当前位置:网站首页>[515. find the maximum value in each tree row]
[515. find the maximum value in each tree row]
2022-06-25 08:31:00 【Sugar_ wolf】
Given the root node of a binary tree root , Please find the maximum value of each layer in the binary tree .
Example 1:

Input : root = [1,3,2,5,3,null,9]
Output : [1,3,9]
Example 2:
Input : root = [1,2,3]
Output : [1,3]
Tips :
- The range of the number of nodes in a binary tree is [0,104]
- -231 <= Node.val <= 231 - 1
Method 1 : Depth-first search
Ideas and algorithms
We use trees 「 The first sequence traversal 」 To carry out 「 Depth-first search 」 Handle , And use \textit{curHeight}curHeight To mark the height of the current node traversed . When traversal to \textit{curHeight}curHeight The height node determines whether to update the maximum value of the layer node .
Code :
class Solution {
public:
void dfs(vector<int>& res, TreeNode* root, int curHeight) {
if (curHeight == res.size()) {
res.push_back(root->val);
} else {
res[curHeight] = max(res[curHeight], root->val);
}
if (root->left) {
dfs(res, root->left, curHeight + 1);
}
if (root->right) {
dfs(res, root->right, curHeight + 1);
}
}
vector<int> largestValues(TreeNode* root) {
if (!root) {
return {
};
}
vector<int> res;
dfs(res, root, 0);
return res;
}
};
Execution time :8 ms, In all C++ Defeated in submission 80.00% Users of
Memory consumption :21.4 MB, In all C++ Defeated in submission 94.52% Users of
Complexity analysis
Time complexity : O(n), among n Is the number of binary tree nodes . In the traversal of binary tree, each node will be visited once and only once .
Spatial complexity : O(height). among height Represents the height of the binary tree . Recursive functions require stack space , And stack space depends on the depth of recursion , So the space complexity is equivalent to the height of the binary tree .
Method 2 : Breadth first search
Ideas and algorithms
We can also use 「 Breadth first search 」 To solve this problem .「 Breadth first search 」 In the queue, there are 「 All nodes of the current layer 」. Every time you expand to the next level , differ 「 Breadth first search 」 Only one node is taken from the queue at a time , We take out all the nodes in the current queue for expansion , This ensures that all nodes of the next layer are stored in the queue after each expansion , That is, we expand layer by layer , Then on each floor we use maxVal To mark the maximum value of this layer node . When all nodes of this layer are processed , maxVal Is the maximum value of all nodes in this layer .
Code :
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> largestValues(TreeNode* root) {
if (!root) {
return {
};
}
vector<int> res;
queue<TreeNode*> q;
q.push(root);
while (!q.empty()) {
int len = q.size();
int maxVal = INT_MIN;
while (len > 0) {
len--;
auto t = q.front();
q.pop();
maxVal = max(maxVal, t->val);
if (t->left) {
q.push(t->left);
}
if (t->right) {
q.push(t->right);
}
}
res.push_back(maxVal);
}
return res;
}
};
Execution time :8 ms, In all C++ Defeated in submission 80.00% Users of
Memory consumption :21.5 MB, In all C++ Defeated in submission 88.01% Users of
Complexity analysis
Time complexity : O(n), among n Is the number of binary tree nodes , Each node will enter and leave the queue only once .
Spatial complexity : O(n), The space cost of storing binary tree nodes .
author: LeetCode-Solution
边栏推荐
- 2021 "Ai China" selection
- Meaning of Jieba participle part of speech tagging
- 想转行学软件测试担心哪些问题?
- Find out the possible memory leaks caused by the handler and the solutions
- Retrieval model rough hnsw
- 在二叉树(搜索树)中找到两个节点的最近公共祖先(剑指offer)
- Quickly build a real-time face mask detection system in five minutes (opencv+paddlehub with source code)
- 各种同步学习笔记
- Scanpy (VII) spatial data analysis based on scanorama integrated scrna seq
- How to calculate the D value and W value of statistics in normality test?
猜你喜欢

故障:Outlook 收发邮件时的 0x800CCC1A 错误

使用pytorch搭建MobileNetV2并基于迁移学习训练

Day 5 script and UI System

First experience Amazon Neptune, a fully managed map database
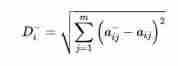
How to calculate the positive and negative ideal solution and the positive and negative ideal distance in TOPSIS method?

How to calculate critical weight indicators?

Data-centric vs. Model-centric. The Answer is Clear!

双周投融报:资本埋伏Web3基础设施

使用apt-get命令如何安装软件?

家庭服务器门户Easy-Gate
随机推荐
Prepare these before the interview. The offer is soft. The general will not fight unprepared battles
Quickly build a real-time face mask detection system in five minutes (opencv+paddlehub with source code)
[unexpected token o in JSON at position 1 causes and solutions]
Can I grant database tables permission to delete column objects? Why?
如何成为一名软件测试高手? 月薪3K到17K,我做了什么?
堆栈认知——栈溢出实例(ret2libc)
Self made ramp, but it really smells good
打新债安不安全 有风险吗
Rosparam statement
Websocket understanding and application scenarios
浏览器查看当前页面所有的监听事件
What are the indicators of DEA?
Almost taken away by this wave of handler interview cannons~
In 2022, which industry will graduates prefer when looking for jobs?
Getting to know the generation confrontation network (11) -- using pytoch to build wgan to generate handwritten digits
How to calculate the correlation coefficient and correlation degree in grey correlation analysis?
linux中的mysql有10061错误怎么解决
在哪个平台买股票开户安全?求分享
A solution to slow startup of Anaconda navigator
【总结】1361- package.json 与 package-lock.json 的关系