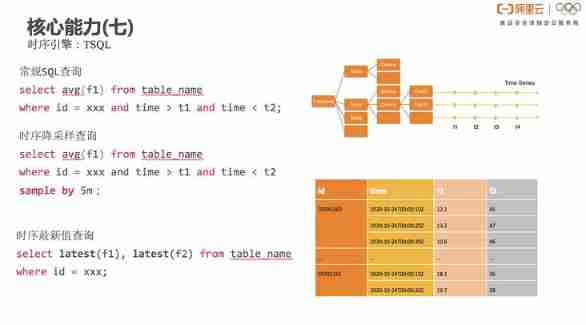
BGFX Multithreaded rendering
1. Multithreading Foundation
1. The concept of concurrency
1. Introduction to concurrent tasks
Years ago , On the cell phone 、pc End 、 Game consoles, etc , It's all a single core CPU. such , On the hardware level , When dealing with multiple tasks , It is also to cut some tasks into small tasks . Switch tasks at certain times , from A The task switches to B Mission , In the process , Every time the system switches tasks , All need to switch context , This also explains a problem from the side , Switching tasks also has time overhead .
Some people will say why big tasks are cut into small tasks , Switch between small tasks ? In fact, this is an objective demand . For example , If big tasks are performed in line , No cutting , If you open a app It's a mission , Open the other app It's also a task , If you click A And in A When doing something in , I want to open it at this time B, Obviously , If this task is not cut , Then I need to close A, In the open B, That's how it works . But I want to go back to A Time of operation , I'm sorry , You can only reopen . Maybe the example I gave is not very appropriate , But just to describe a problem : Even a single core processor , The operating system also divides some big tasks into small tasks , To meet the actual needs just mentioned , Meet the requirement of concurrency to a certain extent .
In this day and age ,2000 Years later, , Multi core gradually replaced single core processor . The traditional single core processor has obviously reached the bottleneck by increasing the frequency to improve the performance of the processor , That's Moore's law . however , For some developers today , Most of the software engineering developed is still concentrated in one task , Although mentioned above , Single core CPU In fact, it is also a form of multitasking . This makes the multi-core hardware feature very embarrassing , This is often the case , The main core CPU Busy to death , The other cores are sleeping .
2. Concurrent implementation approach
As mentioned in the previous section, in fact, whether it is single core hardware , Or dual core hardware . Our system divides some tasks into small tasks one by one , Constantly switching , And protect the split switching area , Encapsulate different small tasks by categories . But no introduction , How to achieve .
This section briefly introduces the way to realize concurrency . Simply speaking , One is thread based concurrency , One is process based concurrency ;
remarks : part c++ In the programming guide , There is no distinction between concurrency and parallelism , Just collectively referred to as concurrency . stay UE The source code distinguishes the difference between the two ; part c++ Relevant books point out , In multi-core physical devices , Two or more threads simultaneously , No collaboration is called parallelism , If there is switch waiting or exchange synchronization, it is called concurrency ; Specific differences , You can consult relevant materials and books for verification ; This article will not distinguish between concurrency and parallelism ; Rigorous description is not parallel to science , People with knowledge are welcome to explain and analyze
Thread is different from process
process
Process is the basic unit of resource allocation and management in the process of concurrent execution . A process can be understood as the execution of an application , Once the application is executed , It's a process . Each process has its own address space , Every time a process is started , The system will allocate address space for it , Create data tables to maintain code snippets 、 Stack and data segments
Threads
A thread is the smallest unit of program execution , yes CPU The basic unit for performing tasks and switching , Is process dependent , One virtual processor per thread , Register group , Instruction counter , Core processor status , Multiple threads share the address space of the current process
Differential connection
A process contains multiple threads , Threads in the current process share the address space of the process , The address space between different processes is independent
Independent processes have their own execution entry , Execution order , Threads cannot run independently , Depending on the process, it is controlled by multithreading control mechanism
The cost of switching processes is greater than that of switching threads , The process creation and destruction costs a lot , But high reliability , Low thread overhead , Fast switching speed , But thread crash will cause the process to crash , But it won't affect other processes
Based on process concurrency
Create multiple processes , Then each process is assigned a task , If there is communication between multiple processes , Then use pipes , System ipc( Message queue 、 Semaphore 、 The signal 、 Shared memory ) And socket . Safe and reliable , High code robustness , But it costs a lot . If used on remote Links , Processes running independently on different machines , On a well-designed system , It may also be a low-cost way to improve parallelism and performance
Based on thread concurrency
stay c++11 Before , We realize multithreaded programming , It can be said that the eight immortals cross the sea and show their magical powers ; Have use pthread Of , Have use boost::thread Of , There is also the use of multithreading provided according to each system platform API. stay C++11 after ,c++ The organization has incorporated multithreading into its component library , This brings great convenience to multithreading development . Less dependence , High portability .
Create multiple threads , Assign tasks to each thread , If multiple threads have communication , Then use semaphore , Condition variables, , Mutually exclusive lock and other means . This is just a brief introduction , True multithreading implementation , There are also various issues to consider , Resource security , Rationality of task allocation , And reduce the switching performance overhead . Corresponding to some new technologies , For example, thread pool , Mission system , Thread safe smart pointer and so on .
2. Multithreaded concurrency
1. The reason for using concurrency
Of course, multi-core processing system has been born for a long time , But for program developers , Some people still ignore these , Now this time , It is necessary to incorporate it into your professional skills .
The reason for using concurrency : One is the separation of concerns (SOC) And improve performance
Separation of concerns (SOC)
Separation of concerns ; Simply speaking , By classifying some code that implements logic or calculation , Separate some non cohesive code , This will make the program easier to understand and more robust , And when we deal with concurrency , Easier to deal with critical areas .
Improve performance
There are two ways to use concurrency to improve performance
Task concurrency
Split a task into several parts , Each part runs concurrently , So as to reduce the total running time ;
It's easy to say , But this needs to deal with the possible dependency between various sub tasks , Sometimes it takes a lot of energy to deal with .
Data concurrency
Execute the same instructions on different data parts
Task concurrency is , A thread executes part of an algorithm , Another thread executes another part of the algorithm ; But data concurrency is , The instructions executed by the two threads are the same , But the execution data is different
2. When not concurrent
since 2000 Since then , After multicore became the mainstream form ; I often see some people talking about , If the performance doesn't work , Poor performance , Then open a few more threads , Will improve performance . In a sense , It makes sense , But it doesn't make perfect sense .
When concurrency cannot be used is as important as when it can be used . The core reason is that there are several situations in which the income can not compare with the cost , As shown below
The benefits are not comparable to the costs
The performance improvement is less than the maintenance cost
Most of the time , Using concurrency increases the complexity of the program , Make the code difficult to understand . It is possible that the party concerned wrote clearly , But later maintenance is not clear , Even when there are documents, you will be confused , It is also very likely to cause more problems . under these circumstances , If the performance improvement is very small , Then there is no need to do concurrency . Unless the potential performance improvement and separation of concerns are very clear , Then please don't use concurrency
Performance improvement is less than expected
We often say , How can I kill a chicken with a butcher's knife . This sentence is also very practical here , The operating system allocates for each thread : Virtual processors 、 Register group 、 Instruction counter 、 Operating system resources such as core processor status , So every time the thread starts , There will also be fixed expenses , Then the thread will be added to the scheduler . So, for example , The task in the thread takes less time to complete than the thread startup time , Then the gains are not worth the losses , It's not too much to describe how to kill a chicken and how to kill an ox with a knife
Threads are finite resources
Let's give you a simple example ; We all know that threads need system resources , Suppose every thread has 1MB Stack space of , For an available address space 4GB(32bit) For the process of flat Architecture ,4096 One thread will consume all the address space . Then leave it to the code 、 What is the space for static data or heap data 0, So how can efficiency be high ? Although we use thread pool to optimize the resources occupied by threads , But it's not a panacea , In the case of many threads , Consumes a lot of system resources , It will also cause the whole system to run more slowly . At this point , We must balance this node , let me put it another way , We turn on concurrency mode , Some limitations must be ignored for more valuable things , For example, concurrency can make the design clearer , The separation of concerns is more complete , Make the current load more balanced , Improve the performance of the system , Then concurrency is worth doing .
remarks : In fact, write these two sections , I'm very tangled , If you don't write , So some of the background and basic concepts of concurrency will be introduced in vague terms , For those who read this article , It may not be clear what kind of problems concurrency is designed to solve , Or whether the next multi-threaded rendering is the mainstream trend of the industry , Without a clear understanding . But I wrote this paragraph , I feel a lot less , For example, some actual profile Data proving ; In addition, I read some books and blogs , Organize what you write , I always feel that something is missing , What's not accurate . If someone with knowledge corrects or discusses with me , I welcome you very much .
3. Producer consumer model
Why do you want to bring out this basic multithreading model alone . In fact, it is mainly to make a basic preheating for the later multi-threaded rendering scheme , In fact, the multithreaded rendering scheme mentioned in the second section below , Mainly around producers and consumers . If you want to consider modern api Some characteristics of , Will revolve around 、 Is it worth introducing , Some specific thinking and understanding , It will be briefly expanded in Section 3 , By their new rendering api The depth and limitations of mastery , Maybe the direction of thinking is not completely right , There are people who correct , I would be very grateful .
This section only introduces the single producer single consumer model , As for the more complex single producer multi consumer 、 Multiple producers and single consumers 、 Many producers, many consumers , I won't go over it here , Interested parties can consult relevant materials and documents by themselves .
3.1 Thread basis
This article focuses on pthread Of api Discuss some basics of threads ,c++11 Related to api Will not be within the scope of this article .
pthread Medium p It stands for POSIX,pthread yes IEEE( Institute of electronic and Electrical Engineers ) A set of threaded interfaces developed by the Committee , Responsible for specifying the portable operating system interface (POSIX)
1. Thread management
Thread creation
int pthread_create (pthread_t *thread,pthread_attr_t *attr,void *(*start_routine)(void *),void *arg)
pthread_t
This data type represents the unique identifier of the thread in the process , Is an unsigned long integer data (32 The bit system is 4 byte , stay vc as well as MinGW64 In Chinese, it means 4 byte ,GCC(POSIX System and Cygwin) by 8 byte ). The value is not specified by the user , Is to assign this variable to the identifier of the new thread created in the function .
pthread_attr_t
Specifies the properties of the thread , have access to NULL Indicates the default attribute ; By default , When a thread is created, it should be given some properties , This property is stored in pthread_attr_t variable , Including thread scheduling policy , Stack related information ,join perhaps detach And so on
start_routine And arg
Specify the function that the thread starts running , and arg yes start_routine Required parameters , Is a typeless pointer
Thread properties
Thread creation , By default, it has some properties , Developers can change some of these properties through the thread property object . among pthread_attr_init And pthread_attr_destroy For initialization / Destroy the thread property object
Then use the properties api To query or set specific properties in the thread property object , as follows :
Detached or linkable state
Scheduling inheritance
Scheduling strategy
Scheduling parameters
Dispatch scope
Stack size
Stack position
Stack protection size
After creating the thread , How to know when the operating system is scheduled to run , Which processor or kernel will it run on ?
Once the thread is created , Threads are equal , And you can create other threads , Moreover, there is no implicit hierarchy or dependency between threads
pthreads Provided some api To schedule execution , Threads can be scheduled to run as FIFO( fifo )、RR( loop ) perhaps OTHER( The operating system determines ), It also provides the ability to set thread scheduling priority , Can be specific in sched_setscheduler View in manual
pthreads API Binding a thread to a specific is not provided CPU/ Some examples of the core .pthread_setaffinity_np Yes no standard , Can handle binding a thread to a cpu, For details, please check the relevant api( The local operating system will provide some api To deal with these problems ).
Thread end
void pthread_exit (void *retval);
int pthread_cancel (pthread_t thread);Threads will be when the following situations occur , Will terminate the thread
start_routine function return 了 , The work done by the thread has been completed
Called pthread_exit function , Will stop all threads
The current thread is called by another thread pthread_cancel Cancel
By calling exec() perhaps exit() To terminate the thread
main() Function completion , But it doesn't show the call pthread_exit function , The thread will terminate . But if main() The display calls pthread_exit,main() The function will be blocked and wait for the thread to exit after execution
pthread_exit function ,retval The developer specifies the parameters , This parameter can be in pthread_exit Some status of thread exit after execution
pthread_cancel function , The current thread passes pthread_t Parameter specifies the name of another thread id To cancel another thread ; Of course, this can only cancel another thread under the same process , Successfully returns 0, Failure returns the corresponding error code
Thread blocking
There are two types of threads after they are created , One is separate , A kind of linkable
Shows how to create linkable or separable threads , Use thread property objects , Its typical four steps are as follows :
Statement pthread_attr_t Attribute variable of data type
Initialize property variables pthread_attr_init()
Set the property separation status pthread_attr_setdetachstate()
After completion , Release resources used by attributes pthread_attr_destory()
pthread_join Function is a way of synchronization between threads
Other threads can pass through the specified threadid To wait for the thread to complete
The same thread cannot be executed by multiple threads join, Otherwise, unexpected problems will arise
pthread_detach The specified thread available for display is separable , But it is already separable and cannot be specified as linkable
If the thread needs to be linkable , Then consider setting the thread to be linkable . If before creating the thread , It is clear that the thread does not need a link , After running , It's over , Then set it to be separable when creating the thread , So after the thread runs , Some system resources will also be recycled together . Because the system resources are limited , If you create a lot of linkable threads , It is possible that creating a new thread will cause the error of insufficient stack resources .
Thread stack
Developers tend to ignore this problem , But this will always cause some problems ,POSIX The standard does not specify the stack size of threads , And developers always like to use the default stack , When the system resources used exceed the default stack size , It usually leads to program termination or data corruption , Then it takes a lot of effort and time to query this problem .
Stack managed API as follows :
pthread_attr_getstacksize (attr, stacksize);
pthread_attr_setstacksize (attr, stacksize);
pthread_attr_getstackaddr (attr, stackaddr);
pthread_attr_setstackaddr (attr, stackaddr);from api You can roughly understand the functions of these functions by their names , I'm not going to repeat it here
remind :POSIX The standard does not specify the stack size of a thread ( Once again, this issue is emphasized ), Therefore, I want to write a high-quality, safe and reliable program with strong portability , Don't rely on default stack settings , It's about calling pthread_attr_setstacksize To allocate enough stack space ( a key ).
2. The mutex
summary
The mutex API
pthread_mutex_init (mutex,attr)
pthread_mutex_destroy (pthread_mutex_t *mutex)
pthread_mutexattr_init (attr)
pthread_mutexattr_destroy (attr)
phtread_mutex_lock(pthread_mutex_t *mutex)
phtread_mutex_trylock(pthread_mutex_t *mutex)
phtread_mutex_unlock(pthread_mutex_t *mutex)Concrete api effect , I won't repeat it here , If you need to query the specific use, you can check it pthread The development manual for
Mutex usage order
Create and initialize mutexes
Multiple threads tried to lock the mutex
Only one is successful and the thread has a mutex
The owner thread performs some operations
The owner thread releases the mutex
Another thread gets the mutex repeatedly 4、5 operation
The mutex is destroyed
pthread The basic concept of mutex in is , Only one thread can have a mutex at any time , Even if multiple threads try to get the mutex , Only one thread will succeed in getting .
establish / The destruction
establish
The mutex declaration is in pthread_mutex_t, And it is unlocked after initialization , Initialization is required before use , The two initialization methods are as follows :
static state : pthread_mutex_t mymutex = PTHREAD_MUTEX_INITIALIZE
dynamic : Initialize in the normal way , You can set the properties of the mutex
The destruction
pthread_mutex_destroy() Release unwanted mutex objects
attribute
attr Is a property that can set a mutex , You can also specify NULL To set the default value .pthread There are three mutex attributes in the standard as follows :
protocol: Specifies the protocol used to prevent priority reversal of mutex
prioceiling: Specifies the upper priority limit of the mutex
process-shared: Specifies that the mutex is shared by the process
remarks : Not all systems provide three optional mutex properties
lock / Unlock
lock
pthread_mutex_lock Function to obtain the lock of the mutex , If the current mutex is already locked by another thread , Then it will be blocked , Until the mutex is unlocked ; There will be a problem here , A thread gets the mutex , Another thread will always poll the mutex , This will consume system resources , So developers should use this method with caution .
pthread_mutex_trylock() Try locking the mutex , If the mutex is locked , So it will return "busy" Error code . It can prevent deadlock , For example, priority reversal
Unlock
pthread_mutex_unlock() Function to unlock the mutex , After unlocking the mutex , Only other threads can get the ownership of the lock . However, there are two cases of wrong use , as follows :
The mutex has been unlocked , Unlock again
The mutex is owned by another thread lock , Unlock the current thread
3. Condition variables,
summary
If it's a mutex , Then there are two states , In this way, if some threads do not get the ownership of the mutex , Then you will be polling and waiting for the mutex to be released , Then take ownership , Going to do something . This will waste some system performance ,pthread The standard provides conditional variables , When a thread is blocked , Is signaled by another thread , When a signal is received , The blocked thread is awakened and gets the mutex associated with it .
pthread The use of conditional variables in the standard should be matched with mutual exclusion . Conditional variables are only awakened to operate the critical area when a thread meets certain conditions , It avoids the problem of wasting system resources by constantly polling to check whether the conditions are true . Use of mutexes , Make sure that at the same time , There won't be multiple threads to do pthread_cond_wait as well as pthread_cond_signal, Cause unforeseen problems .
pthread_cond_init (condition,attr);
pthread_cond_destroy (condition);
pthread_condattr_init (attr);
pthread_condattr_destroy (attr);
pthread_cond_wait(condition,mutex);
pthread_cond_signal(condition);
pthread_cond_broadcast(condition);establish / The destruction
establish
The declaration type of condition variable is pthread_cond_t, Initialization is required before use , There are two kinds of initialization :
static state : pthread_cond_t mycond = PTHREAD_COND_INITIALIZER
dynamic : Use pthread_cond_init Function to create , Conditional variable id Return through the parameters of the function ;attr You can set the properties of condition variables ,attr It can be set to process-shared( Not all systems can set process sharing properties ), Creating and destroying conditional variable attribute objects is done using pthread_condattr_init() And pthread_condattr_destory() function
The destruction
Release unnecessary condition variables and use pthread_cond_destory() function
wait for / Release
wait for
pthread_cond_wait function , This function blocks the current thread . Blocking time , Lock the mutex first , Automatically release the mutex while waiting for the condition variable . Wake up the thread when receiving the signal , Then automatically lock the mutex , Unlocking requires developers to unlock .
Release
pthread_cond_signal/pthread_cond_broadcast function , When the thread has finished operating the critical area , Need to unlock the mutex , In this way, the thread waiting for the semaphore will acquire the mutex and lock . When more than one thread is waiting for a signal , use pthread_cond_broadcast Instead of pthread_cond_signal
matters needing attention
Waiting for semaphores pthread_cond_wait Lock the mutex before , Otherwise, the thread will not be blocked
Releasing the semaphore pthread_cond_signal Then unlock the mutex , Otherwise, other threads will not get the mutex , Not allowed to match pthread_cond_wait
4. additional : Semaphore
Just briefly
Strictly speaking ,semaphores Not at all pthread Part of the standard , By POSIX Standard definition of , Is that you can and pthread Use it together , But I didn't bring pthread_ The prefix can be seen .
The creation of semaphores is divided into famous semaphores and unknown semaphores , Developers often use anonymous semaphores , Because it allows multiple threads to operate on critical resources , That's why it doesn't have security such as conditional variables and events .
In addition, for semaphores , stay window The platform can use pthread_win32 This pthread The library of , To use semaphores . stay unix、 as well as linux、macos have access to pthread, But it doesn't mean , These platforms can use semaphores , Semaphores are not pthread Standards for , yes POSIX Standards for . In the latest macos as well as ios In the system , Semaphores can no longer be used (macos as well as ios Can be used in dispatch_semaphore_t,bgfx For in the macos as well as ios Also use this api), It's already undefined 了 , So you want to use semaphores , You need to consult relevant information , I'm making a layer of encapsulation for the semaphore , For ease of use and portability . Concrete api And some precautions , There will be no more details here , If you want to know, you can check some materials to learn .
summary : This is a digression , For engines , The portability of the engine is a very important indicator , So when developing multithreading , You can't just rely on a platform api 了 , It is necessary to have different interfaces with the same functions in each platform api, Encapsulated into a unified interface for engine development . It's a troublesome thing , However, this process can understand the differences of various platforms , Be familiar with api Specific capabilities and deficiencies , Select or encapsulate an efficient unified interface , This is the basic skill of engine developers . So the engine is for some basic things , It's not as difficult as you think , It's just a combination , Let artists better show something , Instead of worrying about problems other than effects . So please don't be afraid of engine development , Ten thousand Zhang tall buildings rise from the ground , It's all simple things. It's not simple .
3.2 Producer consumer
summary
Go back to the original question first , Multithreading is to focus on separation points and improve performance ; Then use the producer consumer model , Dismantling task , The task is divided into submission and execution , The code framework is clearer , Easier to expand . in addition , The critical area resource protection of producer consumer model is relatively clear , Multitasking , Improve the efficiency of data concurrent processing ; And now this kind of hardware , Easier to improve the performance of the program . In other words, the producer consumer model also follows this rule .
Specific ideas
Using semaphores , Divide the tasks of producers and consumers , Producer as task submitter , Consumers as task performers , In this way, the logical code will be split and processed . Protect and synchronize resources in dual queues and semaphore critical areas . Simply provide a producer consumer example to illustrate some problems .
The code in the example is an interface that encapsulates semaphores and threads , If you are interested, you can refer to the source code of some open source engines , recommend ue. General multithreading development , It will not directly call threads provided by some thread libraries or platforms api, Instead, it is encapsulated in a certain sense , Provide unified interface to the outside world . This makes the interface easy to use , And if the platform is thread to thread api It's been modified , It can also be better maintained , In short, robustness and expansibility will be improved .
explain : The code is a tool for the author to learn and verify some multithreading schemes demo Case study , Although it is relatively simple , But there is no problem with the general framework and ideas
#pragma once
#include "ThreadSemaphore.h"
#include "ThreadMutex.h"
#include "ThreadQueue.h"
#include <unistd.h>
namespace ThreadMultiRender
{
class ThreadDoubleQueue :public ThreadQueue
{
public:
// Distinguish between initialization and assignment ,c++ In the regulations , The initialization action of the member variable of the object occurs before entering the constructor ontology
// And the assignment , First, call the default constructor to set the initial value of the member variable , Then give a new value , By comparison, the performance is obvious , If there are many objects, it is obvious
// For example, memory alignment of member variables , Simple manual alignment , There are more complicated ways , Of course, they are assembled by some simple things
// Of course, this example is just a case , More rules and coding details are not followed , But this is what we should do
// For example, the read and write properties of methods , If the confirmation method is called by itself within 100% of the class , Then declare it private , Prevent ambiguity and errors in use
// And notes , Don't ask for complex standards , But the most basic notes must be written , Fangzheng Luoli, a pile of wordy , Try to make your code elegant
// There are other basic rules , I suggest you try your best to do , If you don't know , You can read more EffectiveC++ series
ThreadDoubleQueue()
: m_EncoderList(0)
, m_RenderList(0)
{
}
virtual ~ThreadDoubleQueue()
{
}
//MainThread call this function
virtual void EngineUpdate()
{
BeginRender();
//Submit Render CMD
m_PrintMutex.Lock();
m_EncoderList += 1;
LOGI("MainThread=================================:%f", m_EncoderList);
m_PrintMutex.UnLock();
Present();
}
//RenderThread Call this function
virtual void RenderOneFrame()
{
m_RenderSem.WaitForSignal();
//m_RenderList = 2;
m_PrintMutex.Lock();
LOGI("RenderThread===:%f", m_RenderList);
m_PrintMutex.UnLock();
SimulationBusy();
m_MainSem.Signal();
}
private:
void Swap(float lhs,float rhs)
{
float temp = lhs;
lhs = rhs;
rhs = lhs;
}
void SimulationBusy()
{
sleep(3000);
for (int i = 0; i < 10000000; i++)
{
float value = 10 * 20 * 4.234 * 2341;
}
}
// Wake up the rendering thread
void BeginRender()
{
m_RenderSem.Signal();
}
// Wait for the rendering thread to finish rendering , Swap buffer queue
void Present()
{
m_MainSem.WaitForSignal();
//Swap(m_EncoderList,m_RenderList);
float temp = m_EncoderList;
//m_EncoderList = m_RenderList;
m_RenderList = temp;
m_PrintMutex.Lock();
LOGI("Swap CMD m_EncoderList ===:%f", m_EncoderList);
LOGI("Swap CMD m_RenderList ===:%f", m_RenderList);
m_PrintMutex.UnLock();
}
private:
float m_EncoderList;
float m_RenderList;
ThreadSemaphore m_MainSem;
ThreadSemaphore m_RenderSem;
ThreadMutex m_PrintMutex;
};
}This code does not run , Just a framework for learning demo, Some of these classes are encapsulated in the library written by the author .
Other codes are not provided here , Interested parties can encapsulate a set of simple cross platform thread libraries . Only the task splitting of core producer consumption is provided here , Critical area data protection , Synchronization strategies .
Task split
The main thread wakes up the rendering thread , Production rendering instructions
When the rendering thread wakes up , Execute rendering instructions
Data protection
The rendering thread executes the rendering queue ( Rendering buffer) The order of , Or read the rendering command of the rendering queue ; The main thread goes to the coding queue ( code buffer) Submission of orders , Or write rendering commands to the coding queue . Under certain conditions , Exchange commands for rendering queue and encoding queue , In this way, reading and writing are separated , Don't read and write one at the same time buffer Or a queue , Ensure that the data is secure , Logical processing is also clearer .
Synchronization strategies
The main thread produces rendering instructions , Request encoding queue and rendering queue exchange , If the rendering thread does not finish executing the last rendering queue instruction , Then the main thread is blocked ;
The rendering thread has finished executing the last rendering queue instruction , The main thread ends blocking , The encoding queue and the rendering queue are interchanged . The rendering thread executes the switched rendering queue instruction , The main thread encodes the next encoding queue instruction , So circular .
summary
This is a typical dual queue synchronization solution , It is a solution for producers and consumers . Of course, there are other options , For example, ring lockless queue , Of course, this scheme will not be discussed here , Interested parties can consult the classical mode of ring lockless queue . Someone asked why we should introduce the dual queue synchronization scheme , That's because the next bgfx The multithreading scheme is based on the framework just introduced .
Dual queue synchronization scheme , One characteristic is , The main thread encodes instructions one time faster than the rendering thread , In other words, the rendering instructions executed by the rendering thread are lagging , This in the game engine is called differential frame rendering . The advantage of this way is , Apportion computing power , No longer let the rendering thread perform some logic related operations , Only focus on the execution of your own rendering instructions , such GPU The execution time will be more stable , There will be no more extreme peaks and troughs , Cause excessive frame rate fluctuation . The main thread does not need to care about the submission of rendering instructions , Just care about the relevant logic and some CPU Operator processing .
2. bgfx Multithreaded scheme
summary
Bgfx Multithreaded rendering is based on producers and consumers , Split logic into production threads , Split the execution to the rendering thread , Use dual queues ( Double buffering ) To protect critical resources . But this is not really multithreaded rendering , The real multi-threaded rendering is that there is no concept of rendering thread , Such as Vulkan、Metal as well as Dx12, Multiple threads can access graphics at the same time API. Current graphics API, Such as OpenGL、OpenGLES、DX9 And DX10 Multiple threads are not allowed to access the graph at the same time API( Multithreaded simultaneous access to graphics API There are many limitations ).
Bgfx Immediate rendering mode is not supported in , Its overall frame design , There is no distinction between mobile terminals and PC End , Is a delay mode in which the main thread is up to one frame faster than the rendering thread .UE4 In the multithreaded rendering framework , It provides immediate mode and delayed mode , Personally, I think this framework design can better release the characteristics of different platforms . After all, the mobile terminal GPU Architecture and PC Terminal GPU The architecture is different ( Mobile terminal is TBR The architecture of , and PC The end is IBR framework ).
Bgfx Although the encapsulation of multithreading is not as flexible and complex as some commercial engines , however Bgfx The victory lies in light weight . If you let developers UE4 Extract from the rendering system of , Why don't you just sacrifice this developer to heaven , So developers can be happier . And that is Bgfx Although the multithreading architecture is not very flexible and easy to use , But it is encapsulated in the driver layer ,OpenGL、Metal、Vulkan as well as DX series , Include most of the interfaces required for rendering , Therefore, this is one of the reasons why many people are willing to use it .
Although the author is for Bgfx Lack of understanding of Bgfx One out of ten designers , But the author is learning Bgfx There will also be some of their own views and ideas in the process of , as follows :
Memory management is not flexible enough
Bgfx In, it starts from initialization , Defines the largest Drawcall Number , And applied for a very large memory pool for its use . Then memory recycling is not managed with thread safe smart pointers , Instead, you manage the resource manually. It's time to recycle . If you need to draw within a frame Drawcall The quantity exceeds the maximum , It will collapse , If you change its maximum Drawcall Number , That will double the overall memory . More than Drawcall The maximum number of frames exists in a few . So it's for some heavy game engines ,bgfx The way of memory management needs to be expanded .
Code stack & The sky is full of macros
Bgfx Code logic in , From a developer's point of view , It's really clear . But in terms of readers ,Bgfx The code is completely stacked in one file , This leads to Bgfx It's very difficult to get started , Often in order to clarify a logic , Look at the code for a long time to sort it out . Another problem is ,Bgfx The macro definition in is really everywhere , sometimes , I was completely stunned when I looked at it . This leads to Bgfx Your code is extremely unreadable .
Bgfx Of Encoder With new graphics API The difference between
Bgfx There is the concept of encoder pool in , namely EncoderPool,Encoder from EncoderPool Out of . The rendering thread holds EncoderPool pool , Each thread can be from EncoderPool Apply for at most one Encoder. But everyone holds Encoder Thread coded rendering commands are submitted to m_submit( One of the double buffered queues ) when ,Bgfx There is no sequential processing . And the new graphics API in , for example Vulkan in , Different threads hold CommandBuffer( But with Bgfx Of Encoder analogy ) It comes from different CommandBufferPool in , also CommandBuffer Events and barriers can be used for synchronization between , This is different CommandBuffer The time sequence can also be defined artificially , Not like it Bgfx As uncontrollable , If you want to control, you need developers to expand themselves . therefore Bgfx Multithreaded framework pair Vulkan、Metal as well as DX12 It's extremely unfriendly for . And this better engine is U3D 了 , For new graphics API Provides GraphicsJobs Multithread rendering mode of , Better use of graphics API characteristic .
although Bgfx There are some disadvantages , But on the whole, it's very light , And the support of various rendering capabilities is relatively complete , Compared with some mature commercial engines, there are some deficiencies , But it's lightweight and complete enough to make it the rendering base of some small engines .
1. Bgfx frame
Bgfx Although the code is stacked in one file , Macro definitions fly everywhere , But its overall framework level boundary is still very clear .
The interface layer
Mainly in the Bgfx.h This header file , It mainly includes some interfaces used in rendering 、 The data structure used externally
Coding layer
This layer is a little more complicated , Mainly involves Context、Encoder as well as CommandBuffer Three categories . It is mainly some thread synchronization 、 Safety protection of resources in critical areas 、Encoder How to safely submit encoded data to m_submit queue .
Driver layer
This layer is relatively simple and intuitive , By a base class RenderContextI, There is a corresponding figure API Subclasses of , And contains some individual graphics API Corresponding resource encapsulation class . And its interaction with the coding layer , There are two aspects
Creation of rendering resources ( for example CreateXXX、SetXXXX And so on, traversed by the rendering thread CommandBuffer To call )
RenderQueue( Contains all the... In a frame drawcall data ) Execution of one frame rendering command data in ( stay Submit Function for Loop execution )

1. The interface layer
bgfx The external interface of is focused on bgfx.h In this header file . Its main interface is provided in two ways , as follows
C Language type interface
Encoder Class provides the interface
The two interfaces are related ,C Language interface , Part is to code the command into CommandBuffer(m_submit Queue member variable ), Part of it is called Encoder Class interface . so C The interface of language type contains Encoder Class .
1.1 External interface
Encoder Interface
void setMarker(const char* _marker);
void setState(uint64_t _state, uint32_t _rgba=0);
void setCondition(OcclusionQueryHandle _handle,bool _visible);
void setStencil(uint32_t _fstencil,uint32_t _bstencil=BGFX_STENCIL_NONE);
uint16_t setScissor(uint16_t _x, uint16_t _y, uint16_t _width, uint16_t _height);
void setScissor(uint16_t _cache = UINT16_MAX);
uint32_t setTransform(const void* _mtx,uint16_t _num=1);
uint32_t allocTransform(Transform* _transform,uint16_t _num);
void setTransform(uint32_t _cache,uint16_t _num = 1);
void setUniform(UniformHandle _handle,const void* _value,uint16_t _num=1);
void setIndexBuffer(IndexBufferHandle _handle);
void setIndexBuffer(IndexBufferHandle _handle,uint32_t _firstIndex,uint32_t_numIndices);
void setIndexBuffer(DynamicIndexBufferHandle _handle);
void setIndexBuffer(DynamicIndexBufferHandle _handle,uint32_t _firstIndex,uint32_t _numIndices);
void setIndexBuffer(const TransientIndexBuffer* _tib);
void setIndexBuffer(const TransientIndexBuffer* _tib,uint32_t _firstIndex,uint32_t _numIndices);
void setVertexBuffer(uint8_t _stream,VertexBufferHandle _handle);
void setVertexBuffer(uint8_t _stream,VertexBufferHandle _handle,uint32_t _startVertex
,uint32_t _numVertices,VertexLayoutHandle _layoutHandle = BGFX_INVALID_HANDLE);
void setVertexBuffer(uint8_t _stream,DynamicVertexBufferHandle _handle);
void setVertexBuffer(uint8_t _stream,DynamicVertexBufferHandle _handle,uint32_t _startVertex
, uint32_t _numVertices, VertexLayoutHandle _layoutHandle = BGFX_INVALID_HANDLE);
void setVertexBuffer(uint8_t _stream,const TransientVertexBuffer* _tvb);
void setVertexBuffer(uint8_t _stream,const TransientVertexBuffer* _tvb,uint32_t _startVertex
, uint32_t _numVertices,VertexLayoutHandle _layoutHandle=BGFX_INVALID_HANDLE);
void setVertexCount(uint32_t _numVertices);
void setInstanceDataBuffer(const InstanceDataBuffer* _idb);
void setInstanceDataBuffer(const InstanceDataBuffer* _idb,uint32_t _start,uint32_t _num);
void setInstanceDataBuffer(VertexBufferHandle _handle,uint32_t _start,uint32_t _num);
void setInstanceDataBuffer(DynamicVertexBufferHandle _handle,uint32_t _start,uint32_t _num);
void setInstanceCount(uint32_t _numInstances);
void setTexture(uint8_t _stage,UniformHandle _sampler
,TextureHandle _handle,uint32_t _flags=UINT32_MAX);
void touch(ViewId _id);
void submit(ViewId _id,ProgramHandle _program,uint32_t _depth=0,uint8_t _flags= BGFX_DISCARD_ALL);
void submit(ViewId _id,ProgramHandle _program,OcclusionQueryHandle _occlusionQuery
,uint32_t _depth=0,uint8_t _flags=BGFX_DISCARD_ALL);
void submit(ViewId _id,ProgramHandle _program,IndirectBufferHandle _indirectHandle
,uint16_t _start=0,uint16_t _num=1,uint32_t _depth=0,uint8_t _flags=BGFX_DISCARD_ALL);
void setBuffer(uint8_t _stage,IndexBufferHandle _handle,Access::Enum _access);
void setBuffer(uint8_t _stage,VertexBufferHandle _handle,Access::Enum _access);
void setBuffer(uint8_t _stage,DynamicIndexBufferHandle _handle,Access::Enum _access);
void setBuffer(uint8_t _stage,DynamicVertexBufferHandle _handle,Access::Enum _access);
void setBuffer(uint8_t _stage,IndirectBufferHandle _handle,Access::Enum _access);
void setImage(uint8_t _stage,TextureHandle _handle,uint8_t _mip
,Access::Enum _access,TextureFormat::Enum _format=TextureFormat::Count);
void dispatch(ViewId _id,ProgramHandle _handle,uint32_t _numX=1
,uint32_t _numY=1,uint32_t _numZ=1,uint8_t _flags=BGFX_DISCARD_ALL);
void dispatch(ViewId _id,ProgramHandle _handle,IndirectBufferHandle _indirectHandle
,uint16_t _start=0,uint16_t _num=1,uint8_t _flags=BGFX_DISCARD_ALL);
void discard(uint8_t _flags = BGFX_DISCARD_ALL);
void blit(ViewId _id,TextureHandle _dst,uint16_t _dstX,uint16_t _dstY,TextureHandle _src
,uint16_t _srcX=0,uint16_t _srcY=0,uint16_t _width=UINT16_MAX,uint16_t _height=UINT16_MAX);
void blit(ViewId _id,TextureHandle _dst,uint8_t _dstMip,uint16_t _dstX,uint16_t _dstY
,uint16_t _dstZ,TextureHandle _src,uint8_t _srcMip=0,uint16_t _srcX=0
,uint16_t _srcY=0,uint16_t _srcZ=0,uint16_t _width=UINT16_MAX
,uint16_t _height=UINT16_MAX,uint16_t _depth=UINT16_MAX);From the interface point of view , Includes setting the render state ( blend 、 Templates 、 Tailoring 、 depth 、 Winding, etc )、 Set up the matrix 、 Set vertex 、 Indexes 、 texture 、 picture 、 Geometric instantiation data, etc Drawcall The required rendering resources and the interface of the State . Through these interfaces, developers set rendering resources and state to Encoder in , And store it in its own cache , stay submit When the function is called , Submitted to the m_submit In line .
C Language type interface
// establish GPU resources , And related Enum Enumeration tag
IndexBufferHandle createIndexBuffer(const Memory* _mem, uint16_t _flags);
void setName(IndexBufferHandle _handle, const bx::StringView& _name);
void destroyIndexBuffer(IndexBufferHandle _handle);
VertexLayoutHandle createVertexLayout(const VertexLayout& _layout);
void destroyVertexLayout(VertexLayoutHandle _handle);
VertexBufferHandle createVertexBuffer(const Memory* _mem, const VertexLayout& _layout, uint16_t _flags);
void destroyVertexBuffer(VertexBufferHandle _handle);
DynamicIndexBufferHandle createDynamicIndexBuffer(uint32_t _num, uint16_t _flags);
DynamicIndexBufferHandle createDynamicIndexBuffer(const Memory* _mem, uint16_t _flags);
void update(DynamicIndexBufferHandle _handle, uint32_t _startIndex, const Memory* _mem);
DynamicVertexBufferHandle createDynamicVertexBuffer(uint32_t _num, const VertexLayout& _layout, uint16_t _flags);
DynamicVertexBufferHandle createDynamicVertexBuffer(const Memory* _mem, const VertexLayout& _layout, uint16_t _flags);
void update(DynamicVertexBufferHandle _handle, uint32_t _startVertex, const Memory* _mem);
uint32_t getAvailTransientIndexBuffer(uint32_t _num);
uint32_t getAvailTransientVertexBuffer(uint32_t _num, uint16_t _stride);
void allocTransientIndexBuffer(TransientIndexBuffer* _tib, uint32_t _num);
void allocTransientVertexBuffer(TransientVertexBuffer* _tvb, uint32_t _num, const VertexLayout& _layout);
void allocInstanceDataBuffer(InstanceDataBuffer* _idb, uint32_t _num, uint16_t _stride);
IndirectBufferHandle createIndirectBuffer(uint32_t _num);
ShaderHandle createShader(const Memory* _mem);
uint16_t getShaderUniforms(ShaderHandle _handle, UniformHandle* _uniforms, uint16_t _max);
void destroy(ShaderHandle _handle);
ProgramHandle createProgram(ShaderHandle _vsh, ShaderHandle _fsh, bool _destroyShaders);
ProgramHandle createProgram(ShaderHandle _vsh, bool _destroyShader);
void destroyProgram(ProgramHandle _handle);
TextureHandle createTexture(const Memory* _mem);
void* getDirectAccessPtr(TextureHandle _handle);
void destroyTexture(TextureHandle _handle);
uint32_t readTexture(TextureHandle _handle, void* _data, uint8_t _mip);
TextureHandle createTexture(...);
TextureHandle createTexture2D(...);
TextureHandle createTexture3D(...);
TextureHandle createTextureCube(...);
void updateTexture(TextureHandle _handle,...);
void updateTextureCube(TextureHandle _handle,...);
void updateTexture2D(TextureHandle _handle,...);
void updateTexture3D(TextureHandle _handle,...);
FrameBufferHandle createFrameBuffer(...);
void destroy(FrameBufferHandle _handle);
TextureHandle getTexture(FrameBufferHandle _handle, uint8_t _attachment);
UniformHandle createUniform(const char* _name, UniformType::Enum _type, uint16_t _num);
void getUniformInfo(UniformHandle _handle, UniformInfo& _info);
void destroyUniform(UniformHandle _handle);
OcclusionQueryHandle createOcclusionQuery();
OcclusionQueryResult::Enum getResult(OcclusionQueryHandle _handle, int32_t* _result);
void destroy(OcclusionQueryHandle _handle);
void setPaletteColor(...);
void setViewXXXX(ViewId _id, const char* _name);
// Show create encoder interface 、 And synchronization interface
Encoder* begin(bool _forThread = false);
void end(Encoder* _encoder);
// The main thread applies for the exchange queue interface
uint32_t frame(bool _capture = false);There are several important interfaces ( In addition, a small number of other functional interfaces will not be introduced )
bgfx External category c About... In the interface GPU The creation of resources , This part of the interface will return XXHandle Data structure of .XXHandle Used to index graphics API Handle returned ID( Pay attention to data structures with high probability of occurrence Memory)
Part of it is called Encoder The interface ( Not on display ).
About encoder creation , Encoder synchronous communication interface .
Synchronous communication between the main thread and the rendering thread .
1.2 External data structure
External data structure , It is for better synchronous data exchange with the main thread and rendering thread . It involves the following parts
bgfx Initialize the data structure encapsulation related to the setting ; Platform properties , Initialize settings , And graphics API Ability support
struct PlatformData
{};
struct Init
{};
struct Caps
{};
const Caps* getCaps();
const Stats* getStats();Yes with GPU Abstract encapsulation of rendering resources that handle the return value
#define BGFX_HANDLE(_name) \
struct _name { uint16_t idx; }; \
inline bool isValid(_name _handle) { return bgfx::kInvalidHandle != _handle.idx; }
BGFX_HANDLE(DynamicIndexBufferHandle)
BGFX_HANDLE(DynamicVertexBufferHandle)
BGFX_HANDLE(FrameBufferHandle)
BGFX_HANDLE(IndexBufferHandle)
BGFX_HANDLE(IndirectBufferHandle)
BGFX_HANDLE(OcclusionQueryHandle)
BGFX_HANDLE(ProgramHandle)
BGFX_HANDLE(ShaderHandle)
BGFX_HANDLE(TextureHandle)
BGFX_HANDLE(UniformHandle)
BGFX_HANDLE(VertexBufferHandle)
BGFX_HANDLE(VertexLayoutHandle)From the perspective of data structure encapsulation , It is not difficult to see that they are all with GPU Some resources that handle the return value , For these resources ,bgfx Provide its corresponding data structure encapsulation , More convenient for the main thread ( Encoding threads ) Interaction with rendering threads , At the same time, it also prevents mistransmission of values (EffectiveC++ I have introduced this idea )
once Drawcall Abstract encapsulation of rendering resources required , And a frame of all data statistics package
struct TransientIndexBuffer
{};
struct TransientVertexBuffer
{};
struct TextureInfo
{};
struct UniformInfo
{};
struct Attachment
{};
struct Attrib
{};
struct AttribType
{};
struct TextureFormat
{};
struct UniformType
{};
struct BackbufferRatio
{};
struct OcclusionQueryResult
{};
struct ViewMode
{};
struct Resolution
{};
struct Stats// Encapsulation of related states in a frame
{};Memory related ;
This data structure is very important , The main thread ( Encoder thread ) Production rendering instructions , But some instructions are needed cpu End data , For example, vertex data . Then there will be a time when both the main thread and the rendering thread will have the ownership of the data , Then if it is not read-write protected , Then there will be read-write conflict and other problems .bgfx The solution in is , utilize Memory This external data structure , Put the main thread's CPU Copy a copy of the data to the rendering thread , In this way, the main thread and the rendering thread each hold their own data , You won't worry about the resources in the critical area .(bgfx It also provides a way , The main thread provides a data release function , Then it is handed over to the rendering thread in the form of function pointer , However, the release of this memory is still attributed to the rendering thread management )
struct Memory
{};
struct Access
{};
const Memory* alloc(uint32_t _size);
const Memory* copy(const void* _data,uint32_t _size);
const Memory* makeRef(const void* _data,uint32_t _size
,ReleaseFn _releaseFn=NULL,void* _userData=NULL);Sorting optimization related
At present, the author has not touched on , However, according to the author's understanding, there are some problems related to optimization processing ; Another part is vertex packing , Vertex layout is also some processing related to optimization ( Vertex layout related processing , stay ue as well as u3d There are corresponding schemes to optimize the processing , Those who are interested can check it out )
struct Topology
{};
struct TopologyConvert
{};
struct TopologySort
{};
void vertexPack(...);
void vertexUnpack(...);
uint32_t topologyConvert(...);
void topologySortTriList(...);
VertexLayoutHandle createVertexLayout(const VertexLayout& _layout);
void destroy(VertexLayoutHandle _handle);
2. Coding layer
Coding layer , The main classes are Context、EncoderI as well as ComandBuffer. The specific implementation of the interface layer , Processing of multithreaded synchronous communication ,Encoder And CommandBuffer Differences and connections , Critical resource protection zone .
Encapsulation of synchronization between main thread and rendering thread
Based on producer consumer model , Using semaphore mechanism , Encapsulate the synchronization between rendering thread and main thread . The dual queue function of the main thread application exchange is Frame(), The rendering function of the rendering thread is RenderFrame() function .
Encapsulation of synchronization between coding thread and main thread
Based on producer consumer model , Using semaphore mechanism , Encapsulate the synchronization between the coding thread and the main thread .
Encoder And CommandBuffer Differences and connections
Encoder By EncoderPool Distribute , It can allocate up to eight encoders ( If you want to add changeable code ), And apply for Encoder when , Protected by a lock , Prevent multiple threads from applying for encoder at the same time , It has RenderDraw、RenderBind as well as RenderCompute And other data structures and variables , You can cache one time encoded by the encoding thread Drawcall data , The data is to be submitted to m_submit Queue .
CommandBuffer yes m_submit Member variables of , The main thread ( Encoding threads ) Create with GPU Handle to the rendering resource , With Key-value The format is encoded to CommandBuffer in (Key by XXHandle,Value For memory data or XXHandle).
When the rendering thread starts , Do it first m_render In line CommandBuffer Rendering commands ( Call the interface encapsulated by the driver layer ), And then the m_render In line N individual Drawcall Do it all over ( Call the driver layer Submit() function ).
Safety protection of resources in critical areas
CommandBuffer Face multiple coding threads to code at the same time , Mutex protection is used here
m_submit The queue faces multiple encoding threads encoding at the same time , Use a spin lock pair m_submit To protect
CommandBuffer If the rendering command encoded in has graphics API Handle returned ,bgfx Is to return a XXHandle Object for the encoding thread to use ( This one has a memory pool ). One is to prevent return GPU The value of the handle , Error in value transmission during external use (EffectiveC++ Introduction ); Second, use memory pool , Small memory is allocated from the pool , Prevent debris , Improve object creation performance ; third , The main thread doesn't really care about real graphics API Returns the value of the handle ,bgfx according to XXHandle Index to the corresponding real graphics API Handle can be reused .
3. Driver layer
The driver layer mainly includes several aspects , Create a unified interface for rendering resources , perform m_render Render the command queue , Data structure encapsulation of rendering resources .
GPU Resource creation
Rendering API Unified interface encapsulation , Its base class RenderContextI, For example, create FBO、 Create vertex 、 Create pure virtual function interfaces such as shader objects , Each subclass must implement the interface in the base class .
RenderQueue perform
The coding layer will take precedence m_render Queue CommandBuffer Perform traversal and execute ,CommandBuffer The recorded rendering command is to create some with GPU Handle to the rendering resource , Then call the corresponding function to create. .
Encapsulation of rendering resources
Put each figure api The corresponding rendering resources are abstracted as data structures , For ease of use .
Personal view :
Let's repeat here Bgfx About China OpenGL Development of ,Bgfx about OpenGL Did a lot of API expand , This is also the ultimate squeeze on the performance of the hardware platform , It is also an extreme improvement of engine effect and performance . Interested students can check the relevant information by themselves ( expand ) Code . For the drive layer , The author has his own views and understanding . as follows
OpenGL Render state every time Drawcall All have to be reset
bfx For in the OpenGL&ES Execution of rendering commands (submit) function , For rendering state ,bgfx It's every time drawcall Will turn on and off a large number of rendering states . and OpenGL It's the state machine , A change of state , If developers don't change ,OpenGL It's going to stay that way , If developers frequently change some state , This is important for performance , It is also consumed .UE4 It is cached in , every time Drawcall Compared with the last time , This reduces the problem of repeatedly resetting some render States .
The encapsulation of rendering resources is not flexible enough
About the encapsulation of rendering resources ,bgfx It's more like simply encapsulating the rendered data for ease of use , It is not abstracted , then opengl、dx、vulkan as well as metal Each has its own set of resource data structure . It can't be said that this model is not good , But if you want to rely on smart pointers ( Thread safety ) Manage the lifecycle of resources , You need to expand in ; Or do common LRU Cache handling , It's also a headache , To write several copies of code . Interested students can view this package , You can also check UE4 The treatment scheme for this piece in , Think about it at the same time UE4 Why do you do this ?

2. Dual queue synchronization
In the previous section, we introduced the general framework or hierarchy in combination with some interfaces or details Bgfx, This will also affect Bgfx There is a preliminary understanding . This section will mainly analyze Bgfx Some schemes and details of multithreaded rendering in . Mainly from the following aspects , The main thread communicates synchronously with the rendering thread , The encoding thread communicates synchronously with the main thread ,GPUHandle Mechanism design .
2.1 The rendering thread is synchronized with the main thread

As shown in Figure 3 above , The main thread wakes up the rendering thread first frame , And then execute Init operation , Then the main thread encodes the rendering command of the first frame , And cache the command to m_submit In line . When the first frame Update Walk the , It indicates that the first frame encoding command of the main thread has ended , Call at this time Frame The function requests to exchange the command queue with the rendering thread , If the rendering thread at this time Init The function is finished , Then the queue will be exchanged . Main thread continues Update Update the coded rendering command to m_submit In line , The rendering thread executes the rendering command of the first frame in parallel ( Submit rendering commands to GPU in ), So back and forth . If the main thread runs faster than the rendering thread , The main thread is N+1 The frame has been encoded , Rendering thread No N The frame has not been executed yet , Main thread blocking ; If the rendering thread is faster than the main thread , Rendering thread No N Frame execution has ended , The main thread is N+1 Frame uncoded end , Rendering thread blocking . This will ensure that Zhu Xiangcheng runs at least one frame more than the rendering thread , Except that the exchange queue is serial , Other times are parallel .
For ease of understanding , Here the author will bgfx The dual queue scheme is implemented with simple pseudo code , This is more convenient for everyone to understand the knowledge introduced in the previous paragraph .
class Context
{
public:
Context()
{
}
void Init()
{
// The main thread calls once at the beginning of the first frame
m_ApiSem.Post();
}
//Each Frame is called by the MainThread
void Frame()
{
m_RenderSem.Wait();
Swap();
m_ApiSem.Post();
}
//Each Frame is called by the RenderThread
void RenderFrame()
{
m_ApiSem.Wait();
// The rendering command of the encoding tag is executed by the driver layer to create the real rendering resource
CommandBuffer.Render();
Render();
m_RenderSem.Post();
}
private:
Render()
{
//m_Render Rendering queue execution
}
void Swap()
{
Frame temp;
temp = m_Submit;
m_Submit = m_Render;
m_Render = temp;
}
private:
RenderSem m_RenderSem;
APISem m_ApiSem;
Frame m_Submit;
Frame m_Render;
};
This is pseudo code , Not too rigorous or can run , But it can clearly describe the implementation of dual queue frame synchronization , It's easier to understand . Careful people may have found , This pseudo code is very similar to the producer consumer model in the previous chapter ( Strictly speaking, as like as two peas. ). This shows a truth , Often very complex schemes or technologies are extended from some very basic knowledge , Adding some simple knowledge together will become not simple .
2.2 The encoding thread is synchronized with the main thread
Part of this section has been briefly introduced in the second small part of section 1 , In this section, we will introduce... In detail in the form of diagram .
1. Synchronization strategies

As shown in Figure 4 , stay bgfx in , If you don't apply for an encoder ,bgfx Yes, there is an encoder for the main thread by default . Encoding threads , Or worker threads , Code some rendering commands , Coding thread finished coding ( If there are multiple coding threads , The main thread waits for all coding threads to finish coding when applying for the exchange queue ), Then the main thread exchanges with the rendering thread m_submit And m_render queue .
2. Encoder And CommandBuffer

As shown in Figure 5 above , among Encoder Yes, there can be more than one ,CommandBuffer stay m_submit There is only one queue ( Specific for CMDPre And CMDPos).CommandBuffer Coding band GPU Render command that returns the handle , Returns the Bgfx Packaged XXHandle.Encoder Set once Drawcall Related rendering commands ,XXHandle It's also one of the parameters . such Drawcall establish Shader、 establish FBO、 establish VBO、 Set render state ( blend 、 depth 、 Templates 、 Tailoring, etc ) Wait is a complete Pipeline 了 , Then this time at the right time Drawcall Submitted to the m_submit In line .
3. SubmitQueue safeguard

As shown in Figure 6 , Whether it's a coding thread , Or the main thread , Strictly speaking , Can be uniformly called coding thread . The difference is that it operates synchronously with the main thread and the rendering thread , The encoding thread is synchronized with the main thread . The main thread ( Encoding threads ) In the CommandBuffer When writing rendering commands, you need to get the resource lock before coding , Prevent multiple threads from going to CommandBuffer Middle write data . Once in the encoder Drawcall Cached rendering resources ( call submit(...) Function to start the commit ) towards m_submit When submitted in , You need a lock ( spinlocks ), Confirm current m_submit Safe in can be written once Drawcall The location of the rendered data , And then write .
remarks : This article is not about bgfx Of view The mechanism of ( Due to limited space , The number of words seriously exceeds the standard ), Interested students can check the source code by themselves .
3. GPUHandle encapsulation
Main thread or coding thread , Use CommandBuffer When encoding render commands , graphics APi Will return to GPU Handle to the ( In fact, it's just a int value ), But graphics API The handle of ID It will not be returned to the main thread for use , It's a return of XXHandle The object comes back .
This XXHandle The specific function is , stay bgfx As an array in ID To find the real graphics API Value , And operate on it . In other words, it's more like an intermediate proxy value ,XXHandle What figure does it represent API The return value of .
bgfx about XXHandle Its function is as follows
Creation of a large number of rendering commands , With graphics API Return value (XXHandle object ), These values are just integers , Memory will be released frequently ;bgfx Memory pool is used for management , Avoid memory fragmentation , Lifting performance ( About this piece ,bgfx An idea of using memory for time , Those who are interested can consult by themselves )
If you really return a graph to the main thread API The integer value of , It is likely to be misinterpreted when used , If it is a formal parameter of structure type , The compilation period can't pass , It's also easier to check problems during operation . After all, pass a number , It belongs to the magic series , About this piece EffectiveC++ The series has an introduction . And the main thread or coding thread doesn't care much about real graphics API What is the return value of , As long as you can find the corresponding figure through an object or pointer API The return value of , And use it .
The other is security , This XXHandle When to create , When to release . and bgfx Who used to create , Who released ; Main thread or coding thread creation XXHandle, Reference count plus one , The destruction XXHandle when , Its reference count is minus one , Wait for 0 when , code DestroyXX Command to destroy real graphics API resources , After the next frame encoding of the main thread is completed , When applying for an exchange queue , Releasing XXHandle, Avoid the rendering thread using the data created by the main thread and deleted in the current frame XXHandle object ( Delay one frame delete XXHandle).

As shown in Figure 7 above , The main thread sends a signal to create a rendering command ,CommandBuffer Code it , Then return XXHandle object , The main thread gets XXHandle Objects are passing through Encoder Set to Drawcall In your rendering resources . When you destroy rendering resources ,CommandBuffer Also code it , Then the rendering thread actually destroys the graphics API Resources for . When the main thread switches the queue at the next frame , Delete the last frame in the memory pool XXHandle Object's data , Its memory is reserved for newly applied XXHandle Use .
About returning Handle The way ,UE4 Thread safe intelligent pointer is used for management, and a XXRef, This unifies the logical relationship between the resources of the driver layer and the coding layer , It's easier to manage . But if there is a performance problem , The author has not personally tested the performance of these two methods .UE4 For thread safe reference counting processing ( spinlocks ), and bgfx The code rendering command in is also after taking a lock , It's going on XXHandle Related treatment , In fact, it is comparable . Therefore, the author prefers UE4 Design method of ,UE4 The design method unifies the encapsulation of rendering resources in the driver layer and coding layer .
3. Vulkan Encoder design
As Khronos The organization's new generation of cross platform graphics API, With his brother OpenGL Or is it GLES It's completely different , Not to GL compatible . Completely abandoned GL Some shortcomings of , More oriented to multi-core programming development . Its core concept is more friendly to multi-threaded rendering development .
new generation Vulkan It's a complete separation from OpenGL Restricted graphics API, There is no longer the concept of rendering thread , There is no longer the concept of rendering context . You can set the creation and rendering state settings of all renderings in a frame to one CommandBuffer( You can have more than one ), After one frame coding , Do it once. submit Submitted to the VKQueue in , As shown in Figure 8 below

If it's multiple threads , Each coding thread can be assigned one CommandBufferPool(bgfx Only one of them EncoderPool), And then to get CommandBuffer, Encoding . Here's a hint , Different threads CommandBuffer Can't come from the same CommandBuffer in , If it's from the same , Then you need external synchronization , It's not cost-effective , graphics API Hierarchical synchronization must be much faster than external synchronization . And taking into account , If a thread wants to have multiple CommandBuffer coding , Then the thread has its own CommandBufferPool Just fine .Vulkan The coding thread also needs to be synchronized with the main thread , Then submit the rendering command queue to GPU To perform , This is related to bgfx It's very similar , The difference is bgfx It is the main thread that submits the rendering command to the rendering thread . See Figure 9 below 、 Figure ten


Since there are multiple threads to code , Then there must be relevant synchronization processing in it ,vulkan It also provides comprehensive support for this .semaphore( The signal ) For synchronization Queue(VKQueue There can be more than one );Fence( fence ) For synchronization GPU and CPU;Event( event ) and Barrier( barrier ) For synchronization Command Buffer. As shown in Figure 11

Figure eleven
About Vulkan Introduction to , It's still relatively simple , Therefore, some details of its multi-threaded rendering may not be introduced clearly ( In fact, what the author knows is relatively simple , I haven't mastered the essence yet ), If you are proficient in Vulkan Big guy , Also hope not hesitate to grant advice , I am very grateful here .
additional : Here's the picture , Use Vulkan The process required to draw a triangle , If you are interested, you can check it by yourself Vulkan Documents .

4. Conclusion
Contemporary multi-core parallel computing architecture has been the standard configuration of modern hardware , Whether it's a commercial game engine UE4 as well as U3D The hardware architecture of multi-core parallel computing has been adjusted by multi-threaded rendering architecture , Open source bgfx Rendering engines support multi-threaded rendering . So the future era , With technology and graphics API Progress , Multithreaded rendering will do better and better , Multithreaded rendering will become a basic technical discipline .
I wanted to write more , But it says discover , The number of chapter words has become abnormally large , Therefore, some chapters and details have been deleted , As a result, some parts can only introduce a general framework , A lot of details were not introduced , I hope there will be time to add it in the future .
Vulkan In the introduction , Some pictures are from the Internet , If there is any infringement , Please contact the , Will delete .
Thanks to the authors in the references .
Finally, I hope this article can give you a chance to learn bgfx Bring some help to our readers , If there is an error , Please leave a message , Thank you for your attention and collection .
reference
https://www.bookstack.cn/read/Cpp_Concurrency_In_Action/content-chapter1-1.2-chinese.md
https://hpc.llnl.gov/documentation/tutorials/introduction-parallel-computing-tutorial
https://www.cnblogs.com/timlly/p/14327537.html#2533-rhi%E7%BA%BF%E7%A8%8B%E7%9A%84%E5%AE%9E%E7%8E%B0
BGFX More articles on multithreaded rendering
- Unity4、Unity5 Multithreading rendering on mobile platforms can cause flashback on some Android phones
What you see crash The stack might look like this : SIGSEGV(SEGV_MAPERR) #00 pc 0001276c /system/lib/libc ...
- HTML5 Touch screen version of multi thread rendering template technology sharing
Preface : understand js Losers of compiler theory all know ,js It's single threaded , In order to realize js The multithreading , In order to solve innerHTML Output large section HTML Card page disease , They've designed fake ones “ Multithreading “ Realization , I'm writing open source myself ...
- Unity3D Implementation of seawater multithreading rendering algorithm
The author introduces : Jiang Xuewei ,IT Technical partner of the company ,IT Senior lecturer ,CSDN Community experts , Special editor , Best selling author , Published books :< Hands on architecture 3D The game engine > Electronic Industry Press and <Unity3D Detailed explanation of actual combat core technology ...
- DirectX* 11 Performance of multithreaded rendering 、 Methods and practices
For in CPU Running on PC game , Rendering is often the main performance bottleneck : Multithreaded rendering is an effective method to eliminate bottlenecks . This paper studies DirectX* 11 Performance scalability of multithreaded rendering , Two basic methods of multithreading rendering are discussed , And introduce ...
- Depth analysis OpenGL ES Multi thread and multi window rendering technology in
from Innovation network editor On Friday , 2014-04-11 14:56 publish In mobile devices CPU and GPU Has become very powerful , Devices with one or more high-resolution screens are everywhere , The need to use complex interactions with graphical drivers is also increasing . stay ...
- Unity Native rendering scheme
Unity Native rendering scheme author :3dimensions [email protected] This is the original content , Reprint please indicate the source . The motivation for doing this is to use... In native code Unity Material system drawing , meanwhile ...
- D3D Rendering process -- Reprint
http://www.cnblogs.com/ixnehc/articles/1282350.html Start with the most basic , About Device Rendering process of . D3D9 Of Device Namely D3D Give us a ...
- Talking about Unity Rendering optimization (1): Performance analysis and bottleneck judgment ( Part 1 )
http://www.taidous.com/article-667-1.html Preface First , This series of articles gives a general introduction , subject " Talking about Unity", Because the company and most of the domestic 3D Mobile game development ...
- 2019-10-23-WPF- Use -SharpDx- Asynchronous rendering
title author date CreateTime categories WPF Use SharpDx Asynchronous rendering lindexi 2019-10-23 21:18:38 +0800 2018-0 ...
- WPF Use SharpDx Asynchronous rendering
This article tells you how to pass SharpDx Render asynchronously , But because in WPF It is necessary to use D3DImage Draw out , So rendering is just drawing pictures , The final display still needs WPF Rendering in his own main thread This article is a series , Greek ...
Random recommendation
- The thinking logic of computer programs (30) - analyse StringBuilder
Last section introduced String, It is mentioned that if string modification operations are frequent , Should adopt StringBuilder and StringBuffer class , The methods of these two classes are basically the same , Their implementation code is almost the same , The only difference is ,St ...
- the second day ci Project planning Database design
the second day ci Project planning Database design goods + user + Order Database design ideas and methods About commodity brands , classification , attribute How to say With a field Or design another table Brands and goods It's a message Or two kinds of information A watch usually only ...
- wpf Get the animation in the templated control .
Use directly in the template blend Add animation , By default, it will be placed in ControlTemplate Of Resources below , You can't get it correctly by using many methods Storyboard.. <ControlTemplate ...
- Git establish project
One . github Shangchuang set up a project After the user logs in, the system , stay github home page , Click on the bottom right corner of the page “New Repository” Fill in project information : project name: hibernate-demo d ...
- SQL There are two parts in the Wengu series ( Two )
.Sql Insert statements to get automatically generated incremental ID value Insert into Table(name,des,num) values(’ltp’,’thisisbest’,10); Select @@ident ...
- JS unit testing
JS unit testing , I work mainly with mocha + chai The following is the specific document : mocha: https://mochajs.org/#asynchronous-code Chai: http://chai ...
- hive union all Use
function : Put... In the two tables The same fields are stitched together Testing : create external table IF NOT EXISTS temp_uniontest_ta ( a1 string, a2 strin ...
- Project practice 3—Keepalived High availability
Implementation is based on Keepalived High availability cluster website architecture Environmental Science : As the business grows , More and more visits to the website , Website visits have gone from the original 1000QPS, Turn into 3000QPS, At present, the business has passed through the cluster LVS The architecture can be expanded at any time , Back end ...
- Hibernate Frame notes 03 Table operation many to many configuration
Catalog 1. The relationship between database tables 1.1 One-to-many relation 1.2 Many to many relationship 1.3 One to one relationship [ understand ] 2. Hibernate One to many association mapping of 2.1 Create a project , To introduce the relevant jar package 2.2. establish ...
- CentOS Next Crontab Detailed instructions for installation and use ( turn )
come from :http://www.centoscn.com/CentOS/help/2014/1220/4346.html crontab Orders are common in Unix and Linux In the operating system , Used to set the periodic execution ...
![[academic related] it is suggested to collect. Which behaviors are academic misconduct?](/img/a7/2140744ebad9f1dc0a609254cc618e.jpg)