当前位置:网站首页>[source code interpretation] | source code interpretation of livelistenerbus
[source code interpretation] | source code interpretation of livelistenerbus
2022-07-07 17:07:00 【857 technology community】
Reading guide
/**
* Asynchronously passes SparkListenerEvents to registered SparkListeners.
* Asynchronous will SparkListenerEvents Pass to registered SparkListeners.
*
* Until `start()` is called, all posted events are only buffered. Only after this listener bus
* has started will events be actually propagated to all attached listeners. This listener bus
* is stopped when `stop()` is called, and it will drop further events after stopping.
* Calling “ start()” Before , All published events are only buffered .
* Only after this listener bus starts , The event will actually propagate to all connected listeners .
* When calling `stop()` when , This listener bus stops , And it will discard other events after it stops .
*/
Why use event listening ? Imagine if Spark The event notification adopts Scala Function call mode , With the increase of cluster size , Will call more and more functions , Will eventually be JVM The limit of the number of threads affects the update of monitoring data , Even the monitoring data cannot be provided to users . Function calls are mostly synchronous calls , This will also cause thread blocking , And be occupied for a long time . What are the benefits of using the event listening mechanism ? The function call will be replaced by event sending or event delivery , The processing of events is asynchronous , The current thread can continue to execute subsequent logic , Threads in the thread pool can also be reused , The concurrency of the whole system will be greatly increased . The sent event will enter the cache , From the scheduled scheduling , The listener assigned to listen to this event updates the monitoring data .
queue
Asynchronous event queue
Asynchronous event queuing is mainly composed of LinkedBlockingQueue[SparkListenerEvent] structure , The default size is 10000
The event listening thread will continue from LinkedBlockingQueue Get events in . Any event will happen in LinkedBlockingQueue Store for a period of time , When the thread finishes processing this event , Will clear it .
// LiveListenerBus.scala
private val queues = new CopyOnWriteArrayList[AsyncEventQueue]()
// AsyncEventQueue.scala
// Cap the capacity of the queue so we get an explicit error (rather than an OOM exception) if
// it's perpetually being added to more quickly than it's being drained.
private val eventQueue = new LinkedBlockingQueue[SparkListenerEvent](
conf.get(LISTENER_BUS_EVENT_QUEUE_CAPACITY)) // The default value is 10000
Listener queue
/** Add a listener to queue shared by all non-internal listeners. */
/**
* Mainly by SparkContext call , That is, users can add Listener,
* Or add Listener And reflect the call [ Realize in SparkContext Medium setupAndStartListenerBus()]
* */
def addToSharedQueue(listener: SparkListenerInterface): Unit = {
addToQueue(listener, SHARED_QUEUE)
}
/** Add a listener to the executor management queue. */
/**
* Can increase HeartbeatReceiver( For monitoring Executor Of Add and Remove, And use threads to regularly judge each Executor The heartbeat time of , Timeout Kill
* Executor), In addition, through ExecutorAllocationManager increase ExecutorAllocationListener
* ( By calculating the total task Sum of numbers Excutor Parallelism matching , Dynamic increase 、 Reduce Executor, Need configuration , Off by default )
* */
def addToManagementQueue(listener: SparkListenerInterface): Unit = {
addToQueue(listener, EXECUTOR_MANAGEMENT_QUEUE)
}
/** Add a listener to the application status queue. */
/**
* Mainly increased AppStatusListener, by AppStatusStore Provide Job、Stage、Task Of UI Display data ,
* And added SQLAppStatusListener, by SQLAppStatesStore Provide SQLUI Display data
* */
def addToStatusQueue(listener: SparkListenerInterface): Unit = {
addToQueue(listener, APP_STATUS_QUEUE)
}
/** Add a listener to the event log queue. */
/** Set the monitored events as Json Write out to log storage , Need configuration , The default is off */
def addToEventLogQueue(listener: SparkListenerInterface): Unit = {
addToQueue(listener, EVENT_LOG_QUEUE)
}
/**
* Add a listener to a specific queue, creating a new queue if needed. Queues are independent
* of each other (each one uses a separate thread for delivering events), allowing slower
* listeners to be somewhat isolated from others.
* This method is called internally in the previous methods
* in addition :spark structured streaming Flow calculation corresponds to StreamingQueryListenerBus adopt addToQueue() Methods add "streams" queue
* ( Used to listen for streams start、process、terminate Time , among process Event can get the detailed progress of stream processing , Include stream name 、id、 Watermark time 、
* source offsets、sink offsets etc. )
*/
private[spark] def addToQueue(
listener: SparkListenerInterface,
queue: String): Unit = synchronized {
if (stopped.get()) {
throw new IllegalStateException("LiveListenerBus is stopped.")
}
queues.asScala.find(_.name == queue) match {
case Some(queue) =>
queue.addListener(listener)
case None =>
val newQueue = new AsyncEventQueue(queue, conf, metrics, this)
newQueue.addListener(listener)
if (started.get()) {
newQueue.start(sparkContext)
}
queues.add(newQueue)
}
}
Event delivery
SparkListenerEvent Event type
SparkListenerEvent It's a trait , Here are some subclasses , It can be used for the display of events 、 Record .
@DeveloperApi
@JsonTypeInfo(use = JsonTypeInfo.Id.CLASS, include = JsonTypeInfo.As.PROPERTY, property = "Event")
trait SparkListenerEvent {
/* Whether output this event to the event log */
protected[spark] def logEvent: Boolean = true
}
@DeveloperApi
case class SparkListenerStageSubmitted(stageInfo: StageInfo, properties: Properties = null)
extends SparkListenerEvent
@DeveloperApi
case class SparkListenerStageCompleted(stageInfo: StageInfo) extends SparkListenerEvent
@DeveloperApi
case class SparkListenerTaskStart(stageId: Int, stageAttemptId: Int, taskInfo: TaskInfo)
extends SparkListenerEvent
@DeveloperApi
case class SparkListenerTaskGettingResult(taskInfo: TaskInfo) extends SparkListenerEvent
@DeveloperApi
case class SparkListenerSpeculativeTaskSubmitted(stageId: Int) extends SparkListenerEvent
External public event delivery interface POST
External event delivery interface ,SparkContext、DAGScheduler 、CoarseGrainedSchedulerBackend And so on post, Submit events to the bus .
Delivery process :
- Bus start , call postToQueues() Method to put the event into the corresponding named queue .
- Bus not started , Save the event to ListBuffer[SparkListenerEvent] In line , Wait for the event to be delivered when the bus starts , Empty cache
The event delivery process code is as follows
// stay SparkContext Events will be called in start Method to start the bus
def start(sc: SparkContext, metricsSystem: MetricsSystem): Unit = synchronized {
// Mark the bus as started
if (!started.compareAndSet(false, true)) {
throw new IllegalStateException("LiveListenerBus already started.")
}
this.sparkContext = sc
// After the bus starts , take queuedEvents The cache queue is emptied after delivery
queues.asScala.foreach { q =>
q.start(sc)
queuedEvents.foreach(q.post)
}
queuedEvents = null
metricsSystem.registerSource(metrics)
}
// stay post In the method , Can judge whether the bus is started and delivered
def post(event: SparkListenerEvent): Unit = {
if (stopped.get()) {
return
}
metrics.numEventsPosted.inc()
// If the event buffer is null, it means the bus has been started and we can avoid
// synchronization and post events directly to the queues. This should be the most
// common case during the life of the bus.
// The bus has started , Cache queue queuedEvents Has been set to null, Direct delivery
if (queuedEvents == null) {
postToQueues(event)
return
}
// Otherwise, need to synchronize to check whether the bus is started, to make sure the thread
// calling start() picks up the new event.
synchronized {
if (!started.get()) {
// Bus not started , Then put the event into the cache queue first
queuedEvents += event
return
}
}
// If the bus was already started when the check above was made, just post directly to the queues.
// Delivery events
postToQueues(event)
}
DAGScheduler Delivery event analysis
Update monitoring indicators
def executorHeartbeatReceived(
execId: String,
// (taskId, stageId, stageAttemptId, accumUpdates)
accumUpdates: Array[(Long, Int, Int, Seq[AccumulableInfo])],
blockManagerId: BlockManagerId): Boolean = {
listenerBus.post(SparkListenerExecutorMetricsUpdate(execId, accumUpdates))
blockManagerMaster.driverEndpoint.askSync[Boolean](
BlockManagerHeartbeat(blockManagerId), new RpcTimeout(600 seconds, "BlockManagerHeartbeat"))
}
Task Execute startup and acquisition Result
private[scheduler] def handleBeginEvent(task: Task[_], taskInfo: TaskInfo) {
// Note that there is a chance that this task is launched after the stage is cancelled.
// In that case, we wouldn't have the stage anymore in stageIdToStage.
val stageAttemptId =
stageIdToStage.get(task.stageId).map(_.latestInfo.attemptNumber).getOrElse(-1)
listenerBus.post(SparkListenerTaskStart(task.stageId, stageAttemptId, taskInfo))
}
private[scheduler] def handleSpeculativeTaskSubmitted(task: Task[_]): Unit = {
listenerBus.post(SparkListenerSpeculativeTaskSubmitted(task.stageId))
}
private[scheduler] def handleGetTaskResult(taskInfo: TaskInfo) {
listenerBus.post(SparkListenerTaskGettingResult(taskInfo))
}
.........................................
Stage Start stop of
/** Called when stage's parents are available and we can now do its task.
* stay stages When the parent class is free , You can do it task
* */
private def submitMissingTasks(stage: Stage, jobId: Int) {
logDebug("submitMissingTasks(" + stage + ")")
// First figure out the indexes of partition ids to compute.
//1. At present Stage The index corresponding to the partition that has not been calculated
val partitionsToCompute: Seq[Int] = stage.findMissingPartitions()
// Use the scheduling pool, job group, description, etc. from an ActiveJob associated
// with this Stage
//2. relation ActiveJob Scheduling pool in , Functional group , Description, etc.
val properties = jobIdToActiveJob(jobId).properties
//3. Will the current stage Join in runningStages aggregate
runningStages += stage
// SparkListenerStageSubmitted should be posted before testing whether tasks are
// serializable. If tasks are not serializable, a SparkListenerStageCompleted event
// will be posted, which should always come after a corresponding SparkListenerStageSubmitted
// event.
//4. according to Stage Category , Calculate partition location
stage match {
case s: ShuffleMapStage =>
outputCommitCoordinator.stageStart(stage = s.id, maxPartitionId = s.numPartitions - 1)
case s: ResultStage =>
outputCommitCoordinator.stageStart(
stage = s.id, maxPartitionId = s.rdd.partitions.length - 1)
}
val taskIdToLocations: Map[Int, Seq[TaskLocation]] = try {
stage match {
case s: ShuffleMapStage =>
partitionsToCompute.map { id => (id, getPreferredLocs(stage.rdd, id))}.toMap
case s: ResultStage =>
partitionsToCompute.map { id =>
val p = s.partitions(id)
(id, getPreferredLocs(stage.rdd, p))
}.toMap
}
} catch {
case NonFatal(e) =>
stage.makeNewStageAttempt(partitionsToCompute.size)
listenerBus.post(SparkListenerStageSubmitted(stage.latestInfo, properties))
abortStage(stage, s"Task creation failed: $e\n${Utils.exceptionString(e)}", Some(e))
runningStages -= stage
return
}
Job Start stop
private[scheduler] def handleJobSubmitted(jobId: Int,
finalRDD: RDD[_], //
func: (TaskContext, Iterator[_]) => _,
partitions: Array[Int],
callSite: CallSite,
listener: JobListener,
properties: Properties) {
var finalStage: ResultStage = null
try {
// New stage creation may throw an exception if, for example, jobs are run on a
// HadoopRDD whose underlying HDFS files have been deleted.
finalStage = createResultStage(finalRDD, func, partitions, jobId, callSite) //1. Create the final FinalStage(ResultStage)
} catch {
case e: BarrierJobSlotsNumberCheckFailed =>
logWarning(s"The job $jobId requires to run a barrier stage that requires more slots " +
"than the total number of slots in the cluster currently.")
// If jobId doesn't exist in the map, Scala coverts its value null to 0: Int automatically.
val numCheckFailures = barrierJobIdToNumTasksCheckFailures.compute(jobId,
new BiFunction[Int, Int, Int] {
override def apply(key: Int, value: Int): Int = value + 1
})
if (numCheckFailures <= maxFailureNumTasksCheck) {
messageScheduler.schedule(
new Runnable {
override def run(): Unit = eventProcessLoop.post(JobSubmitted(jobId, finalRDD, func,
partitions, callSite, listener, properties))
},
timeIntervalNumTasksCheck,
TimeUnit.SECONDS
)
return
} else {
// Job failed, clear internal data.....
...
private[scheduler] def cleanUpAfterSchedulerStop() {
for (job <- activeJobs) {
val error =
new SparkException(s"Job ${job.jobId} cancelled because SparkContext was shut down")
job.listener.jobFailed(error)
// Tell the listeners that all of the running stages have ended. Don't bother
// cancelling the stages because if the DAG scheduler is stopped, the entire application
// is in the process of getting stopped.
val stageFailedMessage = "Stage cancelled because SparkContext was shut down"
// The `toArray` here is necessary so that we don't iterate over `runningStages` while
// mutating it.
runningStages.toArray.foreach { stage =>
markStageAsFinished(stage, Some(stageFailedMessage))
}
listenerBus.post(SparkListenerJobEnd(job.jobId, clock.getTimeMillis(), JobFailed(error)))
}
}
AsyncEventQueue Asynchronous event handling
AsyncEventQueue Class diagram inheritance structure
AsyncEventQueue Method list
AsyncEventQueue The function point
- dispatchThread AsyncEventQueue There is a single thread inside dispatchThread, call
dispatch()–>postToAll()–>doPostEvent()Method continuous processing eventQueue Middle event , Let all registered listener Responding to events
AsyncEventQueue Parent class doPostEvent Method realization
StreamingListenerBus And StreamingQueryListenerBus Rewrote doPostEvent(), Only focus on events related to processing flow .
It can be seen from the method that , In addition to event matching, it also uses SparkListenerInterface
protected override def doPostEvent(
listener: SparkListenerInterface,
event: SparkListenerEvent): Unit = {
event match {
case stageSubmitted: SparkListenerStageSubmitted =>
listener.onStageSubmitted(stageSubmitted)
case stageCompleted: SparkListenerStageCompleted =>
listener.onStageCompleted(stageCompleted)
case jobStart: SparkListenerJobStart =>
listener.onJobStart(jobStart)
case jobEnd: SparkListenerJobEnd =>
listener.onJobEnd(jobEnd)
case taskStart: SparkListenerTaskStart =>
listener.onTaskStart(taskStart)
case taskGettingResult: SparkListenerTaskGettingResult =>
listener.onTaskGettingResult(taskGettingResult)
case taskEnd: SparkListenerTaskEnd =>
listener.onTaskEnd(taskEnd)
case environmentUpdate: SparkListenerEnvironmentUpdate =>
listener.onEnvironmentUpdate(environmentUpdate)
case blockManagerAdded: SparkListenerBlockManagerAdded =>
listener.onBlockManagerAdded(blockManagerAdded)
case blockManagerRemoved: SparkListenerBlockManagerRemoved =>
listener.onBlockManagerRemoved(blockManagerRemoved)
case unpersistRDD: SparkListenerUnpersistRDD =>
listener.onUnpersistRDD(unpersistRDD)
case applicationStart: SparkListenerApplicationStart =>
listener.onApplicationStart(applicationStart)
case applicationEnd: SparkListenerApplicationEnd =>
listener.onApplicationEnd(applicationEnd)
case metricsUpdate: SparkListenerExecutorMetricsUpdate =>
listener.onExecutorMetricsUpdate(metricsUpdate)
case executorAdded: SparkListenerExecutorAdded =>
listener.onExecutorAdded(executorAdded)
case executorRemoved: SparkListenerExecutorRemoved =>
listener.onExecutorRemoved(executorRemoved)
case executorBlacklistedForStage: SparkListenerExecutorBlacklistedForStage =>
listener.onExecutorBlacklistedForStage(executorBlacklistedForStage)
case nodeBlacklistedForStage: SparkListenerNodeBlacklistedForStage =>
listener.onNodeBlacklistedForStage(nodeBlacklistedForStage)
case executorBlacklisted: SparkListenerExecutorBlacklisted =>
listener.onExecutorBlacklisted(executorBlacklisted)
case executorUnblacklisted: SparkListenerExecutorUnblacklisted =>
listener.onExecutorUnblacklisted(executorUnblacklisted)
case nodeBlacklisted: SparkListenerNodeBlacklisted =>
listener.onNodeBlacklisted(nodeBlacklisted)
case nodeUnblacklisted: SparkListenerNodeUnblacklisted =>
listener.onNodeUnblacklisted(nodeUnblacklisted)
case blockUpdated: SparkListenerBlockUpdated =>
listener.onBlockUpdated(blockUpdated)
case speculativeTaskSubmitted: SparkListenerSpeculativeTaskSubmitted =>
listener.onSpeculativeTaskSubmitted(speculativeTaskSubmitted)
case _ => listener.onOtherEvent(event)
}
}
AsyncEventQueue Event handling process
SparkListenerInterface analysis
Streaming It will be analyzed in detail later
AppStatusListener
Spark UI in Job、Stage、Task page , call AppStatusStore Methods provided , Read kvstore Stored in the rdd Task related information .
**
* A Spark listener that writes application information to a data store. The types written to the
* store are defined in the `storeTypes.scala` file and are based on the public REST API.
* Spark Monitor , Write application information to the data store . Type written
* store It's defined in ' storeTypes in .scala ' file , And based on public REST API.
* @param lastUpdateTime When replaying logs, the log's last update time, so that the duration of
* unfinished tasks can be more accurately calculated (see SPARK-21922).
*/
private[spark] class AppStatusListener(
kvstore: ElementTrackingStore,
conf: SparkConf,
live: Boolean,
lastUpdateTime: Option[Long] = None) extends SparkListener with Logging {
SQLAppStatusListener
Spark UI in SQL page , call SQLAppStatusStore Methods provided , Read kvstore Stored in the SparkPlan Physical plan (SQL Real execution process ) Related information .
class SQLAppStatusListener(
conf: SparkConf,
kvstore: ElementTrackingStore,
live: Boolean) extends SparkListener with Logging {
KVStore Subsequent updates ~~
Good night, ~~
边栏推荐
- LeetCode 1986. The minimum working time to complete the task is one question per day
- [designmode] proxy pattern
- Pisa-Proxy SQL 解析之 Lex & Yacc
- Reflections on "product managers must read: five classic innovative thinking models"
- ORACLE进阶(六)ORACLE expdp/impdp详解
- typescript ts基础知识之tsconfig.json配置选项
- skimage学习(2)——RGB转灰度、RGB 转 HSV、直方图匹配
- 第九届 蓝桥杯 决赛 交换次数
- The latest interview experience of Android manufacturers in 2022, Android view+handler+binder
- 【图像传感器】相关双采样CDS
猜你喜欢
Sort out several important Android knowledge and advanced Android development interview questions
面向接口编程
QT中自定义控件的创建到封装到工具栏过程(二):自定义控件封装到工具栏
QML初学

《产品经理必读:五种经典的创新思维模型》的读后感
![[designmode] proxy pattern](/img/ed/642aebc7b49cbf4d30b517665b2438.png)
[designmode] proxy pattern
Master this promotion path and share interview materials
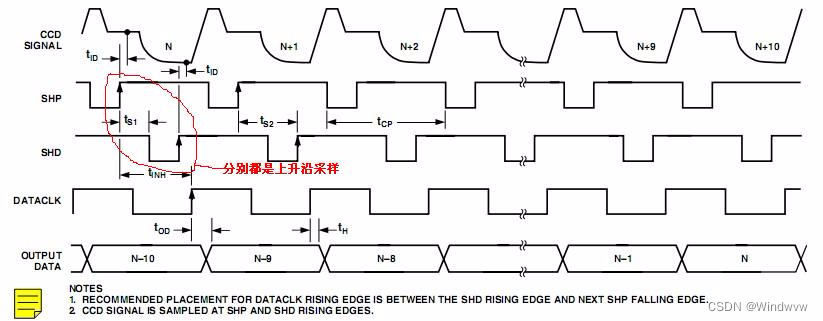
【图像传感器】相关双采样CDS

低代码(lowcode)帮助运输公司增强供应链管理的4种方式
最新Android高级面试题汇总,Android面试题及答案
随机推荐
ORACLE进阶(六)ORACLE expdp/impdp详解
Test case management tool recommendation
[medical segmentation] attention Unet
Module VI
Flask搭建api服务
Pisa-Proxy SQL 解析之 Lex & Yacc
QT视频传输
SlashData开发者工具榜首等你而定!!!
ATM系统
LeetCode 1774. The dessert cost closest to the target price is one question per day
LeetCode 312. Poke balloon daily
谈谈 SAP 系统的权限管控和事务记录功能的实现
LeetCode-SQL第一天
LeetCode 120. Triangle minimum path and daily question
Skimage learning (3) -- gamma and log contrast adjustment, histogram equalization, coloring gray images
DNS 系列(一):为什么更新了 DNS 记录不生效?
最新2022年Android大厂面试经验,安卓View+Handler+Binder
LeetCode 1031. 两个非重叠子数组的最大和 每日一题
Advanced C language -- function pointer
LeetCode 300. 最长递增子序列 每日一题
