当前位置:网站首页>User login [next]
User login [next]
2022-06-12 05:54:00 【Snow flies fast】
Back end API Processing flow

build https service
First, you need to https Copy the certificate to Node In the project , Then add the following code :
const fs = require('fs')
const https = require('https')
const privateKey = fs.readFileSync('./https/book.llmysnow.top.key', 'utf8')
const pem = fs.readFileSync('./https/book.llmysnow.top.pem', 'utf8')
const credentials = {
key: privateKey,
cert: pem,
}
const httpsServer = https.createServer(credentials, app)
httpsServer.listen(18082, () => {
console.log('running on https://127.0.0.1:%s', 18082)
})
establish /user/login API
stay router/user.js Add the following code to :
router.post('/login', (req, res) => {
res.json({
code: 0,
msg: ' Login successful ',
})
})
Here I use Postman Tested interface , You can also use
curl http://127.0.0.1:3003/user/login -X POST -d "username=ll&password=123"Shorthand for :
curl http://127.0.0.1:3003/user/login -d "username=ll&password=123"
Here we go through req.body obtain POST Request parameters failed , We need to pass body-parser Middleware to solve this problem , The new version express Built in POST Argument parsing
app.use(express.urlencoded({
extended: true }))
app.use(express.json())
app.use('/', router)
Nodejs Advanced :Express Common middleware body-parser For the
body-parser The main implementation is as follows :
- Handle different types of request bodies , such as
text、json、urlencodedetc. , The format of the corresponding message body is different - Dealing with different codes , such as
utf8、gbketc. - Dealing with different types of compression : such as
gzip、deflareetc. - Other borders 、 Exception handling
Return to the front end and use the login button to request the login interface , Found that the console reported an error :
Access to XMLHttpRequest at 'http://127.0.0.1:3003/user/login' from origin 'http://localhost:9527' has been blocked by CORS policy:
Response to preflight request doesn't pass access control check: No 'Access-Control-Allow-Origin' header is present on the requested resource.
Because the front end is deployed in http://localhost:9527 , The backend is deployed in http://localhost:3003, So it leads to a cross domain error , We need to be in Node Add cross domain Middleware in cors
npm i cors
You can successfully request again , Here we are Network It will be found that it was launched twice http request , This is because cross domain triggers , So we'll start with OPTIONS request , Judge whether the server allows cross domain requests , If allowed, the request can actually be made
app.use(cors())
Response result encapsulation
stay /user/login The return value we see is :
res.json({
code: 0,
msg: ' Login successful '
})
Then we will define the error return value , But if each interface writes the above code, it will be very redundant , And it's not easy to maintain . To solve this problem , We create a Result Class to solve this problem
const {
CODE_ERROR, CODE_SUCCESS } = require('../utils/constant')
class Result {
constructor(data, msg = ' Successful operation ', options) {
this.data = null
if (arguments.length === 0) {
this.msg = ' Successful operation '
} else if (arguments.length === 1) {
this.msg = data
} else {
this.data = data
this.msg = msg
if (options) {
this.options = options
}
}
}
createResult() {
if (!this.code) {
this.code = CODE_SUCCESS
}
let base = {
code: this.code,
msg: this.msg,
}
if (this.data) {
base.data = this.data
}
if (this.options) {
base = {
...base, ...this.options }
}
console.log(base)
return base
}
json(res) {
res.json(this.createResult())
}
success(res) {
this.code = CODE_SUCCESS
this.json(res)
}
fail(res) {
this.code = CODE_ERROR
this.json(res)
}
}
module.exports = Result
We also need to create /utils/constant.js:
module.exports = {
CODE_ERROR: -1,
CODE_SUCCESS: 0,
DEBUG: false
}
Result Used ES6 Of Class, How to use it is as follows :
// When the call succeeds
new Result().success(res)
new Result(' Login successful ').success(res)
// When the call succeeds , Include parameters
new Result({
token }, ' Login successful ').success(res)
// When the call fails
new Result(' The user name or password does not exist ').fail(res)
With Result After the class , We can log in API Change it to :
router.post('/login', (req, res) => {
const {
username, password } = req.body
if (username === 'admin' && password === '123456') {
new Result(' Login successful ').success(res)
} else {
new Result(' Login failed ').fail(res)
}
})
Log in to the user database to query
After the response process is encapsulated , We need to query the user information in the database to verify whether the user name and password are accurate

install mysql library :
npm i mysql
establish db Catalog , Create two files index.js and config.js, stay config.js Add the following code to :
- Because my computer has many mysql, So I need to specify the port number , The default is 3306
module.exports = {
host: '127.0.0.1',
user: 'root',
password: 'root',
database: 'book',
port: 3308
}
Connect to database :
const mysql = require('mysql')
const config = require('./config')
function connect() {
return mysql.createConnection({
host: config.host,
user: config.user,
password: config.password,
database: config.database,
port: config.port,
multipleStatements: true,
})
}
When querying, call connection Object's query Method
- Be careful
connAfter the object is used, you need to call end Shut down , Otherwise, it will cause memory leakage
function querySql(sql) {
const conn = connect()
DEBUG && console.log(sql)
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
try {
conn.query(sql, (err, results) => {
if (err) {
DEBUG && console.log(' The query fails , reason :' + JSON.stringify(err))
reject(err)
} else {
DEBUG && console.log(' The query is successful ', JSON.stringify(results))
resolve(results)
}
})
} catch (err) {
reject(err)
} finally {
conn.end()
}
})
}
You can put sql The statement is written directly in router/user.js, A better approach is to encapsulate a layer sevice, Used to coordinate business logic and database queries , establish service/user.js
The password uses MD5 + SALT encryption
Of course, there are many other encryption methods , You can read my article : Front and rear ends JS Common encryption methods ( Asymmetric encryption 、 Symmetric encryption )
npm i cryptoCreated in
utils/index.js, Add the following :const crypto = require('crypto') function md5(s) { return crypto.createHash('md5').update(String(s)).digest('hex') } module.exports = { md5 }
utils/constant.js To add the following :
module.exports = {
// ...
PWD_SALT: 'admin_imooc_node'
}
Enter the correct user name and password again admin admin, The query is successful
const {
PWD_SALT } = require('../utils/constant')
router.post('/login', (req, res) => {
let {
username, password } = req.body
password = md5(`${
password}${
PWD_SALT}`)
login(username, password).then(user => {
console.log(user)
if (!user || user.length === 0) {
new Result(' Login failed ').fail(res)
} else {
new Result(' Login successful ').success(res)
}
})
})
express-validator Form validation
- It is a powerful form validator , It is
validator.jsMiddleware
Use express-validator Can be simplified POST Requested parameter validation , How to use it is as follows :
- install
npm i express-validator
- verification
router.post(
'/login',
[
body('username').isString().withMessage(' User name must be character '),
body('password').isString().withMessage(' Password must be characters '),
],
(req, res, next) => {
const err = validationResult(req)
if (!err.isEmpty()) {
const [{
msg }] = err.errors
next(boom.badRequest(msg))
} else {
let {
username, password } = req.body
password = md5(`${
password}${
PWD_SALT}`)
login(username, password).then(user => {
console.log(user)
if (!user || user.length === 0) {
new Result(' Login failed ').fail(res)
} else {
new Result(' Login successful ').success(res)
}
})
}
}
)
express-validator Using skills :
- stay
router.postThe second parameter of the method , UsebodyMethod to determine the parameter type , And specify the error prompt - Use
const err = validationResult(req)Get error messages ,err.errorsIs an array , Contains all error messages , Iferr.errorsIf it is empty, the verification is successful , No parameter error - If we find an error, we can use
next(boom.badRequest(msg))Throw an exception , Give it to our custom exception handling method for handling
JWT
Token
Token The essence is string , Used in the request with the request header , Verify whether the request is legal and determine the user identity
Token、Session、Cookie The difference between
SessionSave on the server , Used when connecting the client and the server , Save user information temporarily , When the user releases the connection ,SessionWill be releasedCookieSave on client , When the client initiates the request ,CookieWill be attached to http header in , It is provided to the server to identify the user's identityTokenWhen requested, it is used to verify whether the user has access to the interface
Other differences , You can refer to my article : HTTP Network layer performance optimization
Token purpose
Block invalid requests , Reduce server processing pressure
Achieve third party API to grant authorization , There is no need to enter user name and password authentication every time
such as : WeChat 、 Microblog third-party authorized login uses Token Realization
Identity verification , prevent CSRF attack
JWT
JSON Web Token(JWT) Is a very popular cross domain authentication solution .jwt Official website

above Encoded Period JWT character string , It is broken down into three parts :
HEADER: ALGORITHM & TOKEN TYPEheaderIs to describeJWTMetadataJSONobject :- alg: Represent encryption algorithm ,
HS256yesHMAC SHA256Abbreviation - type:
Tokentype
{ "alg": "HS256", "typ": "JWT" }- alg: Represent encryption algorithm ,
PAYLOAD: DATApayloadyesJWTThe main content of , Also aJSONcharacter string , Contains data that needs to be passed , Be carefulpayloadSome do not store private data , Prevent information leakage{ "sub": "1234567890", "name": "John Doe", "iat": 1516239022 }VERIFY SIGNATUREJWTThe signature part is the string generated after encrypting the above two parts of data , adoptheaderThe specified algorithm generates an encrypted string , To ensure that data is not tampered withA secret key is required to generate a signature , The secret key is only saved on the server , Cannot expose to users , It's a string , We are free to set
When generating a signature, you need to generate a signature according to
headerThe signature algorithm specified in , And according to the formula below , theheaderandpayloadThe data fromBASE64After encryption, adopt.Connect , And then through the secret keySHA256encryption , By adding the secret key , Therefore, the generated string cannot be decoded and tampered with , Only on the server can restoreHMACSHA256( base64UrlEncode(header) + "." + base64UrlEncode(payload), your-256-bit-secret )
Generate JWT Token
install
npm i jsonwebtoken
Use
const jwt = require('jsonwebtoken')
const {
PRIVATE_KEY, JWT_EXPIRED } = require('../utils/constant')
login(username, password).then(user => {
if (!user || user.length === 0) {
new Result(' Login failed ').fail(res)
} else {
const token = jwt.sign({
username }, PRIVATE_KEY, {
expiresIn: JWT_EXPIRED })
new Result({
token }, ' Login successful ').success(res)
}
})
utils/constant.js, Here we need to define jwt Private key and expiration time of , The expiration time should not be too short , It shouldn't be too long , Control according to business scenarios
module.exports = {
// ...
PRIVATE_KEY: 'admin_imooc_node_private_key',
JWT_EXPIRED: 60 * 60, // token Failure time 1 Hours
}
The front end returns the following results :
{
code: 0,
msg: ' Login successful ',
data: {
token:
'eyJhbGciOiJIUzI1NiIsInR5cCI6IkpXVCJ9.eyJ1c2VybmFtZSI6ImFkbWluIiwiaWF0IjoxNjM3MDMwNjcyLCJleHAiOjE2MzcwMzQyNzJ9.Rc6KMMjs025lT4aVMMfk2bUcJnlSwVGBWaDQm-hVTY8',
},
}
We can Token stay jwt Official website To verify , You can get the following results :
- Mouse over
iatandexpYou can see the generation time and expiration time on the
{
"username": "admin",
"iat": 1637030672,
"exp": 1637034272
}
You can see username Correctly parsed , explain Token Generate successfully
JWT authentication
The main function : Check whether all routes have expired Token, If it does not expire, it will be verified as passing
install
npm i express-jwt
establish router/jwt.js
const expressJwt = require('express-jwt')
const {
PRIVATE_KEY } = require('../utils/constant')
const jwtAuth = expressJwt({
secret: PRIVATE_KEY,
// Set to false No verification , Visitors can visit
credentialsRequired: true,
}).unless({
// Set up jwt Certification white list
path: ['/', '/user/login'],
})
module.exports = jwtAuth
start-up Node You will find an error :
if (!options.algorithms) throw new Error('algorithms should be set');Error: algorithms should be set2020.7.7 after , Installed
express-jwtThe module will default to 6 The latest version of , UpdatedjwtYou need to addalgorithmsattribute , Setting thejwtAlgorithm
adopt express-jwt Middleware to verify , adopt unless Set the whitelist , And use... Before all requests
const expressJwt = require('express-jwt')
const {
PRIVATE_KEY } = require('../utils/constant')
const jwtAuth = expressJwt({
secret: PRIVATE_KEY,
algorithms: ['HS256'],
// Set to false No verification , Visitors can visit
credentialsRequired: true,
}).unless({
// Set up jwt Certification white list
path: ['/', '/user/login'],
})
module.exports = jwtAuth
stay router/index.js Using middleware
- Be careful : Need to be used before all routes
const jwtAuth = require('./jwt')
router.use(jwtAuth)
Restart , Click the login backend to return to the following contents

In order to make Token Overdue error reporting is different from other errors , stay utils/constant.js
module.exports = {
// ...
CODE_TOKEN_EXPIRED: -2
}
Modify custom exception
modify
/model/Result.jsjwtError(res) { this.code = CODE_TOKEN_EXPIRED this.json(res) }Yes
UnauthorizedErrorTreat separately (TokenValidation failed ), And for other casesResultMethod to simplify
router.use((err, req, res, next) => {
if (err.name && err.name === 'UnauthorizedError') {
const {
status = 401, message } = err
new Result(null, 'Token Validation failed ', {
error: status,
errorMsg: message,
}).jwtError(res.status(status))
} else {
const msg = (err && err.message) || ' System error '
const statusCode = (err.output && err.output.statusCode) || 500
const errorMsg = (err.output && err.output.payload && err.output.payload.error) || err.message
new Result(null, msg, {
error: statusCode,
errorMsg,
}).fail(res.status(statusCode))
}
})
Restart , Click the login backend to return to the following contents

Front-end processing JWT Token
Front end login request modification , modify src/utils/request.js Response interceptors in
- Yes
errorObject to deconstruct , Take theresponse.data.msg, And prompt it
service.interceptors.response.use(
response => {
const res = response.data
if (res.code !== 0) {
const errMsg = res.msg || ' request was aborted '
Message({
message: errMsg,
type: 'error',
duration: 5 * 1000
})
if (res.code === 2) {
MessageBox.confirm('Token Has lapsed , Please login again ', ' Confirm logout ', {
confirmButtonText: ' Log back in ',
cancelButtonText: ' Cancel ',
type: 'warning'
}).then(() => {
store.dispatch('user/resetToken').then(() => {
location.reload()
})
})
}
return Promise.reject(new Error(errMsg))
} else {
return res
}
},
error => {
console.log({
error }) // for debug
const {
msg } = error.response.data
Message({
message: msg || ' request was aborted ',
type: 'error',
duration: 5 * 1000
})
return Promise.reject(error)
}
)
Add a route to the backend jwt After certification , Ask again /user/info Will throw out 401 error , This is because the front end does not pass a reasonable Token As a result of , You need to request the headers Make changes
- modify
headersIn Chinese, it meansAuthorization - stay
getToken()Add one beforeBearer( There is a space after )
service.interceptors.request.use(
config => {
if (store.getters.token) {
config.headers['Authorization'] = `Bearer ${
getToken()}`
}
return config
},
error => {
return Promise.reject(error)
}
)
Remove the front end /user/info Passed in on request Token, Because we've gone from Token In the middle of , modify src/api/user.js
export function getInfo() {
return request({
url: '/user/info',
method: 'get'
})
}

User query /user/info
There is only one query user ,querySql The query is for multiple people , It returns an array , Need to add one queryOne Method
- stay
/db/index.jsAdd
function queryOne(sql) {
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
querySql(sql)
.then(results => {
if (results && results.length > 0) {
resolve(results[0])
} else {
resolve(null)
}
})
.catch(err => {
reject(err)
})
})
}
- stay
/services/user.jsAdd :
function findUser(username) {
const sql = `select * from admin_user where username='${
username}'`
return queryOne(sql)
}
request /user/info The interface will get the following :
- here
passwordFor sensitive fields , It needs to be deleted

The revised code is as follows ( Of course, you can also get user Deal with it later , But it's not recommended ):
function findUser(username) {
return queryOne(`select id, username, nickname, role, avatar from admin_user where username='${
username}'`)
}
Front-end HTTP header There is Token , adopt Token obtain username You need to be right about jwt token To analyze , stay utils/index.js To add the following
const jwt = require('jsonwebtoken')
const {
PRIVATE_KEY } = require('./constant')
function decoded(req) {
let token = req.get('Authorization')
if (token.indexOf('Bearer') >= 0) {
token = token.replace('Bearer ', '')
}
return jwt.verify(token, PRIVATE_KEY)
}
modify router/user.js
- Log in to the front end again , You can log in
router.get('/info', (req, res) => {
const decode = decoded(req)
if (decode && decode.username) {
findUser(decode.username).then(user => {
if (user) {
user.roles = [user.role]
new Result(user, ' The user information query is successful ').success(res)
} else {
new Result(user, ' User information query failed ').fail(res)
}
})
}else{
new Result(' User information query failed ').fail(res)
}
})
logout Method
- modify
src/store/modules/user.js
logout({
commit, state, dispatch }) {
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
try {
commit('SET_TOKEN', '')
commit('SET_ROLES', [])
removeToken()
resetRouter()
dispatch('tagsView/delAllViews', null, {
root: true })
resolve()
} catch (e) {
reject(e)
}
})
}
RefreshToken
scene : Authorization to third parties is required APP
Usually we need to add another one RefreshToken Of API, The API The use of is based on the existing Token Get username , And then you generate a new one Token, The purpose of this is to prevent Token Log out after expiration , therefore APP Generally, it will be refreshed once when it is opened Token
边栏推荐
- nRF52832自定义服务与特性
- 软件项目架构简单总结
- How Wireshark decrypts WiFi data packets
- [speech] how to customize ring back tone according to different countries
- AddUser add user and mount hard disk
- Chapter 8 - structure
- Introduction to Internet Protocol
- Quickly master makefile file writing
- [JS knowledge] easily understand JS anti shake and throttling
- Research Report on water sports shoes industry - market status analysis and development prospect forecast
猜你喜欢

A month's worth of DDD will help you master it

Win10 desktop unlimited refresh

Wireshark filter rule

Chapter 8 - structure

IO to IO multiplexing from traditional network

肝了一个月的 DDD,一文带你掌握

beginning一款非常优秀的emlog主题v3.1,支持Emlog Pro
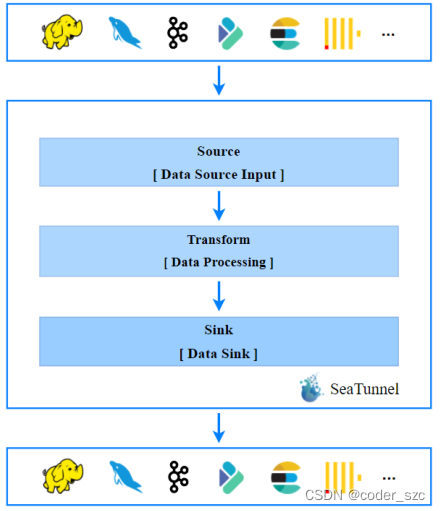
Data integration framework seatunnel learning notes

Redis memory obsolescence strategy

数据集成框架SeaTunnel学习笔记
随机推荐
The relation between virtual function and pure virtual function
Webrtc AEC process analysis
How Wireshark decrypts WiFi data packets
[Yu Yue education] basic reference materials of accounting of Nanjing Normal University
Stack and queue classic interview questions
C语言-数组的定义方式
How to split a row of data into multiple rows in Informix database
Data integration framework seatunnel learning notes
网络加速谁更猛?CDN领域再现新王者
Research Report on market supply and demand and strategy of China's digital camera lens industry
Golang idea configures the agent to improve the speed of packages downloaded by go get
MySQL master-slave, 6 minutes to master
json-c常用API
XML参数架构,同一MTK SW版本兼容两套不同的音频参数
从传统网络IO 到 IO多路复用
Nrf52832 -- official routine ble_ app_ UART adds the LED feature to enable the computer UART and mobile app to control the LED on and off of the development board
GRP development: four communication modes of GRP
BlockingQueue interface introduction
Heap classical problem
Halcon 用点来拟合平面