当前位置:网站首页>LeetCode_ Double pointer_ Medium_ 61. rotating linked list
LeetCode_ Double pointer_ Medium_ 61. rotating linked list
2022-07-06 19:29:00 【Old street of small town】
1. subject
Give you a list of the head node head , Rotate the list , Move each node of the list to the right k A place .
Example 1: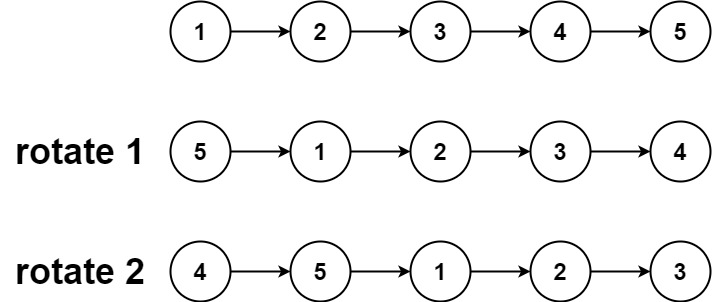
Input :head = [1,2,3,4,5], k = 2
Output :[4,5,1,2,3]
Example 2: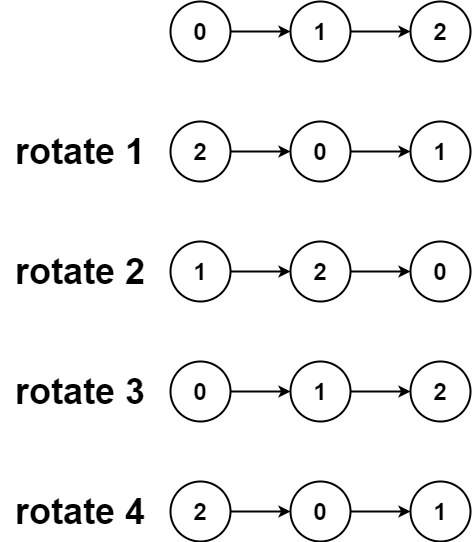
Input :head = [0,1,2], k = 4
Output :[2,0,1]
Tips :
The number of nodes in the linked list is in the range [0, 500] Inside
-100 <= Node.val <= 100
0 <= k <= 2 * 109
source : Power button (LeetCode)
link :https://leetcode.cn/problems/rotate-list
2. Ideas
(1) Double pointer
See the comments in the following code for the detailed analysis process .
3. Code implementation (Java)
// Ideas 1———— Double pointer
/** * Definition for singly-linked list. * public class ListNode { * int val; * ListNode next; * ListNode() {} * ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; } * ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; } * } */
class Solution {
public ListNode rotateRight(ListNode head, int k) {
// Consider special circumstances
if (k == 0 || head == null || head.next == null) {
return head;
}
// Calculate the length of the list
int length = 0;
ListNode aux = head;
while (aux != null) {
aux = aux.next;
length++;
}
// When k > length when , Its rotation results are consistent with k = k % length equally
k = k % length;
if (k == 0) {
// k % length If it is equal to 0, shows length yes k Integer multiple , After the rotation, the result is the same as the original , So go straight back to head
return head;
}
/* set up n = length V1 -> V2 -> ... -> V(n-k-1) -> V(n-k) -> ... -> Vn -> null Move each node of the list to the right k After two positions , obtain : V(n-k) -> ... -> Vn -> V1 -> V2 -> ... -> V(n-k-1) -> null So you just need to find the node first V(n-k-1)、V(n-k) as well as Vn, Then make V(n-k-1).next = null Vn.next = V1( namely head) Finally back to V(n-k) that will do V(n-k-1)、V(n-k) as well as Vn Corresponding to lastNode、newHead And the last while At the end of the cycle aux */
aux = head;
ListNode lastNode = head;
int tmp = length - k;
while (tmp > 0) {
aux = aux.next;
if (tmp != 1) {
lastNode = lastNode.next;
}
tmp--;
}
lastNode.next = null;
ListNode newHead = aux;
while (aux.next != null) {
aux = aux.next;
}
aux.next = head;
return newHead;
}
}
边栏推荐
- 利用 clip-path 绘制不规则的图形
- map的使用(列表的数据赋值到表单,json逗号隔开显示赋值)
- 五金机电行业供应商智慧管理平台解决方案:优化供应链管理,带动企业业绩增长
- Solution of commercial supply chain management platform for packaging industry: layout smart supply system and digitally integrate the supply chain of packaging industry
- [translation] a GPU approach to particle physics
- 黑馬--Redis篇
- 零基础入门PolarDB-X:搭建高可用系统并联动数据大屏
- ROS自定义消息发布订阅示例
- 接雨水问题解析
- GCC【7】- 编译检查的是函数的声明,链接检查的是函数的定义bug
猜你喜欢

黑马--Redis篇
Detailed idea and code implementation of infix expression to suffix expression

Black Horse - - Redis Chapter
Pychrm Community Edition calls matplotlib pyplot. Solution of imshow() function image not popping up
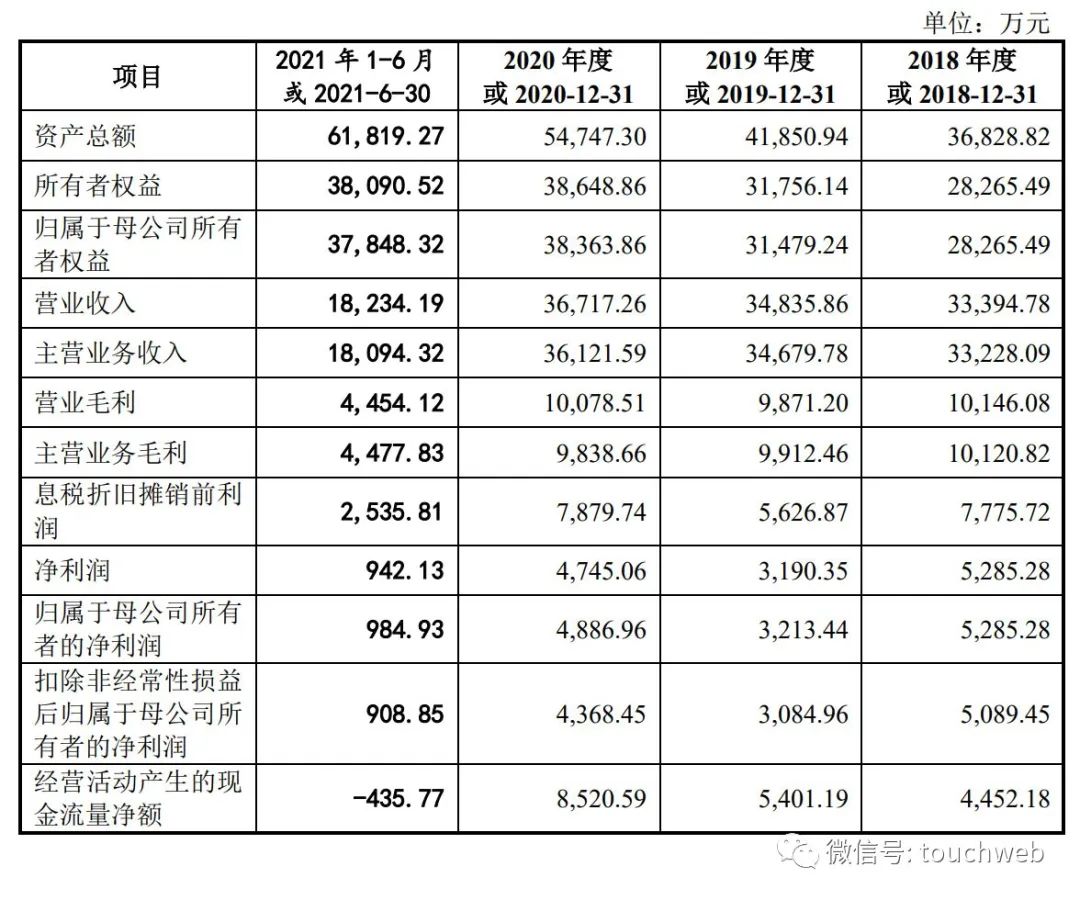
Xingnuochi technology's IPO was terminated: it was planned to raise 350million yuan, with an annual revenue of 367million yuan
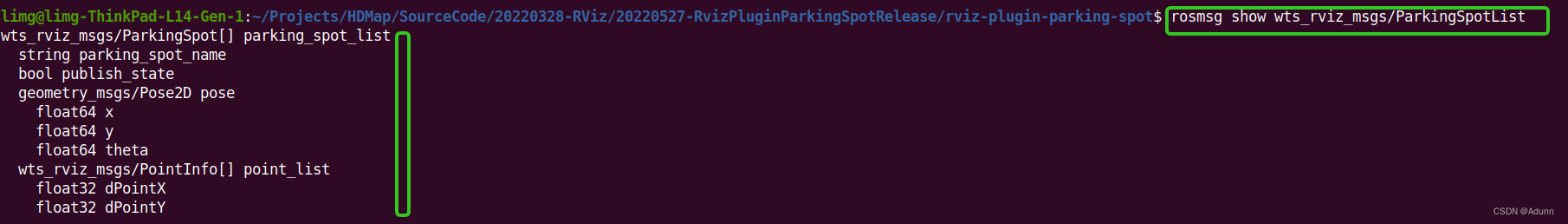
ROS自定义消息发布订阅示例

Don't miss this underestimated movie because of controversy!

五金机电行业智能供应链管理系统解决方案:数智化供应链为传统产业“造新血”

思維導圖+源代碼+筆記+項目,字節跳動+京東+360+網易面試題整理

Synchronous development of business and application: strategic suggestions for application modernization
随机推荐
系统性详解Redis操作Hash类型数据(带源码分析及测试结果)
Black Horse - - Redis Chapter
Low CPU load and high loadavg processing method
MRO工业品企业采购系统:如何精细化采购协同管理?想要升级的工业品企业必看!
R language ggplot2 visualization: use ggviolin function of ggpubr package to visualize violin diagram
Excel 中VBA脚本的简单应用
全套教学资料,阿里快手拼多多等7家大厂Android面试真题
LeetCode-1279. Traffic light intersection
反射及在运用过程中出现的IllegalAccessException异常
LeetCode_格雷编码_中等_89.格雷编码
凤凰架构3——事务处理
学习探索-函数防抖
【翻译】云原生观察能力微调查。普罗米修斯引领潮流,但要了解系统的健康状况仍有障碍...
MATLAB中deg2rad和rad2deg函数的使用
受益匪浅,安卓面试问题
Use of map (the data of the list is assigned to the form, and the JSON comma separated display assignment)
[translation] a GPU approach to particle physics
【计算情与思】扫地僧、打字员、信息恐慌与奥本海默
php+redis实现超时取消订单功能
C # - realize serialization with Marshall class