当前位置:网站首页>PostgreSQL schema (Schema)
PostgreSQL schema (Schema)
2022-08-04 06:10:00 【Rhubarb cat. 1】
A database contains one or more named schemas,模式又包含表.The schema also contains other named objects,包括数据类型、函数,以及操作符.同一个对象名可以在不同的模式里使用而不会导致冲突; 比如,schema1和myschemacan contain called mytable的表.和数据库不同,模式不是严格分离的:一个用户可以访问他所连接的数据库中的任意模式中的对象,as long as he has permission.
We need patterns for a few main reasons:
1). 允许多个用户使用一个数据库而不会干扰其它用户.
2). 把数据库对象组织成逻辑组,让它们更便于管理.
3). 第三方的应用可以放在不同的模式中,这样它们就不会和其它对象的名字冲突.
1. 创建模式:
CREATE SCHEMA myschema;
The above command can create the name as myschema的模式,after the schema is created,It can then have its own set of logical objects,如表、视图和函数等.
2. public模式:
在介绍后面的内容之前,Here we need to explain firstpublic模式.Whenever we create a new database,PostgreSQLwill automatically create the schema for us.when logging into the database,如果没有特殊的指定,We will use this mode(public)Manipulate various data objects in the form of ,如:
CREATE TABLE products ( ... ) 等同于 CREATE TABLE public.products ( ... )
3. 权限:
缺省时,Users cannot see objects in the schema that they do not own.for them to see,The owner of the schema needs to give on the schemaUSAGE权限.为了让用户使用模式中的对象,We may need to grant additional permissions,as long as it suits the object.PostgreSQLDifferent permission types are provided according to different objects,如:
GRANT ALL ON SCHEMA myschema TO public;
上面的ALLKeywords will containCREATE和USAGE两种权限.如果publicMode has itmyschema模式的CREATE权限,Then users logged in to that schema will be able tomyschemaCreate arbitrary objects in the schema,如:
CREATE TABLE myschema.products (
product_no integer,
name text,
price numeric CHECK (price > 0),
);
When granting permissions to all tables in the schema,Permissions need to be split into various different table operations,如:
ALTER DEFAULT PRIVILEGES IN SCHEMA myschema
GRANT INSERT, SELECT, UPDATE, DELETE, TRUNCATE, REFERENCES, TRIGGER ON TABLES TO public;
All in for modeSequenceWhen the sequence object grants permission,Permissions need to be split into different onesSequence操作,如:
ALTER DEFAULT PRIVILEGES IN SCHEMA myschema
GRANT SELECT, UPDATE, USAGE ON SEQUENCES TO public;
When giving permissions to all functions in the schema,Only execute permissions are considered,如:
ALTER DEFAULT PRIVILEGES IN SCHEMA myschema
GRANT EXECUTE ON FUNCTIONS TO public;
可以看出,通过以上方式在public模式下为myschemaPatterns are extremely inconvenient to create various objects.Next we will introduce another way,即通过role对象,Log in directly and connect tomyschema对象,之后便可以在myschemaThe various required objects are created directly in the mode.
CREATE ROLE myschema LOGIN PASSWORD '123456'; --The role object associated with the schema is created.
CREATE SCHEMA myschema AUTHORIZATION myschema; --Associate the schema to the specified role,The schema name and role name may not be equal.
在Linux Shell下,以myschemarole to log in to the databaseMyTest,After the password is entered correctly, the login to the database will be successful.
/> psql -d MyTest -U myschema
Password:
MyTest=> CREATE TABLE test(i integer);
CREATE TABLE
MyTest=> \d --View this mode,As well as the mode has permission to seetables信息列表.
List of relations
Schema | Name | Type | Owner
------------+---------+------+----------
myschema | test | table | myschema
(1 rows)
4. 删除模式:
DROP SCHEMA myschema;
If you want to delete the schema and all its objects,Please use cascade delete:
DROP SCHEMA myschema CASCADE;
5. 模式搜索路径:
When we use a database object, we can use its full name to locate the object,However, doing so is often very cumbersome,Had to type every timeowner_name.object_name.PostgreSQLSchema search paths are provided in ,这有些类似于Linux中的$PATH环境变量,当我们执行一个Shell命令时,Only this command is located$PATH的目录列表中,We can execute it directly through the command name,Otherwise, you need to enter its full pathname.PostgreSQLIt also determines which table a table is by looking up a search path,This path is a list of patterns to look for.The first table found in the search path will be considered the selected table.if in the search path no match table,那么就报告一个错误,This is true even if the name of the match table exists in other schemas in the database.
The first schema in the search path is called the current schema.除了是搜索的第一个模式之外,它还是在CREATE TABLE没有声明模式名的时候,The schema to which the new table belongs.要显示当前搜索路径,使用下面的命令:
MyTest=> SHOW search_path;
search_path
----------------
"$user",public
(1 row)
New patterns can be added to the search path,如:
SET search_path TO myschema,public;
Sets the specified pattern for the search path,如:
SET search_path TO myschema; --will only be included in the current search pathmyschema一种模式.
边栏推荐
- 光条中心提取方法总结(一)
- Kubernetes基本入门-概念介绍(一)
- 【CV-Learning】线性分类器(SVM基础)
- Matplotlib中的fill_between;np.argsort()函数
- TensorFlow2 study notes: 6. Overfitting and underfitting, and their mitigation solutions
- Jupyter Notebook installed library;ModuleNotFoundError: No module named 'plotly' solution.
- 剑指 Offer 2022/7/8
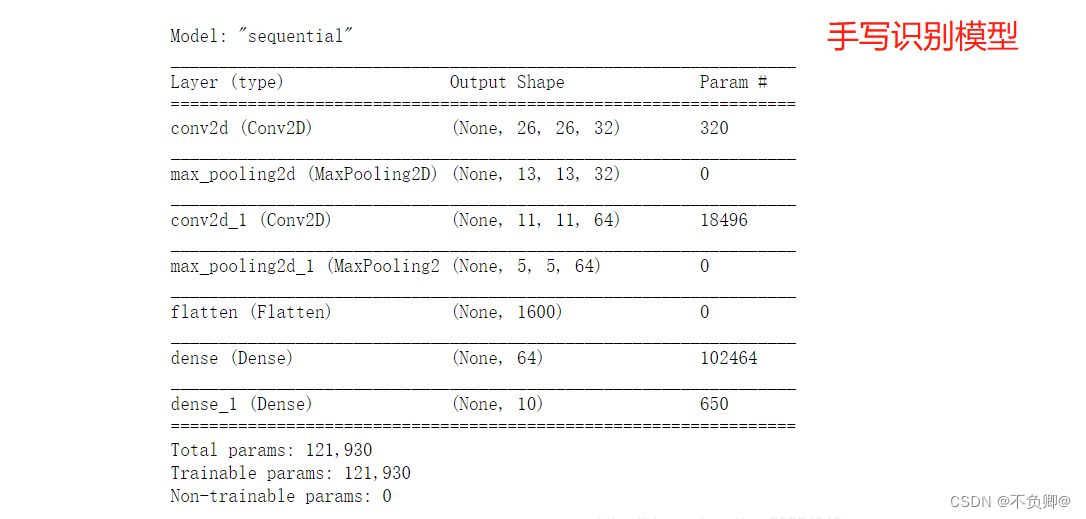
- [Deep Learning 21 Days Learning Challenge] 1. My handwriting was successfully recognized by the model - CNN implements mnist handwritten digit recognition model study notes
- IvNWJVPMLt
- 线性回归02---波士顿房价预测
猜你喜欢
随机推荐
动手学深度学习__张量
基于PyTorch的FCN-8s语义分割模型搭建
(十五)B-Tree树(B-树)与B+树
【CV-Learning】Convolutional Neural Network
Dictionary feature extraction, text feature extraction.
简单明了,数据库设计三大范式
Vision Transformer 论文 + 详解( ViT )
yolov3数据读入(二)
【CV-Learning】卷积神经网络
fill_between in Matplotlib; np.argsort() function
空洞卷积
简单说Q-Q图;stats.probplot(QQ图)
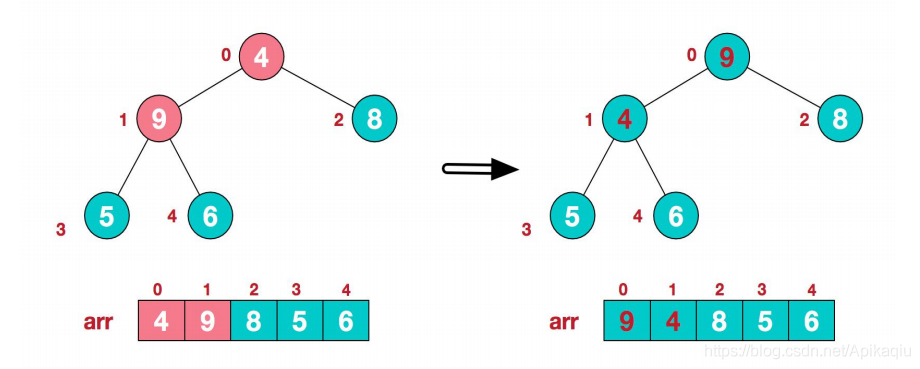
(九)哈希表
RecyclerView的用法
Android connects to mysql database using okhttp
动手学深度学习_线性回归
The difference between oracle temporary table and pg temporary table
MFC 打开与保存点云PCD文件
yolov3中数据读入(一)
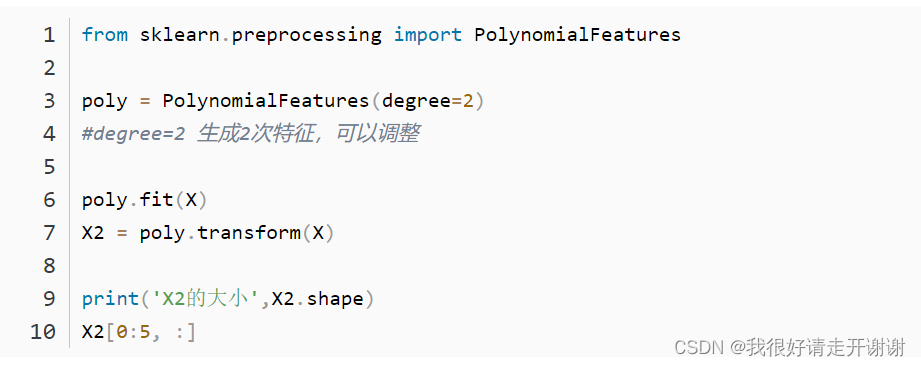
The pipeline mechanism in sklearn
![[CV-Learning] Convolutional Neural Network Preliminary Knowledge](/img/7d/58d9649b06e78eeb019d63615a90c4.png)