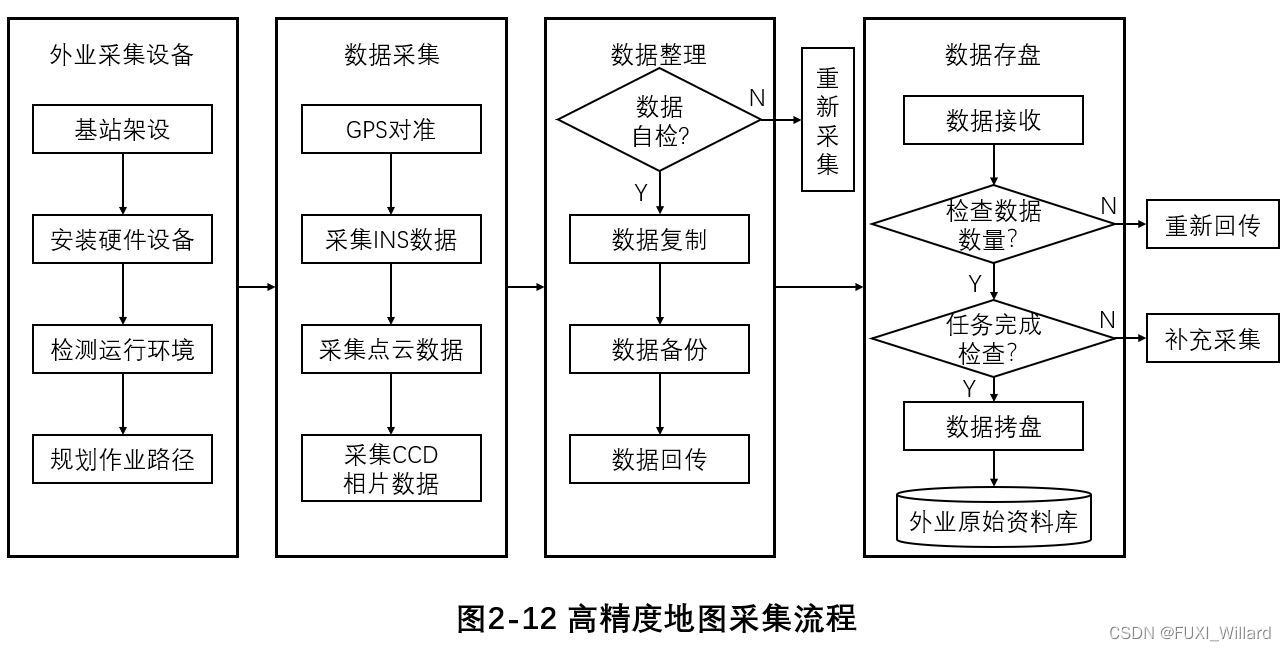
- Acquisition vehicle is the core carrier of data acquisition , It is equipped with global navigation satellite system 、 Inertial navigation system (Inertial Navigation System,INS)、 Laser radar 、 Camera and other systems and sensor equipment ;
- The data collected in the field includes the driving track 、 Images 、 Laser point clouds and other data , Have lane line 、 Along the road 、 guardrail 、 street lamp 、 Traffic signs and other information ;
- In the process of collection , The collector needs to monitor the collection in real time , Constantly confirm whether the acquisition equipment works normally , And we need to choose different camera parameters according to the weather and environmental conditions ;
- The collected data is self checked 、 Copy 、 After backup , Send back , Wait until the data is checked in the warehouse , Save to the original field database ; If data problems are found during data self inspection and warehousing inspection , Supplementary collection is required ;
3.1.1 High precision map acquisition equipment
Mainstream high-precision map acquisition equipment : Laser radar 、 camera 、IMU、GNSS Combination with wheel range finder ; Lidar and camera are used to acquire data about the surrounding environment of the vehicle ,IMU、GNSS And wheel range finder is used to obtain the absolute position of the acquisition vehicle ;
Laser radar (LiDAR)
- Lidar first emits a laser beam to the target object , Determine the actual distance of the target object according to the time interval from transmission to reception ; More laser pulses are emitted in a short time on a single transmitter and receiver , After pulse emission , Touch the object to be detected and reflect it back to the receiver , The specific coordinates of a point can be obtained for each transmission and reception , When the transmission and reception are carried out enough , Form an environmental laser point cloud , So as to quantify the environment around the car ;
- LiDAR The system is generally divided into three parts : One is laser transmitter , The wavelength of emission is 600~1000nm Get laser rays ; Second, scanning and optical components , It is mainly used to collect laser emission points , Obtain the time difference and horizontal angle information from the transmission to reception of the reflection point ; Third, photosensitive components , It mainly detects the intensity of the returned light , Therefore, each detected point includes spatial coordinate information and light intensity information ;
camera (Camera)
The camera captures the surrounding environment information of the car in the form of images , These images are processed to extract key road information , And then complete the preliminary drawing of the map ;
IMU( Inertial measurement unit )
In general use 6 Axis motion processing components , contain 3 Axis accelerometers and 3 Axis gyroscope ; Accelerometers are force sensors , The acceleration on each axis can be calculated according to the force in each direction ; Gyroscope is an angular velocity detector , The angular change on each axis can be obtained according to the angular acceleration on each axis ;
GNSS
GNSS The receiver determines the position of each satellite at each time by the stored ephemeris , Combined with the signal transmission time between the receiver and the satellite, the time distance between them is calculated , The position of the receiver can be calculated according to the three ball positioning principle ;
3.1.2 Data model
The data models of high-precision map elements are divided into four categories : Road model (Road Model)、 Lane model (Lane Model)、 Road marking model (Road Mark)、 Basic object model (Object);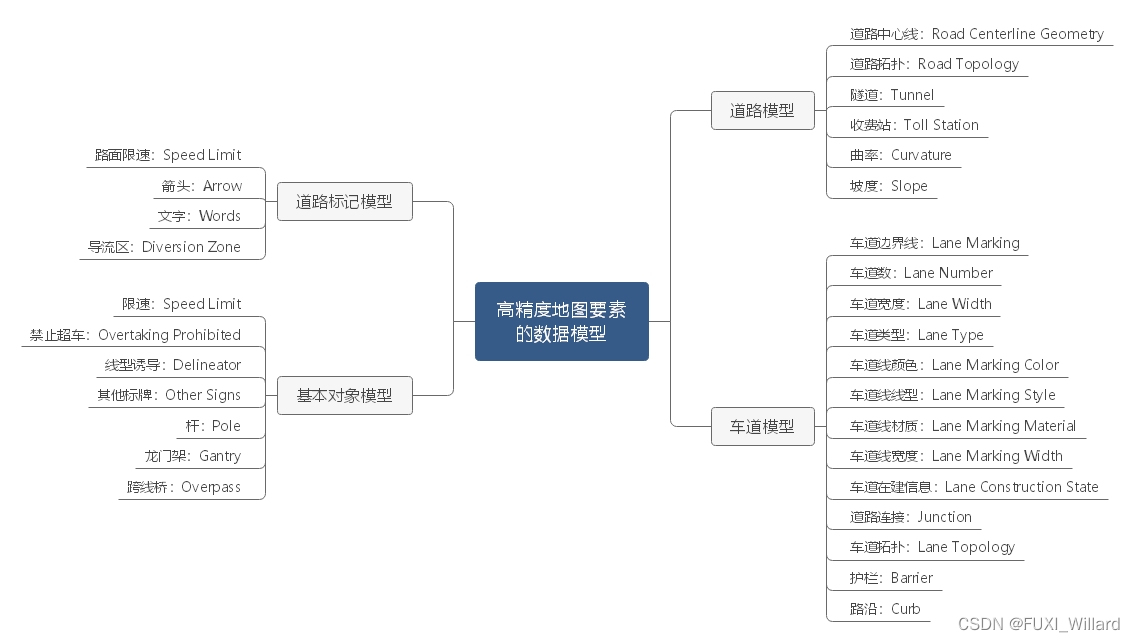
Road model
- Road geometry : Refers to data production , The geometric shape of the road connected by shape points ; When describing the geometry of the road through shape points , Shape points are described in coordinate form , Such as road centerline and road topology ;
- Curvature : Indicates the curvature of the road , The greater the degree of bending, the greater the curvature value , The smaller the bending degree, the smaller the curvature value ; When calculating , Adopt curve fitting method , Get the reciprocal of the radius of curvature of each shape point , According to the geometry of the road , Calculate the curvature value of discrete points after curve fitting ;
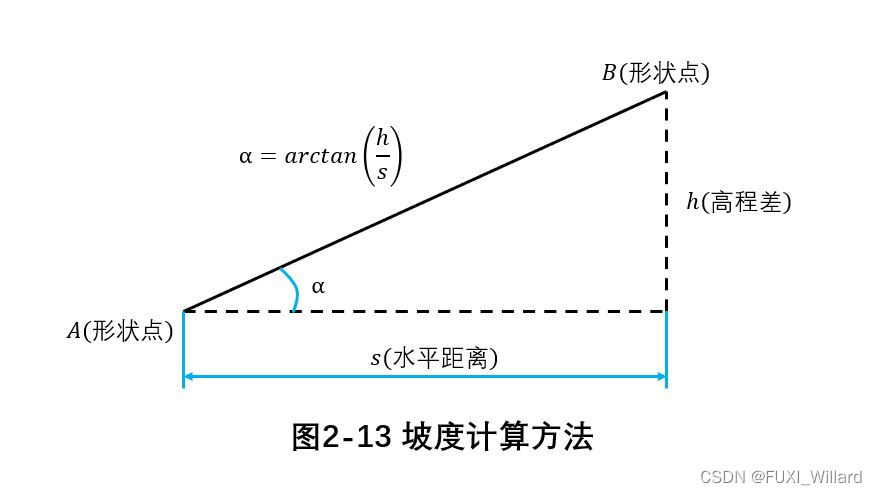
- slope : Refers to the longitudinal fluctuation of the road , The greater the road undulation, the greater the slope , The smaller the road undulation, the smaller the slope ; When calculating , Take the inverse tangent between the elevation difference of the shape point and the horizontal distance to calculate the slope ;
Lane model
- Lane type : Refers to the type of the lane on the ground road , It mainly includes : Ordinary driveway 、 Entrance driveway 、 Exit lane 、 Enter the ramp 、 Exit ramp 、 Emergency Vehicle Lane 、 Connecting ramps, etc ; The lane type will be assigned to this lane ;
- Ordinary driveway : Refers to lanes without special attributes , Generally, the main carriageway ; Ordinary Lane generally refers to the main road in Expressway , Make the expression according to the actual Lane shape , And assign the main road attribute on the right lane ;
Road marking model
- Road marking model : It mainly refers to the form of lane line , Include : No attributes 、 Single solid line 、 Long dotted line 、 Double solid line 、 Left solid right dotted line 、 Right solid left dotted line 、 Double dotted line 、 Along the road 、 Guardrail line ; The road markings will be assigned on the corresponding lane line ;
Basic object model
- The types of objects in high-precision maps include : rod 、 card 、 Longmen frame 、 Ground markings, etc ; Rod types include : Lamp post 、 Base station pole 、 Camera lever 、 Poles attached to traffic signs, etc ; The ground markings are divided into : Ground arrow 、 Ground text 、 Diversion area 、 Ground speed limit, etc ;
3.2 High precision map making and compilation
After the acquisition vehicle collects the data that meets the requirements and sends it back to save , Advanced data processing , The data of each sensor is fused to recognize and label various objects , Check and correct the errors manually , Then it is compiled into a high-precision map that meets the format specification for automatic driving applications .
3.2.1 High precision map data processing
- Data processing : It refers to sorting out the collected data 、 Sort and clean to get the initial map template , It does not include any semantic information or comments , Then it is registered by laser point cloud 、 Laser point cloud recognition and image recognition AI technology , Fuse the data collected by different sensors , Namely the GNSS、 Laser point cloud 、 Images and other data are superimposed , Conduct road marking 、 Along the road 、 Road signs 、 Identification and classification of road elements such as traffic signs ;
- Generally, the data processed in the mapping process is mainly laser point cloud , A small part is mainly visual ; Using real-time dynamic difference technology in urban roads (Real Time Kinematic,RTK) Plan to get location information , However, the influence of high-rise buildings or tree lined roads on the stability of the signal cannot be avoided , After collecting the laser point cloud, you need to use SLAM Or other options , Optimize the posture , Then the laser point cloud can be spliced accurately , Form a complete laser point cloud ; After splicing into a highly accurate laser point cloud map , Identify it 、 Mark to draw high-precision map ;
- Laser point cloud recognition includes : Element recognition based on deep learning and laser point cloud classification based on deep learning ;
3.2.2 High precision map compilation and format specification
- The last step of high-precision map generation is data compilation , Compile the high-precision map edited in the above steps into a high-precision map that can be used for automatic driving and meets the format specification ;
- Mainstream general format specifications : Navigation data standard (Navigation Data Standard,NDS) and OpenDRIVE;
- Other standards :JDRMA standard 、KIWI Format standard 、GDF standard 、Etak standard 、NavTech standard ;
3.3 Quality control and release of high-precision maps
3.3.1 Quality control process of high-precision map
The quality requirements of high-precision map run through the whole map production process , Including the inspection methods of each generation process 、 Inspection content 、 Achievement quality evaluation standard ; Specific to all links of map production , Include : High precision map data collection 、 Field data collection 、 Indoor data production 、 Map compilation 、 High precision map product testing and product release ;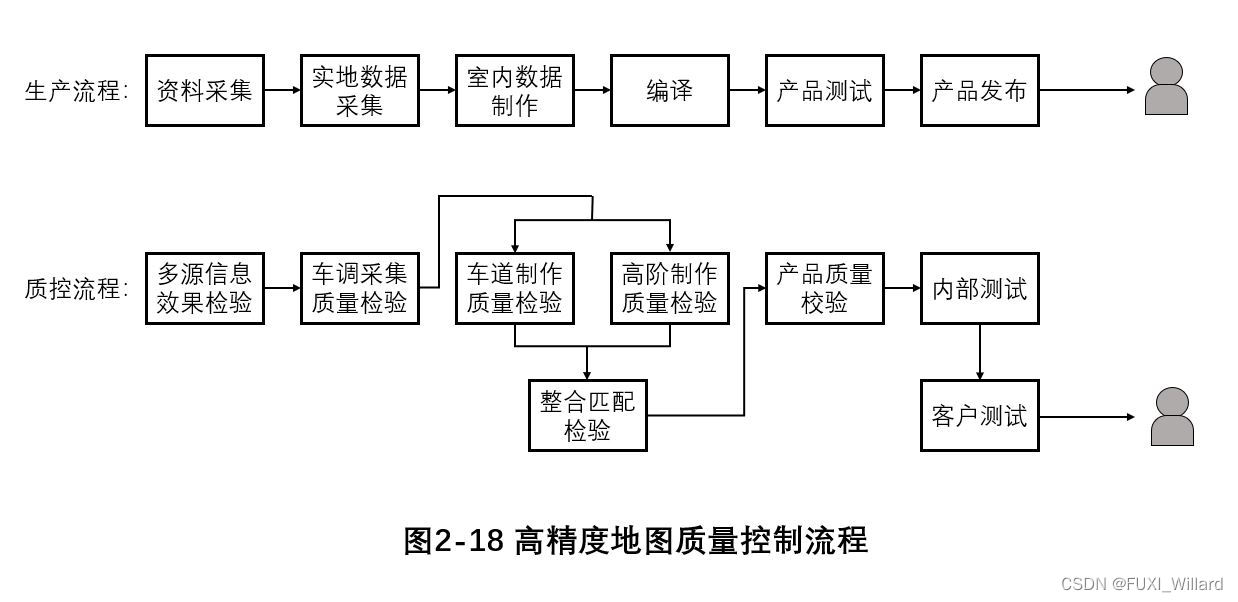
- Field collection quality control
- First level quality inspection : The team leader inspects , Mainly for effectiveness test ;
- Secondary quality inspection : Quality control inspection , Mainly carry out effectiveness test and field test ;
- Three level quality inspection : Acceptance of quality department , Mainly for effectiveness test 、 Indoor inspection and field inspection ;
- Validity test : Check the completeness of the collection guidelines 、 Validity and correctness ; Test method : artificial , Collect guidance and maintenance data according to the city , Check the results collected in the field ; At the same time, sub cities 、 Subregion 、 Result statistics of sub elements ;
- Indoor inspection : Check the integrity of the collected results 、 Logical consistency and availability ; Automated processing is carried out by inspectors in cities or regions , Quickly identify and detect effective problem points , Quickly identify and test through human-computer interaction ;
- Field inspection : Check the completeness relative to the field 、 correctness ; Test method : Before inspection , According to the important areas of the city 、 Select quality inspection areas for important road sections , Then carry out the actual collection and inspection according to the route design , Record problems ;
- Quality control of indoor production
- The first stage : Program processing inspection . Test method : First , Before inspection , The inspectors evenly extract various scenes , then , According to the requirements of specifications and Standards , Check the availability of automated data processing , Output call rate ;
- The second stage : Basic elements and high-order elements test . Test method : Conduct self inspection in the operation stage 、 The quality inspector conducts spot check 、 Quality assurance acceptance ;
- The third stage : Data connection inspection and delivery inspection ;
- Product quality control
- Data logic and threshold inspection use product theory inspection tools to check data connectivity according to high-precision data exchange specifications 、 Threshold, etc., and output the results ;
- Data consistency inspection uses product visual inspection tools , Manually check the consistency between high-precision product data and reality , And record data problems ;
3.3.2 Data quality standard of high-precision map
The data quality control objectives of high-precision maps are divided into : Data integrity 、 Logical consistency 、 Position accuracy 、 Topic accuracy 、 Time accuracy ;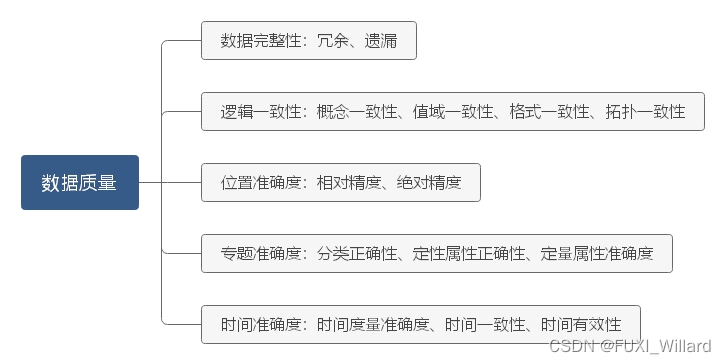
High precision map attribute quality standard table :
| elements | False positive rate standard | Under reporting rate standard |
|---|---|---|
| Lane line geometry | 0.50% | 0.50% |
| Lane type | 0.30% | 0.30% |
| Lane traffic status | 0.10% | 0.10% |
| Lane charges | 0.10% | 0.10% |
| Lane line type | 0.20% | 0.20% |
| Lane line color | 0.20% | 0.20% |
| Lane line thickness | 0.10% | 0.10% |
| Along the road | 0.50% | 0.50% |
| guardrail | 0.50% | 0.50% |
| The speed limit | 1% | 1% |
| intersection | 0.50% | 0.50% |
3.3.3 Map engine and publishing
- " Map engine " Provide application programming interface for reading and writing high-precision map data (Application Programming Interface,API);
- From the application layer ," Map engine " It provides a set of driving and managing map data , Implement rendering 、 Query and other functions of a set of function library , All application layer software only needs to call " Map engine " Provided API You can read 、 Add 、 Delete and modify high-precision map , So as to maintain the freshness of the car end map ;
- " Map engine " Based on the mutual transmission mechanism of vehicle end data , Collect vehicle end status and road data , Update through map 、 Data return forms a data closed loop from cloud to vehicle , Continue to optimize high-precision maps .
边栏推荐
- SAP UI5 ObjectPageLayout 控件使用方法分享
- Cerebral cortex: directed brain connection recognition widespread functional network abnormalities in Parkinson's disease
- php解决redis的缓存雪崩,缓存穿透,缓存击穿的问题
- Universal double button or single button pop-up
- AtCoder Beginner Contest 258「ABCDEFG」
- 【JS】数组降维
- @JsonAdapter注解使用
- 一个程序员的职业生涯到底该怎么规划?
- 官网给的这个依赖是不是应该为flink-sql-connector-mysql-cdc啊,加了依赖调
- How does redis implement multiple zones?
猜你喜欢
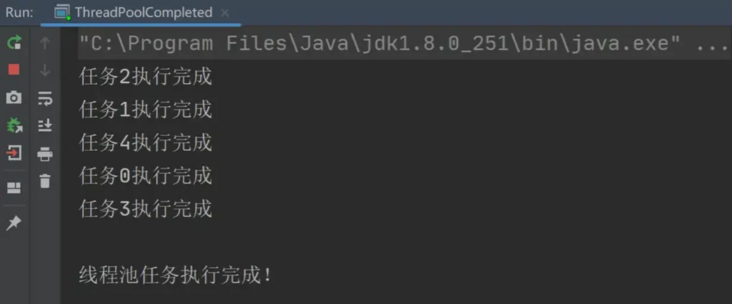
How to judge that the thread pool has completed all tasks?
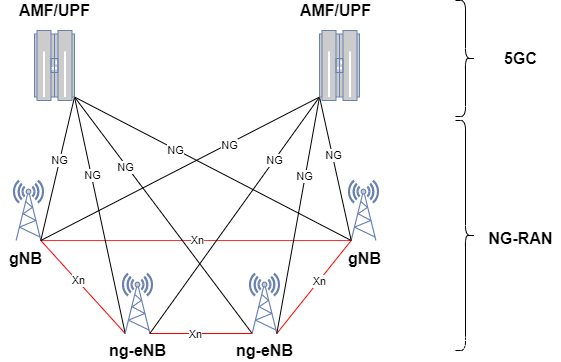
5G NR系统架构

苹果 5G 芯片研发失败?想要摆脱高通为时过早
@SerializedName注解使用
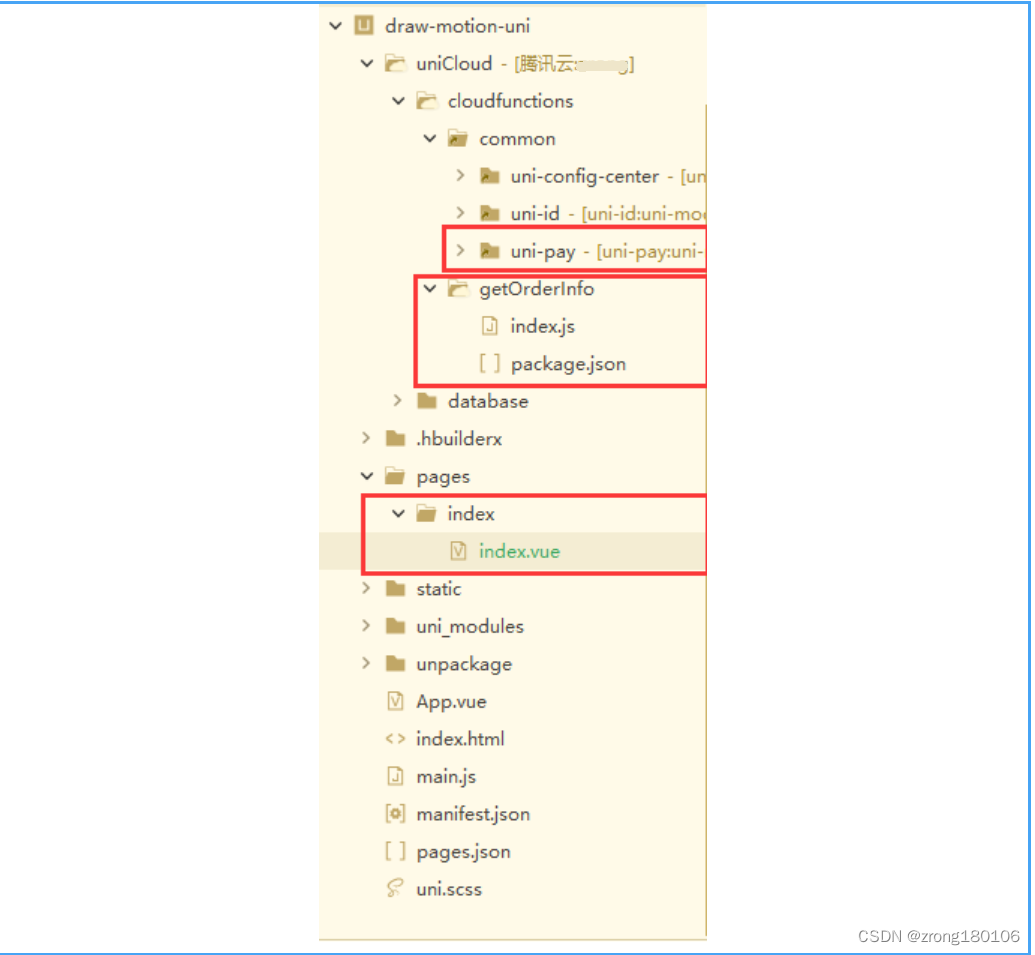
uniapp + uniCloud+unipay 实现微信小程序支付功能
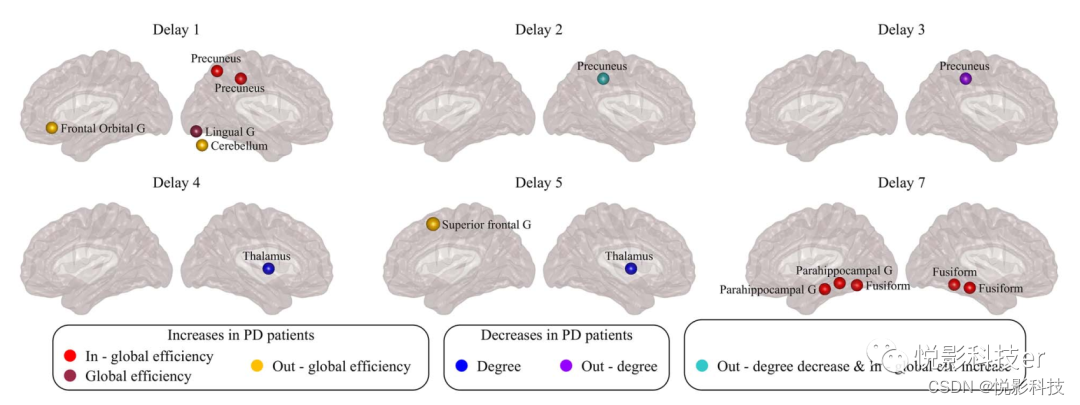
Cerebral cortex: directed brain connection recognition widespread functional network abnormalities in Parkinson's disease

Timed disappearance pop-up
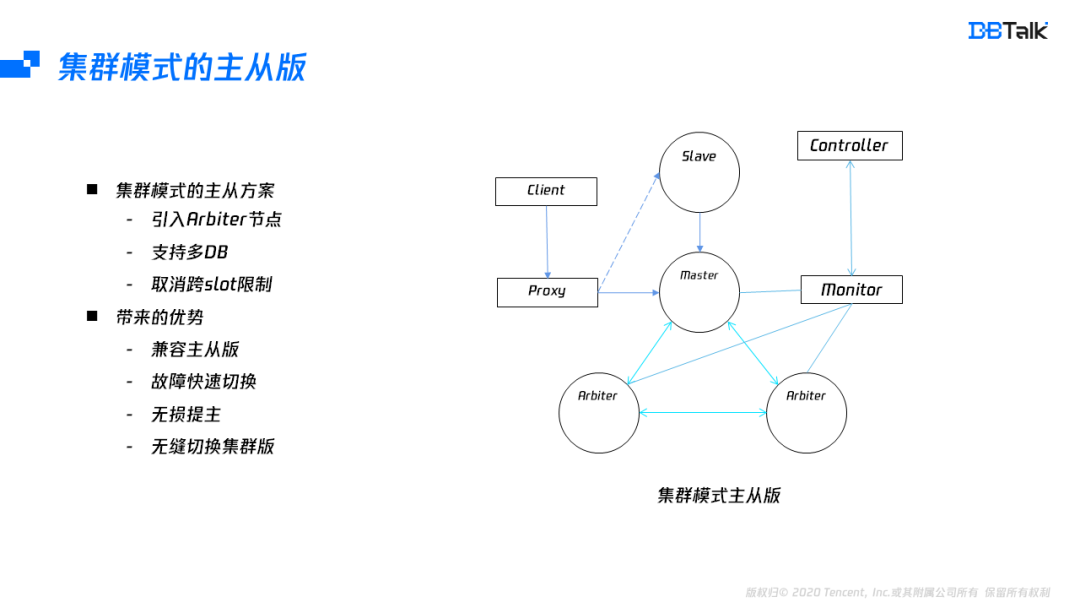
Redis如何实现多可用区?
![[system design] index monitoring and alarm system](/img/83/81534fa31b525c4c7b3175d8312808.png)
[system design] index monitoring and alarm system
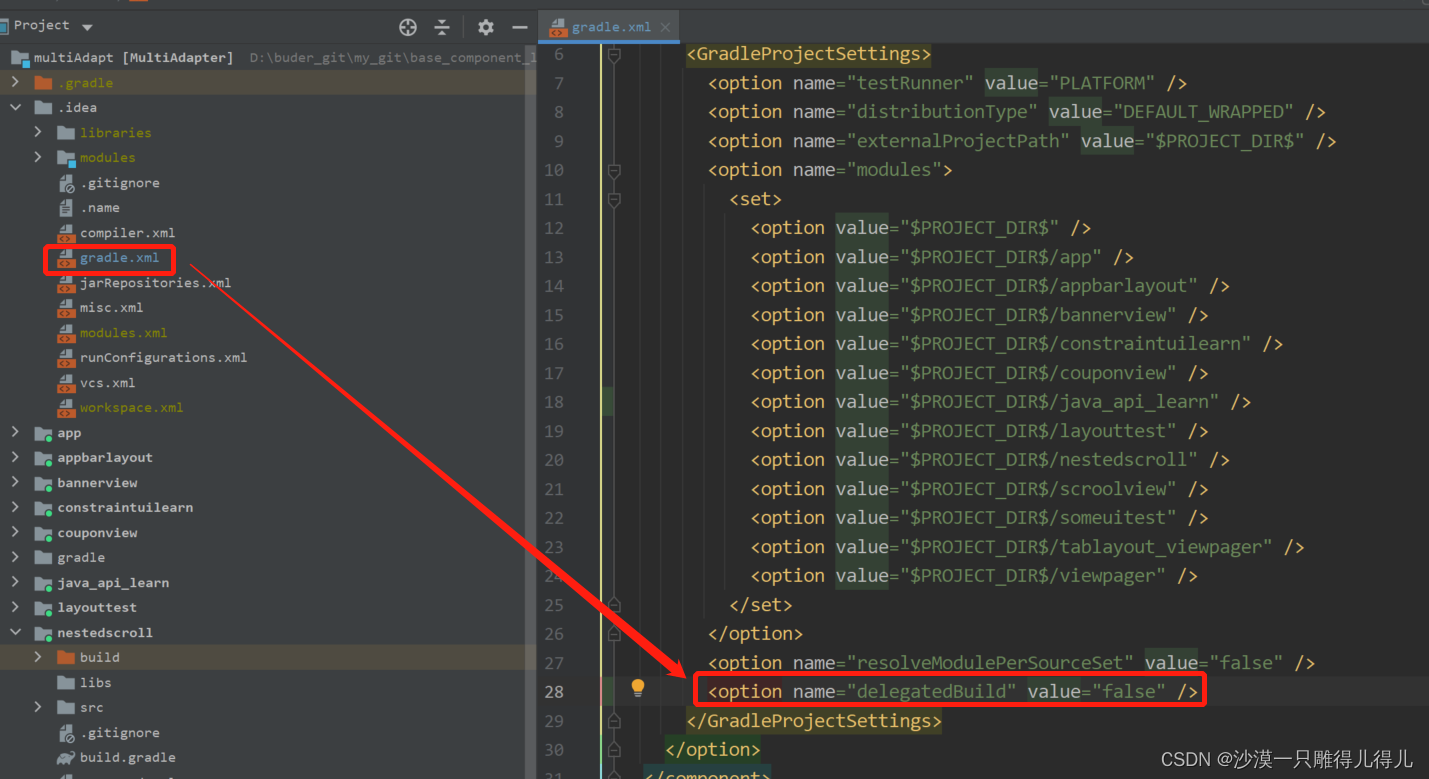
> Could not create task ‘:app:MyTest. main()‘. > SourceSet with name ‘main‘ not found. Problem repair
随机推荐
《通信软件开发与应用》课程结业报告
“军备竞赛”时期的对比学习
Swift set pickerview to white on black background
StaticLayout的使用详解
Excerpt from "sword comes" (VII)
自动化规范检查软件如何发展而来?
TypeError: Cannot read properties of undefined (reading ‘cancelToken‘)
Dedecms website building tutorial
[system design] index monitoring and alarm system
横向滚动的RecycleView一屏显示五个半,低于五个平均分布
WorkManager學習一
Uni app running to wechat development tool cannot Preview
How did automated specification inspection software develop?
一种用于干式脑电图的高密度256通道电极帽
WorkManager学习一
Timed disappearance pop-up
Z-blog template installation and use tutorial
微信小程序中,从一个页面跳转到另一个页面后,在返回后发现页面同步滚动了
WorkManager的学习二
Coffeescript Chinese character to pinyin code