当前位置:网站首页>C language uses random number to generate matrix to realize fast transposition of triples.
C language uses random number to generate matrix to realize fast transposition of triples.
2020-11-10 10:51:00 【osc_b9r67jnt】
Sparse matrix compression and transposition
1、 Random number generation matrix algorithm idea : Use time() Function to plant random numbers , Get the total number of rows of the matrix , The total number of columns , The number of nonzero elements . The values of total row number and total column number can be directly stored in triplet . After each generation of a non-zero row and column , Enter the size of nonzero by keyboard e; And store it in a two-dimensional array first a[][].
2、 The algorithm idea of compressing matrix to triple : After getting the matrix , Compress it into a triple table , The number of nonzero elements of a triple is initially 0, Because the same rows may appear in the process of generating random matrix 、 Column , Causes the nonzero elements of a matrix to be covered , So the specific number of nonzero elements in the matrix is the standard . ergodic matrix , If there are nonzero elements , The line mark of the element will be i And column labels j, Save triples , At the same time, the number of nonzero elements +1.
3、 The algorithm idea of printing matrix : Print the elements of each line first , If i,j And in the triple table i,j Match , Then print the elements , Otherwise print 0.
4、 The idea of fast transposition of triples : Find the transposed matrix M The number of nonzero elements in each column of , Then, the first nonzero element of each column is obtained T.data Where it should be in , So we need two auxiliary vectors :num And copt. First of all T.mu=M.nu、T.nu=M.mu、T.tu=M.tu. If T.tu It's not equal to 0, Then we first find the number of nonzero elements in each column num[col],col from 1 To M.nu; Find the position again copt[col],copt[col]=copt[col-1]+num[col-1] ,col from 2 To M.nu,copt[1]=1; Finally, transpose , Make M Of i,j swap , Exchange one element at a time ++copt[col].
5、 The specific implementation code is as follows :
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<time.h>
#define MAXSIZE 200
#define OK 1
#define FALSE 0
#define OVERFLOW -2
#define ERROR 0
typedef int Status;
typedef int ElemType;
typedef struct
{
int i,j;
ElemType e;
}Triple;
typedef struct
{
Triple data[MAXSIZE+1];
int mu,nu,tu;
}TSMatrix;
Status CreateMatrix(TSMatrix *M)
{
int i,j,n,k; // That's ok , Column , The number of nonzero elements
int a[50][50]={
0}; // Storage matrix , The initial value is 0
ElemType e;
printf(" The number of rows and columns of this sparse matrix are generated by random numbers !\n");
srand((unsigned)time(NULL) + (unsigned)rand()); // With time() Generate random numbers for seeds
(*M).mu=rand()%10+6; // Random row size , The remainder is a definite range ,mu stay (6~15) Between
(*M).nu=rand()%10+7; // Random column size
k=rand()%10+6; // The number of random nonzero elements
printf(" The number of rows of the sparse matrix is %d, The number of columns is %d, The number of nonzero elements is %d.",(*M).mu,(*M).nu,k);
(*M).data[0].i=0;
for(n = 1; n <= k; n++) // Generating random number matrix
{
i=rand()%(*M).mu+1;
j=rand()%(*M).nu+1;
printf(" Please enter... In line order %d A non-zero element , That's ok %d, Column %d, Element value :\n",n,i,j);
scanf("%d",&e);
a[i][j]=e;
}
(*M).tu=1;
for(i=1;i<=(*M).mu;i++) // Store triples in the main order of behavior
{
for(j=1;j<=(*M).nu;j++)
{
if(a[i][j]!=0)
{
(*M).data[M->tu].i = i; // Line subscript
(*M).data[M->tu].j = j; // Column subscript
(*M).data[M->tu].e = a[i][j]; // The value of the subscript
M->tu++;
}
}
}
M->tu--;
return OK;
}
Status PrintMatrix(TSMatrix M)
{
int i,j,n=1;
printf("\n\n");
for(i=1;i<=M.mu;i++)
{
for(j=1;j<=M.nu;j++)
{
if(M.data[n].i==i&&M.data[n].j==j)
{
printf("%4d",M.data[n].e);
n++;
}
else
printf("%4d",0);
}
printf("\n");
}
}
Status FastTransposeSMatrix(TSMatrix M,TSMatrix *T)
{
int col,t,p,q;
int *num,*copt;
num=(int*)malloc((M.nu+1)*sizeof(int)); // to num Allocate memory space ; The size is M Columns of +1,num[1] Start
copt=(int*)malloc((M.nu+1)*sizeof(int)); //copt Indicates that the first nonzero element of the column is in T.data Position in ,copt Size and num equal
T->mu=M.nu; T->nu=M.mu; T->tu=M.tu; //T The number of rows is equal to M Columns of , The number of columns equals the number of rows , The number of nonzero elements is equal
if(T->tu) // Non empty
{
for(col=1;col<=M.nu;++col)
num[col]=0; // Reset operation
for(t=1;t<=M.tu;++t)
++num[M.data[t].j]; // seek M The number of nonzero elements in each column of
copt[1]=1; //M The first nonzero element of the first column of is in T The first position
for(col=2;col<=M.nu;++col)
copt[col]=copt[col-1]+num[col-1]; // Accumulation operation , More complicated , Find the first nonzero element of each column in T.data Position in
for(p=1;p<=M.tu;++p)
{
col=M.data[p].j; q=copt[col];
T->data[q].i=M.data[p].j; // Transpose operation
T->data[q].j=M.data[p].i;
T->data[q].e=M.data[p].e;
++copt[col]; // The position has been used , Counting plus one
}
}
return OK;
}
void main()
{
TSMatrix M,T;
CreateMatrix(&M);
printf(" The original matrix is as follows :\n");
PrintMatrix(M); // Print M
FastTransposeSMatrix(M,&T);
printf(" The transpose matrix is as follows :\n");
PrintMatrix(T); // Print T
}
6、 On the number of fans 50, Next time, add the flow chart , It's not easy to create , Thank you for your support .
版权声明
本文为[osc_b9r67jnt]所创,转载请带上原文链接,感谢
边栏推荐
- 设计 API 时通过 POST 获取数据需要注意哪些问题
- Centos7 local source Yum configuration
- One task is not enough, but another valuetask. I'm really confused!
- I have a crossed translation tool in my hand!
- Summary of basic concepts and common operations of elasticsearch cluster (recommended Collection)
- leetcode1-两数之和
- 微服务授权应该怎么做?
- 《Python Cookbook 3rd》笔记(2.4):字符串匹配和搜索
- [C.NET] 11: the most basic thread knowledge
- 2020-11-07
猜你喜欢
express -- 学习笔记(慕课)
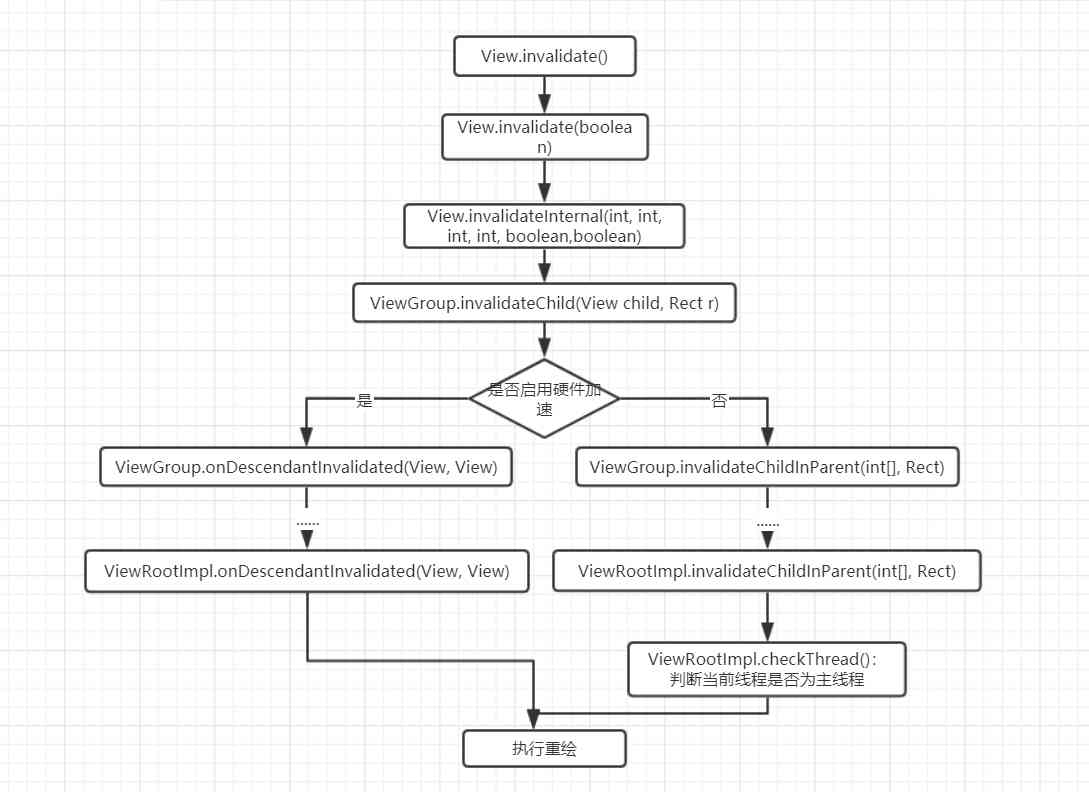
子线程调用invalidate()产生“Only the original thread that created a view hierarchy can touch its views.”原因分析

CSDN bug10: to be added
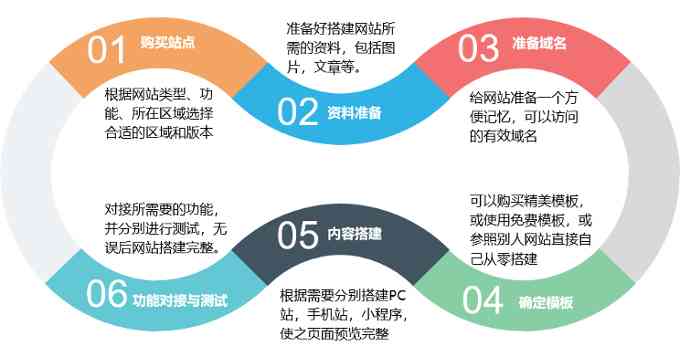
Do not understand the code, can type can build a station? 1111 yuan gift bag to help you with one stop!

Getiservicemanager () source code analysis
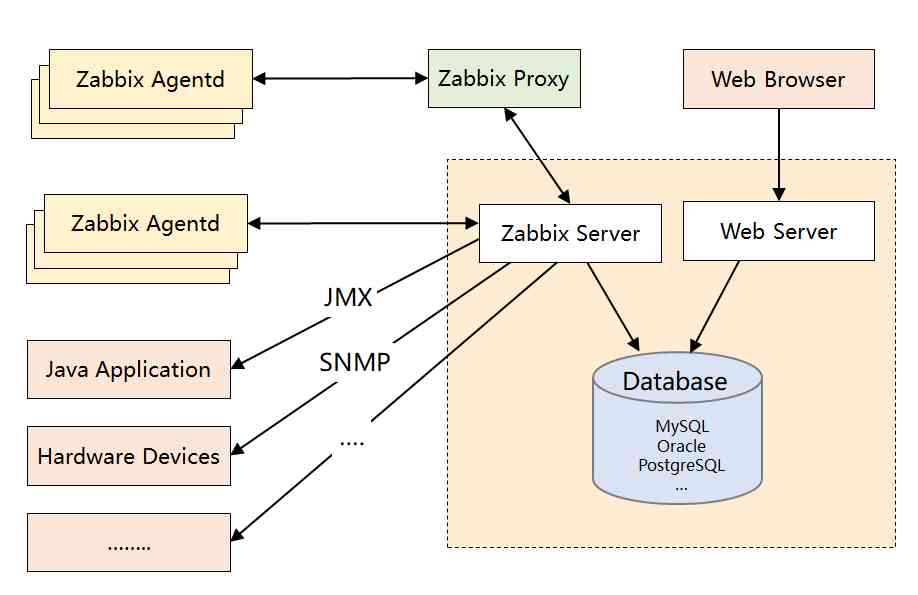
监控系统选型,这篇不可不读!

GNU assembly language uses inline assembly to extend ASM
网络时间服务器(医院时钟系统)相关问题汇总

ASP.NET Core框架揭秘[博文汇总

A professional tour -- a quick tour of GitHub hot spots Vol.45
随机推荐
基于FPGA的MCP4725驱动程序
Centos7 Rsync + crontab scheduled backup
如何更好地理解中间件和洋葱模型
用例子理解递归
计算机专业的学生要怎样做才能避免成为低级的码农?
What should be paid attention to when designing API to get data through post
csdn bug1:待加
Magicodes.IE 3.0重磅设计畅谈
TCP性能分析与调优策略
Do not understand the code, can type can build a station? 1111 yuan gift bag to help you with one stop!
STATISTICS STATS 380
Sign in with apple
CCR coin robot: novel coronavirus pneumonia has accelerated the interest of regulators in CBDC.
ASP.NET Core framework revealed
Bartender2021实现安全远程标签打印,年终全新发布
Centos7 local source Yum configuration
How can computer major students avoid becoming low-level code farmers?
子线程调用invalidate()产生“Only the original thread that created a view hierarchy can touch its views.”原因分析
C++ 标准库头文件
自定义注解!绝对是程序员装逼的利器!!