当前位置:网站首页>Reading and understanding of eventbus source code
Reading and understanding of eventbus source code
2022-07-07 14:22:00 【LLAiden】
EventBus
Android Mainstream event delivery Library in , Simplify callbacks and thread operations in our code
EventBus introduce
implementation 'org.greenrobot:eventbus:3.2.0'
register
EventBus.getDefault().register(this);
Next, let's see how to register here
public static EventBus getDefault() {
EventBus instance = defaultInstance;
if (instance == null) {
synchronized (EventBus.class) {
instance = EventBus.defaultInstance;
if (instance == null) {
instance = EventBus.defaultInstance = new EventBus();
}
}
}
return instance;
}
The first is a single example of a standard double lock hungry man , Let's look at
regsiter()
public void register(Object subscriber) {
Class<?> subscriberClass = subscriber.getClass();
List<SubscriberMethod> subscriberMethods = subscriberMethodFinder.findSubscriberMethods(subscriberClass);
synchronized (this) {
for (SubscriberMethod subscriberMethod : subscriberMethods) {
subscribe(subscriber, subscriberMethod);
}
}
}
First of all to see
List<SubscriberMethod> subscriberMethods = subscriberMethodFinder.findSubscriberMethods(subscriberClass);
List<SubscriberMethod> findSubscriberMethods(Class<?> subscriberClass) {
List<SubscriberMethod> subscriberMethods = METHOD_CACHE.get(subscriberClass);
if (subscriberMethods != null) {
return subscriberMethods;
}
if (ignoreGeneratedIndex) {
subscriberMethods = findUsingReflection(subscriberClass);
} else {
subscriberMethods = findUsingInfo(subscriberClass);
}
if (subscriberMethods.isEmpty()) {
throw new EventBusException("Subscriber " + subscriberClass
+ " and its super classes have no public methods with the @Subscribe annotation");
} else {
// Use in this class Subscribe Annotated functions are added to the cache
METHOD_CACHE.put(subscriberClass, subscriberMethods);
return subscriberMethods;
}
}
If there is no cache, it will execute
subscriberMethods = findUsingInfo(subscriberClass);Let's move on
private List<SubscriberMethod> findUsingInfo(Class<?> subscriberClass) {
FindState findState = prepareFindState();
findState.initForSubscriber(subscriberClass);
// there findState.clazz It was passed in when we registered this
while (findState.clazz != null) {
findState.subscriberInfo = getSubscriberInfo(findState);
// Here for null Executive else Branch
if (findState.subscriberInfo != null) {
SubscriberMethod[] array = findState.subscriberInfo.getSubscriberMethods();
for (SubscriberMethod subscriberMethod : array) {
if (findState.checkAdd(subscriberMethod.method, subscriberMethod.eventType)) {
findState.subscriberMethods.add(subscriberMethod);
}
}
} else {
// Continue to look at the source code here
findUsingReflectionInSingleClass(findState);
}
findState.moveToSuperclass();
}
return getMethodsAndRelease(findState);
}
private void findUsingReflectionInSingleClass(FindState findState) {
Method[] methods;
try {
methods = findState.clazz.getDeclaredMethods();
} catch (Throwable th) {
methods = findState.clazz.getMethods();
findState.skipSuperClasses = true;
}
// Get the function in this class in the signature
for (Method method : methods) {
int modifiers = method.getModifiers();
if ((modifiers & Modifier.PUBLIC) != 0 && (modifiers & MODIFIERS_IGNORE) == 0) {
Class<?>[] parameterTypes = method.getParameterTypes();
if (parameterTypes.length == 1) {
// Check whether this function has Subscribe annotation
Subscribe subscribeAnnotation = method.getAnnotation(Subscribe.class);
if (subscribeAnnotation != null) {
// Get the parameters of this function class It's the event we deliver class
Class<?> eventType = parameterTypes[0];
if (findState.checkAdd(method, eventType)) {
// Get what we set threadMode
ThreadMode threadMode = subscribeAnnotation.threadMode();
// Use this class Subscribe Annotated functions are added subscriberMethods in
findState.subscriberMethods.add(new SubscriberMethod(method, eventType, threadMode,
subscribeAnnotation.priority(), subscribeAnnotation.sticky()));
}
}
}
}
}
}
It's over findSubscriberMethods() Let's keep looking subscribe() What have you done
private void subscribe(Object subscriber, SubscriberMethod subscriberMethod) {
Class<?> eventType = subscriberMethod.eventType;
// This object holds our subscription class and subscriber Annotated functions
Subscription newSubscription = new Subscription(subscriber, subscriberMethod);
CopyOnWriteArrayList<Subscription> subscriptions = subscriptionsByEventType.get(eventType);
if (subscriptions == null) {
subscriptions = new CopyOnWriteArrayList<>();
// Put this type of Event Add to this Map
subscriptionsByEventType.put(eventType, subscriptions);
} else {
if (subscriptions.contains(newSubscription)) {
throw new EventBusException("Subscriber " + subscriber.getClass() + " already registered to event "
+ eventType);
}
}
int size = subscriptions.size();
for (int i = 0; i <= size; i++) {
if (i == size || subscriberMethod.priority > subscriptions.get(i).subscriberMethod.priority) {
// This List In the above function, it has been stored in subscriptionsByEventType It's in
subscriptions.add(i, newSubscription);
break;
}
}
List<Class<?>> subscribedEvents = typesBySubscriber.get(subscriber);
if (subscribedEvents == null) {
subscribedEvents = new ArrayList<>();
// Which types of events this class focuses on are stored in typesBySubscriber
typesBySubscriber.put(subscriber, subscribedEvents);
}
subscribedEvents.add(eventType);
// Each registration will trigger a sticky Event Sending of
if (subscriberMethod.sticky) {
if (eventInheritance) {
// Existing sticky events of all subclasses of eventType have to be considered.
// Note: Iterating over all events may be inefficient with lots of sticky events,
// thus data structure should be changed to allow a more efficient lookup
// (e.g. an additional map storing sub classes of super classes: Class -> List<Class>).
Set<Map.Entry<Class<?>, Object>> entries = stickyEvents.entrySet();
for (Map.Entry<Class<?>, Object> entry : entries) {
Class<?> candidateEventType = entry.getKey();
if (eventType.isAssignableFrom(candidateEventType)) {
Object stickyEvent = entry.getValue();
checkPostStickyEventToSubscription(newSubscription, stickyEvent);
}
}
} else {
Object stickyEvent = stickyEvents.get(eventType);
checkPostStickyEventToSubscription(newSubscription, stickyEvent);
}
}
}
Come here register I have finished reading , This is actually getting it for use Subscribe Annotated functions and related information ( Thread mode , priority , Whether it is a sticky event )
Event sending
Let's continue to look at the sending of events and how they are called , Take a look first EventBus.getDefaule().post()
public void post(Object event) {
// First, get the thread status , Because the default threadMode yes ThreadMode.POSTING
PostingThreadState postingState = currentPostingThreadState.get();
List<Object> eventQueue = postingState.eventQueue;
eventQueue.add(event);
if (!postingState.isPosting) {
postingState.isMainThread = isMainThread();
postingState.isPosting = true;
if (postingState.canceled) {
throw new EventBusException("Internal error. Abort state was not reset");
}
try {
while (!eventQueue.isEmpty()) {
// Send this event , Add this to the front list
postSingleEvent(eventQueue.remove(0), postingState);
}
} finally {
postingState.isPosting = false;
postingState.isMainThread = false;
}
}
}
private void postSingleEvent(Object event, PostingThreadState postingState) throws Error {
Class<?> eventClass = event.getClass();
boolean subscriptionFound = false;
// Creating EventBus Whether this of the object is true Of
if (eventInheritance) {
// Here, the event class class as well as Object.class Save in eventTypes
List<Class<?>> eventTypes = lookupAllEventTypes(eventClass);
int countTypes = eventTypes.size();
for (int h = 0; h < countTypes; h++) {
Class<?> clazz = eventTypes.get(h);
subscriptionFound |= postSingleEventForEventType(event, postingState, clazz);
}
} else {
subscriptionFound = postSingleEventForEventType(event, postingState, eventClass);
}
if (!subscriptionFound) {
if (logNoSubscriberMessages) {
logger.log(Level.FINE, "No subscribers registered for event " + eventClass);
}
if (sendNoSubscriberEvent && eventClass != NoSubscriberEvent.class &&
eventClass != SubscriberExceptionEvent.class) {
post(new NoSubscriberEvent(this, event));
}
}
}
private static List<Class<?>> lookupAllEventTypes(Class<?> eventClass) {
synchronized (eventTypesCache) {
// Get the... In the cache first
List<Class<?>> eventTypes = eventTypesCache.get(eventClass);
if (eventTypes == null) {
eventTypes = new ArrayList<>();
Class<?> clazz = eventClass;
while (clazz != null) {
// Our event class
eventTypes.add(clazz);
// This function will not execute internally without inheriting the interface
addInterfaces(eventTypes, clazz.getInterfaces());
// The second loop will add the parent of the event class to this list
clazz = clazz.getSuperclass();
}
// Add to cache , Go down and get it directly from the cache , It's better
eventTypesCache.put(eventClass, eventTypes);
}
// Now there are events class,Object.class, Because all classes implicitly inherit Object
return eventTypes;
}
}
private boolean postSingleEventForEventType(Object event, PostingThreadState postingState, Class<?> eventClass) {
CopyOnWriteArrayList<Subscription> subscriptions;
synchronized (this) {
// stay register Called subscribe The function takes eventClass Events of type are stored in subscriptionsByEventType
// All this here if you register this type Event,subscriptions Not for null
// For details of this data storage, please see subscribe()
subscriptions = subscriptionsByEventType.get(eventClass);
}
if (subscriptions != null && !subscriptions.isEmpty()) {
for (Subscription subscription : subscriptions) {
postingState.event = event;
postingState.subscription = subscription;
boolean aborted;
try {
// Here is the sending of events , Continue to look at the source code of this function
postToSubscription(subscription, event, postingState.isMainThread);
aborted = postingState.canceled;
} finally {
postingState.event = null;
postingState.subscription = null;
postingState.canceled = false;
}
if (aborted) {
break;
}
}
return true;
}
return false;
}
private void postToSubscription(Subscription subscription, Object event, boolean isMainThread) {
switch (subscription.subscriberMethod.threadMode) {
//threadMode The default is POSTING
case POSTING:
invokeSubscriber(subscription, event);
break;
case MAIN:
//Android Main thread execution
if (isMainThread) {
invokeSubscriber(subscription, event);
} else {
//mainThreadPoster When it was created, it was passed into Looper.getMainLooper()
// And use this Looper Created Handler object , So here is the use of Handler The mechanism is executed in the main thread
mainThreadPoster.enqueue(subscription, event);
}
break;
case MAIN_ORDERED:
// Execute in the main thread first ,mainThreadPoster==null Execute in the sending thread
if (mainThreadPoster != null) {
mainThreadPoster.enqueue(subscription, event);
} else {
// temporary: technically not correct as poster not decoupled from subscriber
invokeSubscriber(subscription, event);
}
break;
case BACKGROUND:
// Execute... In the process pool
if (isMainThread) {
backgroundPoster.enqueue(subscription, event);
} else {
invokeSubscriber(subscription, event);
}
break;
case ASYNC:
// Asynchronous execution , Like and BACKGROUND There's no difference
asyncPoster.enqueue(subscription, event);
break;
default:
throw new IllegalStateException("Unknown thread mode: " + subscription.subscriberMethod.threadMode);
}
}
// Here is the function to be executed , Use reflection to execute
void invokeSubscriber(Subscription subscription, Object event) {
try {
subscription.subscriberMethod.method.invoke(subscription.subscriber, event);
} catch (InvocationTargetException e) {
handleSubscriberException(subscription, event, e.getCause());
} catch (IllegalAccessException e) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Unexpected exception", e);
}
}
clazz = clazz.getSuperclass();It's worth noting , That is to say, we write a parameter of type Object Function of , And use Subscribe Annotation, then it can receive all our events
summary
- stay EventBus Instantiation time , Use the standard double lock mechanism to realize the singleton
- In execution
register()Function EventBus You will find that the modifier under this class is public, The number of parameters is 1, And use Subscribe Annotated functions , stay map For storage register()The function also sends sticky events , This is why we send sticky events first , Later, you can also receive the reason for the event by subscribing- stay
post()We will first find the event type in Map The corresponding function in , And use reflection to execute this function - EventBus Use in Handler Thread scheduling
边栏推荐
- [network security] SQL injection syntax summary
- c#利用 TCP 协议建立连接
- Mrs offline data analysis: process OBS data through Flink job
- 数据流图,数据字典
- PERT图(工程网络图)
- LeetCode 648. 单词替换
- Is the compass stock software reliable? Is it safe to trade stocks?
- call undefined function openssl_ cipher_ iv_ length
- 接口自动化测试-接口间数据依赖问题解决
- Laravel5 call to undefined function OpenSSL cipher IV length() error php7 failed to open OpenSSL extension
猜你喜欢
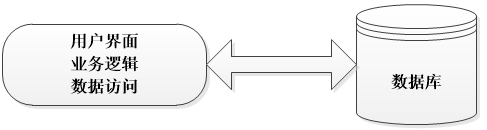
带你掌握三层架构(建议收藏)
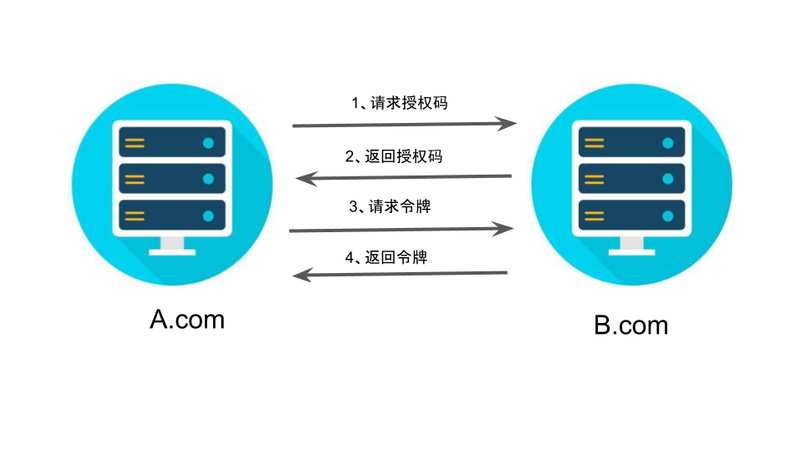
OAuth 2.0 + JWT protect API security

UML 状态图

Navigation — 这么好用的导航框架你确定不来看看?

Parsing of XML files
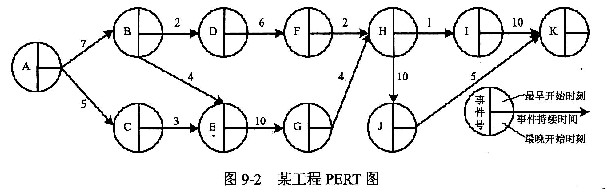
Pert diagram (engineering network diagram)
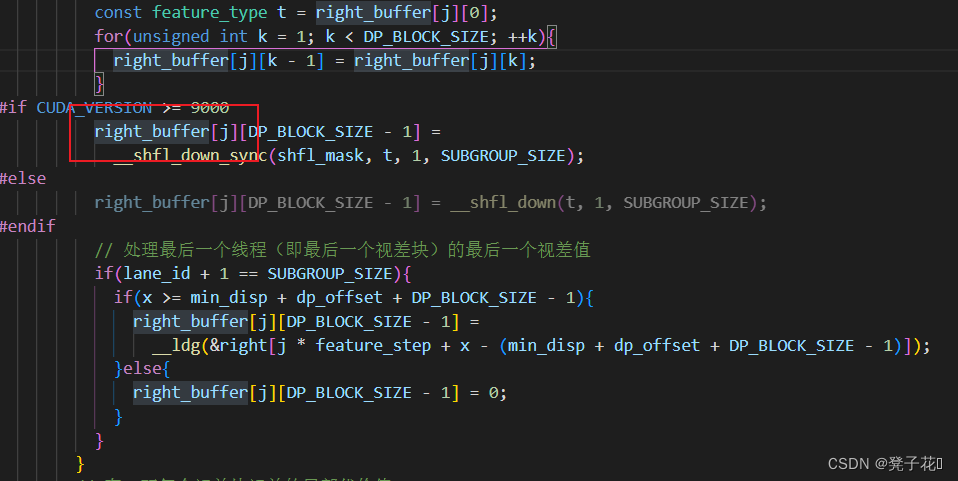
libSGM的horizontal_path_aggregation程序解读
gvim【三】【_vimrc配置】
Assign a dynamic value to the background color of DataGrid through ivalueconverter
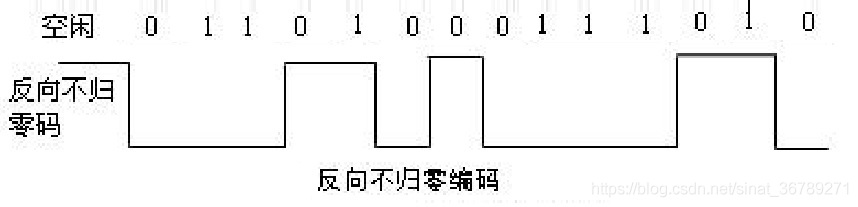
Reverse non return to zero code, Manchester code and differential Manchester code of common digital signal coding
随机推荐
The difference between memory overflow and memory leak
Interface automation test - solution of data dependency between interfaces
Excellent open source system recommendation of ThinkPHP framework
Excuse me, why is it that there are no consumption messages in redis and they are all piled up in redis? Cerely is used.
Million data document access of course design
使用day.js让时间 (显示为几分钟前 几小时前 几天前 几个月前 )
libSGM的horizontal_path_aggregation程序解读
请问,PTS对数据库压测有好方案么?
Clickhouse (03) how to install and deploy Clickhouse
Use day JS let time (displayed as minutes, hours, days, months, and so on)
PERT图(工程网络图)
Lavarel之环境配置 .env
Attribute keywords aliases, calculated, cardinality, ClientName
FCOS3D label assignment
参数关键字Final,Flags,Internal,映射关键字Internal
请问,我kafka 3个分区,flinksql 任务中 写了 join操作,,我怎么单独给join
UML sequence diagram (sequence diagram)
C # use TCP protocol to establish connection
mysql ”Invalid use of null value“ 解决方法
Demis Hassabis谈AlphaFold未来目标