当前位置:网站首页>Matplotlib drawing
Matplotlib drawing
2022-07-03 10:09:00 【Most appropriate commitment】
Catalog
Various attributes of graphics
Directly in figure Upper foundation drawing
figure Basic drawing + line attribute
Axes: Subgraphs 、 Axis domain , For display figure Small figure in the panel
Axes: Axis , scale and Axis title
Axes:plot mapping , legend, Text , mark , grid , In the picture , Different axis drawing
library
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
# 0.3 - 3.5 Between Set up 100 A little bit
x = np.linspace(0.3, 3.5, 100)
# random number
# Will return 0-1 Random number between
np.random.rand()
# Will return contain 2 individual 0 To 1 List of random numbers between
y = np.random.rand(n)
# Will return n1 X n2 The random number matrix of
y = np,random,rand(n1,n2)
# np.random.randn() Usage is similar. , however The return is The mean for 0,
# The standard deviation is 1 Of Normal distribution , That is, the return value will exceed (0-1)
# stay 0~10 Inside formation 100 A little bit
boxWeight = np.random.randint(0,10,100)
Various attributes of graphics
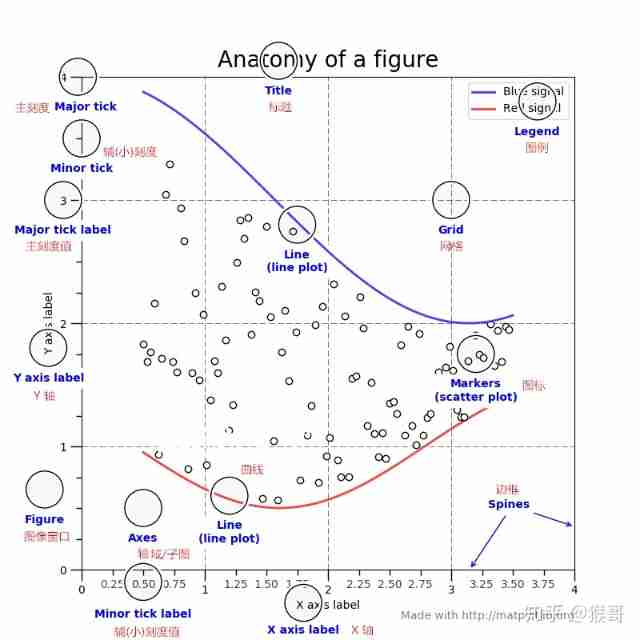
Figure:
Image window , contain Axes,tiles,Legends Wait for the outermost window , yes windows Application window .
figure attribute
fig = plt.figure()
fig = plt.figure(figsize=(8, 6), dpi=80)
## Set the handle
fig = plt.gcf() # Get the current figure
fig = ax1.figure # Gets the window to which the specified sub graph belongs
### fig Title settings for
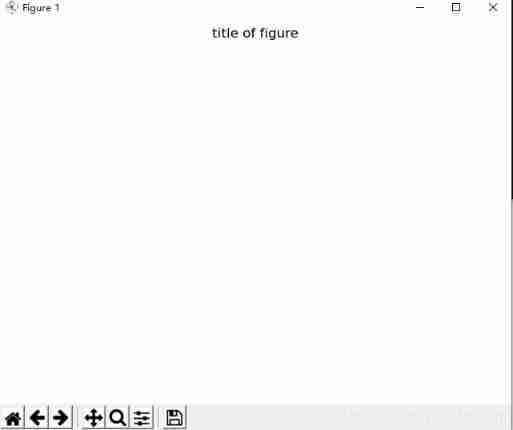
fig.suptitle('title of figure')
# Title of picture
# fig.suptitle() Is the title of the canvas , plt.title() Is the title of the diagram
plt.title('title of picture')
plt.savefig('aa.jpg',dpi=400,bbox_inches='tight')
#savefig Save the picture ,dpi The resolution of the ,bbox_inches The size of the white space around the subgraph
Directly in figure Upper foundation drawing
### Not recommended , It is recommended to use Axes
x = np.linespace(-2,6,50) # from -2 to 6, total 50 points
y1 = x + 3
y2 = 3 - x
plt.figure()
plt.plot(x,y1)
plt.plot(x,y2)
plt.show()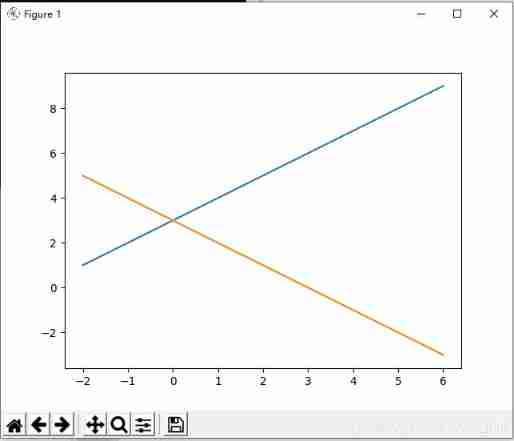
figure Basic drawing + line attribute
x = np.linspace(-2,6,50) # from -2 to 6, total 50 points
y1 = x + 3
y2 = 3 - x
# Directly generate one at a time ax Subgraphs , Then operate directly in the subgraph
plt.subplot(2,1,1)
plt.plot(x,y1)
# Set the width of the line , Color , Linetype , obtain Line2D Handle of attribute list
# plt.plot() Medium label='y1' Have to add plt.legend() Will show
line = plt.plot(x,y,label='y1',color='purple',linewidth=2, linestyle='--')
plt.legend()
line[0].set_linewidth(5) # plt.plot and ax.plot Can get the drawing Line set
# axis limit
plt.axis([-2,-2, 6,10])
## The same thing
plt.xlim(-2,6)
plt.ylim(-2,10)
plt.subplot(2,1,2)
plt.plot(x,y2)
# Set up Level , Vertical line
plt.axhline(y=0, c='r', ls='--', lw=2) # Level
plt.axvline(x=4, c='r', ls='--', lw=2) # Vertical line
# Set up vertical / level Reference area + Fill color
plt.axvspan(xmin=4, xmax=6, facecolor='y', alpha=0.3)
plt.axhspan(ymin=0, ymax =0.5, facecolor='y', alpha=0.3)
# Set up arrow
plt.annotate('important point', xy=(2, 6), xytext=(3, 1.5),
weight='bold', color='b', arrowprops=dict(facecolor='black', shrink=0.05)
)
plt.show()
shortcoming :
figure Drawing directly on , Can't change axis Related properties , So it's not recommended , Recommended settings figure, Then set the axes( Even if there is only one axes), Then set the Related properties of subgraph , And draw .
advantage
But directly figure Draw on , Able to use Vertical line , Level , Add special points , Mark, etc
Axes: Subgraphs 、 Axis domain , For display figure Small figure in the panel
# axes[0] axes[1] axes[2] axes[3] Can be used to axis call
fig,axes = plt.subplots(2,2)
# You can also define a subgraph at a time
ax = plt.subplot(2,2,1)

axis: Corresponding ax Medium x axis and y axis.
Axes: Axis , scale and Axis title
## Subgraph title
ax.set_title(' ')
## Name of coordinate axis of subgraph
ax.set_xlabel(' ')
ax.set_ylabel(' ')
## Change the axis range
ax.set_xlim([-5,6])
ax.set_ylim([-2,10])
## Change the axis scale
ax.set_xticks([-1,0,1])
ax.set_yticks(range(-2,10,1))
## Change axis scale name
ax.set_yticklabels([r'-1', r'0', r'+1'])
ax.set_xticklabels(labels=['x1','x2','x3','x4','x5'],rotation=-30,fontsize='small')
# Set the display text of the scale ,rotation Rotation Angle ,fontsize font size
### Set the size scale
from matplotlib.ticker import MultipleLocator
# Main scale
xmajorLocator = MultipleLocator(2)
# Define the scale difference of the horizontal major scale label as 2 Multiple . It's just a few ticks apart to show a label text
ymajorLocator = MultipleLocator(3)
# Define the scale difference of the vertical major scale label as 3 Multiple . It's just a few ticks apart to show a label text
ax.xaxis.set_major_locator(xmajorLocator)
ax.yaxis.set_major_locator(ymajorLocator)
# Secondary scale
# take x The axis scale label is set to 5 Multiple
xminorLocator = MultipleLocator(5)
# Put this y The axis scale label is set to 0.2 Multiple
yminorLocator = MultipleLocator(0.2)
# Display the position of the secondary scale label , No label text
ax.xaxis.set_minor_locator(xminorLocator)
ax.yaxis.set_minor_locator(yminorLocator)
### Set up grid
ax1.xaxis.grid(True, which='major') #x The grid of the axis uses the defined major scale format
ax1.yaxis.grid(True, which='major') #x The grid of the axis uses the defined major scale format major, minor
### Set up Axis scale ( Size scale ) Of Format
from matplotlib.ticker import FormatStrFormatter
xmajorFormatter = FormatStrFormatter('%3.1f')
ymajorFormatter = FormatStrFormatter('%1.1f')
ax.xaxis.set_major_formatter(xmajorFormatter)
ax.yaxis.set_major_formatter(ymajorFormatter)
### hide That is not used ax
axes[j].axis('off')
### Axis inversion
axes[i].invert_yaxis()
### Sets the position of the axis
axes[i].xaxis.set_ticks_position('top')

Axes:plot mapping , legend, Text , mark , grid , In the picture , Different axis drawing
x = np.linspace(-2,6,50) # from -2 to 6, total 50 points
y1 = x + 3
y2 = 3 - x
y3 = 1000+ 1000*x
ax = plt.subplot(1,1,1)
### Set line handle
line1, line2 = ax.plot(x,y1,'r', x,y2,'b')
### Set the line width under the line handle
line1.set_linewidth(2)
line2.set_linewidth(2)
### color Color change linestyle Change Linetype linewidth Change the line width marker Change point type
### markersize Change the size of the point alpha transparency
line = ax.plot(x,y,label='y',alpha=0.5, color='purple',linewidth=2, linestyle='--',
marker='p', markersize=5 )
### Color , Point type , Linetype Can be abbreviated to :
### ax.plot(x,y,'rp-')
## line[0].set_linewidth = 5; line Get is plot Line set of drawing
### Set the line legend
ax.legend([line1,line2],['y = x+3','y = 3 - x'],loc='best')
## loc = 'best', 'upper right', 'upper left', 'lower left', 'lower right', 'right',
## 'center left',
## 'center right', 'lower center', 'upper center', 'center'
# Display text at specified location ,plt.text()
#weight : normal | bold | bolder | lighter | 100 | 200 | 300 | 400 | 500 | 600 | 700 |
# 800 | 900
ax.text(2.8, 7, r'y=3*x', weight='bold',color='b')
# Add labels , Parameters : Annotated text 、 Point of reference 、 Text location 、 Text font , Text color , Arrow properties
ax.annotate('important point', xy=(2, 6), xytext=(3, 1.5),
weight='bold', color='b', arrowprops=dict(facecolor='black', shrink=0.05)
)
# Show grid .which The value of the parameter is major( Just draw the big scale )、minor( Just draw small scales )、both, The default value is major.
# axis by 'x','y','both'
ax.grid(b=True,which='major',axis='both',alpha= 0.5,
color='skyblue',linestyle='--',linewidth=2)
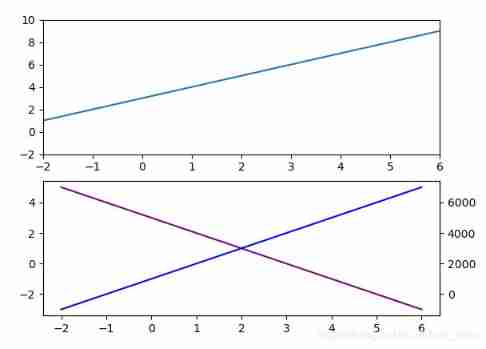
In the picture
axes1 = plt.axes([.2, .3, .1, .1], facecolor='y')
# Add a sub graph to the current window ,rect=[ Left , Next , wide , high ],
# It's using The proportion Locate
axes1.plot(x,y2)
# In a subgraph Same as x Axis , Different y Axis ; Same as y Axis , Different x Axis
# ax1.twinx() ax1.twiny()
ax2 = ax1.twinx()
ax2.plot(x,y3,label='y3',color='blue')

color property color

Linetype properties linestyle
- Solid line : '-'
- Dotted line : '--'
- Dotted line : '-.'
- Dotted line : ':'
- spot : '.'
Point type marker
Pixels : ','
circular : 'o'
Upper triangle : '^'
Lower triangle : 'v'
Left triangle : '<'
Right triangle : '>'
square : 's'
plus : '+'
Fork : 'x'
Prismatic : 'D'
Fine prismatic : 'd'
Tripod down : '1'( It's Ya )
Tripod up : '2'
The tripod faces left : '3'
The tripod faces right : '4'
hexagon : 'h'
Rotate hexagon : 'H'
Pentagonal : 'p'
Vertical line : '|'
Level : '_'
graphics
Scatter plot
It can be used to set special points , And use annotate() Annotate ; You can set the scatter chart
## s : size Size of points , The default is 20 ; c / color Color ; marker Point type ; alpha : 0-1 transparency
## linewidth : The peripheral line width of the point , The default is 0
plt.scatter([3],[6],s=20, c='blue', marker='o', alpha = None,linewidth=None)
## x,y by list
plt.scatter(x,y)
### Bubble chart
a= np.random.randn(100)
b= np.random.randn(100)
plt.scatter(a,b,s=np.power(10*a+20*b,2), c=np.random.rand(100),
cmap= plt.cm.RdYlBu,marker='o')
Histogram , Bar chart and Histogram + Stacked graph
# x Express x coordinate , The data type is int, float
# height Indicates the height of the histogram , The data type is int , float type
# width Express The width of the histogram , stay 0~1 Between
# bottom Indicates the starting position of the histogram , That is to say y The starting coordinates of the axis , You can't do it from 0 Start
# align = 'center', 'edge' Indicate whether the scale is in the middle or on the side of each column
# hatch = '\\' '/' '\\/' '-'
# edgecolor Indicates the border color
# linewidth Indicates the width of the border
# tick_label: Subscript label , Quantity and sum x,height The quantity is the same , Used in substitution x Axis number
# log : Histogram yz The axis uses scientific counting , Bool type
# alpha : Express transparency
### vertial Histogram
plt.bar(x, height, width=0.8, align='edge',color='c',hatch='/', tick_label=['A','B','C','D'])
plt.xlabel()
plt.ylabel()
### horizontal Bar chart
### The parameters are the same as above , however bottom Change it into left
plt.barh()
### hist() Used to draw histograms For display x Distribution of data in
# x Express The data points for example Distribution in (0,10) Between 100 It's an integer
# bins Express Points of distribution for example Express (0,10) Of Distribution point
# histtype : step, stepfilled, barstacked: Two bar charts with stacked bars ,
# bar: The width of the bar can be different
# rwidth Express Strip shape Width
# alpha Presentation transparency
# density False , True Express Y Number of shafts , Or density
# Histograms are used to show Distribution of data , Only x Need to define , bin Used to describe The range of data
plt.hist(x, bins=bins, color='g', histtype='')
# Stacked graph
# Used to place one bar chart above another ,eg: Indicates quarterly growth
# practice : Put the second histogram / The design of bar chart bottom( For histogram ) perhaps left ( For bar charts ) Set as the first histogram / Bar chart bottom/left = y/ height
x = [1,2,3,4,5]
y1 = [6,10,4,5,1]
y2 = [2,6,3,8,5]
# First create y1 label stay legend It will be displayed later
plt.bar( x,y1, align='center',color = 'k', tick_label = ['A','B','C','D','E'] ,label = ' First quarter ')
# And then in y1 Create above y2
plt.bar( x,y2, align='center', bottom=y1, color = 'k', label = ' The two quarter ')
plt.xlabel(' Different branches ')
plt.ylabel(' results ')
plt.legend()
plt.show()
# Bar chart barh take bottom Switch to left
Block diagram ( Bar chart / The histogram is placed side by side )
The pie chart
# nums: Represents the number of each part
# labels: Label representing each part
# colors: Represents the color of each part
# explode = [0,0.1,0,0] Represents the prominent part of each part
# autopct = '%3.1f%%' Express The percentage displayed in each section
# startangle=60 The starting angle is 60°
# shadow = False ; True Indicates whether there is a shadow
plt.pie(nums, explode, labels=labels, autopct='%3.1f%%',startangle=60,
colors=colors,shadow=False)
# Indicates that the pie chart is circular , Not oval
plt.axis('equal')
Cotton stick chart
###
# x: Indicates that the baseline is x Position on the shaft , y: Express The difference is y The length on the shaft
# linefmt Indicates the form of cotton stick
# markerfmt Indicates dot
# basefmt Represents the style of the baseline
plt.stem(x,y,linefmt='-.',markerfmt='o',basefmt='-')
boxplot
# x: Represents a data list
plt.boxplot(x)
# plt.ylabel() Express y The title of the axis
# plt.title() Indicates the title of the box diagram
# plt.xtick([1],[' Random number generator AlphaRM']) Error bar chart
plt.errorbar(x,y,fmt='bo:',yerr=0.2,xerr=0.02)Two dimensional cloud image
### Two dimensional cloud image
### vmin by minimum value , vmax by Maximum . The maximum and minimum colors in the gradient
ax.imshow( matrix ,cmap=plt.cm.cool,vmin=-5, vmax=5,alpha = None) cmap Color
| autumn | red - orange - yellow |
| bone | black - white ,x Line |
| cool | green - Magenta |
| copper | black - copper |
| flag | red - white - blue - black |
| gray | black - white |
| hot | black - red - yellow - white |
| hsv | hsv Color space , red - yellow - green - green - blue - Magenta - red |
| inferno | black - red - yellow |
| jet | blue - green - yellow - red |
| magma | black - red - white |
| pink | black - powder - white |
| plasma | green - red - yellow |
| prism | red - yellow - green - blue - purple -...- Green mode |
| spring | Magenta - yellow |
| summer | green - yellow |
| viridis | blue - green - yellow |
| winter | blue - green |
Epipolar diagram
theta = np.linspace(0, 2*np.pi, 12, endpoint=False)
r = 30* np.random.rand(12)
# theta : angle
# r: distance
# color: Line color
# linewidth Line width
# marker Point type ; mfc The color of the point ; ms Size of points
plt.polar( theta,r, color = 'chartreuse', linewidth=2, marker='*', mfc='b',ms=10 )
Three dimensional diagram
ax = fig.add_subplot(1,1,1,projection='3d') # 3d drawing
## 3D lines
theta = np.linspace(-4 * np.pi, 4 * np.pi, 100)
z = np.linspace(-2, 2, 100)
r = z**2 + 1
x = r * np.sin(theta)
y = r * np.cos(theta)
ax.plot(x, y, z, label='parametric curve')
## Surface map
x,y=np.mgrid[-2:2:20j,-2:2:20j] # obtain x Axis data ,y Axis data X,Y = np.meshgrid(X,Y)
z=x*np.exp(-x**2-y**2) # obtain z Axis data
surf = ax.plot_surface(x,y,z,rstride=2,cstride=1,cmap=plt.cm.coolwarm,alpha=0.8)
ax.set_zlim(z_min, z_max)
fig.colorbar(surf, shrink=0.5, aspect=5)
Reference and copy the link source :
python Drawing books - The search results - You know
Python The line type when drawing in _lei_jw The blog of -CSDN Blog
边栏推荐
- 2312、卖木头块 | 面试官与狂徒张三的那些事(leetcode,附思维导图 + 全部解法)
- Of course, the most widely used 8-bit single chip microcomputer is also the single chip microcomputer that beginners are most easy to learn
- CV learning notes convolutional neural network
- 4G module designed by charging pile obtains signal strength and quality
- Crash工具基本使用及实战分享
- Leetcode interview question 17.20 Continuous median (large top pile + small top pile)
- 2021-10-27
- SCM is now overwhelming, a wide variety, so that developers are overwhelmed
- Wireshark use
- (1) 什么是Lambda表达式
猜你喜欢
03 FastJson 解决循环引用

JS foundation - prototype prototype chain and macro task / micro task / event mechanism
Opencv Harris corner detection

Opencv image rotation

LeetCode - 900. RLE 迭代器

Of course, the most widely used 8-bit single chip microcomputer is also the single chip microcomputer that beginners are most easy to learn

LeetCode - 508. Sum of subtree elements with the most occurrences (traversal of binary tree)

Adaptiveavgpool1d internal implementation
Working mode of 80C51 Serial Port

openEuler kernel 技術分享 - 第1期 - kdump 基本原理、使用及案例介紹
随机推荐
Windows下MySQL的安装和删除
2312、卖木头块 | 面试官与狂徒张三的那些事(leetcode,附思维导图 + 全部解法)
Markdown latex full quantifier and existential quantifier (for all, existential)
CV learning notes - Stereo Vision (point cloud model, spin image, 3D reconstruction)
Wireshark use
After clicking the Save button, you can only click it once
Notes on C language learning of migrant workers majoring in electronic information engineering
CV learning notes ransca & image similarity comparison hash
Installation and removal of MySQL under Windows
Leetcode 300 longest ascending subsequence
(1) What is a lambda expression
使用密钥对的形式连接阿里云服务器
LeetCode - 1670 设计前中后队列(设计 - 两个双端队列)
4G module IMEI of charging pile design
Opencv image rotation
Pycharm cannot import custom package
Of course, the most widely used 8-bit single chip microcomputer is also the single chip microcomputer that beginners are most easy to learn
QT detection card reader analog keyboard input
3.2 Off-Policy Monte Carlo Methods & case study: Blackjack of off-Policy Evaluation
SCM is now overwhelming, a wide variety, so that developers are overwhelmed