当前位置:网站首页>Leetcode featured 200 channels -- array article
Leetcode featured 200 channels -- array article
2022-07-08 02:12:00 【Little snail】
Preface
The purpose of writing this kind of article is to improve the algorithm ability , Get a good job
resources
Brush question website
Random code recording (programmercarl.com)
Drawing software
OneNote
Note taking software
Typoral
The basis of array theory
Array is a very basic data structure , In the interview , Generally speaking, it is not difficult to think about the question of array , It's about the ability to control the code
The first thing to know is How arrays are stored in memory , Only in this way can we really understand the array related interview questions
An array is a collection of the same type of data stored in continuous memory space .
Array can easily get the corresponding data under subscript by subscript index .
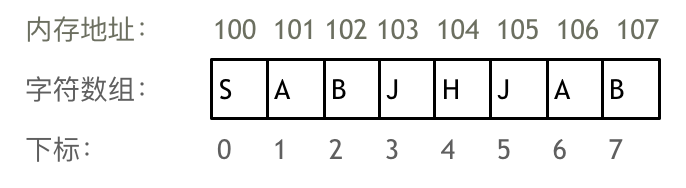
There are two points to note in the array :
- Array subscript is from 0 At the beginning
- Array memory space addresses are contiguous
Because the memory space of the array is continuous , So when we delete or add elements , It's hard to avoid moving the addresses of other elements
As shown below
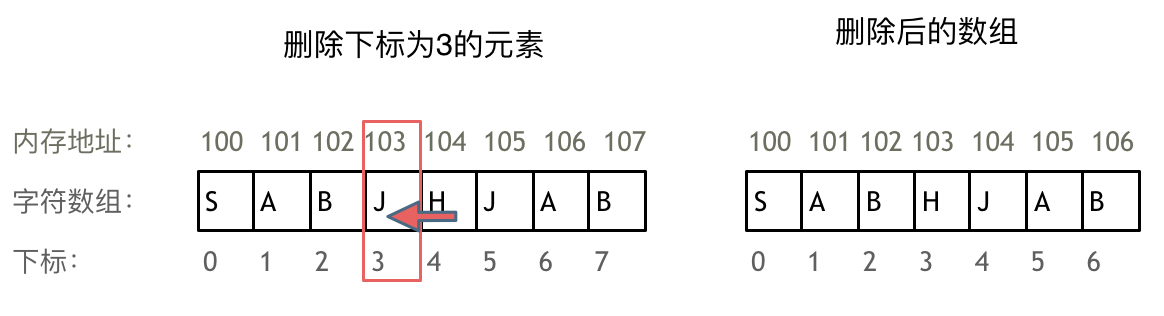
The elements of an array cannot be deleted , Can only cover
Ok, A two-dimensional array
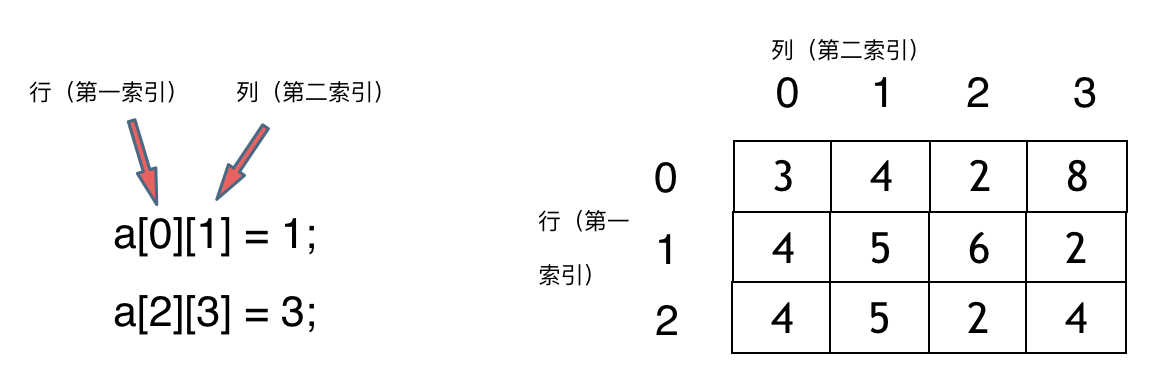
Java The two-dimensional arrays in may be arranged like this
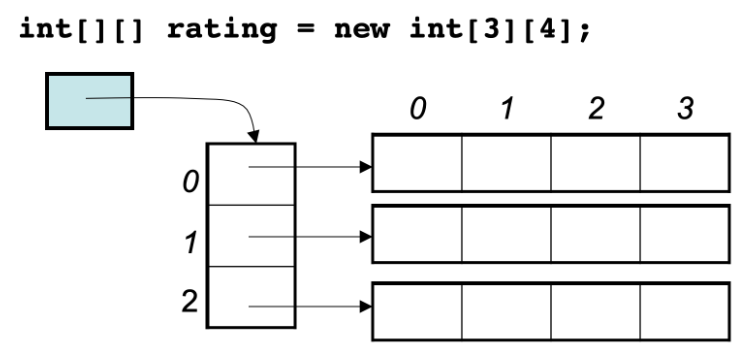
The same line is continuous , The addresses of different lines are discontinuous
Two points search
Given a n The elements are ordered ( Ascending ) integer array nums And a target value target , Write a function search nums Medium target, If the target value has a return subscript , Otherwise return to -1.
Example 1:
Input : nums = [-1,0,3,5,9,12], target = 9
Output : 4
explain : 9 Appear in the nums And the subscript is 4
Example 2:
Input : nums = [-1,0,3,5,9,12], target = 2
Output : -1
explain : 2 non-existent nums So back to -1
Tips :
- You can assume
numsAll elements in are not repeated . nWill be in[1, 10000]Between .numsEach element of will be in[-9999, 9999]Between .
Ideas
The premise of this topic is that the array is an ordered array , At the same time, the title also emphasizes There are no duplicate elements in the array , Because once there's a repeating element , The element subscript returned by binary search method may not be unique , These are the prerequisites for using dichotomy
Binary search involves many boundary conditions , The logic is simple , We should pay attention to the definition of interval and write dichotomy clearly , Interval is generally defined in two ways , Close left and close right [left, right], Or close left and open right [left, right).
public class Binaryforarrays {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] nums = {
1,2,3,4,7,9,12,45};
int i = Binaryforarrays.search1(nums, 12);
System.out.println(i);
}
public static int search1(int[] nums,int target){
if (target < nums[0] || target > nums[nums.length - 1]){
return -1;
}
int start = 0,end = nums.length - 1;
while (start <= end){
int mid = start + ((end - start) >> 1);
if (nums[mid] == target){
return mid;
}else if (nums[mid] < target){
start = mid + 1;
}else if (nums[mid] > target){
end = mid -1;
}
}
return -1;
}
}
about int mid = start + ((end - start) >> 1) explain
First ,(end-start)>>1 Medium >> yes java Bit operators in , The function is to move one bit to the right .
What is bitwise shift right 2 position ?
Is to convert a number into 2 Base number , Shift left operand right by bit number of bits specified by right operand
for example :60 Turn into 2 Into the system for 111100, that 60>>2 It's equivalent to moving the number to the right by two digits to become 1111,1111 Corresponding 10 The hexadecimal number is 15, therefore 60>>2 obtain 15
good , in other words (end-start)>>1 Except 2, Moving two bits is division 4…
Why not write it down 2, except 4? It's more professional to write like this !
Why add start
Because after dichotomy , The initial value of the index is no longer from 0 Here we go
about start = mid + 1 explain
start It's not directly equal to mid Because there is nums[mid] == target The judgment of the ,mid The index that is not the target value will have the following judgment
Remove elements
Give you an array nums And a value val, You need In situ Remove all values equal to val The elements of , And return the new length of the array after removal .
Don't use extra array space , You have to use only O ( 1 ) O(1) O(1) Additional space and In situ Modify input array .
The order of elements can be changed . You don't need to think about the elements in the array that follow the new length .
Example 1: Given nums = [3,2,2,3], val = 3, Function should return the new length 2, also nums The first two elements in are 2. You don't need to think about the elements in the array that follow the new length .
Example 2: Given nums = [0,1,2,2,3,0,4,2], val = 2, Function should return the new length 5, also nums The first five elements in are 0, 1, 3, 0, 4.
You don't need to think about the elements in the array that follow the new length .
Ideas
The elements of the array are contiguous in memory addresses , You cannot delete an element in an array alone , Can only cover .
We use two finger acupuncture , Through a fast pointer and a slow pointer in a for Loop through two for Cycle work .
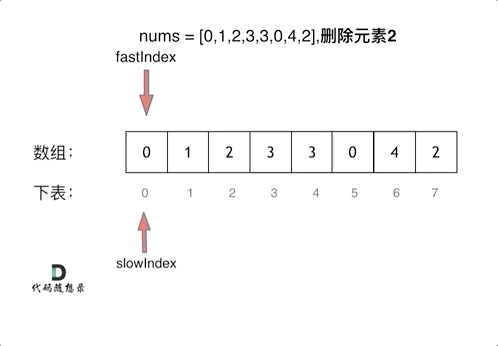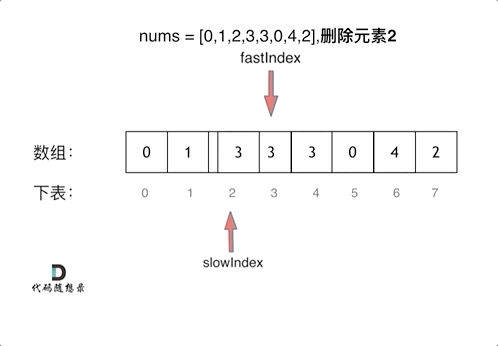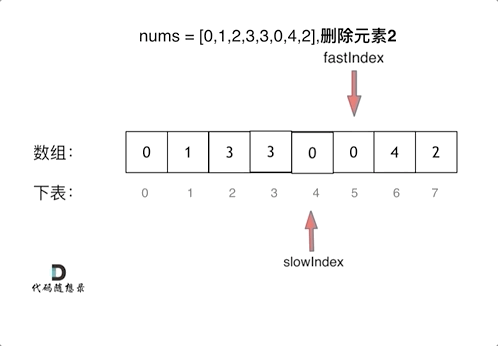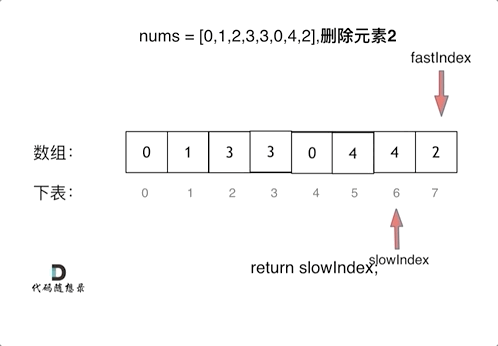
- Time complexity : O ( n ) O(n) O(n)
- Spatial complexity : O ( 1 ) O(1) O(1)
/** * Return the repeating elements in the array , And return the new length of the array after removal */
public class SolutionRemoveElement {
public int removeElement(int[] nums, int val) {
// Speed pointer
int fastIndex = 0;
int slowIndex;
for (slowIndex = 0; fastIndex < nums.length; fastIndex++) {
if (nums[fastIndex] != val) {
nums[slowIndex] = nums[fastIndex];
slowIndex++;
}
}
return slowIndex;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] nums = {
3, 2, 2, 3};
int val = 2;
SolutionRemoveElement solutionRemoveElement = new SolutionRemoveElement();
int i = solutionRemoveElement.removeElement(nums, val);
for (int num : nums) {
System.out.print(num + " ");
}
System.out.println();
System.out.println(i);
}
}
Drawing comprehension
This double pointer will be applied to many , There are many such situations debug Just draw pictures with yourself
Here is the picture I drew

In the initial case, the index is 0 The elements of 3
Then start the cycle of judgment , The first number is not the target value val So the fast and slow pointers move at the same time
The second number is the target value , Come on, the pointer continues to move , Slow pointer does not move
The third number is the target value , Come on, the pointer continues to move , Slow pointer does not move
The fourth value is not the target value , The value of the fast pointer is assigned to the value of the full pointer, so the whole array becomes 3323, How fast and slow the pointer moves at the same time
The fast pointer index equals the length of the array to stop the loop , Returns the full pointer index
The square of an ordered array
Here's a button Non decreasing order Sorted array of integers nums, return The square of each number A new array of , According to the requirements Non decreasing order Sort .
Example 1: Input :nums = [-4,-1,0,3,10] Output :[0,1,9,16,100] explain : After square , The array becomes [16,1,0,9,100], After ordering , The array becomes [0,1,9,16,100]
Example 2: Input :nums = [-7,-3,2,3,11] Output :[4,9,9,49,121]
Ideas
The idea of this diagram is very clear , Don't explain
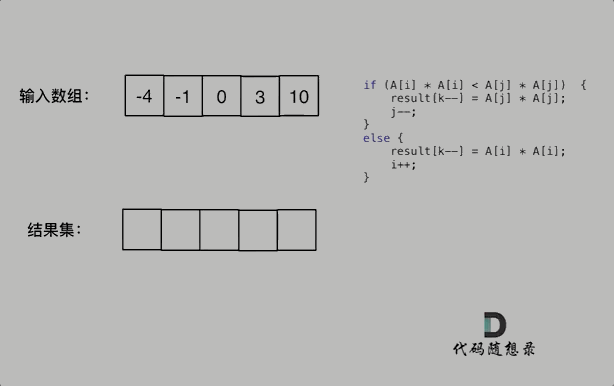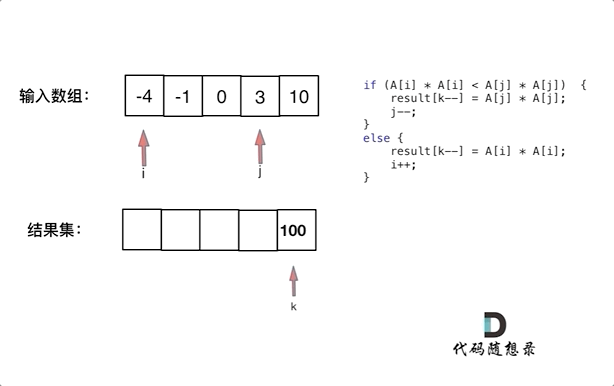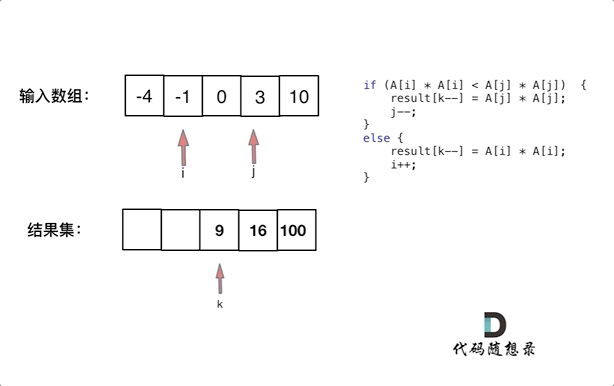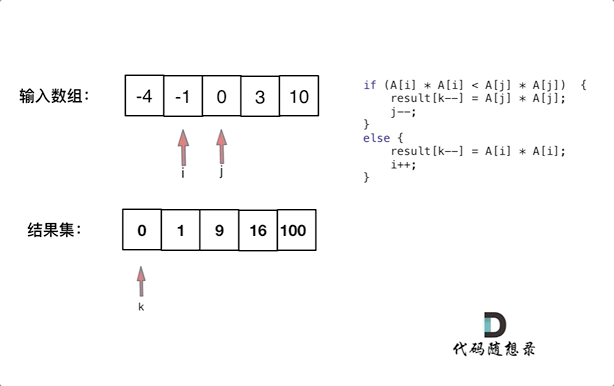
The time complexity is O ( n ) O(n) O(n)
package com.caq.array;
public class SolutionSquareAnOrderArray {
public int[] sortedSquares(int[] nums) {
int right = nums.length - 1;
int left = 0;
int[] result = new int[nums.length];
int index = result.length - 1;
while (left <= right) {
if (nums[left] * nums[left] > nums[right] * nums[right]) {
result[index--] = nums[left] * nums[left];
left++;
} else{
result[index--] = nums[right] * nums[right];
right--;
}
}
return result;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] nums = {
-3, -2, 1, 2, 3};
SolutionSquareAnOrderArray solutionSquareAnOrderArray = new SolutionSquareAnOrderArray();
int[] ints = solutionSquareAnOrderArray.sortedSquares(nums);
for (int anInt : ints) {
System.out.print(anInt+" ");
}
}
}
1 4 4 9 9
Subarray with the smallest length
Given a containing n An array of positive integers and a positive integer s , Find out what to do The array satisfies its sum ≥ s The smallest length of continuity Subarray , And return its length . If there is no sub array that meets the conditions , return 0.
Example :
Input :s = 7, nums = [2,3,1,2,4,3] Output :2
explain : Subarray [4,3] Is the smallest subarray in this condition .
The sliding window
So called sliding window , It's constantly adjusting the starting and ending positions of subsequences , So we can get the result that we want to think about .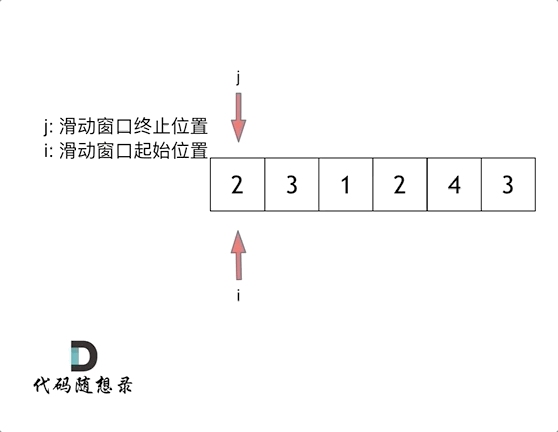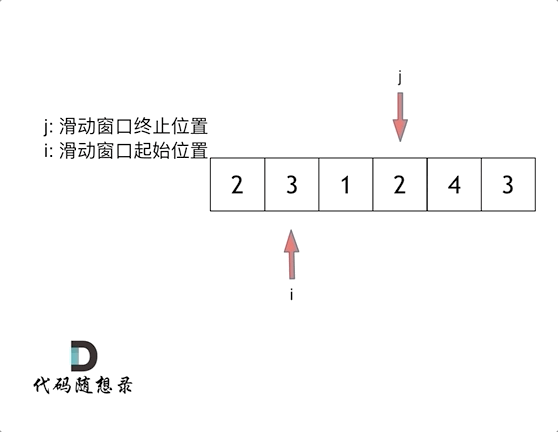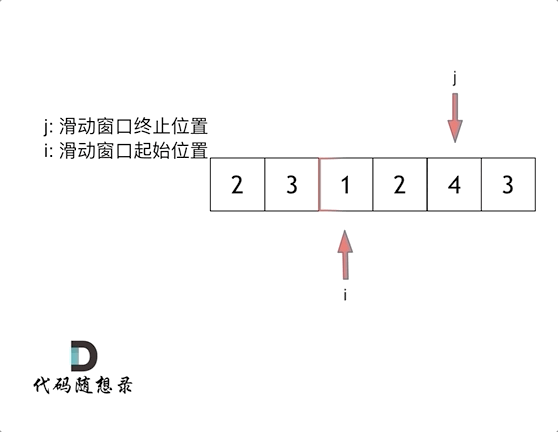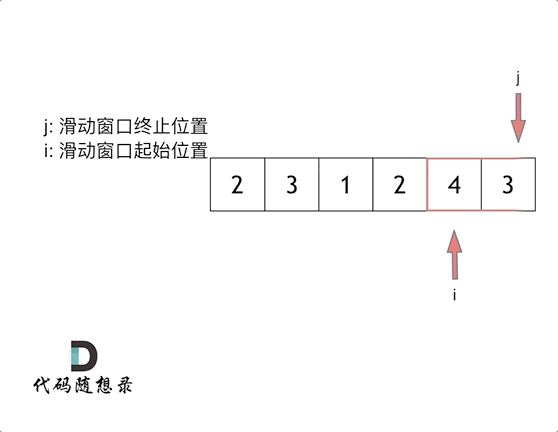
Sliding window is also a kind of double pointer , The time complexity of this question is O(n)
Ideas
In fact, with this good platform, we can directly remember its dynamic , Then use code to implement this dynamic graph
I think this is probably the quickest way to get started
public class SlidingWindows {
public int minSlidingWindows(int s, int[] nums) {
int left = 0, right, sum = 0;
int result = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
for (right = 0; right < nums.length; right++) {
sum += nums[right];
while (sum >= s) {
result = Math.min(result, right - left + 1);
sum -= nums[left++];
}
}
return result == Integer.MAX_VALUE ? 0 : result;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] nums = {
2, 3, 1, 2, 4, 3};
SlidingWindows slidingWindows = new SlidingWindows();
int i = slidingWindows.minSlidingWindows(7, nums);
System.out.println(i);
}
}
Integer.MAX_VALUE
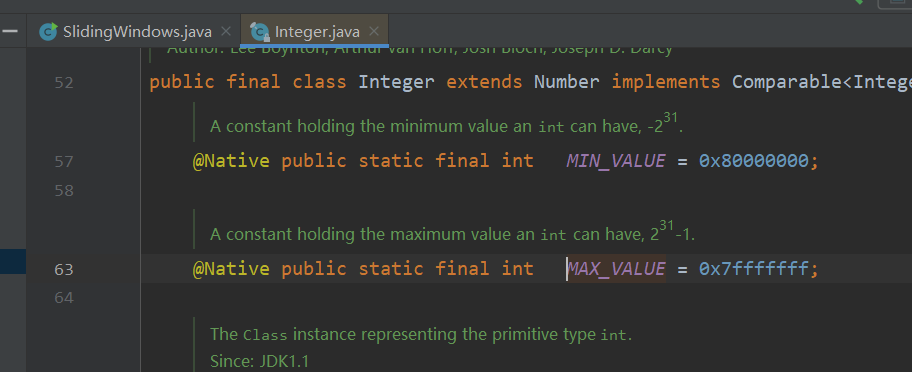
result The initial value is set to 2 Of 31 Power -1
Math.min
Compare a,b Size , The return value is the small number .
right - left + 1
This is the length of the smallest array , Why add 1 Well , Because the array index is from 0 At the beginning
like 0 To 5 Yes 5-0+1 The number is the same , If it is 1 To 5 That's it 5 Number
Spiral matrix
Given a positive integer n, Generate a include 1 To n^2 All the elements , A square matrix in which the elements are spirally arranged in a clockwise order .
Example :
Input : 3 Output : [ [ 1, 2, 3 ], [ 8, 9, 4 ], [ 7, 6, 5 ] ]
This question does not involve any algorithm , Is the simulation process , But they are very concerned about the ability to control the code .
Here is an official conclusion , The dynamic graph inside can help us understand !
Spiral matrix II - Spiral matrix II - Power button (LeetCode) (leetcode-cn.com)
Ideas
Using the second method of official answer , Print by layer
I haven't understood it for several times , And then on and on debug Not yet. .
Later, I drew the animation for you on the paper , Then write the program , Manual debug I'll see in a moment

In the middle of the if(left < right && top < bottom) What's this for ?
Because the whole thought right,left,top,bottom One round of the cycle will shrink in , Add this to make a judgment. If you don't continue printing after shrinking, print and type n The square of
Then another key point is to ensure the principle of left opening and right closing or left closing and right opening when printing , What do you mean , When printing the first line , Sure =right
But when printing the third line right != left
Printing up and down is the same , When moving down = Bottom , So when you move up, you have to !=top
After reading for several days, I always understand , Still too impetuous , take your time ~~~
The description is not good , I will continue to work hard in the future !!!
public class SpiralMatrix {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpiralMatrix sm = new SpiralMatrix();
int[][] ints = sm.generateMatrix3(3);
for (int[] anInt : ints) {
for (int i : anInt) {
System.out.print(i + "\t");
}
System.out.println();
}
}
public int[][] generateMatrix3(int n) {
int num = 1;
int[][] matrix = new int[n][n]; // Define a two-dimensional array
int left = 0, right = n - 1, top = 0, bottom = n - 1; // Layer by layer simulation
while (left <= right && top <= bottom) {
// Complete the assignment of the first line
for (int column = left; column <= right; column++) {
//column Column
matrix[top][column] = num;
num++;
}
// Assign the second line
for (int row = top + 1; row <= bottom; row++) {
//row That's ok
matrix[row][right] = num;
num++;
}
if (left < right && top < bottom) {
for (int column = right - 1; column > left; column--) {
matrix[bottom][column] = num;
num++;
}
for (int row = bottom; row > top; row--) {
matrix[row][left] = num;
num++;
}
}
left++;
right--;
top++;
bottom--;
}
return matrix;
}
}
Conclusion
Basic review
An array is a collection of the same type of data stored in continuous memory space .
- Array subscripts are all from 0 At the beginning .
- The address of array memory space is continuous
It is Because the address of array in memory space is continuous , So when we delete or add elements , It's hard to avoid moving the addresses of other elements .
The elements of an array cannot be deleted , Can only cover .
Dichotomy
Loop invariant principle , It's only in the loop that you stick to the definition of intervals , In order to clearly grasp the various details of the cycle .
Dichotomy is a common question in algorithmic interview , It is suggested that this topic be adopted , Exercise your ability to tear your hands apart .
Double finger needling
Double finger needling ( Fast and slow pointer method ): Through a fast pointer and a slow pointer in a for Loop through two for Cycle work .
The sliding window
Another important idea in array operation : The sliding window . The beauty of sliding windows is based on the current subsequence and size , Constantly adjust the starting position of subsequences . So that O ( n 2 ) O(n^2) O(n2) The solution of violence is reduced to O ( n ) O(n) O(n).
Two dimensional data is not in memory 3\*4 Continuous address space of , It's made up of four contiguous address spaces !
Simulation behavior
Simulation class titles are common in arrays , There's no algorithm involved , It's pure simulation , It is very important to investigate your control of the code .
In this topic , Once again, we introduce Loop invariant principle , In fact, this is also an important principle in programming .
I believe you have encountered this situation again : I feel that there are too many boundary adjustment problems , Wave after wave of judgment , Look for the border , Step on the east wall to pay Paul , It's not easy to run through , The code is very redundant , No rules , Actually It's all about simple code , Or principled , You can see this in this topic
边栏推荐
- Redisson分布式锁解锁异常
- Talk about the realization of authority control and transaction record function of SAP system
- CorelDRAW2022下载安装电脑系统要求技术规格
- 2022国内十大工业级三维视觉引导企业一览
- #797div3 A---C
- 咋吃都不胖的朋友,Nature告诉你原因:是基因突变了
- The circuit is shown in the figure, r1=2k Ω, r2=2k Ω, r3=4k Ω, rf=4k Ω. Find the expression of the relationship between output and input.
- [knowledge map paper] r2d2: knowledge map reasoning based on debate dynamics
- JVM memory and garbage collection-3-direct memory
- 进程和线程的退出
猜你喜欢

很多小伙伴不太了解ORM框架的底层原理,这不,冰河带你10分钟手撸一个极简版ORM框架(赶快收藏吧)

保姆级教程:Azkaban执行jar包(带测试样例及结果)

OpenGL/WebGL着色器开发入门指南
![[knowledge map paper] Devine: a generative anti imitation learning framework for knowledge map reasoning](/img/c1/4c147a613ba46d81c6805cdfd13901.jpg)
[knowledge map paper] Devine: a generative anti imitation learning framework for knowledge map reasoning
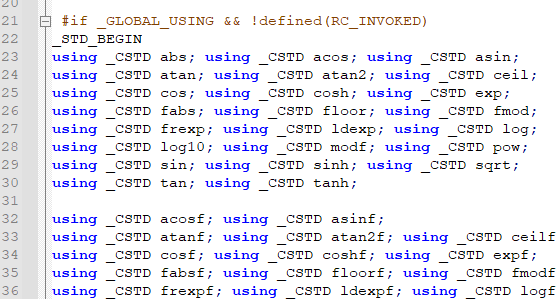
See how names are added to namespace STD from cmath file

leetcode 869. Reordered Power of 2 | 869. 重新排序得到 2 的幂(状态压缩)

Summary of log feature selection (based on Tianchi competition)
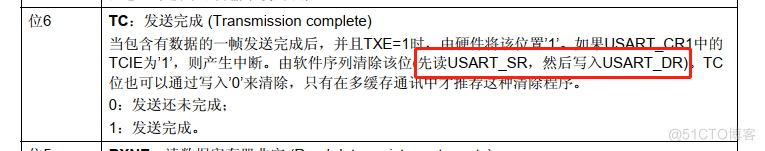
Little knowledge about TXE and TC flag bits

LeetCode精选200道--数组篇
神经网络与深度学习-5- 感知机-PyTorch
随机推荐
鱼和虾走的路
ArrayList源码深度剖析,从最基本的扩容原理,到魔幻的迭代器和fast-fail机制,你想要的这都有!!!
See how names are added to namespace STD from cmath file
nmap工具介绍及常用命令
[recommendation system paper reading] recommendation simulation user feedback based on Reinforcement Learning
JVM memory and garbage collection-3-runtime data area / method area
系统测试的类型有哪些,我给你介绍
《通信软件开发与应用》课程结业报告
云原生应用开发之 gRPC 入门
PHP 计算个人所得税
Exit of processes and threads
MQTT X Newsletter 2022-06 | v1.8.0 发布,新增 MQTT CLI 和 MQTT WebSocket 工具
Vim 字符串替换
Semantic segmentation | learning record (4) expansion convolution (void convolution)
Little knowledge about TXE and TC flag bits
Give some suggestions to friends who are just getting started or preparing to change careers as network engineers
科普 | 什么是灵魂绑定代币SBT?有何价值?
Introduction to Microsoft ad super Foundation
[knowledge map paper] attnpath: integrate the graph attention mechanism into knowledge graph reasoning based on deep reinforcement
leetcode 873. Length of Longest Fibonacci Subsequence | 873. 最长的斐波那契子序列的长度