当前位置:网站首页>TIPC messaging3
TIPC messaging3
2022-07-02 11:08:00 【Cheng Gouzi walking in the clouds】
Messaging
Datagram messaging
Unicast, anycast or multicast, Depends on the type of address used 、- Socket address 、 Service address or service scope .
If there are multiple sockets matching the given service address , Then select the target in a circular way .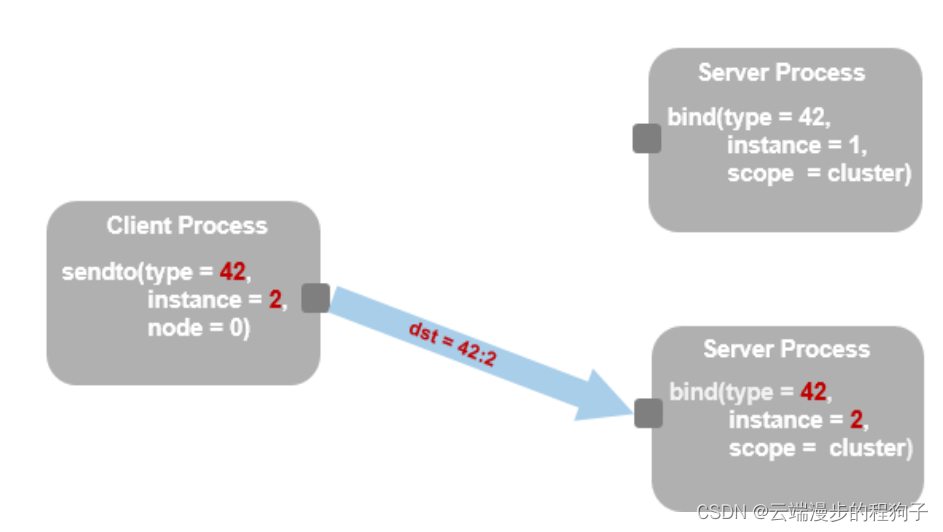
1、 Reliable transmission between nodes .
2、 receive socket Buffer overload protection
3、 There is no end-to-end flow control , Therefore, the message may still be rejected by the receiving socket .
4、 According to the configuration of sending socket , Rejected messages may be discarded or returned to the sender .
5、 If you return , The message will be truncated with an error code .Connections
Establish a connection by using a service address or socket address
1、 Use the one-way setting of data transmission information ( Also known as “0-RTT”)
2、 Or traditional TCP The style is set
1、Stream- or message oriented.
2、End-to-end flow control for socket receive buffer overflow protection.
3、No socket level sequence numbers, acknowledges or retransmissions, - link layer takes care of that.Connection breaks immediately if peer becomes unavailable.
1、Leverages link level heartbeats and kernel/socket cleanup functionality.
2、No socket level “keepalive” heartbeats needed.Communication Groups( Communication group )
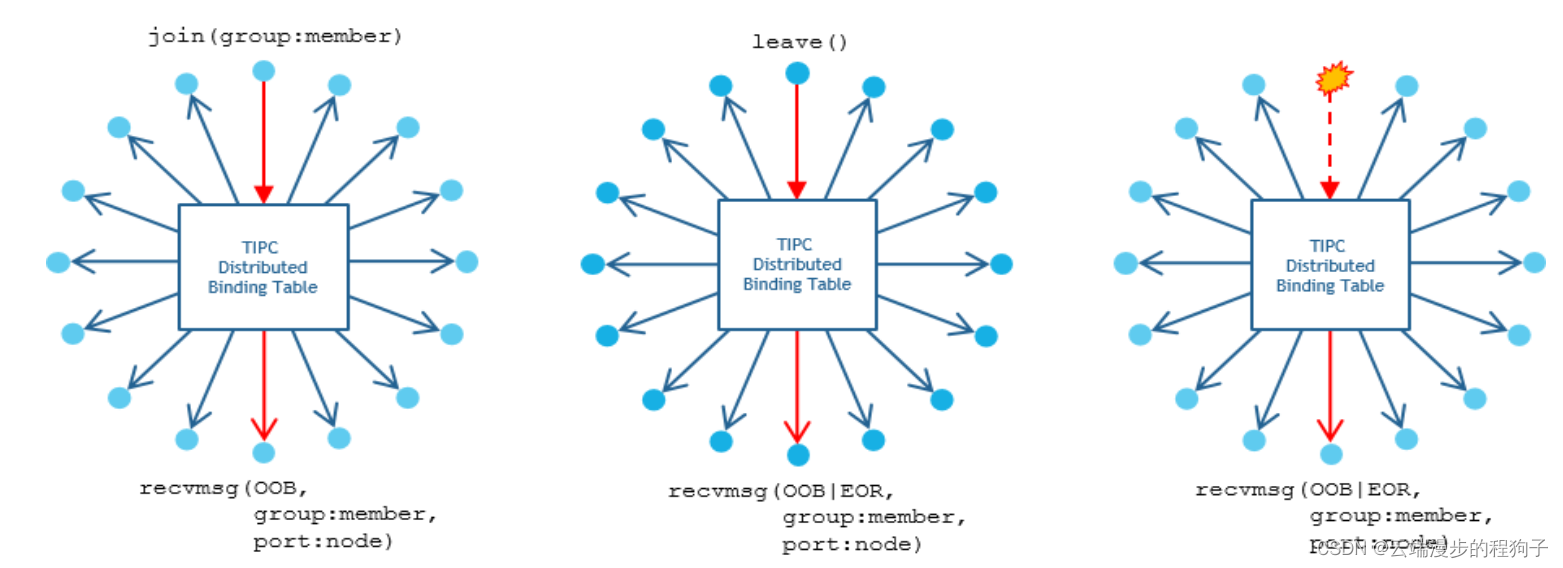
Communication groups can be described as brokerless message bus instances. Such instances are user created, - the first joining member socket implicitly creates the group. This feature is available from Linux 4.14.
A socket joins a group by indicating a service address, - the address type field serves as group identity, the address instance field serves as member identity.
Groups are closed, - members can only exchange messages with other sockets in the same group.
Each member socket has two addresses: a socket address bound by the system and a service address (group:member tuple) bound by the user. Both addresses are delivered to a message receiving user.
Member sockets may optionally provide the user with join/leave events for other group members, leveraging the service tracking capabilities of the binding table.
Member sockets may optionally receive loopback copies of their own anycast/multicast/broadcast messages.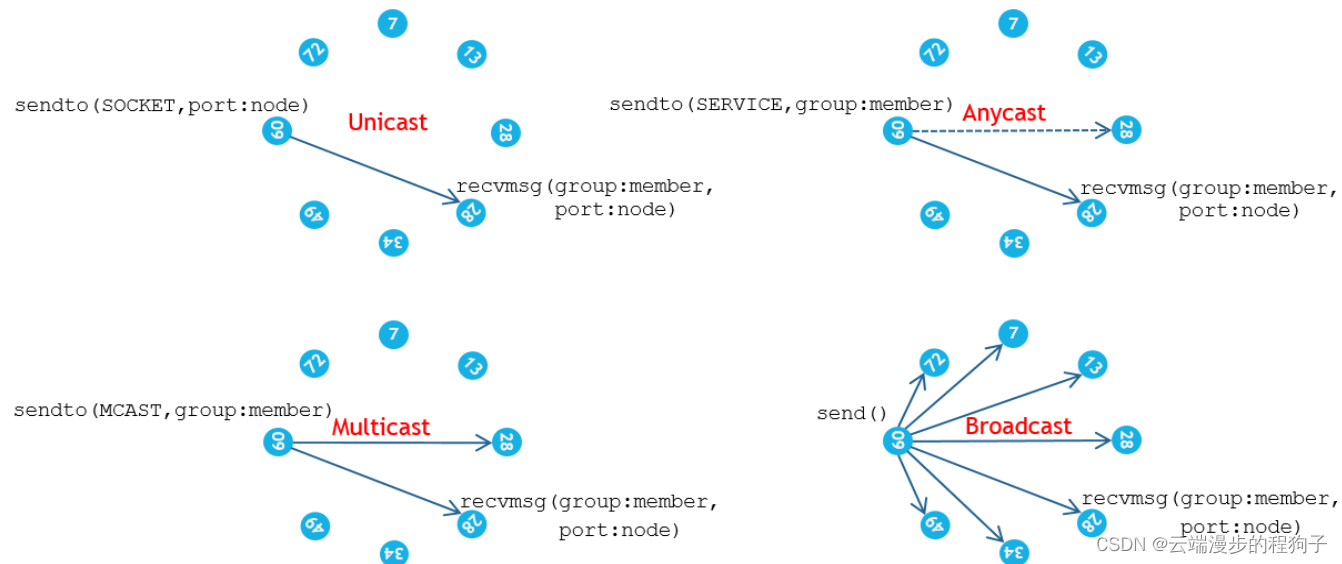
Within a group there are four different transmission modes available.
Unicast when the sender indicates a socket address as destination.
Anycast when the sender indicates a service address as destination. If there is more than one matching destination, one will be selected by round-robin, but also considering the destination’s load, which can be inferred from the destination’s advertised window.
Multicast when the sender indicates a service range as destination. If there is more than one matching destination, all of them will receive a copy of the sent message.
Broadcast when the sender uses the send() primitive with no destination address. All member sockets, irrespective of member instance number, receive a copy of the message.
Both broadcast and multicast leverage Ethernet broadcast/UDP multicast when possible and deemed favorable.
Delivery and sequence order is guaranteed, even between different transmission modes. Among other things, this implies that all messages must be subject to end-to-end flow control.
Messages will never be dropped because of destination buffer overflow.
Same mechanism covers all tranmsmission modes.
Point-to-point and point-to-multipoint: - “sliding window” algorithm.
Multipoint-to-point: - “coordinated sliding window” algorithm, unique for TIPC.
边栏推荐
- [applinking practical case] share in app pictures through applinking
- 6种单例模式的实现方式
- Oracle notes
- JSP webshell免杀——webshell免杀
- JSP webshell free -- the basis of JSP
- Indexer in C #
- Easyexcel, a concise, fast and memory saving excel processing tool
- Calculate the sum of sequences
- Is the account above changtou school safe?
- 从.bag文件中读取并保存.jpg图片和.pcd点云
猜你喜欢

From Read and save in bag file Jpg pictures and PCD point cloud
TIPC Service and Topology Tracking4
【AI应用】海康威视iVMS-4200软件安装
![Binary tree topic -- Luogu p3884 [jloi2009] binary tree problem (DFS for binary tree depth BFS for binary tree width Dijkstra for shortest path)](/img/c2/bb85b681af0f78b380b1d179c7ea49.png)
Binary tree topic -- Luogu p3884 [jloi2009] binary tree problem (DFS for binary tree depth BFS for binary tree width Dijkstra for shortest path)
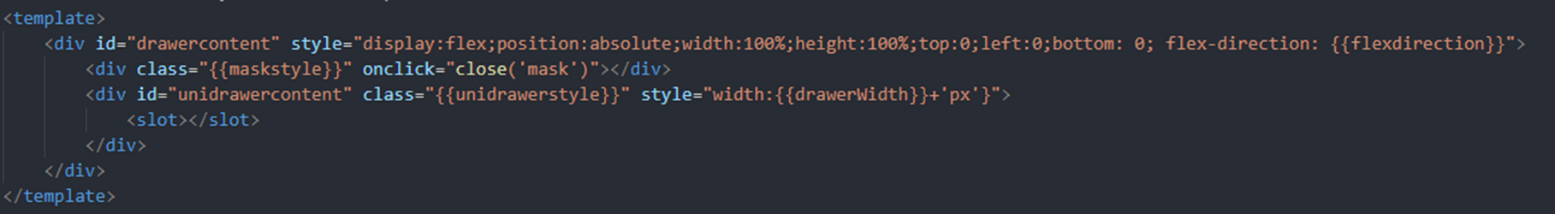
Implement custom drawer component in quick application

OpenMLDB Meetup No.4 会议纪要
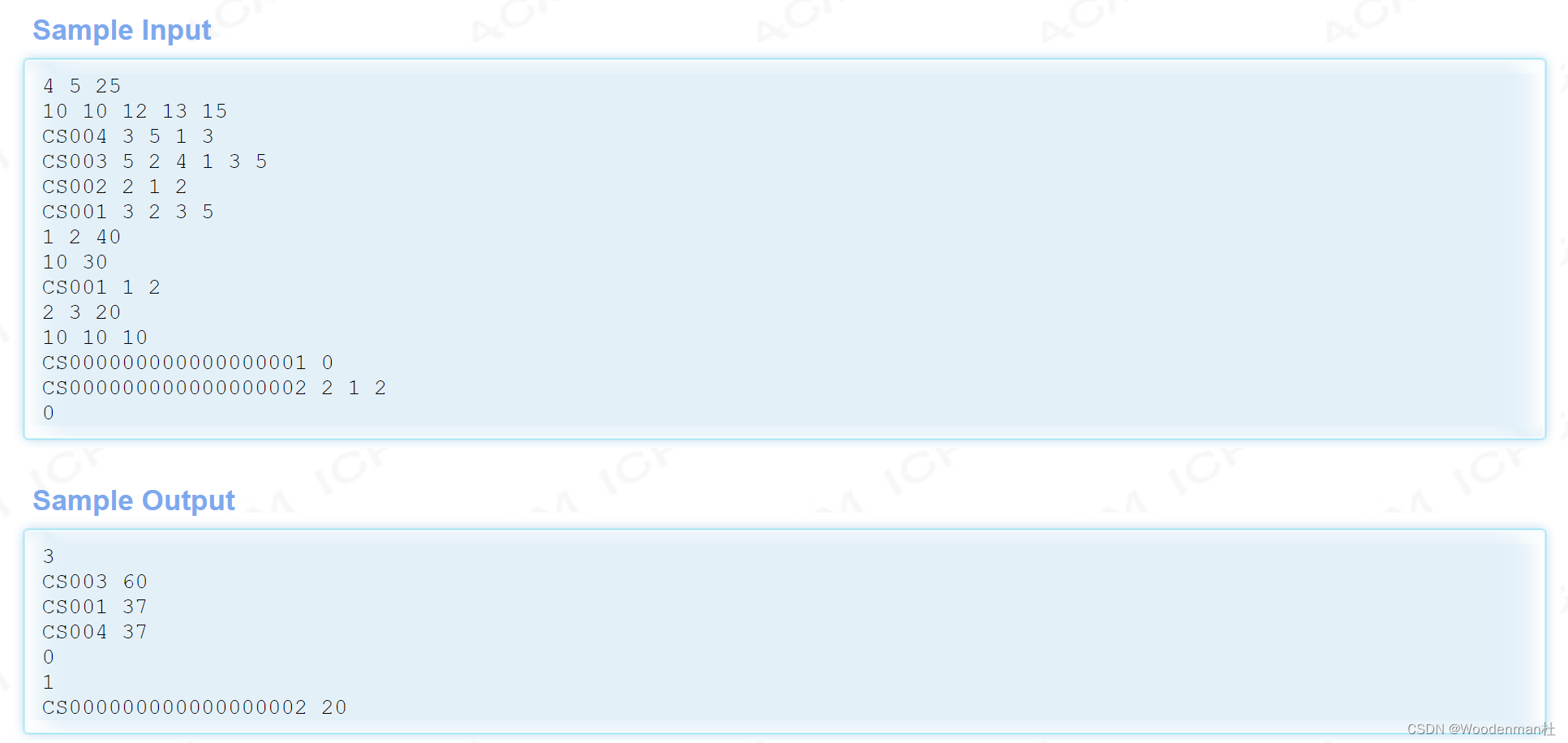
Hdu1236 ranking (structure Sorting)
QT学习日记8——资源文件添加
![2. Hacking lab script off [detailed writeup]](/img/f3/29745761cd5ad4df84c78ac904ea51.png)
2. Hacking lab script off [detailed writeup]

【深入浅出玩转FPGA学习4----漫谈状态机设计】
随机推荐
二叉树专题--AcWing 47. 二叉树中和为某一值的路径(前序遍历)
TIPC Getting Started6
二叉树专题--洛谷 P3884 [JLOI2009]二叉树问题(dfs求二叉树深度 bfs求二叉树宽度 dijkstra求最短路)
【深入浅出玩转FPGA学习3-----基本语法】
Special topic of binary tree -- acwing 19 The next node of the binary tree (find the successor of the node in the tree)
[quick application] win7 system cannot run and debug projects using Huawei ide
MySQL lethal serial question 3 -- are you familiar with MySQL locks?
洛谷 P3398 仓鼠找 sugar(树上倍增 lca 判断树中两条路径是否相交 结论)
【AppLinking实战案例】通过AppLinking分享应用内图片
Luogu p5536 [xr-3] core city (greed + tree DP looking for the center of the tree)
PCL extracts a subset from a point cloud
Matlab processing of distance measurement of experimental electron microscope
二叉树专题--【深基16.例7】普通二叉树(简化版)(multiset 求前驱 后继 哨兵法)
Static variables in static function
Dialogue Wu Gang: why do I believe in the rise of "big country brands"?
HDU1228 A + B(map映射)
如何使用IDE自动签名调试鸿蒙应用
Learn open62541 -- [66] UA_ Generation method of string
洛谷 P5536 【XR-3】核心城市(贪心 + 树形 dp 寻找树的中心)
【AGC】构建服务3-认证服务示例