当前位置:网站首页>C language - stack
C language - stack
2022-07-04 10:24:00 【sqjddb】
Definition of stack
Stack (stack) Also known as the stack , It's a limitation Insert and delete only at the end of the table Operation of the The linear table
This end is called To the top of the stack , The other end is called At the bottom of the stack . The data elements in the stack comply with Last in, first out Principles .
To a stack Insert The new element is also called Into the stack 、 Push or push , Make it the new top element
From a stack Delete Elements are also called Out of stack or out of stack .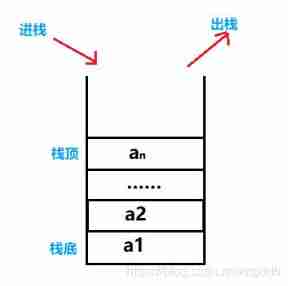
C Language implementation stack
analysis :
You can use arrays or linked lists to achieve , But the cost of inserting data into the tail of the array is relatively small . The complete procedure is as follows :
The header file
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdbool.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<assert.h>
typedef int STDatatype;
typedef struct Stack
{
STDatatype* p;
int top;
int capacity;
}ST;
// Initialization stack
void StackInit(ST* ps);
// Free up stack space
void StackDestroy(ST* ps);
// Element stack
void StackPush(ST* ps, STDatatype x);
// Out of the stack
void StackPop(ST* ps);
// Sentenced to empty
bool StackEmpty(ST* ps);
// Calculate the number of elements in the stack
int StackSize(ST* ps);
// Back to top of stack element
STDatatype StackTop(ST* ps);
Function implementation file
#include "Stack.h"
void StackInit(ST* ps)
{
assert(ps);
ps->p = NULL;
ps->top = 0;
ps->capacity = 0;
}
void StackDestroy(ST* ps)
{
assert(ps);
if (ps->p)// If p by NULL, Can not be free
{
free(ps->p);
}
ps->p= NULL; //free After the empty , Avoid wild pointer problems
ps->top = 0;
ps->capacity = 0;
}
void StackPush(ST* ps, STDatatype x)
{
assert(ps);
// Check if there's enough space , Not enough capacity
if (ps->top == ps->capacity)
{
int newcapacity = ps->capacity == 0 ? 4 : ps->capacity * 2;
STDatatype* tmp = realloc(ps->p, sizeof(STDatatype)*newcapacity);
ps->p= tmp;
ps->capacity = newcapacity;
}
ps->p[ps->top] = x;
ps->top++;
}
bool StackEmpty(ST* ps)
{
assert(ps);
return ps->top == 0;
}
void StackPop(ST* ps)
{
assert(ps);
assert(!StackEmpty(ps));
ps->top--;//-> Priority over --
}
int StackSize(ST* ps)
{
assert(ps);
return ps->top;
}
STDatatype StackTop(ST* ps)
{
assert(ps);
assert(!StackEmpty(ps));
return ps->p[ps->top - 1];
}
Main function test file
#include "Stack.h"
int main()
{
ST st;
StackInit(&st);
StackPush(&st, 1);
StackPush(&st, 2);
StackPush(&st, 3);
printf("%d ", StackTop(&st));
StackPop(&st);
printf("%d ", StackTop(&st));
StackPop(&st);
StackPush(&st, 4);
StackPush(&st, 5);
while (!StackEmpty(&st))
{
printf("%d ", StackTop(&st));
StackPop(&st);
}
printf("\n");
StackDestroy(&st);
return 0;
}
Running results 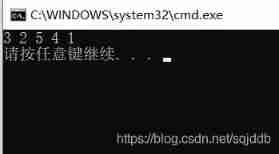
Classical bracket matching problem


Ideas
Traversal string , If the current character is an open parenthesis , Push , Wait for the right parenthesis to determine whether it matches , If it's right bracket , Match the character at the top of the stack with the current character , Stack top element out of stack , Make the character at the top of the stack become an earlier left parenthesis , It is convenient to match with the more backward right parenthesis . Specific ideas and details are shown in the following program notes
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdbool.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<assert.h>
// First, implement a stack
typedef int STDatatype;
typedef struct Stack
{
STDatatype* p;
int top;
int capacity;
}ST;
void StackPush(ST* ps, STDatatype x)
{
assert(ps);
// Check if there's enough space , Not enough capacity
if (ps->top == ps->capacity)
{
int newcapacity = ps->capacity == 0 ? 4 : ps->capacity * 2;
STDatatype* tmp = realloc(ps->p, sizeof(STDatatype)*newcapacity);
ps->p = tmp;
ps->capacity = newcapacity;
}
ps->p[ps->top] = x;
ps->top++;
}
void StackInit(ST* ps)
{
assert(ps);
ps->p = NULL;
ps->top = 0;
ps->capacity = 0;
}
void StackDestroy(ST* ps)
{
assert(ps);
if (ps->p)// If p by NULL, Can not be free
{
free(ps->p);
}
ps->p = NULL; //free After the empty , Avoid wild pointer problems
ps->top = 0;
ps->capacity = 0;
}
bool StackEmpty(ST* ps)
{
assert(ps);
return ps->top == 0;
}
void StackPop(ST* ps)
{
assert(ps);
assert(!StackEmpty(ps));
ps->top--;//-> Priority over --
}
STDatatype StackTop(ST* ps)
{
assert(ps);
assert(!StackEmpty(ps));
return ps->p[ps->top - 1];
}
bool isValid(char * s){
ST st;
StackInit(&st);
bool matchflag = true;
while (*s)
{
if (*s == '{' || *s == '[' || *s == '(')
{
StackPush(&st, *s);// If it's left parenthesis , Push
s++;
}
else
{
// The program comes to this , The current character is the right bracket
// If there are no elements in the stack , Indicates that there is no left parenthesis matching the current right parenthesis
if (StackEmpty(&st))
{
matchflag = false;
break;
}
// If there are elements in the stack , Take it out to match the current right parenthesis
char ch = StackTop(&st);
// The matched left parenthesis should be out of the stack
StackPop(&st);
// See if it matches
if (
(*s == '}'&&ch != '{') ||
(*s == ']'&&ch != '[') ||
(*s == ')'&&ch != '(')
)
{
matchflag = false;
break;
}
else
{
s++;// If the match , Continue traversing backwards
// See whether the following right parenthesis matches the element at the top of the stack
// It makes perfect use of the characteristics of stack first in and last out
}
}
}
if (matchflag == true)
{
matchflag = StackEmpty(&st);
// If the characters are traversed and the stack is not empty , It shows that the left parenthesis in the stack is lonely , Mismatch
}
StackDestroy(&st);
return matchflag;
}
int main()
{
// Test several examples
char *p0 = "{[]}";
printf("%d\n", isValid(p0));
char *p1= "()";
printf("%d\n", isValid(p1));
char *p2 = "()[]{}";
printf("%d\n", isValid(p2));
char *p3 = "(]";
printf("%d\n", isValid(p3));
char *p4 = "([)]";
printf("%d\n", isValid(p4));
}
Running results :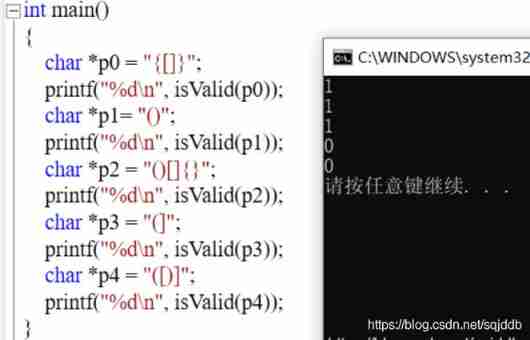
边栏推荐
- Golang defer
- Realsense d435 d435i d415 depth camera obtains RGB map, left and right infrared camera map, depth map and IMU data under ROS
- Summary of reasons for web side automation test failure
- Idea SSH channel configuration
- From programmers to large-scale distributed architects, where are you (2)
- If the uniapp is less than 1000, it will be displayed according to the original number. If the number exceeds 1000, it will be converted into 10w+ 1.3k+ display
- System. Currenttimemillis() and system Nanotime (), which is faster? Don't use it wrong!
- Exercise 7-8 converting strings to decimal integers (15 points)
- Go context basic introduction
- View CSDN personal resource download details
猜你喜欢

Application of safety monitoring in zhizhilu Denggan reservoir area
【Day2】 convolutional-neural-networks

BGP ---- border gateway routing protocol ----- basic experiment

转载:等比数列的求和公式,及其推导过程
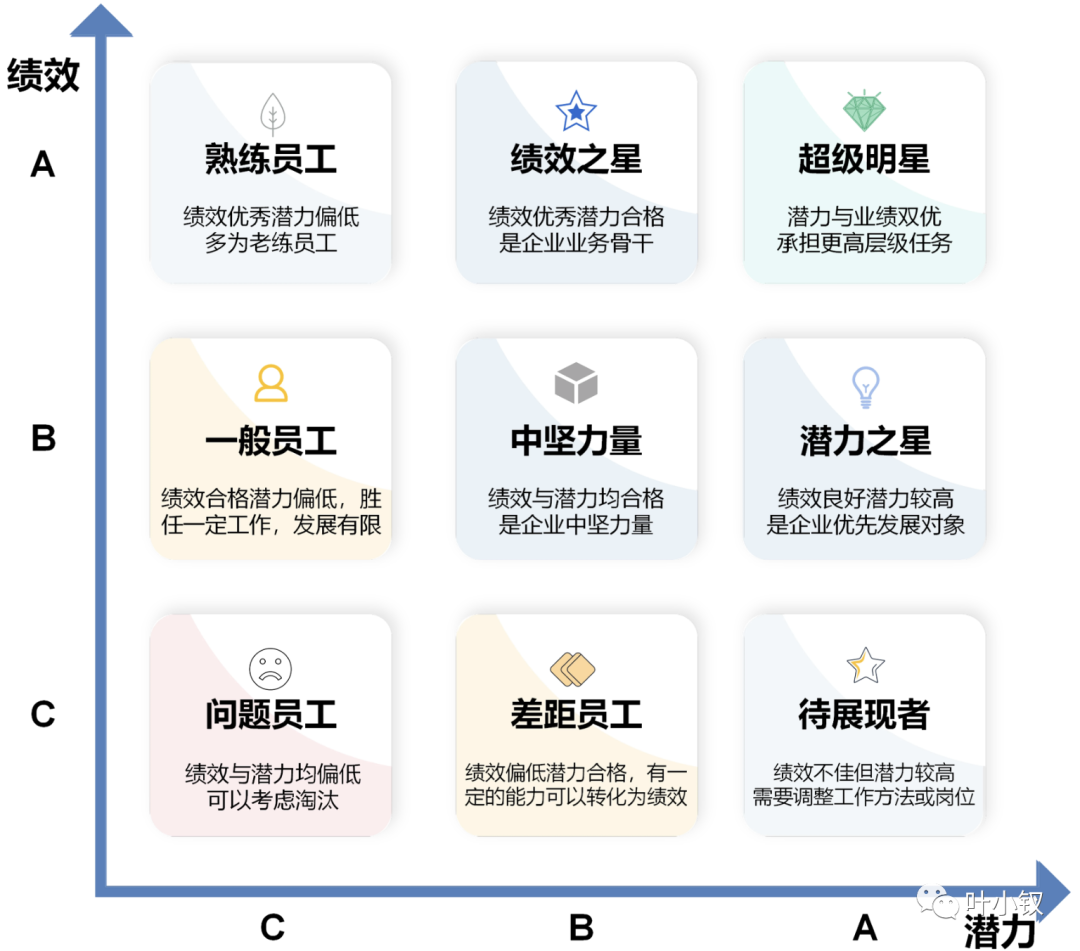
Advanced technology management - how to design and follow up the performance of students at different levels
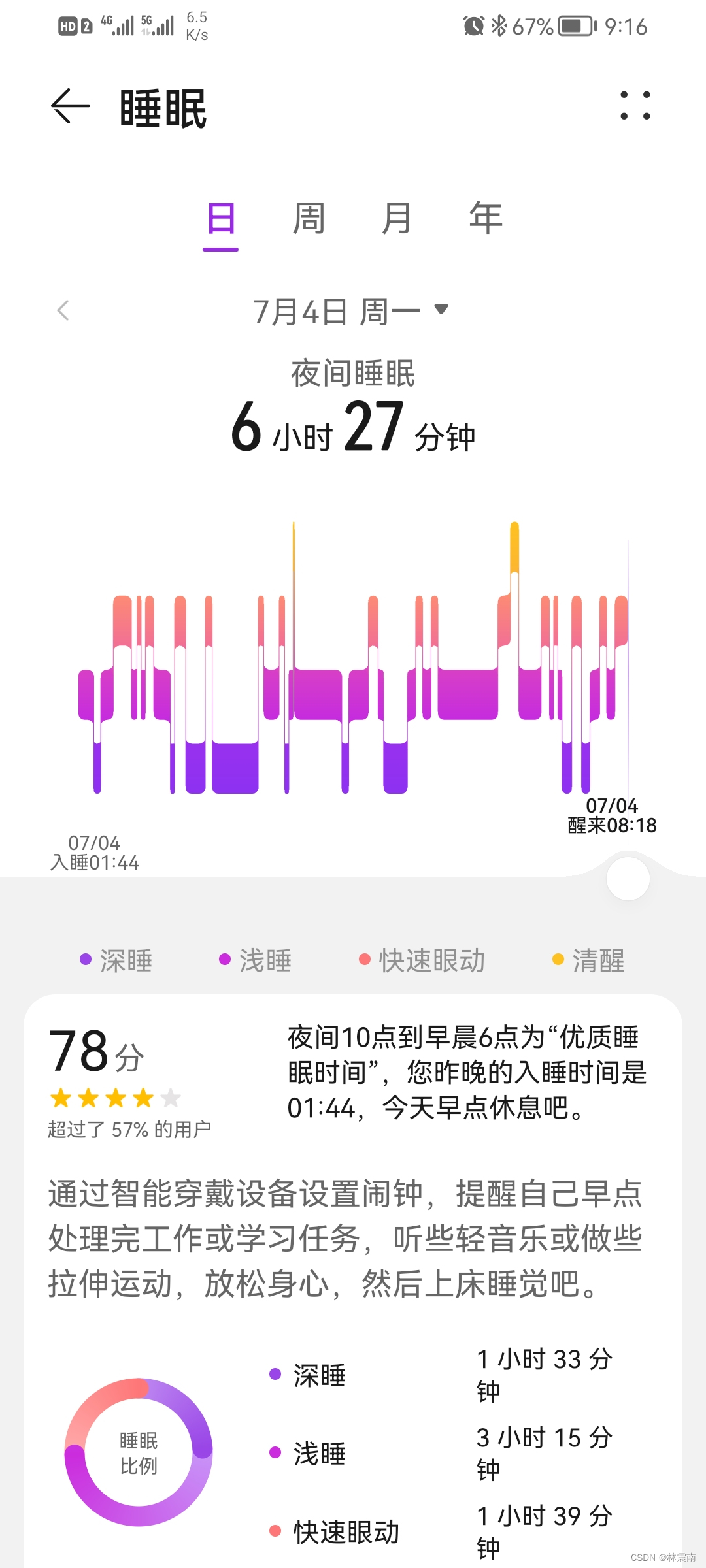
Today's sleep quality record 78 points
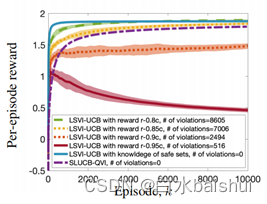
基于线性函数近似的安全强化学习 Safe RL with Linear Function Approximation 翻译 2
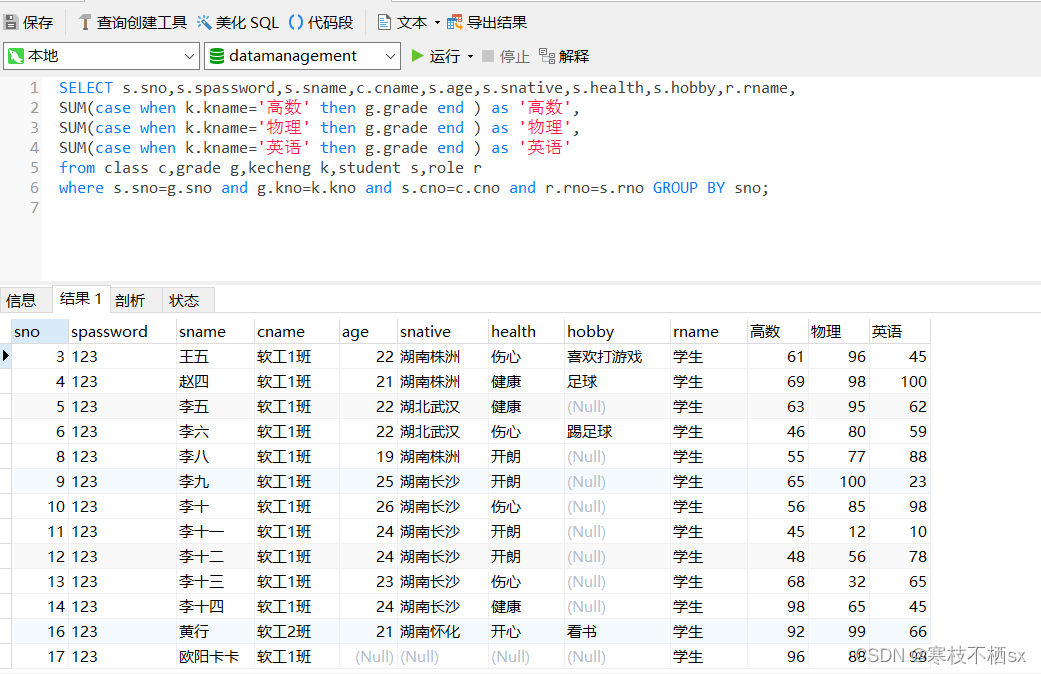
SQL replying to comments
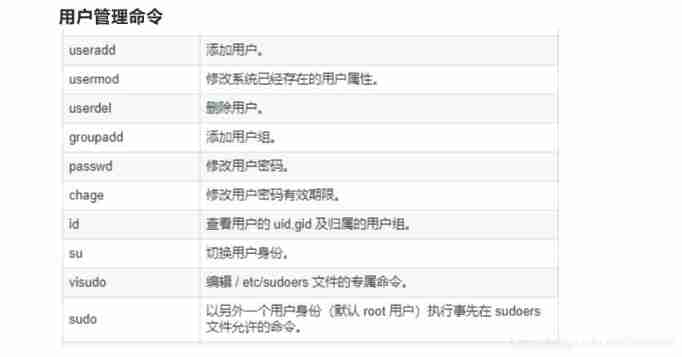
Devop basic command
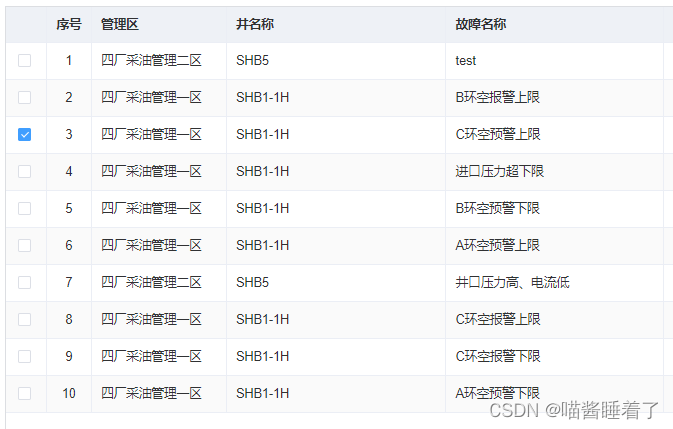
El Table Radio select and hide the select all box
随机推荐
Talk about scalability
Two way process republication + routing policy
Some summaries of the third anniversary of joining Ping An in China
如果不知道這4種緩存模式,敢說懂緩存嗎?
【FAQ】华为帐号服务报错 907135701的常见原因总结和解决方法
[FAQ] summary of common causes and solutions of Huawei account service error 907135701
The future education examination system cannot answer questions, and there is no response after clicking on the options, and the answers will not be recorded
If the uniapp is less than 1000, it will be displayed according to the original number. If the number exceeds 1000, it will be converted into 10w+ 1.3k+ display
2021-08-10 character pointer
Exercise 9-1 time conversion (15 points)
PHP code audit 3 - system reload vulnerability
Hands on deep learning (44) -- seq2seq principle and Implementation
uniapp 处理过去时间对比现在时间的时间差 如刚刚、几分钟前,几小时前,几个月前
入职中国平安三周年的一些总结
Lavel document reading notes -how to use @auth and @guest directives in lavel
OSPF comprehensive experiment
Hlk-w801wifi connection
How can Huawei online match improve the success rate of player matching
Use the data to tell you where is the most difficult province for the college entrance examination!
Si vous ne connaissez pas ces quatre modes de mise en cache, vous osez dire que vous connaissez la mise en cache?