当前位置:网站首页>Review SGI STL secondary space configurator (internal storage pool) | notes for personal use
Review SGI STL secondary space configurator (internal storage pool) | notes for personal use
2022-06-24 08:20:00 【_ Soren】
Preface
Study in the past C++ When the , Wrote some analysis STL Space configurator article , Now look back again , Want to review .
SGI STL Space configurator : 【 View in this directory 】
SGI STL It includes primary space configurator and secondary space configurator , One level of space configurator allocator use malloc and free To manage memory , and C++ Provided in the standard library allocator It's the same , But the secondary space configurator allocator Based on freelist Free linked list principle of memory pool mechanism to achieve memory management .
List of articles
Space configurator related definitions
template <class _Tp, class _Alloc = __STL_DEFAULT_ALLOCATOR(_Tp) >
class vector : protected _Vector_base<_Tp, _Alloc>
The default space configurator for containers is __STL_DEFAULT_ALLOCATOR( _Tp), It is a macro definition , as follows :
# ifndef __STL_DEFAULT_ALLOCATOR
# ifdef __STL_USE_STD_ALLOCATORS
# define __STL_DEFAULT_ALLOCATOR(T) allocator< T >
# else
# define __STL_DEFAULT_ALLOCATOR(T) alloc
# endif
# endif
You can see from above __STL_DEFAULT_ALLOCATOR There are two ways to implement macro control , One is allocator< T >, The other is alloc, The two differences are SGI STL The implementation of the primary space configurator and the secondary space configurator .
According to the English meaning , The default space configurator is the secondary configurator , Application is greater than 128 Bytes of memory blocks are handed over to the first level configurator ....
template <int __inst>
class __malloc_alloc_template // First level space configurator memory management class -- adopt malloc and free Manage memory
template <bool threads, int inst>
class __default_alloc_template {
// Secondary space configurator memory management class -- Realize memory management by customizing memory pool
Important types and variable definitions
First three enumerators , Represents granularity information
// Granularity information of memory pool
enum {
_ALIGN = 8}; // 8 Increasing multiple of
enum {
_MAX_BYTES = 128}; // Maximum number of bytes allocated 128
enum {
_NFREELISTS = 16}; // Number of free linked lists ( The length of the array )
This is each memory chunk Block information , In fact, it can be used as a linked list , This _M_free_list_link amount to next Domain .
// Every memory chunk Block header information
union _Obj {
union _Obj* _M_free_list_link;
char _M_client_data[1]; /* The client sees this. */
};
This pointer array is maintenance 16 A free list , Remember the array name first (_S_free_list)
// Organize an array of all free linked lists , The type of each element of the array is _Obj*, All initialized to 0
static _Obj* __STL_VOLATILE _S_free_list[_NFREELISTS];
These three static variables are the maintenance memory pool ( Applied to the stacking area ). The first two pointer variables , Indicates the start and end positions of the memory pool , and heap_size Indicates the total number of bytes requested from the heap . First initialize them all to 0.
// Chunk allocation state. Record memory chunk Allocation of blocks
static char* _S_start_free;
static char* _S_end_free;
static size_t _S_heap_size;
template <bool __threads, int __inst>
char* __default_alloc_template<__threads, __inst>::_S_start_free = 0;
template <bool __threads, int __inst>
char* __default_alloc_template<__threads, __inst>::_S_end_free = 0;
template <bool __threads, int __inst>
size_t __default_alloc_template<__threads, __inst>::_S_heap_size = 0;
Two important auxiliary interface functions
- ROUND_UP
The meaning is to increase the number of bytes that the client wants to apply to 8 Multiple . For example, apply for 9 Bytes , Up to 16 Bytes ; apply 20 byte , Up to 24 Bytes . The principle is bit operation .
/* take __bytes Up to the nearest 8 Multiple */
static size_t _S_round_up(size_t __bytes) {
return (((__bytes) + (size_t) _ALIGN-1) & ~((size_t) _ALIGN - 1));
}
Example : apply 9 byte
Then this can be regarded as the following binary : After bit and, it becomes 16
00000000 00000000 00000000 00010000
1111 1111 1111 1111 1111 1111 1111 1000
- FREELIST_INDEX
It means to find the specific free linked list to apply for . Subscript from 0 Start , So I used '/' Operator .
/* return __bytes The size of chunk The block is located in free-list Number in */
static size_t _S_freelist_index(size_t __bytes) {
return (((__bytes) + (size_t)_ALIGN-1)/(size_t)_ALIGN - 1);
}
Memory pool management functions
Personally, the most important and difficult thing to understand is chunk_alloc() function , You need to draw more pictures , Go through the process several times .
// An entry function to allocate memory
static void* allocate(size_t __n);
// Be responsible for the assigned chunk Block to connect , Add to the free linked list
static void* _S_refill(size_t __n);
// Allocate the corresponding memory byte size chunk block , And initialize the following three member variables
static char* _S_chunk_alloc(size_t __size, int& __nobjs);
// hold chunk The block is returned to the memory pool
static void deallocate(void* __p, size_t __n);
// Memory pool expansion function
template <bool threads, int inst>
void*
__default_alloc_template<threads, inst>::reallocate(void* __p,
size_t __old_sz,
size_t __new_sz);
The advantages of this memory pool
For each number of bytes chunk Block allocation , Are given a part to use , The other part is for standby , This standby can be used for the current number of bytes , It can also be used for other bytes .
The spare memory pool is divided chunk After block , If there are still very small memory blocks left , When redistributing , These small memory blocks will be allocated again , The spare memory pool is clean !
When the memory allocation for the specified number of bytes fails , There is an exception handling process ,bytes - 128 Byte all chunk Block to view , If any byte number is free chunk block , Just borrow one
If the above operation fails , It also calls _oom_malloc This is set in advance malloc Callback function for memory allocation failure ,
If it is not set, an exception will be thrown (throw_bad_alloc)
If set , Will start an infinite loop for(; ; ), Always call (*oom_malloc_handler)(); function , After that, continue to call malloc()...
边栏推荐
- GraphMAE----論文快速閱讀
- JVM underlying principle analysis
- 一文带你了解Windows操作系统安全,保护自己的电脑不受侵害
- 权限模型 DAC ACL RBAC ABAC
- Utilisation de la fermeture / bloc de base SWIFT (source)
- Transformers pretrainedtokenizer class
- Introduction to software engineering - Chapter 2 - feasibility study
- 根据网络上的视频的m3u8文件通过ffmpeg进行合成视频
- Solution of electric education system for intelligent supervision station
- Vulnhub target: boredhackerblog: social network
猜你喜欢

小样本故障诊断 - 注意力机制代码 - BiGRU代码解析实现
宝塔面板安装php7.2安装phalcon3.3.2

一文带你了解Windows操作系统安全,保护自己的电脑不受侵害

Leetcode 207: course schedule (topological sorting determines whether the loop is formed)
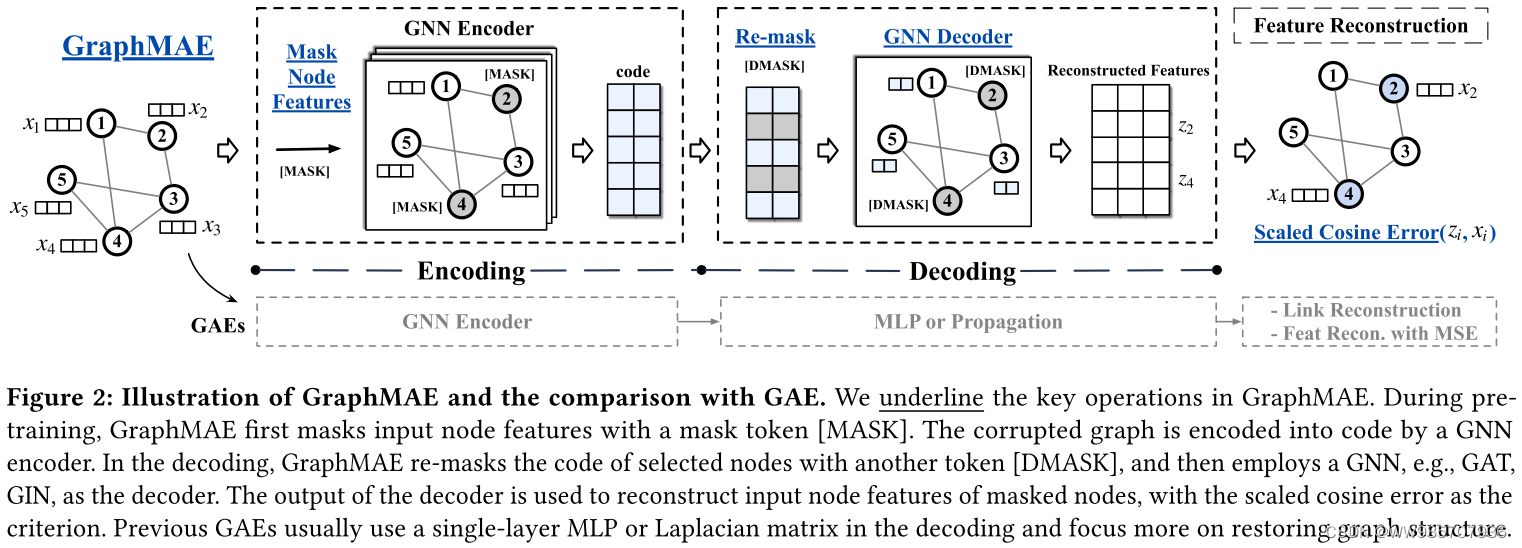
GraphMAE----論文快速閱讀
12--合并两个有序链表

longhorn安装与使用
![[nilm] non intrusive load decomposition module nilmtk installation tutorial](/img/d0/bc5ea1cbca9ee96a2fe168484ffec4.png)
[nilm] non intrusive load decomposition module nilmtk installation tutorial

Vulnhub target: boredhackerblog: social network

FPGA的虚拟时钟如何使用?
随机推荐
疫情下更合适的开发模式
Online education fades
Transformers pretrainedtokenizer class
Decltype usage introduction
js滚动div滚动条到底部
对于flex:1的详细解释,flex:1
Swift Extension NetworkUtil(網絡監聽)(源碼)
Analysis of abnormal problems in domain name resolution in kubernetes
UTC、GMT、CST
io模型初探
June 27, 2021: given a positive array arr, it represents the weight of several people
Getting started with crawler to giving up 06: crawler play Fund (with code)
直播回顾 | 云原生混部系统 Koordinator 架构详解(附完整PPT)
Chart list Performance Optimization: minimum resource consumption in the visualization area
根据网络上的视频的m3u8文件通过ffmpeg进行合成视频
Live broadcast review | detailed explanation of koordinator architecture of cloud native hybrid system (complete ppt attached)
基金的募集,交易与登记
Leetcode 515 find the leetcode path of the maximum [bfs binary tree] heroding in each row
宝塔面板安装php7.2安装phalcon3.3.2
2021-03-16 COMP9021第九节课笔记