One 、Promiz What is it? ?
1、Promiz
- A proper compact promise (promises/A+ spec compliant) library
- A polyfill for ES6-style Promises in 913 bytes (gzip)
( A very small one promise library )
2、Promise/A+ What is the norm ?
Promise/A+ The purpose of the specification is to Promise Provide an interactive then function
The reason for the specification
1、 We don't know when an asynchronous request returns data , So we need some callback functions . But in some cases we need to return data , Then do some processing .
2、 When the operation we handle in an asynchronous callback is still asynchronous , This results in the nesting of asynchronous callbacks
It is in order to put an end to the above two situations , There's a community Promise/a+ standard
Content of specification
1、 Whatever you do, it returns a promise object , This object will have some properties and methods ( The effect is similar to jquery Chain programming in , Go back to yourself )
2、 This promise There are three states
- Unfulfilled( Hang in the air , The initial state )
- Fulfilled( Completed )
- Failed( Failure 、 Refuse )
3、 This promise Objects are used by then Method 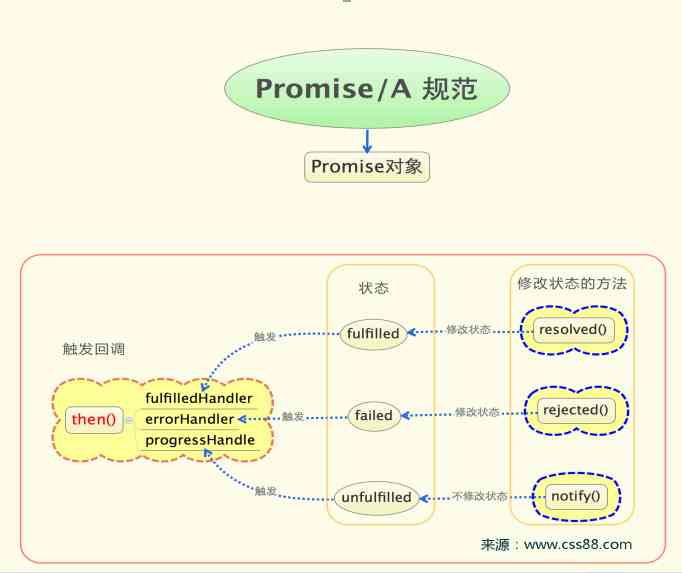
3、Polyfill What is it? ?
Polyfill It mainly smoothes the relationship between different browsers js Differences in implementation . such as ,html5 Of storage(session,local), Different browsers , Different versions , Some support , Some don't .Polyfill You can enable unsupported browsers to support Storage( The typical way is in IE Add... To the browser window.XMLHttpRequest , Internal implementation uses ActiveXObject.)
polyfill It's a piece of code ( Or plug-ins ), It provides features that developers want their browsers to support natively . The library first checks whether the browser supports a certain API, If it is not supported, the corresponding polyfill. Main features :
- Is a browser API Of Shim
- It's about browsers
- No new API, It's just API To implement the missing functions in
- Just import polyfill , It will work quietly
mention Polyfill, Have to mention shim,polyfill yes shim A kind of .
shim The concept of is better than polyfill Bigger , Can be polyfill Specifically compatible with browsers API Of shim .shim It's going to be different api Package it into a kind of , such as jQuery Of $.ajax Encapsulates the XMLHttpRequest and IE use ActiveXObject Way to create xhr object . It will be a new API Introduce into an old environment , And only by means of the old environment . To put it simply , If the browser X Support the functions specified in the standard , that polyfill You can make the browser Y Behavior and browser X equally .
Two 、Promiz How to use it? ?
bower install promiz --save<!-- Browser -->
<script src='promiz.js'></script>Commonly used API:
- new Promise(Function<resolve, reject>)
- Promise.reject({reason})
- Promise.resolve({value})
- promise.then({Function}, {Function})
- promise.catch({Function})
- Promise.all({iterable})
- Promise.race({iterable})
3、 ... and 、Promiz The source code parsing
promiz.js file :
This file contains an immediate function , This includes constructors Deferred, The final will be Deferred export , As node.js Library objects for , Or as global variables . Now look at the code in the file :
if (!global.setImmediate)
global.addEventListener('message', function (e) {
if (e.source == global){
if (isRunningTask)
nextTick(queue[e.data])
else {
isRunningTask = true
try {
queue[e.data]()
} catch (e) {}
delete queue[e.data]
isRunningTask = false
}
}
})The above code listens to message event , Execute asynchronous functions in the queue , among nextTick The method code is as follows , Mainly compatible with various browsers to implement asynchronous function
function nextTick(fn) {
if (global.setImmediate) setImmediate(fn)
// if inside of web worker If in Web Worker The following methods are used in
else if (global.importScripts) setTimeout(fn)
else {
queueId++
queue[queueId] = fn
global.postMessage(queueId, '*')
}
}The above code is mainly promiz adopt setImmediate、setTimeout and postMessage Three ways to execute asynchronous functions . If you want to execute a function asynchronously , The first way we'll think of it will be setTimeout, In order to avoid setTimeout Nesting may get stuck ui Thread situation , by setTimeout Set the minimum execution interval , Different browsers have different minimum execution intervals .chrome Next test setTimeout 0 The actual execution interval of is about 12ms about .
Want to execute a function asynchronously the fastest , have access to setImmediate Method , This method is more effective than setTimeout 0 Faster asynchronous execution , Execution time is closer to 0ms, But only IE Browser support .
In addition to using asynchronous functions , There are also ways to implement asynchronous calls . utilize onmessage: and iframe When communicating, we often use onmessage Method , But if the same window postMessage Give yourself , What will happen? ? In fact, it is also equivalent to executing an asynchronously function.
PostMessage yes H5 The new method in ,setTimeout Best compatibility , It can be used in a variety of scenarios , So in the code above you can use setTimeout Make the bottom of the bag , Ensure that all kinds of browsers can execute asynchronous functions normally .
Let's look at the constructor code :
function Deferred(resolver) {
'use strict'
if (typeof resolver != 'function' && resolver != undefined)
throw TypeError()
if (typeof this != 'object' || (this && this.then))
throw TypeError()
// states
// 0: pending
// 1: resolving
// 2: rejecting
// 3: resolved
// 4: rejected
var self = this,
state = 0,
val = 0,
next = [],
fn, er;
self['promise'] = self
...
}The constructor first stores Promise The state of ( use 0-4 It's five states )、Promise The success value or failure reason of 、 next Promise References to 、Promise Of then The success and failure callback functions in method .
self['resolve'] = function (v) {
fn = self.fn
er = self.er
if (!state) {
val = v
state = 1
nextTick(fire)
}
return self
}
self['reject'] = function (v) {
fn = self.fn
er = self.er
if (!state) {
val = v
state = 2
nextTick(fire)
}
return self
}After storing the data, I declare Promise Of resolve and reject function , In both functions, it changed state Value , And then through nextTick Methods the trigger fire Asynchronous call .
self['then'] = function (_fn, _er) {
if (!(this._d == 1))
throw TypeError()
var d = new Deferred()
d.fn = _fn
d.er = _er
if (state == 3) {
d.resolve(val)
}
else if (state == 4) {
d.reject(val)
}
else {
next.push(d)
}
return d
}
self['catch'] = function (_er) {
return self['then'](null, _er)
}The statement Promise Of then and catch Method , stay then Methods by judging state To determine the current Promise What method to carry out : If state Show Promise become resolved state , So do it immediately resolve, If state Show Promise become rejected state , So do it immediately reject, If neither is , Just put then The two parameters of the method are used as the new Promise Of resolve and reject Method , And return a new Promise.Promise Of catch Method by calling then Method , And set the first parameter to null Realization , namely Promise perform resolve after catch Methods do not process , however Promise perform reject after , Call the passed in _er Method to handle the error .
Here's how fire Method :
function fire() {
// check if it's a thenable
var ref;
try {
ref = val && val.then
} catch (e) {
val = e
state = 2
return fire()
}
thennable(ref, function () {
state = 1
fire()
}, function () {
state = 2
fire()
}, function () {
try {
if (state == 1 && typeof fn == 'function') {
val = fn(val)
}
else if (state == 2 && typeof er == 'function') {
val = er(val)
state = 1
}
} catch (e) {
val = e
return finish()
}
if (val == self) {
val = TypeError()
finish()
} else thennable(ref, function () {
finish(3)
}, finish, function () {
finish(state == 1 && 3)
})
})
}As you can see from the code ,fire It is mainly used to judge ref Is it a thenable object , And then it calls thenable function , Pass the 3 Callback functions . So let's see thennable What does the method do
// ref : reference to 'then' function Point to thenable Object's `then` function
// cb, ec, cn : successCallback, failureCallback, notThennableCallback
function thennable (ref, cb, ec, cn) {
if (state == 2) {
return cn()
}
if ((typeof val == 'object' || typeof val == 'function') && typeof ref == 'function') {
try {
// cnt protects against abuse calls from spec checker
var cnt = 0
ref.call(val, function (v) {
if (cnt++) return
val = v
cb()
}, function (v) {
if (cnt++) return
val = v
ec()
})
} catch (e) {
val = e
ec()
}
} else {
cn()
}
};stay thennable In the method , First judgement , If ref Of state The value is 2 That is to say Promise The state of is rejecting, Just do it directly cn Method , Direct delivery ref Of reject state . When ref No thennable Object time , It's also direct execution cn Method . When ref Of state It's not worth it 2, And ref yes thennable Object time , Through the variable cnt To record ref The state of , According to the state value to execute separately cb and ec Method , That is to say, separate execution ref Of resolve Methods and reject Method .
Let's introduce Deferred Of API:
Deferred.all = function (arr) {
if (!(this._d == 1))
throw TypeError()
if (!(arr instanceof Array))
return Deferred.reject(TypeError())
var d = new Deferred()
function done(e, v) {
if (v)
return d.resolve(v)
if (e)
return d.reject(e)
var unresolved = arr.reduce(function (cnt, v) {
if (v && v.then)
return cnt + 1
return cnt
}, 0)
if(unresolved == 0)
d.resolve(arr)
arr.map(function (v, i) {
if (v && v.then)
v.then(function (r) {
arr[i] = r
done()
return r
}, done)
})
}
done()
return d
}The code implements Deferred Of all Interface , This interface gives each of the arrays Promise All increase then Method , And pass cnt In the array of variable pairs Promise Of resolved Count the number of , When all the quantities become resolved Post state , perform resolve Method . When any one of them Promise become rejected state , perform reject Method .
Deferred.race = function (arr) {
if (!(this._d == 1))
throw TypeError()
if (!(arr instanceof Array))
return Deferred.reject(TypeError())
if (arr.length == 0)
return new Deferred()
var d = new Deferred()
function done(e, v) {
if (v)
return d.resolve(v)
if (e)
return d.reject(e)
var unresolved = arr.reduce(function (cnt, v) {
if (v && v.then)
return cnt + 1
return cnt
}, 0)
if(unresolved == 0)
d.resolve(arr)
arr.map(function (v, i) {
if (v && v.then)
v.then(function (r) {
done(null, r)
}, done)
})
}
done()
return d
}Promise Of race Interface and all Similar interface , Also by giving each of the arrays Promise All increase then Method , And pass cnt In the array of variable pairs Promise Of resolved Count the number of , The difference is race Method pairs will first become resolved State of Promise Conduct resolve.
Four 、 summary
Promiz The source code is concise and easy to read , It mainly contains a constructor to create Promise example , Instance implements the compatible execution of asynchronous functions , And defined Promise Of resolve、reject、all、race Such as the interface , Hundreds of lines of code solved the problem of calling back to hell , The structure and logic are clear .