当前位置:网站首页>Use of promise in ES6
Use of promise in ES6
2022-07-07 02:52:00 【I must win this time】
One .Promise What is it? ?
Promise It's a constructor , There are three states , success (fulfiled), Failure (reject), wait for (pending), There are two parameters resolve and reject.
Code :
const p1 = new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
})Two .Promise Of api Method
1.then Get the value of the status after success .
2.catch Capture the value of the failed state .
3、 ... and .Promise For what ?
To solve the problem of asynchrony , It is usually used on the request interface .
(1) Back to a success (fulfiled) The state of
Code :
const p1 = new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
resolve(' The state of success ')
})
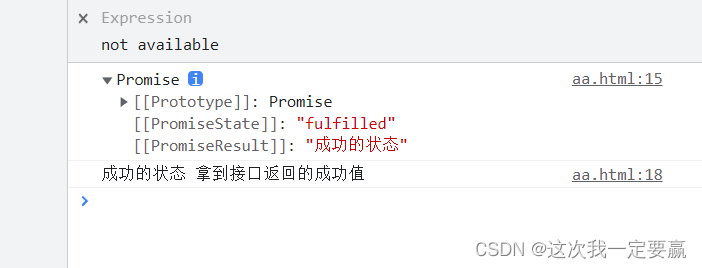
console.log(p1);
p1.then(res => {
console.log(res, ' Get the success value returned by the interface ');
})The state of success :
(2) Back to a Failure (reject) The state of .
Code :
const p1 = new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
reject(' Failed state ')
})
console.log(p1);
p1.then(res => {
console.log(res, ' Get the failure value returned by the interface ');
})Failed state :
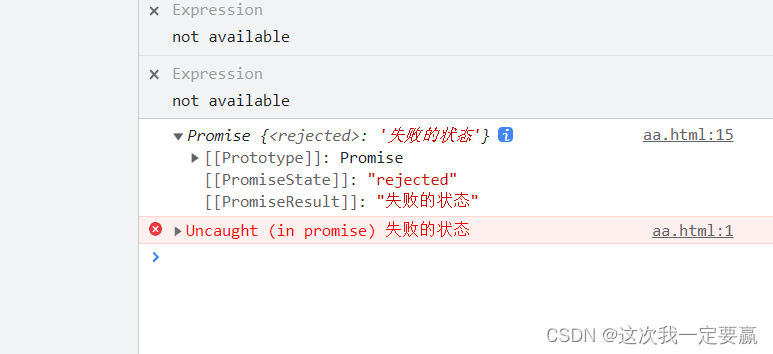
Conclusion :
then Is unable to get the failure status reject The value of the .
At this time, let's try .catch
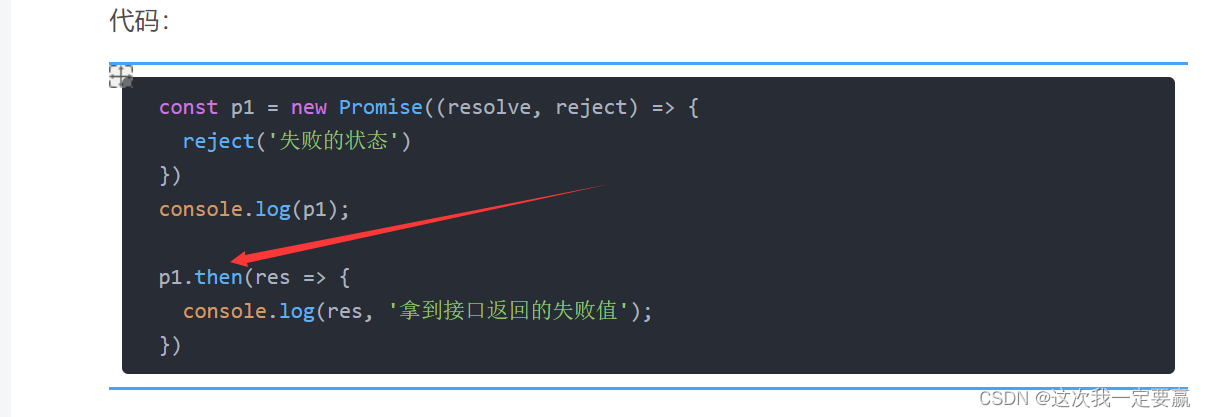
Modify the code :
const p1 = new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
reject(' Failed state ')
})
console.log(p1);
p1.catch(res => {
console.log(res, ' Get the success value returned by the interface ');
})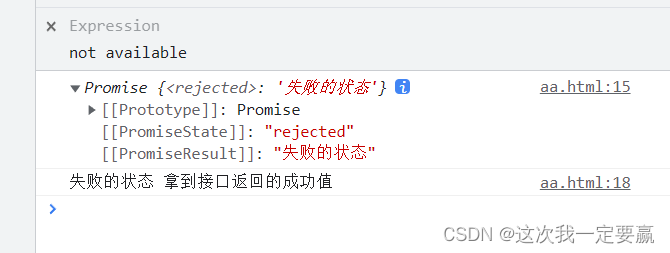
Can capture .
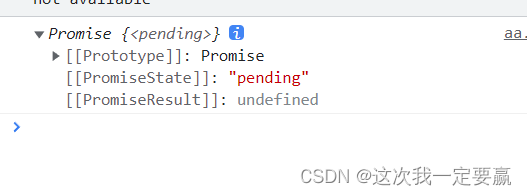
(3) wait for (pending) The state of .
Code :
const p1 = new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
})
console.log(p1);The state of waiting :
(4) Relate to actual api Interface call
Such as :
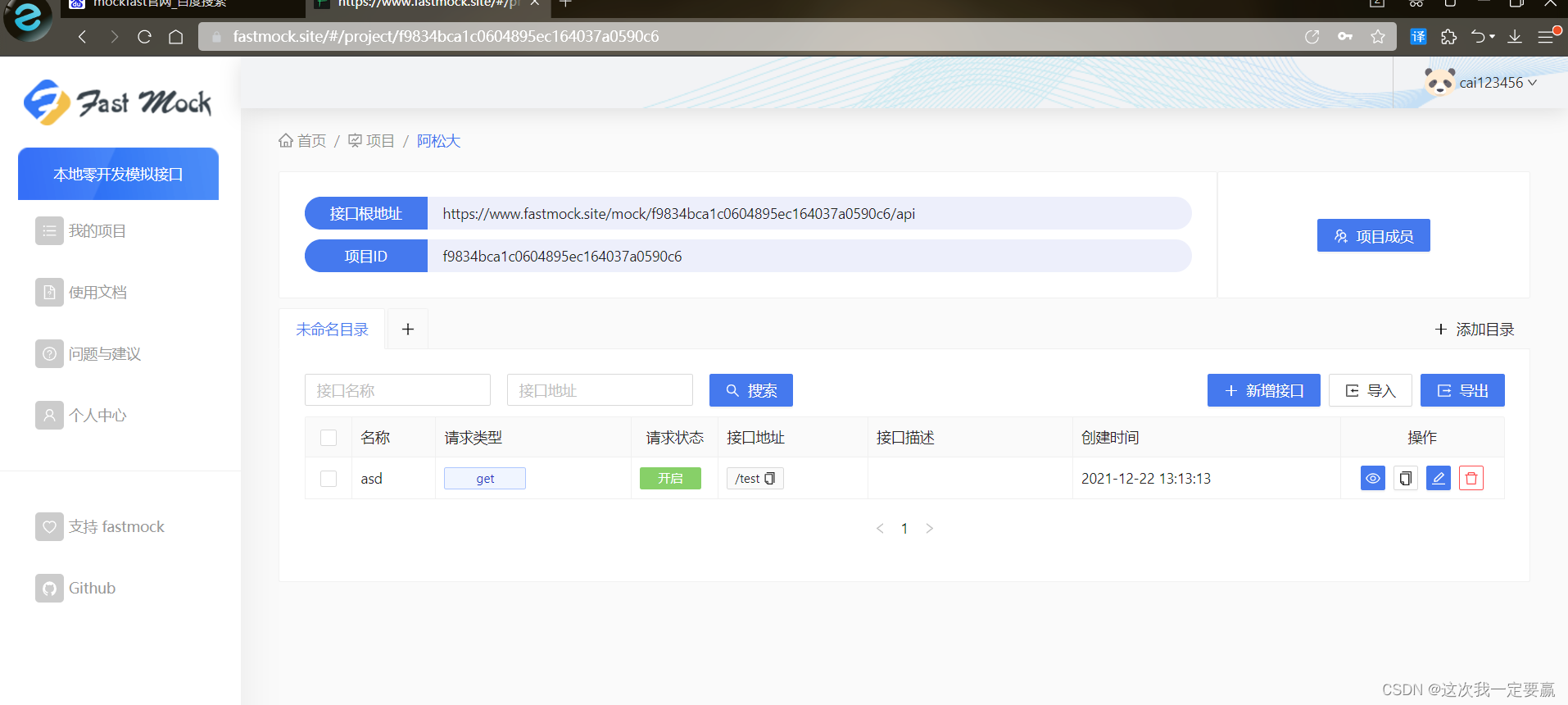
1. use mockfast Simulate an interface
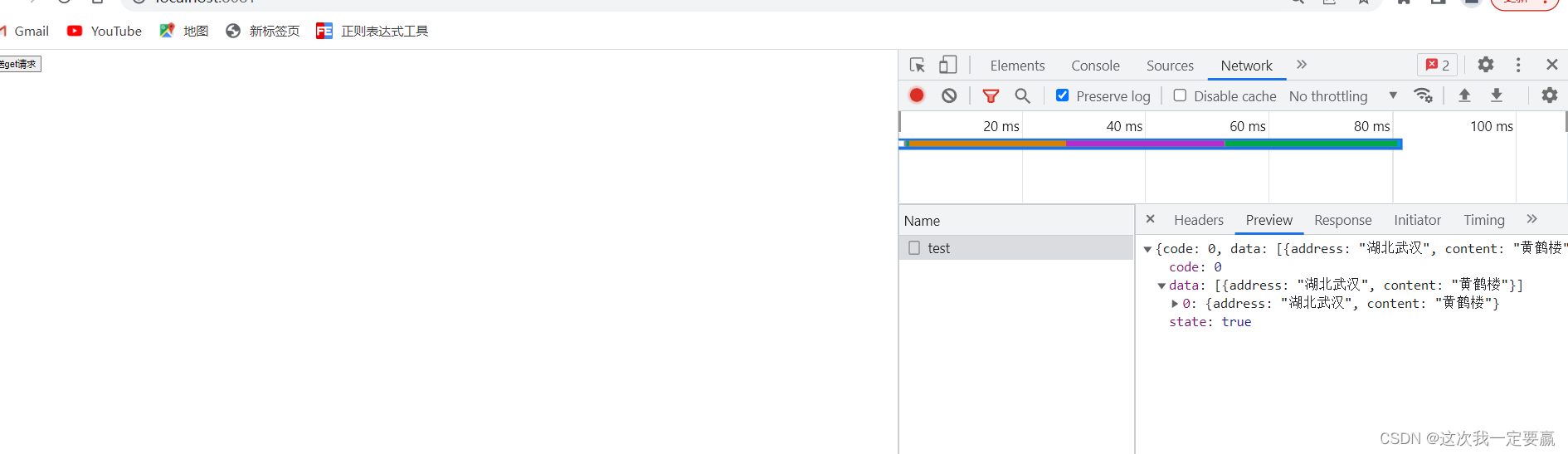
2. Request example
<template>
<div class="">
<button @click="fn"> send out get request </button>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import axios from 'axios'
export default {
data(){return{
}},
name: '',
methods: {
fn(){
// alert('11111111')
axios({
method:'GET',
url:"https://www.fastmock.site/mock/f9834bca1c0604895ec164037a0590c6/api/test",
}).then(res=>console.log(res))
}
},
}
</script>The result returned :
Use when the request fails .catch Capture , The back end will also return data to the front end .
Such as :
401 Not enough permissions
404 Parameter error
500 Server error etc.
We need to use .catch Capture .
Four . The practical application
(1) The way of requesting interfaces is also an asynchronous requirement
<template>
<div class="">
<button @click="fn"> send out get request </button>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import axios from 'axios'
export default {
data(){return{
}},
name: '',
methods: {
fn(){
// alert('11111111')
const p1= axios({
method:'get',
url:"https://www.fastmock.site/mock/f9834bca1c0604895ec164037a0590c6/api/test",
})
console.log(p1,111111111111111111);
}
},
}
</script>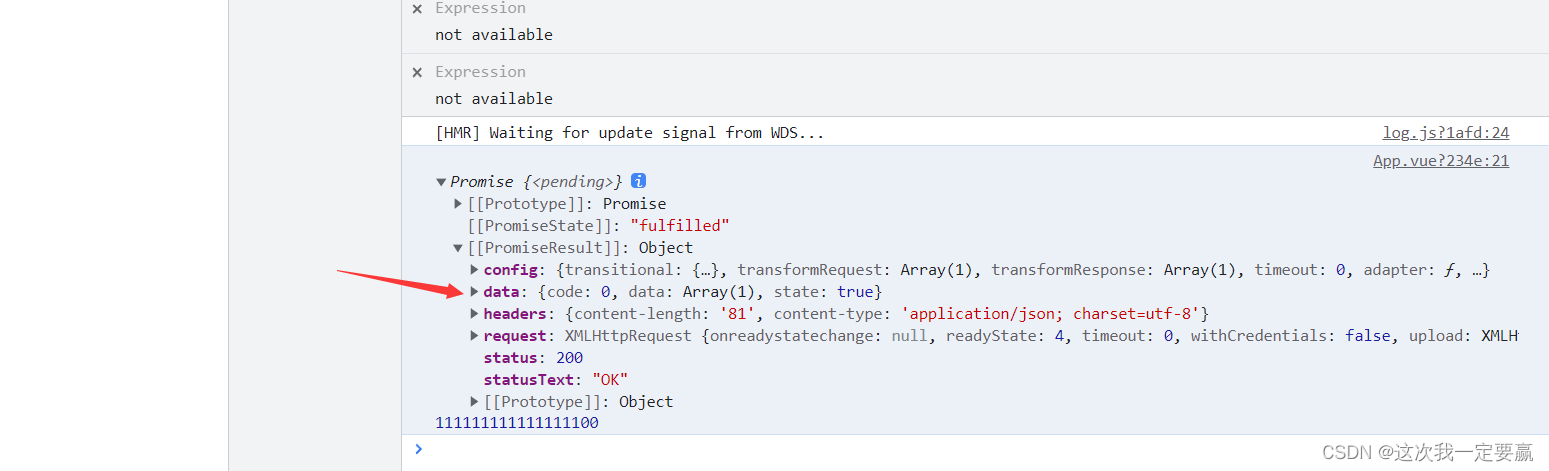
So we can use then perhaps catch To capture the data of the interface .
(2).then and .catch Use it together
<template>
<div class="">
<button @click="fn"> send out get request </button>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import axios from 'axios'
export default {
data(){return{
}},
name: '',
methods: {
fn(){
// alert('11111111')
axios({
method:'get',
url:"https://www.fastmock.site/mock/f9834bca1c0604895ec164037a0590c6/api/test",
}).then(res=>console.log(res)).catch(reject=>console.log(reject))
}
},
}
</script>5、 ... and . Alternatives async await
use Promise There is certainly no problem in solving asynchronous programming , What if you have to send a lot of requests ?
Look at the code below :
let a1 = new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
resolve(' having dinner ')
}).then(res => {
alert(res)
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
resolve(' sleep ')
})
}).then(res => {
alert(res)
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
resolve(' Doudou ')
})
}).then(res => alert(res))If more than one Promise Does it seem very redundant .
solution :
async and await
<SCript>
let a1 = new Promise((resolve) => {
resolve(' having dinner ')
})
let a2 = new Promise((resolve) => {
resolve(' sleep ')
})
let a3 = new Promise((resolve) => {
resolve(' Doudou ')
})
async function fn() {
const res1 = await a1
console.log(res1);
const res2 = await a2
console.log(res2);
const res3 = await a3
console.log(res3);
}
fn()
</SCript>Its usage :
Add async
Followed by await Just receive
Printed results :
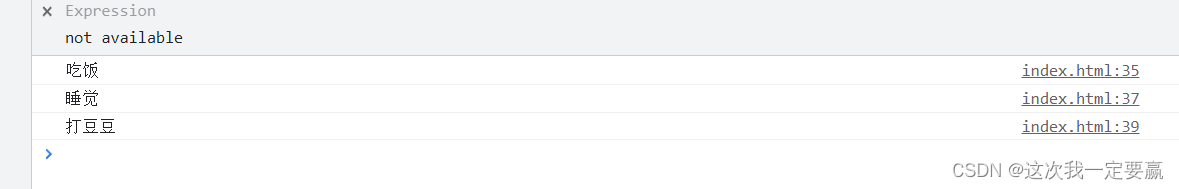
Is it clearer to compare the above results .
6、 ... and . use async Is the modified function an asynchronous function ?
Look at the code below :
async function fn() {
console.log(123);
}
console.log(fn());Printed results :
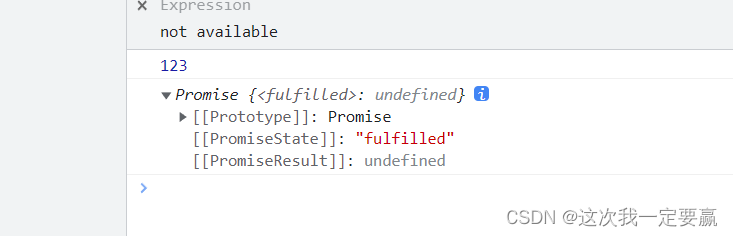
It's a Promise object , He represents only a state .
Prove that it is not asynchronous
Code :
async function fn() {
console.log(123);
}
console.log(fn());
console.log(456);If this function is executed asynchronously, the output result is 456 123
And the actual result is :
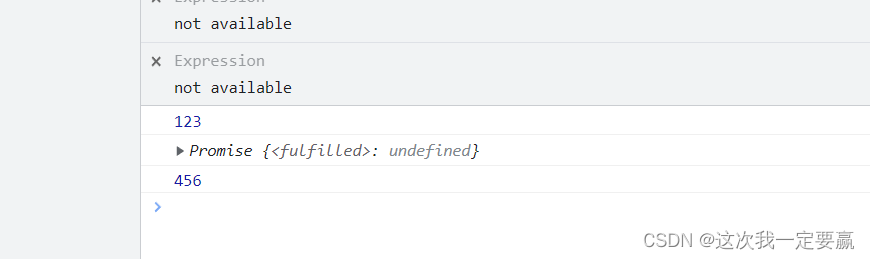
So it doesn't just mean Promise A state of being .
If you add await Well ?
Code :
<SCript>
async function fn() {
await console.log(123);
}
console.log(fn());
console.log(456);
</SCript>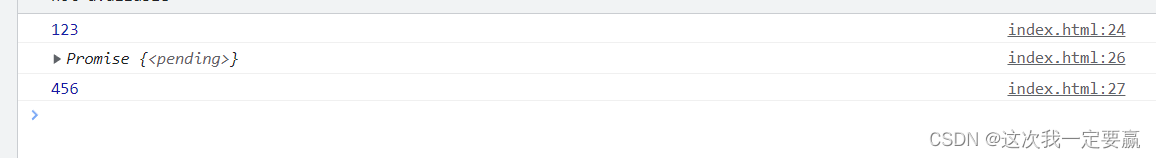
Come to the conclusion
await The following code is executed asynchronously .
in summary :
1. use async Modified functions are not executed asynchronously , It's just becoming Promise A state of being .
2. stay await The latter are executed asynchronously .
7、 ... and . How to interrupt a Promise
Throw a Pending The state of the can be
Code :
new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
resolve(2)
}).then(res => {
// interrupt
throw new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
})
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
resolve(3)
})
}).then(res => console.log(res))8、 ... and .Promise Expand api
(1)Promise.race
Code :
const a1 =
new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
setTimeout(() => {
resolve(20)
}, 2000);
})
const a2 =
new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
setTimeout(() => {
resolve(100)
}, 1000);
})
const a3 =
new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
setTimeout(() => {
resolve(30)
}, 3000);
})
const p1 = Promise.race([a1, a2, a3]).then(res => alert(res))Whoever takes the shortest time will execute .
The result must be 100.
Halfway there reject It's the same , No matter who succeeds or fails, the time is short .
const a1 =
new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
setTimeout(() => {
reject(20)
}, 2000);
})
const a2 =
new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
setTimeout(() => {
resolve(100)
}, 1000);
})
const a3 =
new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
setTimeout(() => {
resolve(30)
}, 3000);
})
const p1 = Promise.race([a1, a2, a3]).then(res => alert(res), err => alert(err))(2)Promise.all
Compared with the racing mechanism, this is implemented together .
const a1 = Promise.resolve(10)
const a2 = Promise.resolve(20)
const a3 = Promise.reject(30)
const p1 = Promise.all([a1, a2, a3]).then(res => console.log(res), err =>
console.log(err))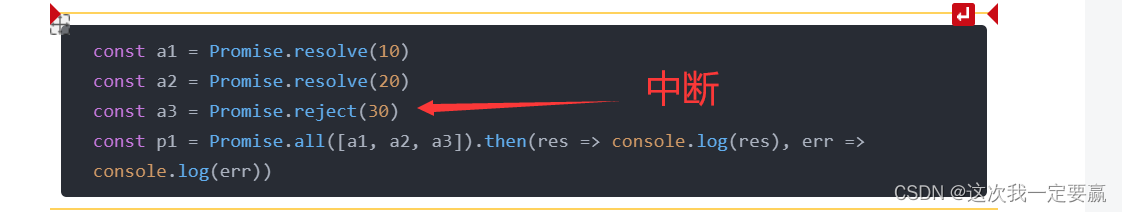
use [] Wrap it up , When the execution inside is completed, get the corresponding instance
If there is an error in the way, it will stop immediately .
This can be used when sending multiple asynchronous requests . Before sending loading The effect of loading .
After asynchronous sending, loading ends .
Note that this has nothing to do with asynchronous time , It has something to do with the sequence of packages .
const a1 = Promise.resolve(10)
const a2 = Promise.resolve(20)
const a3 = Promise.resolve(30)
const p1 = Promise.all([a2, a1, a3]).then(res => console.log(res), err => console.log(err))Output result :
[10,20,30]
Nine .Promise.resolve and Promise.reject
Promise.resolve(2).then(res => console.log(res))
Promise.reject(3).catch(reject => console.log(reject))Its equivalence :
Promise.resolve(2).then(res => console.log(res))
new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
resolve(2)
})Promise.reject(3).then(reject=> console.log(reject))
new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
reject(3)
})边栏推荐
- A complete tutorial for getting started with redis: AOF persistence
- [leetcode]Search for a Range
- Here comes a white paper to uncover the technology behind Clickhouse, a node with 10000 bytes!
- ERROR: Could not find a version that satisfies the requirement xxxxx (from versions: none)解决办法
- Fundamentals of process management
- KYSL 海康摄像头 8247 h9 isapi测试
- Kysl Haikang camera 8247 H9 ISAPI test
- [leetcode]Search for a Range
- Work of safety inspection
- widerperson数据集转化为YOLO格式
猜你喜欢
Hash table and full comments
Apifox, is your API interface document rolled up like this?
The panel floating with the mouse in unity can adapt to the size of text content
The annual salary of general test is 15W, and the annual salary of test and development is 30w+. What is the difference between the two?
Huitong programming introductory course - 2A breakthrough

PSINS中19维组合导航模块sinsgps详解(时间同步部分)
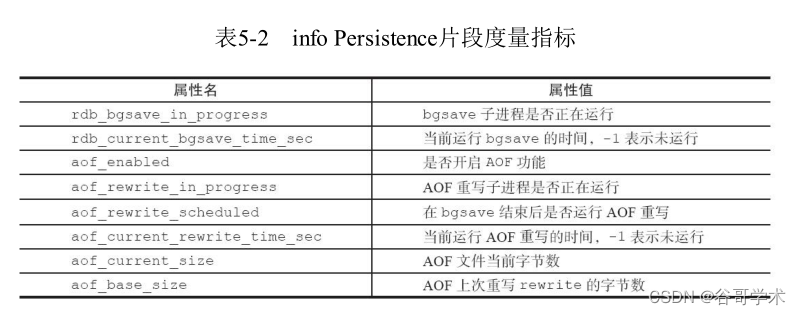
Redis入門完整教程:問題定比特與優化
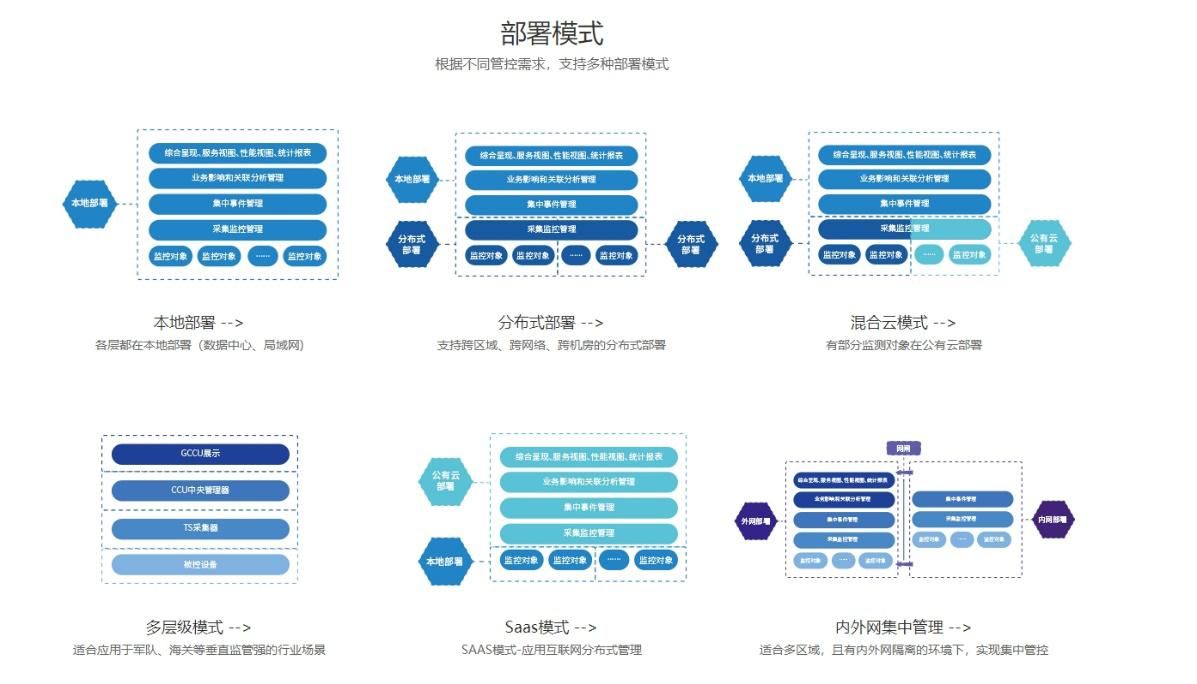
What are the characteristics of the operation and maintenance management system
Google Earth Engine(GEE)——Landsat 全球土地调查 1975年数据集

哈希表及完整注释
随机推荐
基于ensp防火墙双击热备二层网络规划与设计
C language exercises_ one
[socket] ① overview of socket technology
QT common Concepts-1
Qt蓝牙:QBluetoothDeviceInfo
你不可不知道的Selenium 8种元素定位方法,简单且实用
QT常见概念-1
[leetcode]Search for a Range
MySQL is an optimization artifact to improve the efficiency of massive data query
Kubernetes源码分析(二)----资源Resource
用全连接+softmax对图片的feature进行分类
【Socket】①Socket技术概述
CSDN 夏令营课程 项目分析
Contribution of Writing Series
LeetCode 77:组合
QPushButton-》函数精解
Redis入门完整教程:AOF持久化
Read fast RCNN in one article
Static proxy of proxy mode
Redis入门完整教程:复制配置