当前位置:网站首页>Towards an endless language learning framework
Towards an endless language learning framework
2022-07-08 02:08:00 【Wwwilling】
Article
author :Andrew Carlson, Justin Betteridge, Bryan Kisiel, Burr Settles, Estevam R. Hruschka Jr., and Tom M. Mitchell
Literature title : Towards an endless language learning framework
Abstract
- We are here to consider the problem of building an endless language learner ; in other words , An intelligent computer agent that runs forever , Every day must
(1) Extract or read information from the network to fill the growing structured knowledge base , as well as
(2) Learn to complete this task better than the day before . especially , We propose a method and a set of design principles for such agents , Describes the partial implementation of such a system , The system has learned to extract more than 242,000 A knowledge base of beliefs , function 67 After days, the estimation accuracy is 74%, And discuss the lessons learned from the initial attempt to build an endless learning agent .
introduction
- Here we describe the progress towards the long-term goal of cultivating endless language learners . “ Endless language learners ” Means every day 24 Hours 、 Once a week 7 God 、 A computer system that runs forever , Perform two tasks every day :
- Reading task : Extract information from network text , To further fill the growing knowledge base of structured facts and knowledge .
- Learning tasks : Learn to read better every day than the day before , This is reflected in its ability to return to yesterday's text source and extract more information more accurately .
- This research is based on the massive redundancy of network information ( for example , Many facts are stated many times in different ways ) It will make the system with correct learning mechanism successful . One view of this study is , It is a lifelong learning or endless learning case study . The second view is , It attempts to improve the artistic level of natural language processing . The third view is , It attempts to develop the world's largest structured knowledge base —— A knowledge base that reflects the factual content of the World Wide Web , This is useful for many AI jobs .
- This research is based on the massive redundancy of network information ( for example , Many facts are stated many times in different ways ) It will make the system with correct learning mechanism successful . One view of this study is , It is a lifelong learning or endless learning case study . The second view is , It attempts to improve the artistic level of natural language processing . The third view is , It attempts to develop the world's largest structured knowledge base —— A knowledge base that reflects the factual content of the World Wide Web , This is useful for many AI jobs .
- In this paper , We first describe a general approach to building endless language learners , This method uses semi supervised learning 、 A collection of knowledge edge extraction methods , And a flexible knowledge base representation that allows integration of the outputs of these methods . We also discussed the design principles for implementing this approach .
- then , We describe the prototype implementation of our method , Known as the endless language learner (NELL). at present ,NELL Acquire two types of knowledge :(1) Knowledge about which noun phrases refer to which specific semantic categories , Such as city 、 Companies and sports teams ;(2) Knowledge about which noun phrase pairs meet which specific semantic categories . Specified semantic relationship , for example hasOfficesIn(organization, location). NELL Learn to acquire these two types of knowledge in many ways . It learns free-form text patterns to extract knowledge from sentences on the Internet , Learn from semi-structured network data ( Such as tables and lists ) Extract knowledge from , Learn the morphological rules of category instances , And learn probability horn Clause rules , Enable it to infer new relationship instances from other relationship instances it has learned .
- Last , The experiments we show show show that our NELL Realization , Given the initial seed ontology definition 123 Categories and 55 Relationships and run 67 God , use 242,453 A new fact fills this ontology , The estimation accuracy is 74%.
- The main contribution of this work is :(1) Progress has been made in building the architecture of an endless learning agent , And a set of design principles that contribute to the successful implementation of the architecture ,(2) Experimental evaluation of the network scale realized by this architecture , as well as (3) One of the largest and most successful guided learning implementations to date .
Method
- Our approach is around a shared knowledge base (KB) The organization's , The knowledge base is growing , And by a series of complementary knowledge extraction methods to achieve learning / Read subsystem component usage . start KB Defines an ontology ( A collection of predicates that define categories and relationships ), And a few seed examples of each predicate in the ontology ( for example , A dozen sample cities ). The goal of our approach is to grow this knowledge base through reading , And learn to read better .
- The categories and relationship instances added to the knowledge base are divided into candidate facts and beliefs . Subsystem components can read information from the knowledge base and refer to other external resources ( for example , Text corpus or Internet ), Then propose new candidate facts . The component provides each proposed candidate with a probability and a summary of the source evidence supporting it . Knowledge Integrator (KI) The exam will analyze the candidate facts of these proposals , And elevate the most supported facts into a state of belief . The processing flow is shown in Figure 1 Shown .
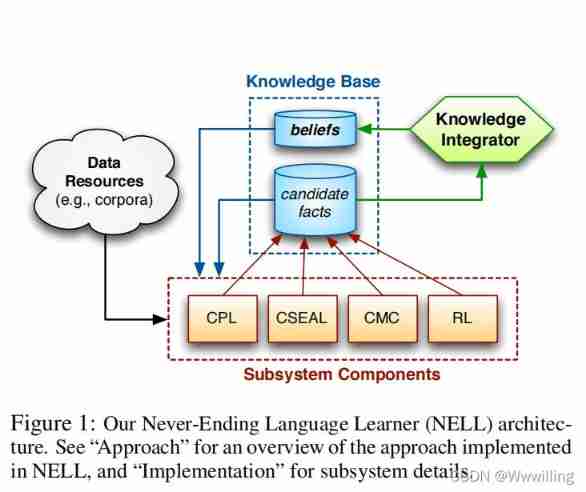
- In our initial implementation , This loop runs iteratively . In each iteration , Given the current KB Each subsystem component of the runs to completion , then KI Decide which newly proposed candidate facts to promote . The knowledge base grows iteratively , Provide more and more beliefs , Then each subsystem component retrains itself with these beliefs , In order to read better in the next iteration . In this way , Our method can be regarded as implementing a coupled semi supervised learning method , Many of these components are learned and shared by KI Supervise complementary types of knowledge . You can think of this approach as maximizing expectations (EM) Approximation of the algorithm , among E The steps involve iterative estimation sharing KB The truth value of a very large set of virtual candidate letters in , and M The steps involve retraining various subsystem component extraction methods .
- If label errors accumulate , This iterative learning method may be affected . To help alleviate this problem , We will allow the system to interact with humans every day 10-15 minute , To help it keep “ a right track ”. however , In the work reported here , Our use of manual input is limited .
- The following design principles are important for implementing our approach :
- Use subsystem components that produce irrelevant errors . When multiple components produce irrelevant errors , The probability that they all produce the same error is the product of their respective error probabilities , As a result, the error rate is much lower .
- Learn many types of interrelated knowledge . for example , We use a component to learn how to extract predicate instances from text resources , Another component learns to infer relational instances from other beliefs in the knowledge base . This provides multiple independent sources of the same type of belief .
- Use a coupled semi supervised learning method to take advantage of the age limit between the predicates being learned (Carl son wait forsomeone ,2010 year ). To provide coupling opportunities , Arrange categories and relationships into a taxonomy , This taxonomy defines which categories are subsets of other categories , And which category pairs are mutually exclusive . Besides , Specify the expected category of each relationship parameter to enable type checking . Subsystem components and KI You can benefit from using coupling .
- Distinguish high confidence beliefs from low confidence candidates in the knowledge base , And keep the source reason of each belief .
- Use uniform KB Representation to capture all types of candidate facts and elevated beliefs , And use relevance reasoning and learning mechanisms that can operate on this shared representation .
Related work
- AI In independent agency 、 Problem solving and learning have a long history of research , for example SOAR(Laird、Newell and Rosenbloom 1987)、PRODIGY(Carbonell wait forsomeone 1991)、EURISKO(Lenat 1983)、ACT-R(Anderson 2004 year ) And Icarus (Langley wait forsomeone ,1991 year ). by comparison , Our focus so far has been on semi supervised learning and reading , Search that pays less attention to problem solving . However , The early work provided us with various design principles for reference . for example ,KB The function in our method is similar to that in the early speech recognition system “ blackboard ” The role of (Erman wait forsomeone ,1980), We KB The frame based representation of is right THEO System (Mitchell wait forsomeone ,1991) The re realization of , The system was originally designed to support integrated representation 、 Reasoning and learning .
- There have been previous studies on lifelong learning , for example Thrun and Mitchell (1995), The focus is on using previously learned functions ( for example , The next state function of the robot ) To learn new functions ( for example , The control function of the robot ). Banko and Etzioni (2007) Consider a lifelong learning environment , One of the agents established a domain theory , And explored different strategies to decide which of the many possible learning tasks to deal with next . Although our current system uses simpler strategies to train all functions in each iteration , But choosing what to learn next is an important ability of lifelong learning .
- Our method adopts semi supervised guided learning , Start with a small set of labeled data , Training models , Then use the model to tag more data . Yarowsky (1995) Use guided learning to train classifiers for word sense disambiguation . Bootstrap Learning has also been successfully applied to many applications , Including web page classification (Blum and Mitchell 1998) And named entity classification (Collins and Singer 1999).
- Bootstrap Learning methods are usually influenced by “ Semantic drift ” Influence , Label errors in the learning process will accumulate (Riloff and Jones 1999;Curran、Murphy and Scholz 2007). There is evidence that , Limiting the learning process helps alleviate this problem . for example , If the classes are mutually exclusive , They can provide counterexamples to each other (Yangarber 2003). You can also type check the relationship parameters , To ensure that they match the expected type (Pas¸ca wait forsomeone ,2006 year ). Carlson wait forsomeone (2010) Adopt such strategies and use a variety of extraction methods , This requires agreement . Carlson The idea of adding many constraints between learned functions is called “ Coupled semi supervised learning ”. Chang、Ratinov and Roth (2007) It also shows that , Enforcing constraints given as domain knowledge can improve semi supervised learning .
- Pennacchiotti and Pantel (2009) A framework is proposed , Used to combine the output of the collection of extraction methods , They call it “ Set semantics ”. Multiple extraction systems provide candidate class instances , Then use the learning function to rank these instances , This function uses data from many different sources ( for example , Query log 、 Wikipedia ) Characteristics of . Their method uses a more complex sorting method than ours , But not iterative . therefore , Their ideas are complementary to our work , Because we can use their ranking method as part of our general method .
- Other previous work has proved , Pattern based and list based extraction methods can be combined in a collaborative manner to achieve significant improvements in recall (Etzioni wait forsomeone ,2004 year ). Downey、Etzioni and Soder land (2005) A probability model for using and training multiple extractors is proposed , Where extractor ( In their work , Different extraction modes ) There will be irrelevant errors . It would be interesting to apply a similar probability model to cover the settings in this article , Many of these extraction methods themselves use multiple extractors ( for example , Text mode 、 Wrappers 、 The rules ).
- Nahm and Mooney (2000) First, it is proved that inference rules can be mined from the beliefs extracted from the text .
- Our work can also be seen as an example of multi task learning , Several different functions are trained together , Such as (Caruana 1997; Yang、Kim and Xing 2009), To improve learning accuracy . Our method involves multi task learning of various types of functions —— There are a total of 531 A function —— Different methods learn different functions with overlapping inputs and outputs , And the constraints provided by ontology ( for example ,“ Athletes ” yes “ people ” Subset , And “ City ” Mutually exclusive ) Support accurate semi supervised learning of the entire function set .
The implementation of
- We have implemented a preliminary version of our method . We call this implementation an endless language learner (NELL). NELL Use four subsystem components ( chart 1):
- Coupling mode learner (CPL): A free text extractor , It learns and uses things like “X The mayor ” and “X by Y Play the role ” And other contextual patterns to extract instances of categories and relationships . CPL Use noun phrases and contextual patterns ( Both use part of speech tag sequence definitions ) Co-occurrence statistics between them to learn the extraction pattern of each predicate of interest , Then use these patterns to find other instances of each predicate . The relationship between predicates is used to filter out overly general patterns . Carlson Et al. Described in detail CPL. (2010). Use the formula 1 − 0. 5 c 1−0.5^c 1−0.5c Heuristic assignment CPL Probability of extracted candidate instances , among c Is to extract the number of candidate promotion patterns . In our experiment ,CPL Is entered with 20 A corpus of 100 million sentences , The corpus is obtained by using OpenNLP Packet from ClueWeb09 Data sets 5 Extracted from the English part of 100 million Web pages 、 Part of speech and POS-tag Sentence generation ( Karan and Hoy 2009).
- Coupled SEAL (CSEAL): A semi-structured extractor , It uses a set of beliefs from each category or relationship to query the Internet , Then mining lists and tables to extract new instances of the corresponding predicates . CSEAL Use mutually exclusive relationships to provide counterexamples , Used to filter out too general lists and tables . Carlson Et al. Also described CSEAL. (2010), And based on Wang and Cohen (2009) Supplied code . Given a set of seed instances ,CSEAL The query is executed by subsampling the beliefs in the knowledge base and using these sampled seeds in the query . CSEAL Configured to issue for each category 5 A query , Send for each relationship 10 A query , And each query gets 50 Pages . CSEAL The extracted candidate facts are used with CPL Assign probability in the same way , except c Is the number of unfiltered packages that extract instances .
- Coupled morphological classifier (CMC): A set of binary L2 Regularized logistic regression model - One per category - According to various morphological characteristics ( word 、 Capitalization 、 affix 、 Part of speech, etc ) Classify noun phrases . ). Beliefs from the knowledge base are used as training examples , But in each iteration ,CMC Limited to having at least 100 Predicates that promote instances . And CSEAL equally , Mutex is used to identify negative instances . CMC Check the candidate facts proposed by other components , And classify each predicate at most in each iteration 30 A new belief , The minimum posterior probability is 0.75. These heuristic measurements help ensure high accuracy .
- Rule Learner (RL): Be similar to FOIL(Quinlan and Cameron-Jones 1993) First order relation learning algorithm , It learns probability Horn Clause . These learned rules are used to infer new relationship instances from other existing relationship instances in the knowledge base .
- We are interested in knowledge integrator (KI) The implementation uses hard coded intuitive strategies to promote candidate facts to belief States . Candidate facts with high confidence from a single source ( Those posterior tests > 0.9 Candidate facts ) Be promoted , If they are proposed by multiple sources , Then the candidate facts with low confidence are promoted . KI Take advantage of the relationship between predicates by respecting mutual exclusion and type checking information . especially , If the candidate class instance already belongs to the mutually exclusive class , Will not enhance them , Unless their parameters are at least candidates of the appropriate class type ( And has not yet been considered an instance of a category ), Otherwise, the relationship instance will not be promoted . Categories that are mutually exclusive with the appropriate type ). In our current implementation , Once the candidate facts are promoted to beliefs , It will never be downgraded . KI It is configured to promote each predicate at most per iteration 250 An example , But this threshold is rarely reached in our experiments .
- NELL Medium KB Based on the Tokyo cabinet ( A kind of speed 、 Lightweight keys / Value store ) Based on the THEO Representation of frames (Mitchell wait forsomeone ,1991 year ) The re realization of . KB Millions of values can be processed on one machine .
Experimental evaluation
- We conducted an experimental evaluation to explore the following issues :
- NELL Can we learn to fill many different categories through dozens of learning iterations (100+) And relationship (50+) And maintain high accuracy ?
- Different component pairs NELL How much does the belief advocated contribute ?
Method
- The input ontology used in our experiment includes 123 Categories , Each category has 10-15 Seed instances and 5 individual CPL Seed mode ( From Hearst mode (Hearst 1992)). Categories include locations ( for example , mountains 、 lakes 、 City 、 The museum )、 figure ( for example , scientists 、 The writer 、 Politician 、 musician )、 animal ( for example , reptile 、 birds 、 Mammal ) organization ( for example , company 、 university 、 Website 、 Sports team ) etc. . It includes 55 A relationship , Every relationship also has 10-15 Seed instances and 5 Negative examples ( It is usually generated by arranging the parameters of the seed in the position ). Relationships capture different categories ( for example ,teamPlaysSport、bookWriter、companyProducesProduct) The relationship between .
- In our experiment ,CPL、CSEAL and CMC Run once per iteration . RL In each batch 10 Run after iterations , And the proposed output rules are filtered manually . It only takes a few minutes to manually approve these rules .
- To estimate NELL The accuracy of beliefs in the generated knowledge base , Beliefs from the final knowledge base are randomly sampled , And evaluated by several human judges . Before making a decision , We will discuss the differences in detail . The fact that once was right but now is incorrect ( for example , A former coach of a sports team ) Considered correct , because NELL At present, it does not deal with the time range in its belief . False adjectives are allowed ( for example ,“ Today's Chicago Tribune ”), But it's rare .
result
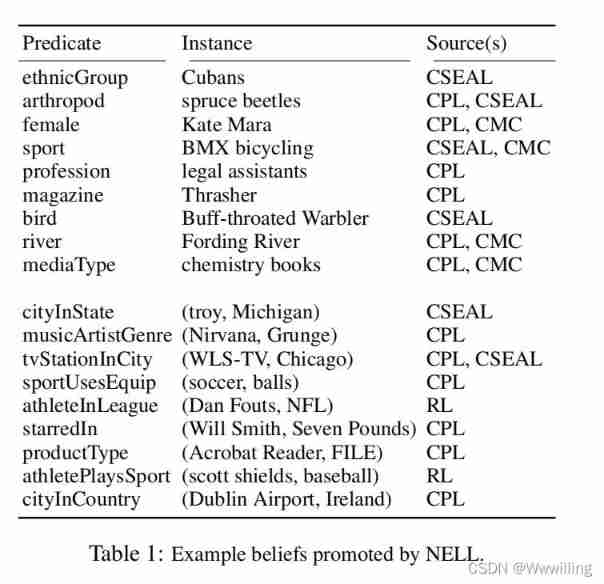
Running 67 Days later ,NELL It's done 66 Perform iterations . In all predicates 242,453 A belief , among 95% Is a category instance ,5% Is a relationship instance . Example beliefs from various predicates , And extract their source components , As shown in the table 1 Shown .
During the first iteration, nearly 10,000 After a belief ,NELL Continue to promote thousands of beliefs in each successive iteration , This means that if you let it run longer , It has great potential to learn more . chart 2 Shows NELL Different views of promotions over time . The left figure shows the total number of categories and relationships promoted in each iteration . The promotion of category instances is quite stable , The promotion of relationship instances is sharp . This is mainly because RL Each component 10 Only run once per iteration , And responsible for many relationship promotions . The chart on the right is a stacked bar chart , Shows the proportion of predicates with different promotion levels during different iteration spans . These graphs show , stay NELL During the whole operation of , Instances are promoted to many different categories and relationships .

chart 2: as time goes on , Propaganda activities of faith .
Left : The number of beliefs raised for all categories and relational predicates in each iteration . stay RL After component operation , Every time 10 There will be periodic spikes between relational predicates in the next iteration .
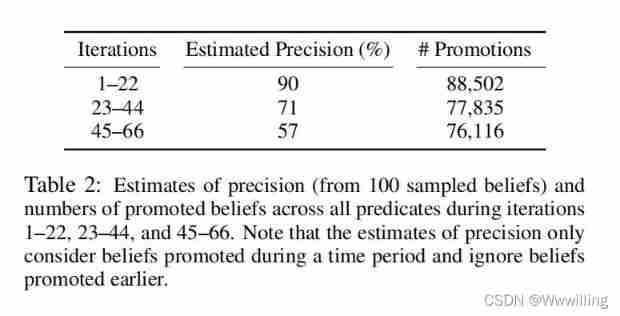
Middle and right : The stacked bar chart details over time , The predicate proportion of categories and relationships at various promotion levels ( And predicate count , Displayed in the bar ). Please note that , Although some predicates became “ Sleep ”, But even in later learning iterations , Most predicates continue to show a healthy level of promotional activity .In order to estimate the accuracy of beliefs improved at different stages of execution , We considered three time periods : iteration 1-22、 iteration 23-44 And iteration 45-66. For each of these time periods , We uniformly extracted 100 Positions promoted during these periods and judge their correctness . Results such as table 2 Shown . In three periods , The promotion rate is very similar , Promoted 76,000 To 89,000 An example . The estimation accuracy has a downward trend , from 90% To 71% Until then 57%. These three precision estimates are weighted average according to the number of promotions , all 66 The overall estimation accuracy of this iteration is 74%.
The judges discussed only a few items : Example is “ Right rear ”, Considered not to refer to body parts ,“ Green leaf salad ”, Considered an acceptable vegetable . “Proceedings” Promoted as a publication , We think this is incorrect ( Probably because of CPL Noun phrase segmentation error in ). Two errors are due to language (“ Klingon ” and “ mandarin ”) It is advertised as an ethnic group . (“Southwest”、“San Diego”) Marked as hasOfficesIn The right example of a relationship , Because Southwest Airlines has no official office there . Many system errors are subtle ; People may think that non-native English readers will make similar mistakes .
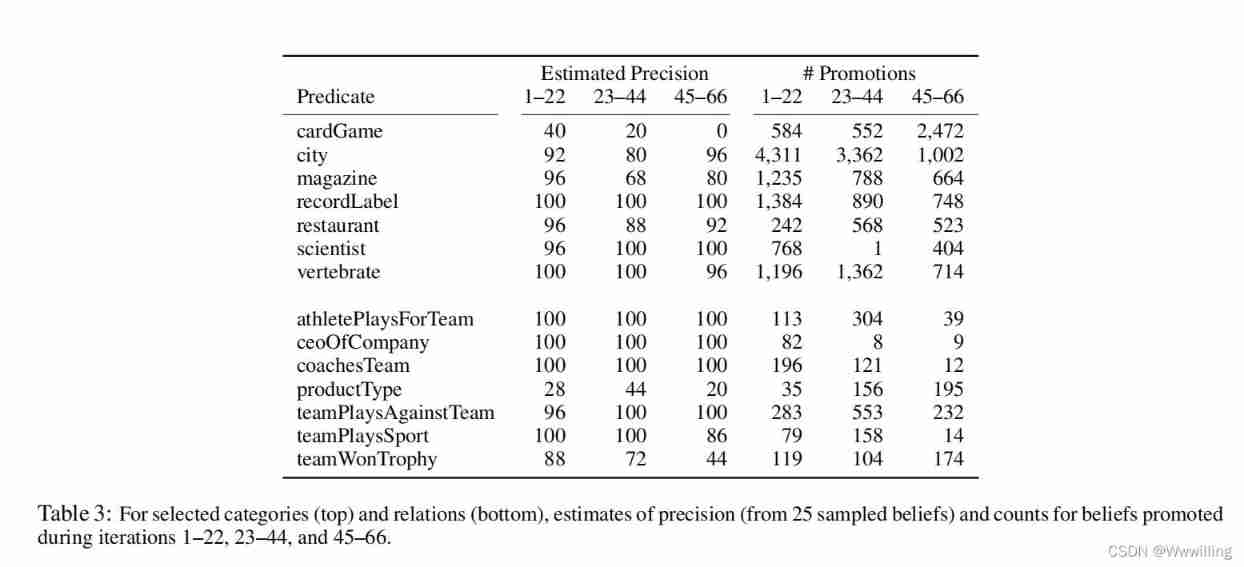
In order to estimate the accuracy of predicate level , We chose... At random 7 Categories and 7 A relationship , These relationships have at least 10 Examples of promotion . For each predicate selected , We start with iteration 1-22、23-44 and 45-66 We've sampled 25 A belief , And judge their correctness . surface 3 These predicates are shown , And the accuracy estimate and the number of beliefs improved in each time period . Most predicates are very accurate , The accuracy is more than 90%. Two predicates , especially cardGame and productType, Performance is much worse . cardGame Categories seem to be affected by a large number of online spam related to casinos and card games , This can lead to parsing errors and other problems . Because of this noise ,NELL Finally, the string of adjectives and nouns ( Such as “ Deposit casino bonus free online list ”) Extract as incorrect card game stance . productType Most of the mistakes in relationships come from associating product names with more common nouns , These nouns have something to do with products , But the type of product is not correctly indicated , for example ,(“Microsoft Office”、“PC” ). The judges debated the lies of some product types , But it was eventually marked as incorrect , for example (“Photoshop”、“ graphics ”). In our noumenon ,productType The category of the second parameter of is general in the hierarchy “ project ” Supercategory ; Let's assume a more specific “ The product type ” Categories may lead to more stringent type checking .
As described in the implementation part ,NELL Use knowledge integrator to improve single source candidate facts with high reliability , And candidate facts with multiple low confidence sources . chart 3 Explain the impact of each component in this integration strategy . Each component displayed contains a count , This count is the number of beliefs increased only based on sources with high confidence in the belief . The line connecting the components is marked with a count , These counts are based on the number of beliefs raised by these components , Each component has a certain degree of confidence in the candidate . CPL and CSEAL Each is responsible for many propaganda of their beliefs . However ,KI More than half of the beliefs advocated are based on multiple sources of evidence . although RL Not responsible for many of the beliefs advocated , But it does put forward the belief with high confidence, which seems to be largely independent of the beliefs of other components .
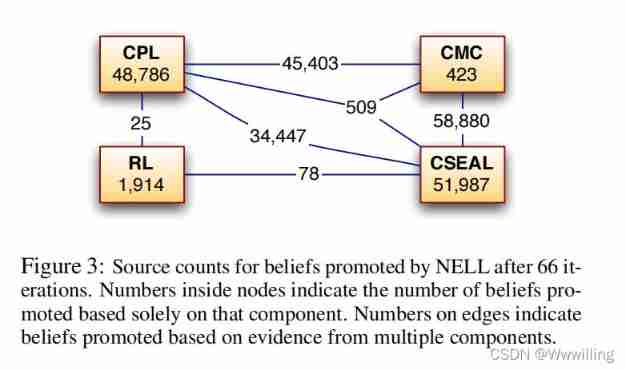
chart 3:NELL stay 66 The source count of generalized beliefs after iterations . The number in the node represents the number of beliefs raised only based on this component . The numbers on the side represent beliefs based on evidence from multiple components .
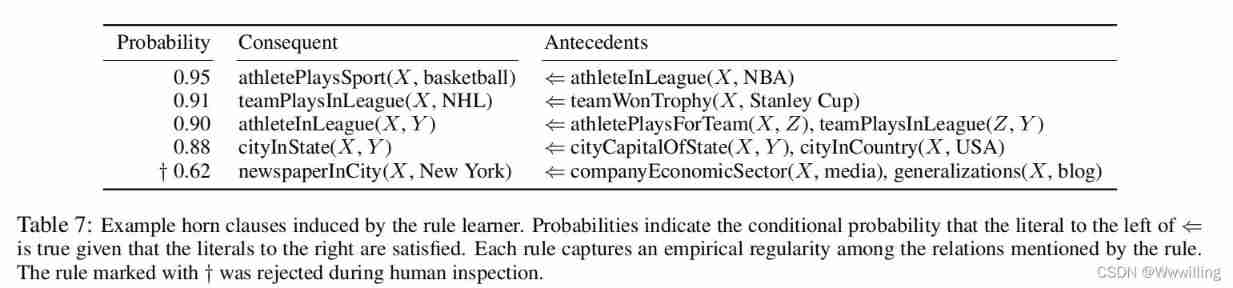
RL Average learning per iteration 66.5 A new rule , among 92% Approved . 12% The approval rule of implies at least one candidate instance that has not been implied by another rule , And these rules mean 69.5 An example of this .
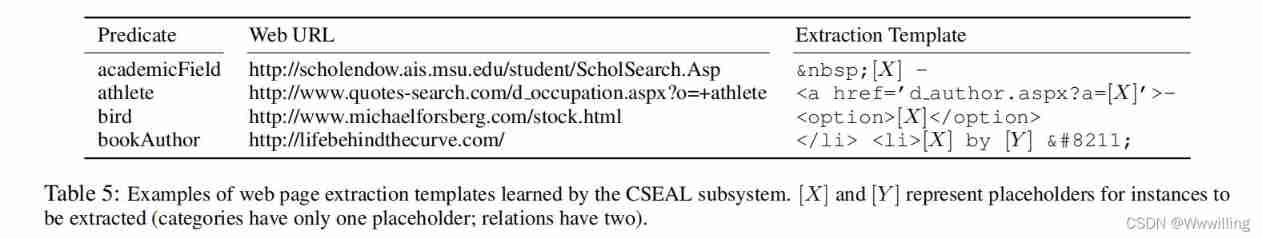
In order to let you know NELL What are the different components used in learning , We provide examples for each component . surface 4 Shows CPL Context mode of learning . surface 5 Shows CSEAL Learning web wrapper . surface 6 Shows from CMC Example weights of learned logistic regression classifiers . Last , surface 7 It's shown by RL Induced example rules .


Supplementary online materials several supplementary materials we evaluate are published online , Include :(1) All promoted instances ,(2) All categories 、 Relationships and seed instances ,(3) All tagged instances are sampled for estimation accuracy , (4) CPL All models promoted , as well as (5) RL All the rules of learning .
Discuss
- These results are promising . NELL Maintain high accuracy in many iterative learning at a consistent rate of knowledge accumulation , All this requires very limited manual guidance . We believe that this is a major progress towards our goal of building endless language learners . NELL A total of 531 A coupling function , because 3 There are different subsystems (CMC、CPL and CSEAL) To study the 123 Categories , and 3 There are different subsystems (CPL、CSEAL and RL) To study the 55 A relationship .
- The established goal of the system is to read more online content every day to further fill its knowledge base , And learn to read more facts more accurately every day . As in the past 67 Days of KB As growth suggests , The system reads more data every day . Every day it also learns new extraction rules to further fill its knowledge base 、 A new extractor based on morphological logic features 、 Infer new information that is not read as a lie from other beliefs in the knowledge base Horn Clause rules , And the use of HTML The new structure is specific to URL Extractor for . Even though NELL Continuous learning enables him to extract more facts every day , But the accuracy of the extracted facts will slowly decline with the passage of time . This is partly because the simplest extraction occurs in early iterations , Later iterations require more accurate extractors to achieve the same level of accuracy . However , Also have NELL Making mistakes leads to learning to make more mistakes . Although we think the current system is promising , But there is still much research to be done .
- The results usually support the importance of using design principles for components that mainly produce independent errors . More than half of the beliefs are based on evidence from multiple sources . However , When checking the errors generated by the system , Obviously CPL and CMC Our mistakes are not completely irrelevant . for example , about bakedGood Category ,CPL learning model “X are enabled in”, Because I believe in examples “cookies”. This leads to CPL extract “ persistence cookie” As a candidate for baked goods . CMC Output to “cookies” High probability of ending phrases , therefore “persistent cookies” Promoted to bakedGood Trusted instances of .
- Such behavior , as well as NELL The accuracy of the advocated beliefs declines slowly but steadily , It shows that there is an opportunity to use more interpersonal interaction in the learning process . at present , This interaction is limited to approval or rejection RL Proposed reasoning rules . however , We plan to explore other forms of manual supervision , The limit is about 10-15 minute . especially , Active learning (Settles 2009) By allowing NELL In its belief 、 The theory even presents uncertain characteristics “ doubt ”, This brings great hope . for example , image “X are enabled in” Such a pattern can only appear in some bakeGood In instances of categories . This may be a bad pattern that leads to semantic drift , It may also be the discovery of some undiscovered bakeGood Opportunities for class subsets . If NELL Be able to fully identify such knowledge opportunities , Humans can easily provide labels for this single model , And convey a lot of information in a few seconds . Previous work shows that , Marker feature ( for example , Context mode ) Instead of instances, it can bring significant improvements in reducing manual annotation time (Druck、Settles and McCallum 2009).
Conclusion
- We propose a framework for the endless language learning agent , And describes the partial implementation of the architecture , The architecture uses four subsystem components to learn to extract knowledge in a complementary way . Running 67 Days later , The implementation is based on 74% The estimation accuracy of fills in more than 242,000 A knowledge base of facts .
- These results illustrate the benefits of using a variety of knowledge extraction methods suitable for learning and a knowledge base that allows the storage of candidate facts and confident beliefs . however , There are many opportunities for improvement , Include :(1) Self reflection to decide what to do next ,(2) Make more effective use of 10-15 Minutes of daily interpersonal interaction ,(3) Discover new predicates to learn ,(4) Learn other types of knowledge about languages ,(5) Entity level ( Instead of string level ) modeling , as well as (6) More complex probability modeling in the whole process perform .
边栏推荐
- 喜欢测特曼的阿洛
- C语言-Cmake-CMakeLists.txt教程
- 鼠标事件-事件对象
- 静态路由配置全面详解,静态路由快速入门指南
- #797div3 A---C
- C language - modularization -clion (static library, dynamic library) use
- Mouse event - event object
- 《ClickHouse原理解析与应用实践》读书笔记(7)
- I don't know. The real interest rate of Huabai installment is so high
- Little knowledge about TXE and TC flag bits
猜你喜欢
Neural network and deep learning-5-perceptron-pytorch
#797div3 A---C

MQTT X Newsletter 2022-06 | v1.8.0 发布,新增 MQTT CLI 和 MQTT WebSocket 工具

JVM memory and garbage collection-3-runtime data area / heap area

Remote Sensing投稿经验分享
nmap工具介绍及常用命令

文盘Rust -- 给程序加个日志

C语言-Cmake-CMakeLists.txt教程

OpenGL/WebGL着色器开发入门指南

XXL job of distributed timed tasks
随机推荐
Ml self realization / linear regression / multivariable
OpenGL/WebGL着色器开发入门指南
《ClickHouse原理解析与应用实践》读书笔记(7)
Beaucoup d'enfants ne savent pas grand - chose sur le principe sous - jacent du cadre orm, non, ice River vous emmène 10 minutes à la main "un cadre orm minimaliste" (collectionnez - le maintenant)
mysql/mariadb怎样生成core文件
leetcode 866. Prime Palindrome | 866. 回文素数
The function of carbon brush slip ring in generator
The body has a mysterious margin of 8px
PHP 计算个人所得税
Introduction to grpc for cloud native application development
VR/AR 的产业发展与技术实现
A comprehensive and detailed explanation of static routing configuration, a quick start guide to static routing
JVM memory and garbage collection-3-object instantiation and memory layout
Little knowledge about TXE and TC flag bits
Uniapp one click Copy function effect demo (finishing)
Is NPDP recognized in China? Look at it and you'll see!
静态路由配置全面详解,静态路由快速入门指南
metasploit
leetcode 865. Smallest Subtree with all the Deepest Nodes | 865. The smallest subtree with all the deepest nodes (BFs of the tree, parent reverse index map)
QML fonts use pixelsize to adapt to the interface