当前位置:网站首页>Deep understanding of ThreadLocal
Deep understanding of ThreadLocal
2022-07-02 17:53:00 【Change with affection】
One 、ThreadLocal
ThreadLocal It's called a thread variable , intend ThreadLocal The variables filled in belong to the current thread , This variable is isolated from other threads
Because of every Thread It has its own instance copy , And this copy can only be made by the current Thread Use . This is also ThreadLocal The origin of the name .
Since each Thread Have your own instance copy , And others Thread inaccessible , Then there is no problem of sharing among multiple threads .
ThreadLocal Provides a thread local instance . It differs from ordinary variables in that , Each thread using this variable initializes a completely independent instance copy .ThreadLocal Variables are usually private static modification . When a thread ends , All that it uses ThreadLocal Relative instance copies can be recycled .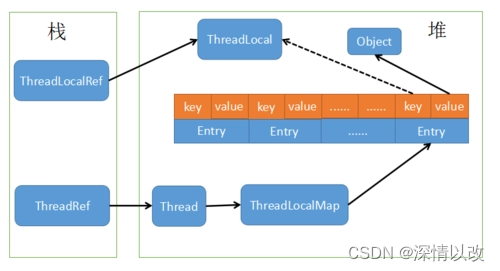
public class SequenceNumber {
//① By anonymous inner class override ThreadLocal Of initialValue() Method , Specify the initial value
private static ThreadLocal<Integer> seqNum = new ThreadLocal<Integer>(){
public Integer initialValue(){
return 0;
}
};
//② Get the next sequence value
public int getNextNum(){
seqNum.set(seqNum.get()+1);
return seqNum.get();
}
public static void main(String[ ] args)
{
SequenceNumber sn = new SequenceNumber();
//③ 3 Thread sharing sn, Each generates a serial number
TestClient t1 = new TestClient(sn);
TestClient t2 = new TestClient(sn);
TestClient t3 = new TestClient(sn);
t1.start();
t2.start();
t3.start();
}
private static class TestClient extends Thread
{
private SequenceNumber sn;
public TestClient(SequenceNumber sn) {
this.sn = sn;
}
public void run() {
//④ Each thread plays 3 Sequence values
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++) {
System.out.println("thread["+Thread.currentThread().getName()+ "] sn["+sn.getNextNum()+"]");
}
}
}
}
Two 、ThreadLocal And Synchronized The difference between
ThreadLocal In fact, it is a variable bound to the thread .ThreadLocal and Synchonized Are used to solve multithreaded concurrent access .
however ThreadLocal And synchronized There are essential differences :
1、Synchronized For data sharing between threads , and ThreadLocal It is used for data isolation between threads .
2、Synchronized It's using the lock mechanism , Make variables or code blocks accessible to only one thread at a time . and ThreadLocal A copy of the variable is provided for each thread , So that each thread at a certain time access is not the same object , This isolates multiple threads from sharing data .
and Synchronized But the opposite is true , It is used to obtain data sharing when communicating among multiple threads .
In a word, understand ThreadLocal,threadlocl Is a property in the current thread ThreadLocalMap One of the sets Entry Of key value Entry(threadlocl,value), Although different threads threadlocal This key The value is the same , But what different threads have ThreadLocalMap It's unique , That is, different threads share the same ThreadLocal(key) Corresponding to the stored value (value) Dissimilarity , Thus, the purpose of variable isolation between threads is achieved , But in the same thread, this value The variable address is the same .
3、 ... and 、ThreadLocal The core approach
ThreadLocal in set Method
ThreadLocal.ThreadLocalMap threadLocals = null;
public void set(T value) {
// Returns a reference to the currently executing thread object .
Thread t = Thread.currentThread();
// To obtain and ThreadLocal Associated mapping ,InheritableThreadLocal<T> extends ThreadLocal<T> Rewrote getMap() Method
ThreadLocalMap map = getMap(t);
if (map != null)
map.set(this, value);
else
//InheritableThreadLocal Rewritten in createMap-> Initialize the ThreadLocalMap->ThreadLocal.ThreadLocalMap
createMap(t, value);
}
ThreadLocal in get Method
public T get() {
Thread t = Thread.currentThread();
ThreadLocalMap map = getMap(t);
if (map != null) {
ThreadLocalMap.Entry e = map.getEntry(this);
if (e != null) {
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
T result = (T)e.value;
return result;
}
}
// Returns the initialized value null
return setInitialValue();
}
ThreadLocal in remove Method
public void remove() {
ThreadLocalMap m = getMap(Thread.currentThread());
if (m != null)
m.remove(this);
remove Method , Direct will ThrealLocal The corresponding value is different from the current value Thread Medium ThreadLocalMap Delete in . Why delete , This involves memory leaks .
ThreadLocal in initialValue Method
protected T initialValue() {
return null;
}
Returns the initial value of the thread's local variable , If you use protected Restrict the methods of the parent class , Then the method is only internal to the parent and child classes ( That is, in the code that defines the parent and child classes ) You can call , So this method is obviously designed for subclass coverage . This method is a delay call method , On thread 1 Secondary call get() or set(Object) Execution only , And only execute 1 Time .ThreadLocal The default implementation in returns a null.
Entry
ThreadLocalMap yes ThreadLocal The inner static class of , And its composition mainly uses Entry To save the data , And it's an inherited weak reference , So when value=null It means that the key is no longer referenced and can be garbage collected . stay Entry For internal use ThreadLocal As key,
static class Entry extends WeakReference<ThreadLocal<?>> {
/** The value associated with this ThreadLocal. */
Object value;
Entry(ThreadLocal<?> k, Object v) {
super(k);
value = v;
}
}

actually ThreadLocalMap Used in key by ThreadLocal The weak references , The characteristic of weak citation is , If this object has only weak references , Then the next time the garbage is recycled, it will be cleaned up .
So if ThreadLocal Without strong external reference , It's going to be cleaned up when it's recycled , thus ThreadLocalMap Use this ThreadLocal Of key It's going to be cleaned up . however ,value Is a strong quote , Will not be cleaned up , In this way, there will be key by null Of value.
ThreadLocal In fact, it is a variable bound to the thread , So there will be a problem : If not ThreadLocal Delete variables in (remove) Or replace , Its life cycle will coexist with threads . Generally, thread reuse is used for thread management in thread pool , Threads in the thread pool are hard to end or never end , This will mean that the thread duration will be unpredictable , Even with JVM The life cycle of . For example , If ThreadLocal It directly or indirectly wraps collection classes or complex objects , At the same time ThreadLocal After taking the object out of the , Then operate on the content , Then the space occupied by internal collection classes and complex objects may continue to expand .
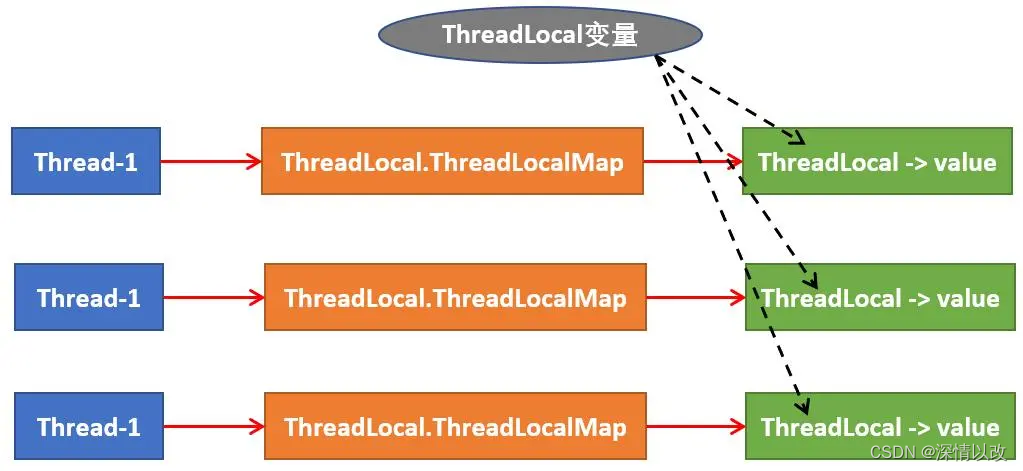
Four 、ThreadLocal And Thread,ThreadLocalMap The relationship between
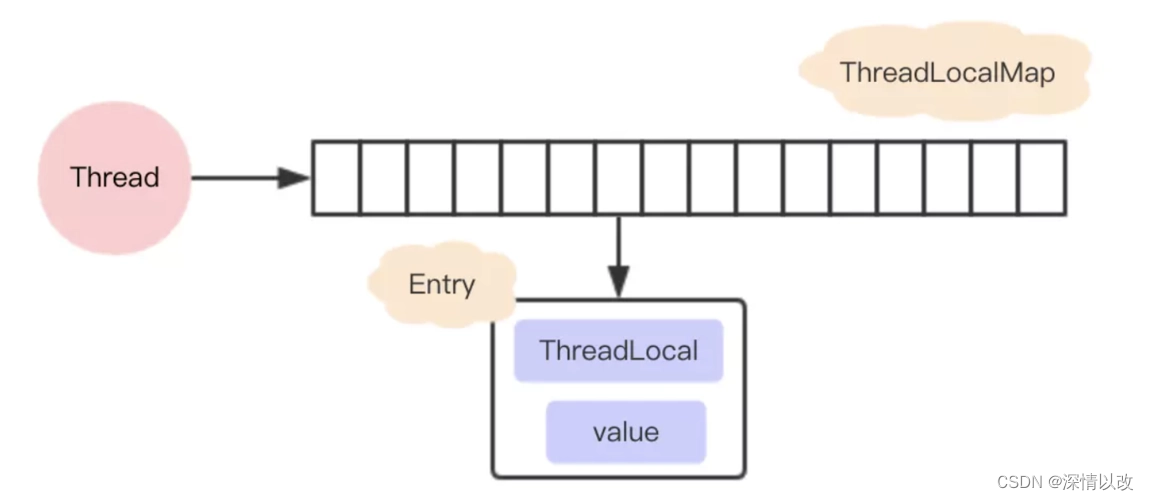
(1) Every Thread There is a... Inside the thread Map (ThreadLocalMap)
( 2 ) Map Inside the store ThreadLocal object (key ) And a variable copy of the thread ( value )
( 3 ) Thread Inside Map By ThreadLocal Maintenance of , from ThreadLocal Responsible for providing map Get and set the variable star value of the thread .
( 4 ) For different threads , Every time you get a copy value , Other threads cannot get the copy value of the current thread , It forms the isolation of copies , Mutual interference .
5、 ... and 、ThreadLocal Common use scenarios
1、 Each thread needs to have its own instance
2、 Instances need to be shared in multiple methods , But don't want to be shared by multiple threads
For the first point , Each thread has its own instance , There are many ways to achieve it . For example, you can build a separate instance inside a thread .ThreadLoca It can meet this demand in a very convenient way .
For the second point , You can meet the first point ( Each thread has its own instance ) Under the condition of , It is implemented in the form of reference passing between methods .ThreadLocal Make code less coupled , And more elegant .
Scene one ThreadLocal To store Session Example
private static final ThreadLocal threadSession = new ThreadLocal();
public static Session getSession() throws InfrastructureException {
Session s = (Session) threadSession.get();
try {
if (s == null) {
s = getSessionFactory().openSession();
threadSession.set(s);
}
} catch (HibernateException ex) {
throw new InfrastructureException(ex);
}
return s;
}
Scene two Solve the problem of thread safety
such as Java7 Medium SimpleDateFormat Not thread safe , It can be used ThreadLocal To solve this problem :
public class DateUtil {
private static final String dateFormatStr = "yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss";
private static ThreadLocal<SimpleDateFormat> dateFormat = new ThreadLocal<SimpleDateFormat>() {
@Override
protected SimpleDateFormat initialValue() {
return new SimpleDateFormat(dateFormatStr);
}
};
public static String formatDate(Date date) {
return dateFormat.get().format(date);
}
}
there DateUtil.formatDate() It's thread safe .(Java8 Inside java.time.format.DateTimeFormatter It's thread safe ,Joda time Inside DateTimeFormat It's also thread safe ).
Scene three 、 Use section print log from beginning to end ThreadLocal solve
@Component
@Slf4j
@Aspect
public class Aspect1 {
ThreadLocal<Long> startTime = new ThreadLocal<>();
@Pointcut("execution(* com.*(..))")
public void webLog(){
}
@Before(value = "webLog()")
public void before(JoinPoint joinPoint) {
// Output connection point information
startTime.set(System.currentTimeMillis());
// Log operations
ServletRequestAttributes attributes = (ServletRequestAttributes)RequestContextHolder.getRequestAttributes();
HttpServletRequest request = attributes.getRequest();
Enumeration<String> headerNames = request.getHeaderNames();
log.info("****************HeaderStart***********************");
while (headerNames.hasMoreElements()){
String headerName = headerNames.nextElement();
log.info("*****<{}: {}>",headerName,request.getHeader(headerName));
}
log.info("****************HeaderEnd***********************");
//------------ Other treatments
}
@AfterReturning(returning = "ret", value = "webLog()")
public void afterThrowing(String ret) {
log.info("RESPONSE: {}",ret);
log.info("SPEND TIME: {}",System.currentTimeMillis()-startTime.get());
}
}
Scene 4 、ThreadLocal stay Spring Application in transaction management
Spring Use ThreadLocal Solving thread safety problems
In general , Only stateless Bean From then on, you can share in a multithreaded environment , stay Spring in , most Bean Can be declared as singleton Scope .(PS:Spring Bean Scope of the instance , Generally by scope Make a designation ,scope Configuration items include 5 Attributes , Used to describe different scopes :1.singleton: Use this attribute to define Bean when ,IOC The container creates only one Bean example ,IOC The container returns the same... Every time Bean example .2.prototype: Use this attribute to define Bean when ,IOC Containers can create multiple Bean example , Each time a new instance is returned .)
most Bean Can be declared as singleton Scope . Because of Spring Yes, some Bean Central Africa thread safe ” State object “ use ThreadLocal encapsulate . So there is state Bean So that we can singleton Working in multithreading .
General Web Applications are divided into presentation layers 、 Service layer and persistence layer , Write corresponding logic in different layers , The lower layer opens the function call to the upper layer through the interface . In general , All program calls from receiving the request to returning the response belong to the same thread .
The following example can reflect Spring Yes, state Bean The idea of transformation :
public class TopicDao{
private Connection conn;// A non thread safe variable
public void addTopic(){
Statement stat=conn.createStatement();
}
}
Because of this conn Is a non thread safe member variable , therefore addTopic() Methods are not thread safe , You must create a new one when using TopicDao example . below , Use ThreadLocal Yes conn This non thread safe state is transformed :
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.Statement;
public class TopicDao{
private static ThreadLocal<Connection> connThreadLocal=new ThreadLocal<Connection>();// Use ThreadLocal preservation Connection Variable
public static Connection getConnection(){
if(connThreadLocal.get()==null){
// If connThreadLocal There is no corresponding Connection Create a new Connection
Connection conn=ConnectionManager.getConnection();
connThreadLocal.set(conn);
return conn;
}
else{
return connThreadLocal.get();// Return directly to thread local variables
}
}
public void addTopic(){
Statement stat=getConnection().createStatement();
}
}
Different threads are using TopicDao when , First judge connThreadLocal.get() Is it null, If it is null, It means that the current thread has no corresponding Connection object , Create a Connection Object and add it to the local thread variable , If not for null, The current thread already has Connection object , Just use it directly . such , It ensures that different threads use their own independent Connection, Instead of using other threads Connection, therefore , This TopicDao You can do that singleton Share the .
6、 ... and 、ThreadLocal Several other points to note
ThreadLocal The cause of the memory leak
Entry take ThreadLocal As Key, Value as value preservation , It is inherited from WeakReference, Notice the first line of code in the constructor super(k), It means ThreadLocal Object is a 「 Weak reference 」. Look at the picture 1.
static class Entry extends WeakReference<ThreadLocal<?>> {
/** The value associated with this ThreadLocal. */
Object value;
Entry(ThreadLocal<?> k, Object v) {
super(k);
value = v;
}
}
There are two main reasons
1 . I didn't delete this manually Entry
2 . CurrentThread The current thread is still running
The first point is easy to understand , Just after using ThreadLocal , Call its remove Method to delete the corresponding Entry , Can avoid memory leaks .
The second point is a little more complicated , because ThreadLocalMap yes Thread A property of , Referenced by the current thread , therefore ThreadLocalMap The life cycle of Thread As long as . If threadlocal Variables are recycled , So the current thread's threadlocal The variable copy points to key=null, That is to say entry(null,value), So this one entry Corresponding value Can never access . actually ThreadLocal All scenarios use thread pools , Threads in the thread pool are reused , This may lead to a lot of entry(null,value) appear , Resulting in memory leaks .
Sum up , ThreadLocal The root cause of the memory leak is :
because ThreadLocalMap The life cycle of Thread As long as , For reusable threads , If you don't manually delete (remove() Method ) Corresponding key It will lead to entry(null,value) More and more objects , This leads to memory leaks .
key If it's a strong quote
Why? ThreadLocalMap Of key To design as a weak reference ? It's very simple , If key Designed as a strong reference without manual remove(), that key Hui He value The same goes with the entire life cycle of the thread .
Suppose it is used up in the business code ThreadLocal, ThreadLocal ref It's recycled , But because threadLocalMap Of Entry Forced to quote threadLocal(key Namely threadLocal), cause ThreadLocal Cannot be recycled . Without manually deleting Entry as well as CurrentThread( Current thread ) Still running , There is always a strong reference chain CurrentThread Ref → CurrentThread →Map(ThreadLocalMap)-> entry, Entry It won't be recycled ( Entry It includes ThreadLocal Instance and value), Lead to Entry Memory leak, that is : ThreadLocalMap Medium key Strong quotes are used , There is no way to completely avoid memory leaks .
Why? key To use weak references
in fact , stay ThreadLocalMap Medium set/getEntry In the method , Would be right key by null( That is to say ThreadLocal by null ) Judge , If null Words , So the value Set as null Of . This means using threadLocal , CurrentThread Still running . Even if you forget to call remove Method , Weak references can provide more protection than strong references : Weakly quoted ThreadLocal Will be recycled . Corresponding value The next time ThreadLocaIMap call set/get/remove Any of the methods will be cleared , To avoid memory leaks .
How to use ThreadLocal
1、 take ThreadLocal Variables are defined as private static Of , In this case ThreadLocal It's a longer life cycle , Because it's always there ThreadLocal A strong reference to , therefore ThreadLocal It won't be recycled , It's guaranteed to be available at any time ThreadLocal A weak reference to Entry Of value value , then remove it , Prevent memory leaks
2、 After each use ThreadLocal, It's called remove() Method , Clear data .
ThreadLocal Advanced interview questions
One .ThreadLocal What is it? ?
ThreadLocal Is a local thread copy variable utility class . It is mainly used to map the private thread and the copy object stored by the thread , Variables between threads do not interfere with each other , In high concurrency scenarios , Stateless calls can be implemented , It is suitable for operations in which all threads do not share variable values .
Two . Why? ThreadLocalMap Of key Is a weak reference ?
1.key Use strong references : This leads to a problem , Refer to the ThreadLocal The object is recycled , however ThreadLocalMap And hold ThreadLocal A strong reference to , If you don't manually delete ,ThreadLocal Will not be recycled , Will cause memory leaks .
2.key Using weak references : In this case , Refer to the ThreadLocal The object is recycled , because ThreadLocalMap hold ThreadLocal The weak references , Even if it's not manually deleted ,ThreadLocal It will also be recycled .value The next time ThreadLocalMap call set、get、remove Will be cleared when .
summary : Compare the above two situations , We can find out : because ThreadLocalMap The life cycle of Thread As long as , If none of them are deleted manually key, Will lead to memory leaks , But using weak references can provide more security , Weak reference ThreadLocal No memory leaks , Corresponding value The next time ThreadLocalMap call set、get、remove When it's cleared , It's the best solution .
3、 ... and .ThreadLocal How to let subclasses access the value of the parent thread ?
1.InheritableThreadLocal class
Inherited from ThreadLocal, A feature is provided , Let the child thread access the local variables set in the parent thread .InheritableThreadLocal Rewrote creatMap Method , So in this class inheritableThreadLocals Instead of threadLocals, therefore get and set It's all this map
2. When creating a child thread, pass in the variables of the parent thread , And assign it to the child thread
边栏推荐
- [target tracking] | data set summary
- 辉芒微IO单片机FT60F11F-MRB
- 【網絡是怎樣連接的】第六章 請求到達服務器以及響應給客戶端(完結)
- This "architect growth note" made 300 people successfully change jobs and enter the big factory, with an annual salary of 50W
- 应广单片机开发流程需要注意哪些?
- Huimang micro IO MCU ft60f010a-urt
- Larvel document reading notes custom authentication login and registration using larvel 8
- How to create a new page for SAP Spartacus storefront
- Keras深度学习实战——基于VGG19模型实现性别分类
- MB10M-ASEMI整流桥MB10M
猜你喜欢

嵌入式 ~ 介绍
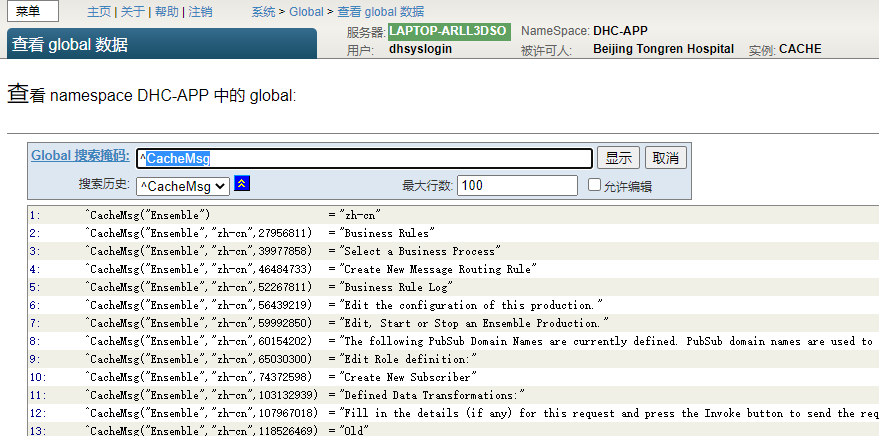
Chapter 15 string localization and message Dictionary (1)
【历史上的今天】7 月 2 日:BitTorrent 问世;商业系统 Linspire 被收购;索尼部署 PlayStation Now

Modbus协议通信异常
wps插入图片后使图片完整显示
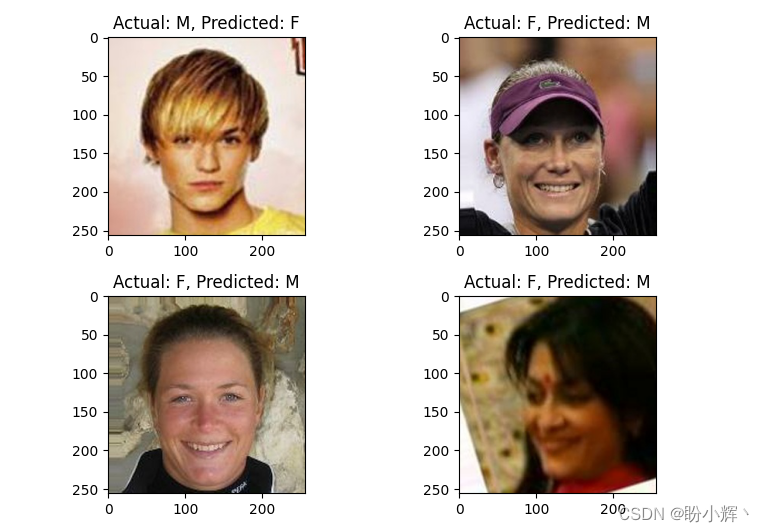
Keras深度学习实战——基于VGG19模型实现性别分类

Daily question - inverted string

每日一题——小乐乐改数字

【Zuul】com. netflix. zuul. exception. ZuulException: Hystrix Readed time out

透过华为军团看科技之变(六):智慧公路
随机推荐
【网络是怎样连接的】第六章 请求到达服务器以及响应给客户端(完结)
Pms150c Yingguang MCU development case
辉芒微IO单片机FT60F11F-MRB
一日2篇Nature!中科大校友段镶锋团队纳米材料新成果,曾是贝尔比奖章第三位华人得主...
[comment le réseau se connecte] chapitre 6: demande d'accès au serveur et réponse au client (terminé)
Redisson 高性能 Redis 分布式锁源码分析
台风来袭,多景区暂时关闭,省文旅厅提醒注意安全!
嵌入式开发板 ~ 说明
第十五章 字符串本地化和消息字典(一)
Virtual lab basic experiment tutorial -7 Polarization (2)
应广单片机开发调试应注意的问题
应广单片机开发 工规 PMC131 带AD芯片检测电池电压单片机SOP8/14
chrome瀏覽器快速訪問stackoverflow
RK1126平台项目总结
uva1169
What are the green field and brown field models in software development - green field development and brown field development
ORA-19838 -- 恢复控制文件到备库
Tips for self defined packaging of Yingguang SCM 003 burner
[target tracking] |siamfc
阿里云子账户 - 权限策略 - 授权给某个账户某个 OSS Bucket 的完全控制权限