当前位置:网站首页>The ORB - SLAM2 extracting feature points
The ORB - SLAM2 extracting feature points
2022-08-03 07:34:00 【Haaaaaaaaaang】
一:构造函数ORBextractor()
说明:
特征点提取器的构造函数
该函数位于Tracking.cc的构造函数中Tracking::Tracking(...),The constructor is mainly from the configuration file loading camera parameters,并计算ORB特征点有关的参数,并新建特征点提取器
mpORBextractorLeft = new ORBextractor(nFeatures,fScaleFactor,nLevels,fIniThFAST,fMinThFAST);
参数说明
int nfeatures | The entire image pyramid,要提取的特征点数目 |
|---|---|
double scaleFactor | Image pyramid zoom factor between layer and layer |
int nlevels | 图像金字塔的层数 |
int iniThFAST | 初始的FASTResponse value threshold |
int minThFAST | 最小的FASTResponse value threshold |
vector<int> mnFeaturesPerLevel | 分配到每层图像中,要提取的特征点数目 |
|---|---|
vector<int> umax | 1/4Circular area of the image lineu轴的边界 |
vector<float> mvScaleFactor | 每层图像的缩放因子 |
vector<float> mvInvScaleFactor | 每层缩放因子的倒数- |
vector<float> mvLevelSigma2 | The square of each layer of the image scaling factor |
vector<float> mvInvLevelSigma2 | Each layer of the image of the inverse square of the zoom factor |
函数流程
构造函数列表初始化
初始化nfeatures,scaleFactor,nlevels,iniThFAST,minThFAST这几个参数
ORBextractor::ORBextractor(int _nfeatures,float _scaleFactor,int _nlevels,int _iniThFAST, int _minThFAST):
nfeatures(_nfeatures), scaleFactor(_scaleFactor), nlevels(_nlevels),iniThFAST(_iniThFAST), minThFAST(_minThFAST)
Each layer of the pyramid zoom coefficient and its several brothers
mvScaleFactor[0] | 1.0 |
|---|---|
mvScaleFactor[1] | 1.2 |
mvScaleFactor[2] | 1.2 * 1.2 |
mvScaleFactor[3 ] | 1.2 * 1.2 * 1.2 |
| … | … |
for(int i=1; i<nlevels; i++)
{
mvScaleFactor[i]=mvScaleFactor[i-1]*scaleFactor;
mvLevelSigma2[i]=mvScaleFactor[i]*mvScaleFactor[i];
}
for(int i=0; i<nlevels; i++)
{
mvInvScaleFactor[i]=1.0f/mvScaleFactor[i];
mvInvLevelSigma2[i]=1.0f/mvLevelSigma2[i];
}
Calculate each layer of the pyramid need to extract the feature points, the number of
金字塔层数越高,The smaller the image area,The less they assigned the number of feature points.
The distribution of each layer of image feature points is proportional to the number of,比例系数为scaleFactor(1.2)
设NAs the total number of feature points,n为层数,则第0Layer distribution of the number of feature points as
N 0 = N ( 1 − s ) ( 1 − s n ) N0 = \frac{N(1-s)}{(1-s^{n})} N0=(1−sn)N(1−s)
N0也就是代码中的nDesiredFeaturesPerScale,And then, in turn, proportionately1-6Layer number of feature points,第7Total number of layer number is minus before6层数目.
mnFeaturesPerLevel.resize(nlevels);
float factor = 1.0f / scaleFactor;
//第0层图像应该分配的特征点数量
float nDesiredFeaturesPerScale = nfeatures*(1 - factor)/(1 - (float)pow((double)factor, (double)nlevels));
int sumFeatures = 0;
//Not to calculate the top image
for( int level = 0; level < nlevels-1; level++ )
{
mnFeaturesPerLevel[level] = cvRound(nDesiredFeaturesPerScale);
sumFeatures += mnFeaturesPerLevel[level];
nDesiredFeaturesPerScale *= factor;
}
//由于前面的特征点个数取整操作,可能会导致剩余一些特征点个数没有被分配,所以这里就将这个余出来的特征点分配到最高的图层中
mnFeaturesPerLevel[nlevels-1] = std::max(nfeatures - sumFeatures, 0);
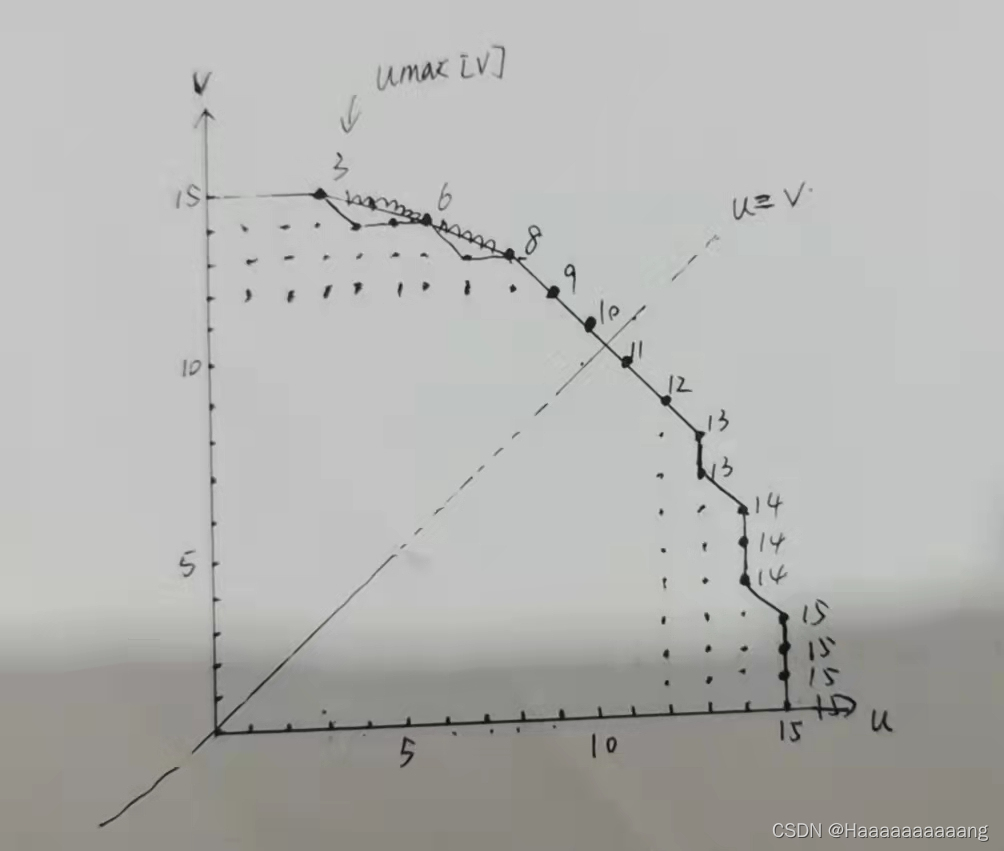
计算1/4圆u坐标最大值
This is in order to use the gray qualitative method to realizeBRIEFDescriptor rotation invariance of.
What is a gray centroid?Gray centroid is an image of calculation in the area of,With the fast image grey value as the center of weight(Just like a piece of uneven distribution of the quality of tablet computing its centre of gravity is the same).
The moment don't care about gray mass loading and rotation invariance meaning,In the above image area first,In fact is a circle,Called the gray centroid round.In order to facilitate subsequent gray centroid calculation,首先要求出umax
参数说明
const int HALF_PATCH_SIZE = 15 | Using gray mass center method when calculating the direction information of feature points,The radius of image block |
|---|---|
vector<int> umax | 1/4Gray centroid round each lineu坐标边界 |
umax.resize(HALF_PATCH_SIZE + 1);
int v,v0,vmax = cvFloor(HALF_PATCH_SIZE * sqrt(2.f) / 2 + 1);
//这里的二分之根2就是对应那个45°圆心角
int vmin = cvCeil(HALF_PATCH_SIZE * sqrt(2.f) / 2);
const double hp2 = HALF_PATCH_SIZE*HALF_PATCH_SIZE;//半径的平方
//利用圆的方程计算每行像素的u坐标边界(max)
for (v = 0; v <= vmax; ++v)
umax[v] = cvRound(sqrt(hp2 - v * v));
//Using the symmetrical one 8 on the way of calculation on the circumference of a circleumax
for (v = HALF_PATCH_SIZE, v0 = 0; v >= vmin; --v)
{
while (umax[v0] == umax[v0 + 1])
++v0;
umax[v] = v0;
++v0;
}
However, image pixel coordinates are integer values,To solve the image area is only an approximate circle.So as far as possible in order to improve the symmetry,Make the selection of point area of two coordinates both axisymmetric,也关于u=v对称.
第一个forCycle calculation due to rounding for the sameu坐标的点,比如v从0增加到3,umax[0]=umax[3]=15保持不变;第二个forCycle is to judgeuThe number of coordinates for the same,保持v=15使u从0增到3,那么umax[15]=3,So on the domain of point aboutu=v对称
After calculating the effect of something like this
二:To extract the feature points function
说明 :
提取图像的ORB特征点,提取的关键点存放在mvKeys,描述子存放在mDescriptors,Corresponding to the copy function_keypoints和_descriptors
void Frame::ExtractORB(int flag, const cv::Mat &im)
{
if(flag==0)
// 左图的话就套使用左图指定的特征点提取器,并将提取结果保存到对应的变量中
// 仿函数,重载括号运算符
(*mpORBextractorLeft)(im,cv::Mat(),mvKeys, mDescriptors);
else
// 右图的话就需要使用右图指定的特征点提取器,并将提取结果保存到对应的变量中
(*mpORBextractorRight)(im,cv::Mat(),mvKeysRight,mDescriptorsRight);
}
Use imitation function complete to extract the feature points of work
输出vector<KeyPoint>& _keypointsEach image feature point coordinates in a pyramid into0层的wholeSizeSize of feature point coordinate,_descriptorsStore the entire pyramid feature points,一列(32维)Corresponds to a feature point.
函数流程
void ORBextractor::operator()( InputArray _image, InputArray _mask, vector<KeyPoint>& _keypoints,OutputArray _descriptors){
/** * @param[in] _image 输入原始图的图像 * @param[in] _mask 掩膜mask * @param[in & out] _keypoints 输出:存储特征点关键点的向量 * @param[in & out] _descriptors 输出:存储特征点描述子的矩阵 */
if(_image.empty())
return;
//获取图像的大小
Mat image = _image.getMat();
//判断图像的格式是否正确,要求是单通道灰度值
assert(image.type() == CV_8UC1 );
}
1.构建图像金字塔
概念:图像金字塔是图像多尺度表达的一种,是一种以多分辨率来解释图像的有效但概念简单的结构.一幅图像的图像金字塔是一系列以金字塔形状(自下而上)逐步降低,且来源于同一张原始图的图像分辨率集合.其通过梯次向下采样获得,直到达到某个终止条件才停止采样.我们将一层一层的图像比喻成金字塔,层级越高,则图像越小,分辨率越低.来自于百度百科
In the process of moving camera,Camera distance of the target observation sometimes sometimes far,People's understanding of intuitive objects is nearly far small,But the resolution of the camera is fixed,Lead to the distance of image to extract the feature points in the nearby observation may no longer be feature points(Far see a point,Closer is a circle),But clearly observed objects are the same,But because of the change of the scale on the match two images can't,干着急.
为了解决这个问题,构建图像金字塔.The idea is to the original image, in turn, according to a certain proportion coefficient scaling down sampling for a total of8张图片,Separately for each image feature extraction,并记录特征所在金字塔的第几层.
Image pyramid sample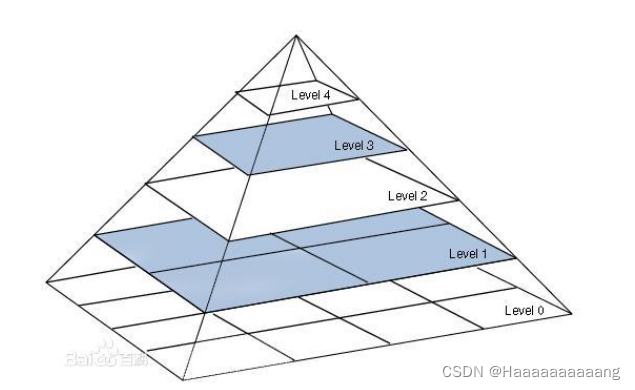
ComputePyramid(image);
2.计算图像的特征点,并且将特征点进行均匀化.均匀的特征点可以提高位姿计算精度
// 存储所有的特征点,The first dimension of storage layers of the pyramid,The second dimension to store all the layers of the pyramid to extract feature points
vector < vector<KeyPoint> > allKeypoints;
//使用四叉树的方式计算每层图像的特征点并进行分配
ComputeKeyPointsOctTree(allKeypoints);
3.拷贝图像描述子到新的矩阵descriptors
4.执行下面的for循环,遍历每一层图像
//设置了Offset变量来保存“寻址”Deviation of the line,辅助进行在总描述子mat中的定位
int offset = 0;
for (int level = 0; level < nlevels; ++level)
{
//获取在allKeypoints中当前层特征点容器的句柄
vector<KeyPoint>& keypoints = allKeypoints[level];
//本层的特征点数
int nkeypointsLevel = (int)keypoints.size();
//如果特征点数目为0,跳出本次循环,继续下一层金字塔
if(nkeypointsLevel==0)
continue;
... ...对图像进行高斯模糊... ...
... ...计算高斯模糊后图像的描述子... ...
... ...对非第0层图像中的特征点的坐标恢复到第0层图像(原图像)的坐标系下... ...
}
5 对图像进行高斯模糊
为减少噪声干扰,先对图像进行高斯滤波,Such subsequent calculation of descriptor just more accurate.
注意:提取特征点的时候,使用的是清晰的原图像;这里计算描述子的时候,为了避免图像噪声的影响,使用了高斯模糊
GaussianBlur(workingMat, //源图像
workingMat, //输出图像
Size(7, 7), //高斯滤波器kernel大小,必须为正的奇数
2, //高斯滤波在x方向的标准差
2, //高斯滤波在y方向的标准差
BORDER_REFLECT_101);//边缘拓展点插值类型
6.计算高斯模糊后图像的描述子
// desc存储当前图层的描述子
Mat desc = descriptors.rowRange(offset, offset + nkeypointsLevel);
// Step
computeDescriptors(workingMat, //高斯模糊之后的图层图像
keypoints, //当前图层中的特征点集合
desc, //存储计算之后的描述子
pattern); //随机采样模板
// 更新偏移量的值
offset += nkeypointsLevel;
7.对非第0层图像中的特征点的坐标恢复到第0Layer image coordinates
// Step 6 对非第0层图像中的特征点的坐标恢复到第0层图像(原图像)的坐标系下
// 对于第0层的图像特征点,他们的坐标就不需要再进行恢复了
if (level != 0)
{
// 获取当前图层上的缩放系数
float scale = mvScaleFactor[level];
// 遍历本层所有的特征点
for (vector<KeyPoint>::iterator keypoint = keypoints.begin(),
keypointEnd = keypoints.end(); keypoint != keypointEnd; ++keypoint)
// 特征点本身直接乘缩放倍数就可以了
keypoint->pt *= scale;
}
// 将keypoints中内容插入到_keypoints 的末尾
// keypoint其实是对allkeypoints中每层图像中特征点的引用,这样allkeypoints中的所有特征点在这里被转存到输出的_keypoints
_keypoints.insert(_keypoints.end(), keypoints.begin(), keypoints.end());
相关函数
1 构建金字塔
对于第0层图像,Directly to the originalimage拷贝到temp的中间,And the all round its symmetric boundary extension;For the other layer image,First the original layer according to the current zoom factorsz缩小,Will shrink again after the image copy to the expansion of the current layer boundary imagetemp中,And the all round its symmetric boundary extension.
其中,定义的Size wholeSizeIs the size of the image after expansion
On the basis of function must be modified
void ORBextractor::ComputePyramid(cv::Mat image)
{
//开始遍历所有的图层
for (int level = 0; level < nlevels; ++level){
//获取本层图像的缩放系数
float scale = mvInvScaleFactor[level];
//计算本层图像的像素尺寸大小
Size sz(cvRound((float)image.cols*scale), cvRound((float)image.rows*scale));
//全尺寸图像.包括无效图像区域的大小.将图像进行“补边”,EDGE_THRESHOLD区域外的图像不进行FAST角点检测
Size wholeSize(sz.width + EDGE_THRESHOLD*2, sz.height + EDGE_THRESHOLD*2);
// 定义了两个变量:temp是扩展了边界的图像,masktemp并未使用
Mat temp(wholeSize, image.type()), masktemp;
// mvImagePyramid 刚开始时是个空的vector<Mat>
// I put the following code commented out,Because write not write does not affect the final result pyramid
//mvImagePyramid[level] = temp(Rect(EDGE_THRESHOLD, EDGE_THRESHOLD, sz.width, sz.height));
//计算第0层以上resize后的图像
if( level != 0 ){
resize(image, //输入图像,Source code for this parameter ismvImagePyramid[level-1],显然是不正确的
mvImagePyramid[level], sz, 0,0,cv::INTER_LINEAR);
//把源图像拷贝到目的图像的中央,四面填充指定的像素.图片如果已经拷贝到中间,只填充边界
copyMakeBorder(mvImagePyramid[level], //源图像
temp, //目标图像(此时其实就已经有大了一圈的尺寸了)
EDGE_THRESHOLD, EDGE_THRESHOLD, //top & bottom 需要扩展的border大小
EDGE_THRESHOLD, EDGE_THRESHOLD, //left & right 需要扩展的border大小
BORDER_REFLECT_101+BORDER_ISOLATED); //扩充方式
}
else{
copyMakeBorder(image,temp,EDGE_THRESHOLD,EDGE_THRESHOLD,
EDGE_THRESHOLD,EDGE_THRESHOLD,BORDER_REFLECT_101);
}
//Here with this,Would extend the edge aftertempAssigned to the pyramid
mvImagePyramid[level] = temp;
}
}
//几种 copyMakeBorderFunction image expansion way
/*Various border types, image boundaries are denoted with '|' * BORDER_REPLICATE: aaaaaa|abcdefgh|hhhhhhh * BORDER_REFLECT: fedcba|abcdefgh|hgfedcb * BORDER_REFLECT_101: gfedcb|abcdefgh|gfedcba * BORDER_WRAP: cdefgh|abcdefgh|abcdefg * BORDER_CONSTANT: iiiiii|abcdefgh|iiiiiii with some specified 'i' */
The final results map,Each layer of the image on the basis of the original image edges are expandedEDGE_THRESHOLD
构
2 提取特征点
Function process about analysis
Each layer of the pyramid is divided into a number ofcell,分别在每个cellTo extract the feature points,Then the feature points by quadtree homogenization treatment.
For each layer image,Calculate the effective boundary layer image,请看图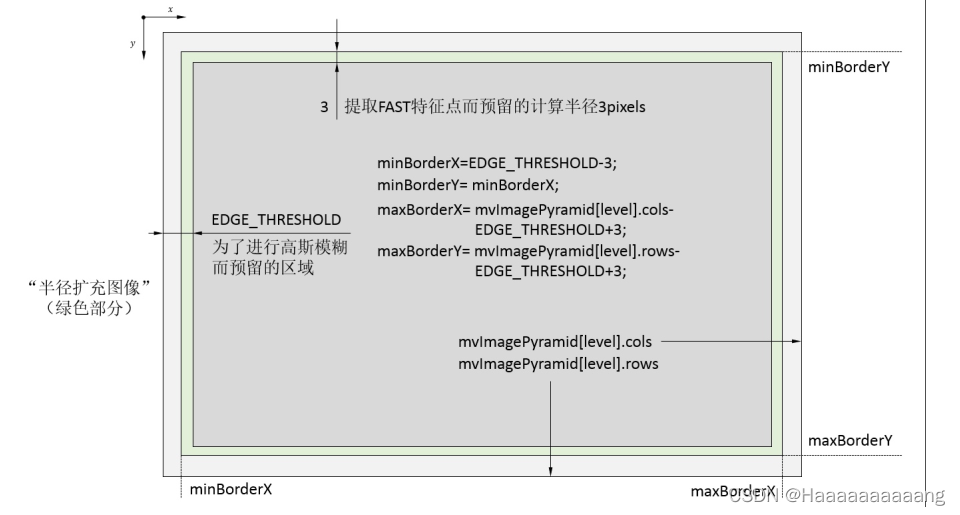
Each layer of the boundary of the pyramid is the most peripheral frame above,Calculate the pyramid function callwholeSize,Generate the image of gold is the purpose of the casing outside the tower when the generation of,Need for gaussian filtering processing,The area is in the original image,And in the middle of the green border is on the basis of the original image edges the expanded3得到的.给它起个名字叫“有效图像边界”,扩充3的目的,是因为在计算FAST特征点的时候,需要建立一个半径为3的圆,如图所示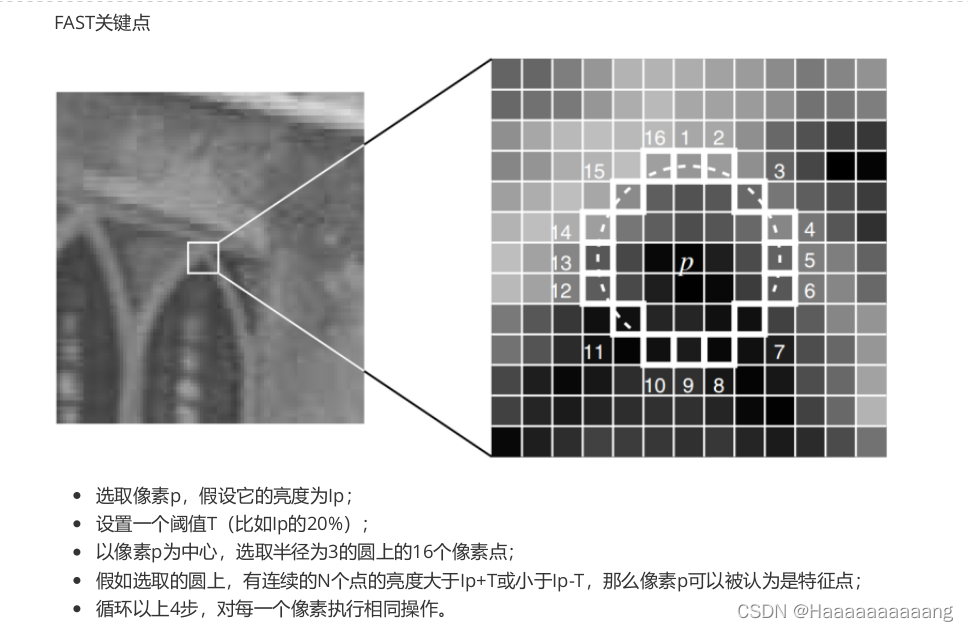
Firstly calculates the horizontal ordinate effective image boundary minimum and maximum,分别是minBorderX、minBorderY、maxBorderX、maxBorderY,The effective width and height of the image boundary,分别为width、height,And then calculate the actual eachcellThe rows and columns of pixelnCols、nRows,Pay attention to the rows and columns is greater than or equal to30的,一般会是30(概率很小)或31或32.
The following start for eachcell进行遍历,首先计算了iniY和maxY,以及iniX和maxX,They are each grid actual boundaries,在width * heightOn the basis of respectively extend3,以计算FAST特征点,而width * heightIs that the area can be extracted feature points.此外,A grid underiniY比当前的maxY小6,Is part of the overlap,So you can make the extractionFASTSome characteristics of the area is continuous.
Function of a littlebug:To determine whether a line initial coordinate effective all the timeif(iniY>=maxBorderY-3),判断
Column initial coordinate is effective if(iniX>=maxBorderX-6),Why is not the same as the reduction of?The answer should be the same.那么应该是-3还是-6呢,我的理解是-6,原因如下:
第i+1个格子的iniY比第i个格子的maxY小6,那么如果第n个格子的iniY大于maxBorderY-6的话,那说明第n-1个格子的maxY已经大于maxBorderY了,Has come to the right side of the effective image boundary,“已经结束啦”.-6包括-3的情况,And it is reasonable judgement conditions,因此认为iniY的判断条件是if(iniY>=maxBorderY-6)
示意图: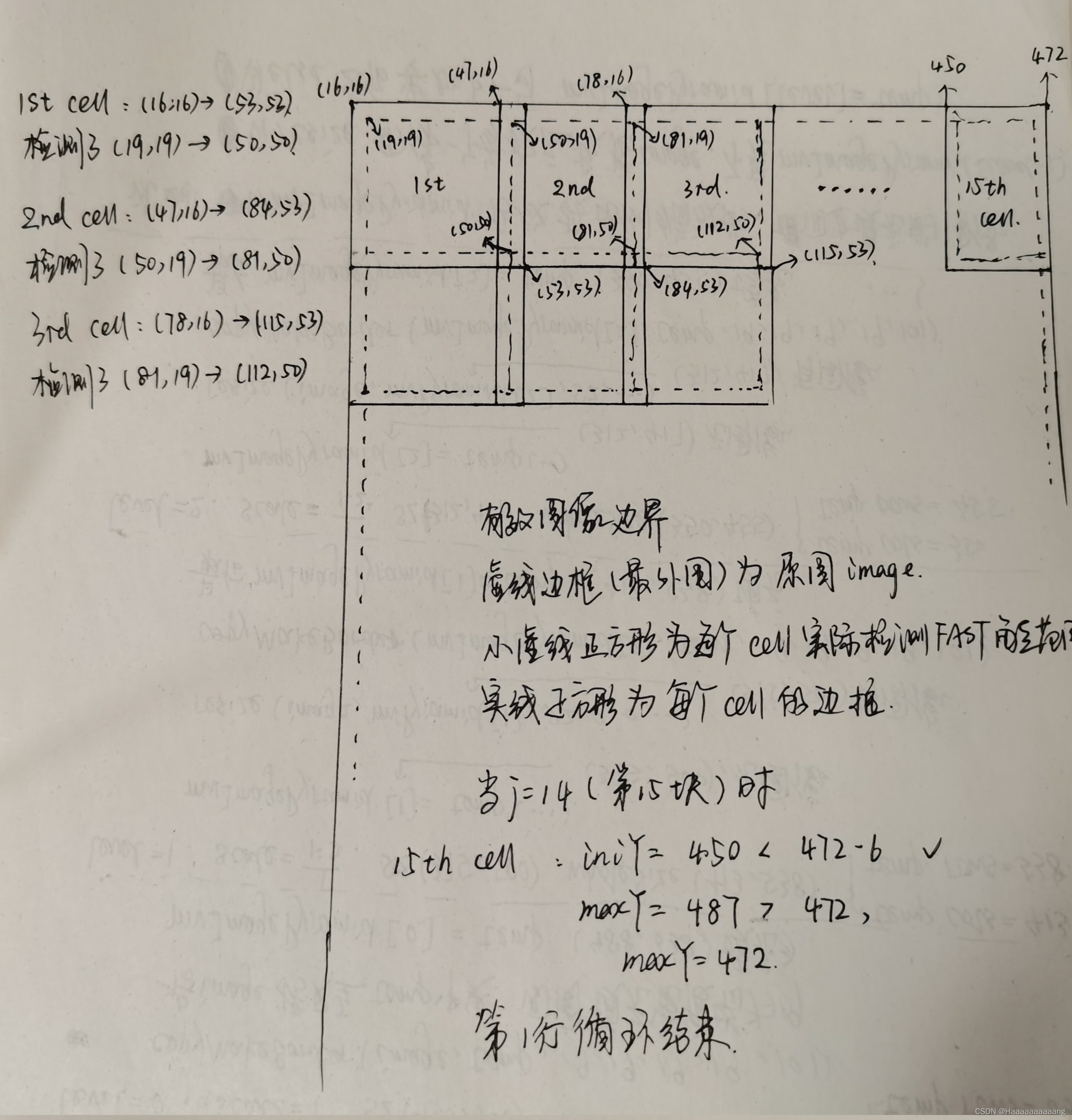
In the grid to extract the feature points stored in vToDistributeKeys中,The coordinate is based on image coordinate border,调用DistributeOctTreeAfter screening the feature points stored in thekeypoints中,vector<KeyPoint> & keypoints = allKeypoints[level].最后 allKeypointsBased on the layer are the coordinates of thewholeSize而言的.
//Calculate the quadtree feature points
void ORBextractor::ComputeKeyPointsOctTree(vector<vector<KeyPoint> >& allKeypoints)
{
allKeypoints.resize(nlevels);
//图像cell的尺寸,是个正方形
const float W = 30;
// 对每一层图像做处理
for (int level = 0; level < nlevels; ++level)
{
const int minBorderX = EDGE_THRESHOLD-3;
const int minBorderY = minBorderX;
const int maxBorderX = mvImagePyramid[level].cols-EDGE_THRESHOLD+3;
const int maxBorderY = mvImagePyramid[level].rows-EDGE_THRESHOLD+3;
//存储需要进行平均分配的特征点
vector<cv::KeyPoint> vToDistributeKeys;
vToDistributeKeys.reserve(nfeatures*10);
//计算进行特征点提取的图像区域尺寸
const float width = (maxBorderX-minBorderX);
const float height = (maxBorderY-minBorderY);
//Computational grid in the current layer image some rows and columns
const int nCols = width/W;
const int nRows = height/W;
//计算每个图像网格所占的像素行数和列数
const int wCell = ceil(width/nCols);
const int hCell = ceil(height/nRows);
//开始遍历图像网格,还是以行开始遍历的
for(int i=0; i<nRows; i++){
const float iniY =minBorderY+i*hCell;//计算当前网格初始行坐标
float maxY = iniY+hCell+6; //The biggest row
//If the initial line coordinates is already more thanmaxBorderY-3?
if(iniY>=maxBorderY-3)
continue;
//如果图像的大小导致不能够正好划分出来整齐的图像网格,那么就要委屈最后一行了
if(maxY>maxBorderY)
maxY = maxBorderY;
//开始列的遍历
for(int j=0; j<nCols; j++){
const float iniX =minBorderX+j*wCell;//计算初始的列坐标
float maxX = iniX+wCell+6;//This the biggest column column grid coordinates
//If the initial column coordinates has been more thanmaxBorderX-6?
if(iniX>=maxBorderX-6)
continue;
//如果最大坐标越界那么委屈一下
if(maxX>maxBorderX)
maxX = maxBorderX;
vector<cv::KeyPoint> vKeysCell;//这个向量存储这个cell中的特征点
FAST(mvImagePyramid[level].rowRange(iniY,maxY).colRange(iniX,maxX), //待检测的图像,这里就是当前遍历到的图像块
vKeysCell, //存储角点位置的容器
iniThFAST, //检测阈值
true); //使能非极大值抑制
//如果这个图像块中使用默认的FAST检测阈值没有能够检测到角点
if(vKeysCell.empty()){
//那么就使用更低的阈值来进行重新检测
FAST(mvImagePyramid[level].rowRange(iniY,maxY).colRange(iniX,maxX),
vKeysCell,minThFAST,true);
}
//当图像cell中检测到FAST角点的时候执行下面的语句
if(!vKeysCell.empty()){
//遍历其中的所有FAST角点
for(vector<cv::KeyPoint>::iterator vit=vKeysCell.begin(); vit!=vKeysCell.end();vit++){
//到目前为止,这些角点的坐标都是基于图像cell的,Under the first to restore to the border of the image coordinates the coordinates of the
(*vit).pt.x+=j*wCell;
(*vit).pt.y+=i*hCell;
//然后将其加入到”等待被分配“的特征点容器中
vToDistributeKeys.push_back(*vit);
}
}
}
}
//声明一个对当前图层的特征点的容器的引用
vector<KeyPoint> & keypoints = allKeypoints[level];
keypoints.reserve(nfeatures);
//返回值是一个保存有特征点的vector容器,含有剔除后的保留下来的特征点
//得到的特征点的坐标,依旧是在当前图层下来讲的
keypoints = DistributeOctTree(vToDistributeKeys, minBorderX, maxBorderX,
minBorderY, maxBorderY,mnFeaturesPerLevel[level],level);
//PATCH_SIZE是对于底层的初始图像来说的,现在要根据当前图层的尺度缩放倍数进行缩放得到缩放后的PATCH大小 和特征点的方向计算有关
const int scaledPatchSize = PATCH_SIZE*mvScaleFactor[level];
//获取剔除过程后保留下来的特征点数目
const int nkps = keypoints.size();
//然后开始遍历这些特征点,恢复其在当前图Layer image coordinates的坐标
for(int i=0; i<nkps ; i++){
//对每一个保留下来的特征点,恢复到相对于当前图层“边缘扩充图像下”的坐标系的坐标
keypoints[i].pt.x+=minBorderX;
keypoints[i].pt.y+=minBorderY;
//记录特征点来源的图像金字塔图层
keypoints[i].octave=level;
//记录计算方向的patch,缩放后对应的大小, 又被称作为特征点半径
keypoints[i].size = scaledPatchSize;
}
}//For each layer image to perform the above operations
//然后计算这些特征点的方向信息,注意这里还是分层计算的
for (int level = 0; level < nlevels; ++level)
computeOrientation(mvImagePyramid[level], //对应的图层的图像
allKeypoints[level], //这个图层中提取并保留下来的特征点容器
umax); //以及PATCH的横坐标边界
}
3 函数中调用的DistributeOctTree
说明 使用四叉树法对一个图像金字塔图层中的特征点进行平均和分发
传入vToDistributeKeys,返回 keypoints(Each layer of the image characteristics after the equalization point,The coordinate is still based on effective image boundary)
原理:
- 如果图片的宽度比较宽,就先把分成左右w/h份.一般的640×480的图像开始的时候只有一个node.
- 如果node里面的点数>1,把每个node分成四个node,如果node里面的特征点为空,就不要了,删掉.
- 新分的node的点数>1,就再分裂成4个node.如此,一直分裂.
- 终止条件为:node的总数量> [公式] ,或者无法再进行分裂.
- 然后从每个node里面选择一个质量最好的FAST点.
参考知乎的一篇文章Feature points on average in the method of quadtree and distribution
4 函数调用的computeOrientation
说明Used to calculate the direction of the feature points
for (vector<KeyPoint>::iterator kpit = keypoints.begin();kpit !=keypoints.end(); ++keypoint)
{
// 调用IC_Angle 函数计算这个特征点的方向
keypoint->angle = IC_Angle(image, //特征点所在的图层的图像
keypoint->pt, //特征点在这张图像中的坐标
umax); //每个特征点所在图像区块的每行的边界 u_max 组成的vector
IC_Angle()函数
The function to calculate the feature points in the direction of the,Return value is a Angle.
Direction of feature points is calculated in order to make the extraction of feature points with rotation invariance.
Calculation for the direction of the feature points is a gray mass loading(Intensity Centriod)
Personal understanding is to describe the son has a rotational deformation,Because of a descriptionpattern是固定的,All images in thispattern,所有人都用.If the image rotation Angle of a,pattern还在原地踏步,Calculated descriptor and before rotating corresponding to the description of the feature points are quite different(I know you when you stand,Now you can't because you lie prone on the ground I can not recognize you),It should be said that even if the image rotation,Description of the corresponding feature points should also be similar,Then through calculating the Angle of the key,即使图像发生旋转,让patternAlso follow the key rotating together,The last to calculate the distance the description of close to,Match, more accurate.因此说,To calculate the key point to calculate a description of the child is calledSteered BRIEF.
Gray mass loading principle believe that everyone should be familiar with,14 speak what it write very clear,或者看这篇文章灰度质心法原理
Before the calculation of hereu_max就派上用场了,We deal with the approximation of image region is a circle,Is to be calculated in one line,首先计算v=0The lines of the image moment,Then, calculations aboutu=0Symmetry of the two rows of pixels image moment,Two lines of two lines of calculation,最后累加即可.
Because the calculation process is according to the row index,So you need to know each pixel coordinates range,还好,之前算过了.就是[-umax[v],umax[v]]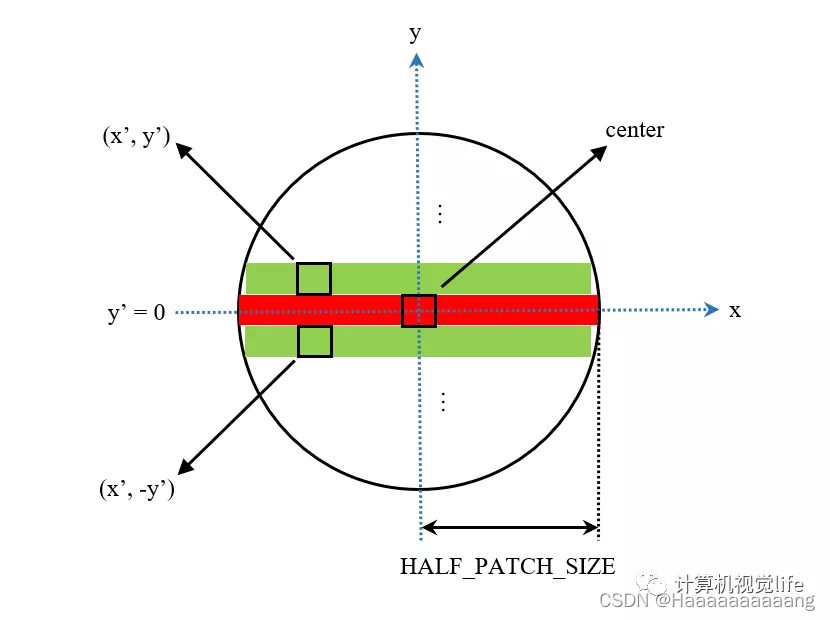
这里的const uchar *centerIs a pointer to the image coordinate point a grey value,This code is point to point in the coordinates of feature points.center[u]取出了[pt.(x+u),pt.y]Point grey value(取的都是v=0The axis of the grey value).
那么怎么取出[pt.(x+u),pt.(y+v)]The pixel values?使用(int)image.step1()Said the image one line the total number of bytes,其像素值为center[u + v * step](在center[u]移动了v行).Other issues are well understood.
static float IC_Angle(const Mat &image, Point2f pt, const vector<int> &u_max)
{
//图像的矩,前者是按照图像块的y坐标加权,后者是按照图像块的x坐标加权
int m_01 = 0, m_10 = 0;
//获得这个特征点所在的图像块的中心点坐标灰度值的指针center
const uchar *center = &image.at<uchar>(cvRound(pt.y), cvRound(pt.x));
//这条v=0中心线的计算需要特殊对待
//后面是以中心行为对称轴,成对遍历行数,所以PATCH_SIZE必须是奇数
for (int u = -HALF_PATCH_SIZE; u <= HALF_PATCH_SIZE; ++u)
m_10 += u * center[u];
//这里的step1表示这个图像一行包含的字节总数.参考
int step = (int)image.step1();
//注意这里是以v=0中心线为对称轴,然后对称地每成对的两行之间进行遍历,这样处理加快了计算速度
for (int v = 1; v <= HALF_PATCH_SIZE; ++v)
{
int v_sum = 0;
int d = u_max[v];
// 假设每次处理的两个点坐标,中心线下方为(x,y),中心线上方为(x,-y)
// 对于某次待处理的两个点:m_10 = Σ x*I(x,y) = x*I(x,y) + x*I(x,-y) = x*(I(x,y) + I(x,-y))
// 对于某次待处理的两个点:m_01 = Σ y*I(x,y) = y*I(x,y) - y*I(x,-y) = y*(I(x,y) - I(x,-y))
for (int u = -d; u <= d; ++u)
{
int val_plus = center[u + v * step], val_minus = center[u - v * step];
//在v(y轴)上,2行所有像素灰度值之差
v_sum += (val_plus - val_minus);
//u轴(x轴)方向上用u坐标加权和,相当于同时计算两行
m_10 += u * (val_plus + val_minus);
}
//将这一行上的和按照y坐标加权
m_01 += v * v_sum;
}
//输出为[0,360)角度,精度为0.3°
return fastAtan2((float)m_01, (float)m_10);
}
最终的返回值(角度)赋给了 keypoint->angle
5 函数中的computeDescriptors
说明 全局静态函数,static修饰符限定其只能够被本文件中的函数调用,计算某层金字塔图像上特征点的描述子
BRIEFDescriptor definition_descriptors.create(nkeypoints, 32,CV_8U),Visible descriptor a total ofnkeypoints行,每行(, that is, each feature point)对应一个描述子,描述子是32维的向量,Each element is stored up8bit的信息(CV_8U)
Calculate descriptor needs to use random sampling points setpattern,它定义在ORBextractor中.将成员变量static int bit_pattern_31_[256 * 4]内容复制给vector<Point> pattern.
256*4表示的是每4A value of a pair of point comparing pixel values of the,得到1bit的数据(Than the one0或者1),Than the total out of the256个bit,其中每8bit的信息就是BRIEFOne element of the descriptor(Said in front of the child element type isCV_8U),所以得到了32个BRIEFDescribe the child value,组成了_descriptors的一列,Is a description of the corresponding feature points are that the son.
而bit_pattern_31_The array isint类型的,Needs to be casts intocv::point类型,Used to calculate the descriptor.This is the code of.
//成员变量pattern的长度,也就是点的个数,这里的512表示512个点(
const int npoints = 512;
//获取用于计算BRIEF描述子的随机采样点点集头指针
//注意到pattern0数据类型为Points*,bit_pattern_31_是int[]型,所以这里需要进行强制类型转换
const Point *pattern0 = (const Point *)bit_pattern_31_;
//将在全局变量区域的、int格式的随机采样点以cv::point格式复制到当前类对象中的成员变量中
std::copy(pattern0, pattern0 + npoints, std::back_inserter(pattern));
The following is a function of a description,里面又调用了computeOrbDescriptor函数
static void computeDescriptors(const Mat &image, vector<KeyPoint> &keypoints,
Mat &descriptors,const vector<Point> &pattern){
for (size_t i = 0; i < keypoints.size(); i++)
computeOrbDescriptor(keypoints[i],image, &pattern[0],descriptors.ptr((int)i));
}
To calculate the descriptor in here,先将patternThe point to be carried out in accordance with the calculating the Angle of rotation x'= xcos(θ) - ysin(θ), y'= xsin(θ) + ycos(θ),To get the pixel valuescenter[ y'* step + x'],进行两两比较,比较的结果.desc[i] = (uchar)val是一种8-bit无符号整形数据,范围为[0, 255].
结果类似于这样
const float factorPI = (float)(CV_PI / 180.f); //乘数因子,一度对应着多少弧度
static void computeOrbDescriptor(const KeyPoint &kpt, const Mat &img, const Point *pattern, uchar *desc)
{
float angle = (float)kpt.angle * factorPI; //得到特征点的角度,用弧度制表示.
float a = (float)cos(angle), b = (float)sin(angle);//计算这个角度的余弦值和正弦值
const uchar *center = &img.at<uchar>(cvRound(kpt.pt.y), cvRound(kpt.pt.x)); //获得图像中心指针
const int step = (int)img.step;//获得图像的每行的字节数
//获得采样点中某个idx所对应的点的灰度值,这里旋转前坐标为(x,y), 旋转后坐标(x',y')
// 下面表示 y'* step + x'
#define GET_VALUE(idx) center[cvRound(pattern[idx].x * b + pattern[idx].y * a) * step + cvRound(pattern[idx].x * a - pattern[idx].y * b)]
//其中每一位是来自于两个像素点灰度的直接比较,所以每比较出8bit结果,需要16个随机点,这也就是pattern需要+=16的原因
for (int i = 0; i < 32; ++i, pattern += 16)
{
int t0, //参与比较的第1个特征点的灰度值
t1, //参与比较的第2个特征点的灰度值
val; //描述子这个字节的比较结果,0或1
t0 = GET_VALUE(0);
t1 = GET_VALUE(1);
val = t0 < t1; //描述子本字节的bit0
t0 = GET_VALUE(2);
t1 = GET_VALUE(3);
val |= (t0 < t1) << 1; //描述子本字节的bit1
t0 = GET_VALUE(4);
t1 = GET_VALUE(5);
val |= (t0 < t1) << 2; //描述子本字节的bit2
t0 = GET_VALUE(6);
t1 = GET_VALUE(7);
val |= (t0 < t1) << 3; //描述子本字节的bit3
t0 = GET_VALUE(8);
t1 = GET_VALUE(9);
val |= (t0 < t1) << 4; //描述子本字节的bit4
t0 = GET_VALUE(10);
t1 = GET_VALUE(11);
val |= (t0 < t1) << 5; //描述子本字节的bit5
t0 = GET_VALUE(12);
t1 = GET_VALUE(13);
val |= (t0 < t1) << 6; //描述子本字节的bit6
t0 = GET_VALUE(14);
t1 = GET_VALUE(15);
val |= (t0 < t1) << 7; //描述子本字节的bit7
desc[i] = (uchar)val;
}
#undef GET_VALUE
}
边栏推荐
猜你喜欢
El - tree to set focus on selected highlight highlighting, the selected node deepen background and change the font color, etc
c现代方法16章基础
Nacos单机模式的安装与启动
Autowired注解与Resource注解的区别
【着色器实现HandDrawn简笔画抖动效果_Shader效果第十二篇】
第五章:指令集
2022年 SQL 优化大全总结详解
Flink的Exactly-Once、状态机制、watermark机制
第一章:ARM公司Cortex-M 系列处理器介绍,第二章:嵌入式软件开发介绍和第三章:Cortex-M3和Cortex-M4处理器的一般介绍
分布式数据库数据一致性的原理、与技术实现方案
随机推荐
Getting started with el-tabs (tab bar)
【playwright】pytest-playwright增加代理服务选项
信息学奥赛一本通T1452:Keyboarding
MySQL日期和时间戳的转换
Detailed explanation and reproduction of AlexNet network
drop database出现1010
Oracle Rac 集群文件目录迁移
信息学奥赛一本通T1449:魔板
El - tree to set focus on selected highlight highlighting, the selected node deepen background and change the font color, etc
Postman will return to the interface to generate a json file to the local
学会可视化大屏布局技巧,让领导都赞不绝口
【多线程进阶】--- 常见锁策略,CAS,synchronized底层工作原理,JUC,线程安全的集合类,死锁
static数据成员
伦敦银现货市场如何使用多条均线?
[机缘参悟-59]:《素书》-6-安于礼仪[安礼章第六]
ISIJ 2022收官,中国初中生再展风采
consul理解
Data warehouse buried point system and attribution practice
pt-online-schema-change工具使用的一次
c现代方法16章基础