当前位置:网站首页>Ideas and methods of system and application monitoring
Ideas and methods of system and application monitoring
2022-07-06 20:05:00 【Impl_ Sunny】
0、 Preface
In the actual performance analysis , A very common phenomenon is , Obviously, there is a performance bottleneck , But when you log in to the server and want to check , But found that the bottleneck has disappeared . Or say , Performance problems always happen from time to time , But it's hard to find the law of occurrence , It's hard to reproduce .
And to solve this problem , We need to build a monitoring system , Monitor the health of systems and Applications , And define a series of strategies , When a problem occurs, the alarm will be notified at the first time . A good monitoring system , It can not only expose various problems of the system in real time , It can also be based on these monitored States , Automatically analyze and locate approximate bottleneck sources , So as to report the problem to the relevant team more accurately . To do a good job of monitoring , The core is comprehensive 、 Quantifiable indicators , This includes system and application .
In terms of system , The monitoring system shall cover the overall resource utilization of the system , such as CPU、 Memory 、 Disk and file system 、 Network and other system resources .
In terms of applications , The monitoring system should cover the internal operation status of the application , This includes both the... Of the process CPU、 disk I/O And so on , More needs to be included, such as time-consuming interface calls 、 Errors in execution 、 Memory usage of internal objects and other internal running conditions of the application .
One 、 System monitoring
1.1 USE Law
Before starting the monitoring system , You must want to know most , How can we use a concise method , To describe the use of system resources . You can certainly use the various performance tools learned in this column , To collect the usage of various resources . But don't forget , There are many performance indicators for each resource , Using too many indicators is time-consuming and labor-consuming. Don't say , It's not easy to establish the overall operation status of the system for you .
ad locum , I'd like to introduce you to a system for performance monitoring USE(Utilization Saturation and Errors) Law .
USE The performance index of system resources , Reduced to three categories , I.e. utilization rate 、 Saturation and number of errors :
- Usage rate : Indicates the percentage of time or capacity that the resource is used for service .100% The usage rate of , Indicates that the capacity has been exhausted or all the time is used for service .
- saturation : Indicates how busy the resource is , Usually related to the length of the waiting queue .100% Saturation of , Indicates that the resource cannot accept more requests .
- Wrong number : Indicates the number of events with errors . The more errors , It indicates that the more serious the problem of the system .
Indicators of these three categories , It covers the common performance bottlenecks of system resources , Therefore, it is often used to quickly locate the performance bottleneck of system resources . such , Both for CPU、 Memory 、 Disk and file system 、 Network and other hardware resources , Or the number of file descriptors 、 The number of connections 、 Connection tracking number and other software resources ,USE Methods can help you quickly locate , Which system resources have performance bottlenecks .
1.2 Performance indicators
The following are common performance indicators :
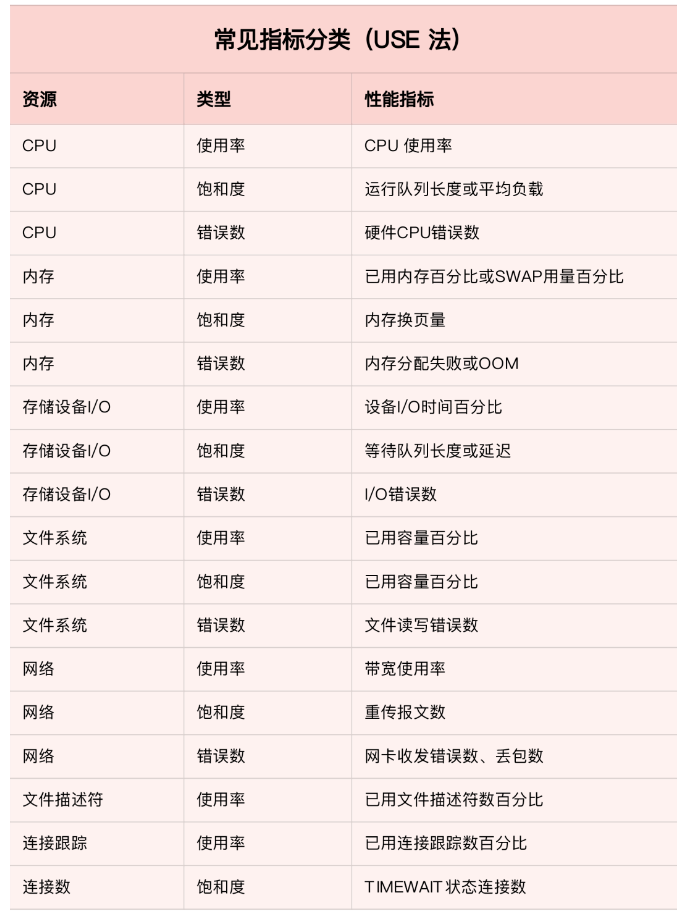
Be careful :USE The method only focuses on the core indicators that can reflect the bottleneck of system resource performance , But this is not to say that other indicators are not important . Such as system log 、 Process resource usage 、 Cache usage and other indicators , We also need to monitor . It's just , They are often used as an aid to performance analysis , and USE Indicators of the method , It directly indicates the resource bottleneck of the system .
1.3 The monitoring system
master USE Methods and performance indicators to be monitored , What to do next , Is to establish a monitoring system , Save these indicators ; then , Based on these monitored States , Automatically analyze and locate approximate bottleneck sources ; Last , Then through the alarm system , Report the problem to the relevant team in time . A complete monitoring system usually consists of data acquisition 、 data storage 、 Data query and processing 、 Alarm, visual display and other modules . therefore , To build a monitoring system from scratch , In fact, it is also a big system engineering .
Refer to the scheme for setting up the monitoring system :
Prometheus and Zabbix Comparison of
Prometheus+Grafana Installation tutorial practice
1.4 Summary
The core of system monitoring is the use of resources , This includes both CPU、 Memory 、 disk 、 file system 、 Network and other hardware resources , It also includes the number of file descriptors 、 The number of connections 、 Connection tracking number and other software resources . To describe these resource bottlenecks , The easiest and most effective way is USE Law .
USE The performance index of system resources , Reduced to three categories : Usage rate 、 Saturation and number of errors . When the indicators of any of these three categories are too high , All represent that the corresponding system resources may have performance bottlenecks .
be based on USE After establishing the performance index , We also need a complete monitoring system , Collect these indicators from 、 Storage 、 Inquire about 、 Handle , Then to alarm and visual display . such , It can not only quickly expose the bottleneck of system resources , You can also use the monitored historical data , To track and locate the root cause of performance problems .
Two 、 Application monitoring
2.1 Application monitoring indicators
Like system monitoring , Before building the application's monitoring system , First of all, we also need to determine , What indicators need to be monitored . Especially be clear , What metrics can be used to quickly identify application performance problems .
2.1.1 Core indicators
Core metrics for applications , It is no longer the use of resources , It's the number of requests 、 Error rate and response time .
These indicators are not only directly related to the user experience , It also reflects the overall availability and reliability of the application . With the number of requests 、 After the three golden indicators of error rate and response time , We can quickly know , Whether the application has performance problems .
Request 、 Details of response time , May refer to :【 Parameters 】 Make it clear QPS、TPS、 Number of concurrent users 、 throughput
2.1.2 Performance evaluation indicators
Although we can know that the application has problems through the core indicators , however , These indicators are obviously not enough , Because after a performance problem , We also want to be able to quickly locate “ Performance bottleneck area ”. therefore , in my opinion , The following indicators , It is also essential when monitoring applications :
Resource usage of the application process :
- describe : For example, the process takes up CPU、 Memory 、 disk I/O、 Network, etc . Using too many system resources , Cause the application to respond slowly or increase the number of errors , Is one of the most common performance problems .
- effect : The bottleneck of system resources can be associated with Applications , So as to quickly locate the performance problems caused by insufficient system resources
Calls between applications :
- describe : For example, call frequency 、 Wrong number 、 Delay, etc . Because applications are not isolated , If the other applications it depends on have performance problems , The performance of the application itself will also be affected .
- effect : It can quickly analyze the call chain of a request processing , Which component is the culprit of performance problems
The operation of the core logic inside the application :
- describe : For example, the time-consuming of key links and errors in the implementation process . Because this is the internal state of the application , Detailed performance data cannot be obtained directly from the outside .
- effect : Can go further , Go directly inside the application , Locate the function of which processing link causes the performance problem .
Based on these ideas , I believe you can build , Performance indicators that describe the running state of an application . Then these indicators are incorporated into the monitoring system ( such as Prometheus + Grafana) in , It can be the same as system monitoring , On the one hand, through the alarm system , Report the problem to the relevant team in time ; On the other hand , Through an intuitive graphical interface , Dynamically demonstrate the overall performance of the application .
2.2 Full link monitoring
Business systems usually involve a series of multiple services , Form a complex distributed call chain . In order to quickly locate such cross application performance bottlenecks , You can still use it skywalking、Zipkin、Jaeger、Pinpoint And other open source tools , To build a full link tracking system .
Full link tracking can help you quickly locate , During a request processing , Which link is the root of the problem .
Full link tracking can not only help you quickly locate cross application performance problems , It can also help you generate the call topology of the online system . These intuitive topologies , In analyzing complex systems ( For example, micro services ) Especially effective when .
2.3 Log monitoring
Monitoring of performance indicators , It allows you to quickly locate the bottleneck , However, only indicators are often not enough . such as , The same interface , When the parameters passed in by the request are different , It can lead to completely different performance problems . therefore , In addition to indicators , We also need to monitor the context information of these indicators , And logs are the best source of these contexts .
By contrast , Indicators are numerical measurement data in a specific period of time , Usually in the form of time series , Suitable for real-time monitoring .
The log is completely different , Logs are string messages at a certain point in time , It is usually necessary to index the search engine , Only then can you perform query and summary analysis .
For log monitoring , The most classic method , Is the use of ELK Technology stack , That is to use Elasticsearch、Logstash and Kibana The combination of these three components . As shown in the figure below , classical ELK Architecture diagram :

- Logstash : Responsible for collecting logs from various log sources , And then preprocess , Finally, the preliminary processed logs , Send to Elasticsearch Index .
- Elasticsearch : Be responsible for indexing the log , It also provides a complete full-text search engine , This will make it easy for you to retrieve the data you need from the log .
- Kibana : Be responsible for visual analysis of logs , Including log search 、 Processing and gorgeous dashboard display .
Here's a picture , It's just one. Kibana Example of dashboard , It intuitively shows Apache An overview of your visit .

Be careful :ELK In the technology stack Logstash Resource consumption is relatively large . therefore , In a resource constrained environment , We tend to use lower resource consumption Fluentd, To replace Logstash( It's called EFK Technology stack ).
2.4 Summary
Application monitoring , It can be divided into indicator monitoring and log monitoring :
- Indicator monitoring : It mainly measures the performance indicators in a certain period of time , Then through the way of time series , To deal with 、 Storage and alarm .
- Log monitoring : More detailed context information can be provided , Usually by ELK Technology stack to collect 、 Indexing and graphical presentation .
In complex business scenarios that span multiple different applications , You can also build a full link tracking system . This can dynamically track the performance of each component in the call chain , Generate the whole call flow diagram , So as to speed up the positioning of performance problems of complex applications .
Reference material :
1. Performance optimization and testing : System monitoring 、 Apply the idea of monitoring
边栏推荐
- Oceanbase Community Edition OBD mode deployment mode stand-alone installation
- 数据的同步为每个站点创建触发器同步表
- [network planning] Chapter 3 data link layer (3) channel division medium access control
- Configuration and simple usage of the EXE backdoor generation tool quasar
- Synchronization of data create trigger synchronization table for each site
- 腾讯安卓开发面试,android开发的基础知识
- 【GET-4】
- 深度剖析原理,看完这一篇就够了
- 5. Nano - Net in wireless body: Top 10 "is it possible?" Questions
- 【Yann LeCun点赞B站UP主使用Minecraft制作的红石神经网络】
猜你喜欢
HMS Core 机器学习服务打造同传翻译新“声”态,AI让国际交流更顺畅
Understand yolov1 Part II non maximum suppression (NMS) in prediction stage
A5000 vGPU显示模式切换
语音识别(ASR)论文优选:全球最大的中英混合开源数据TALCS: An Open-Source Mandarin-English Code-Switching Corpus and a Speech
Introduction to enterprise lean management system
学习打卡web
深度学习分类网络 -- ZFNet
![[network planning] Chapter 3 data link layer (3) channel division medium access control](/img/df/dd84508dfa2449c31d72c808c50dc0.png)
[network planning] Chapter 3 data link layer (3) channel division medium access control
Enumeration gets values based on parameters
BUUCTF---Reverse---easyre
随机推荐
Learning and Exploration - function anti shake
Oceanbase Community Edition OBD mode deployment mode stand-alone installation
腾讯安卓开发面试,android开发的基础知识
部门树递归实现
Enumeration gets values based on parameters
企业精益管理体系介绍
PHP and excel phpexcel
New generation garbage collector ZGC
BUUCTF---Reverse---easyre
MySQL must know and learn
Teach you to learn JS prototype and prototype chain hand in hand, a tutorial that monkeys can understand
语音识别(ASR)论文优选:全球最大的中英混合开源数据TALCS: An Open-Source Mandarin-English Code-Switching Corpus and a Speech
Speech recognition (ASR) paper selection: talcs: an open source Mandarin English code switching corps and a speech
颜色(color)转换为三刺激值(r/g/b)(干股)
学习打卡web
2022年6月语音合成(TTS)和语音识别(ASR)论文月报
HMS Core 机器学习服务打造同传翻译新“声”态,AI让国际交流更顺畅
An East SMS login resurrection installation and deployment tutorial
1805. Number of different integers in the string
121. The best time to buy and sell stocks