当前位置:网站首页>UVM: transaction level modeling (TLM) 1.0 communication standard
UVM: transaction level modeling (TLM) 1.0 communication standard
2022-06-12 00:06:00 【Starry and】
Catalog
For chip design , The whole chip design process involves streaming 、 High cost for hardware testing, etc 、 A time-consuming process , Unlike software development, it is easier to update iteratively 、 Modify and test , therefore IC Development uncertainty is high .
For the above problems , System prototype and IC Verification of the two parts is critical .
System prototype Ability to simulate hardware behavior , Commonly used SystemC To achieve .IC The verification is through SystemVerilog(SV) and UVM Verification methodology to build software test platform , To verify the design RTL Code .
So if SV The built verification platform needs to be borrowed SystemC The prototype of the system , We need a set of communication standards to realize cross language component communication . So transaction level modeling (Transaction Level Modeling, TLM)1.0 Communication standards have been widely used .TLM The biggest feature is that it does not depend on the time span , Seamless component communication without clock driver .
besides , If only SV and UVM Built verification platform , Compared with SV in mailbox Implement thread communication ,TLM1.0 It also has advantages :
● TLM1.0 With the help of Analysis Port realizes one to many broadcast communication .
● meanwhile SV Use mailbox Communication also has the problem of cross level direct communication , and TLM1.0 Loanable export Ports realize layer by layer positioning and connection , There will be no cross - level connectivity problem .
● TLM1.0 More closed , When two component After establishing communication , This communication does not allow other component Participate in .
● initiator Execute data flow methods and target The execution data flow methods are independent of each other (initiator Just call put、get Can be ,target Just need to achieve put、get The method will do ), and SV Must rely on media mailbox
This article talks about TLM1.0
1. Basic concepts
For the verification platform , Communication between components is very important , It's about business (transaction, trans) The transmission of . for example sequencer And driver、monitor And scoreboard、monitor And coverage model.
The communication of these components can use TLM standard , stay UVM There are also corresponding objects and methods in .
TLM Communication is based on the initiation and response of component requests .
Be careful TLM It only applies to component Connection between
initiator And target
This is for components .
Initiate a communication request request The components of are initiator, Respond to request The components of are target.
Be careful Sponsored request It is a communication request , Does not represent a request to obtain transaction. in other words initiator It may be a request to send a transaction , It may also be a request to get a transaction , But it must be initiator First initiated communication request .
1.1. port
Represents the communication interface of the component , Port connection is required for communication .
Here are the elements that make up the port .
Obstructive :blocking And nonblocking
That's easy to understand , Blocking and non blocking .
● blocking: If initiator Port of request Not responded , Will be waiting for a response , Block up .
Blocking will always consume time , So the way to block ports is task type
● nonblocking: If initiator Port of request Not responded , Can return value and continue execution , It won't block .
Non blocking ports do not consume time , Therefore, the methods that the port can call are function type
Data flow :put、get 、peek And transport
Express initiator and target Between trans flow .
● put:initiator requirement towards target send out trans
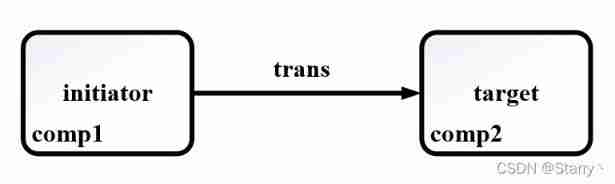
● get:initiator requirement towards target Ask for trans
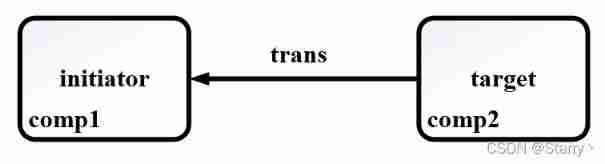
● peek:initiator requirement towards target Ask for trans Copy
● transport:initiator requirement First direction target send out trans, Again to target Ask for trans, One time action .

control flow :port 、export And imp
From initiator towards target Sponsored request Transmission direction .
● port: Express request The sender of .initiator The port in is often port

● export: Express request Transfer Party of . stay Initiator and target The m-server port of is usually export
![]()
● imp: namely import, Express request The recipient of .target The port in is often imp

Once again ,request Direction is about control flow ,trans Direction is data flow , Unequivalence !!!
TLM Establishment and call of communication
With the above elements , It can be based on uvm_ Obstructive _ Data flow _ control flow Combined into port classes , For example, some port classes uvm_blocking_put_port、uvm_nonblocking_get_imp wait .
Communication can be established through the port :
● Definition TLM The type of data transmitted trans
● determine TLM communication initiator component and target component, And in initiator Exemplification port port 、 stay target Instantiate the same type of imp port 、 Instantiate the same type of... At the middle level export port
● stay target The method of realizing the data flow of the port
● stay initiator and target The upper , stay connect_phase Use connect Method to establish a connection
After the above steps, the communication between ports is established , after initiator You can go to run_phase Call the corresponding data flow method , Be careful initiator The data flow method called is in target Data flow method implemented in !!
That is to say ,initiator Call the data flow method to target The effect of , Depending on target How to implement this method
The following is a specific introduction to the above contents
2. One (port) One on one (imp) One way data flow Port communication
each port Only to one imp signal communication , Every imp Accept only one port Communication for , And the data flow is unidirectional .
All communication ports are shown in the following table :
| Data flow | control flow | Obstructive | Composite port class | Single port class | Method prototypes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| put | port | blocking | uvm_put_port#(T) | uvm_blocking_put_port #(T) | task put(T t) |
| nonblocking | uvm_nonblocking_put_port#(T) | function bit try_put(T t) And function bit can_put() | |||
| export | blocking | uvm_put_export#(T) | uvm_blocking_put_export#(T) | task put(T t) | |
| nonblocking | uvm_nonblocking_put_export#(T) | function bit try_put(T t) And function bit can_put() | |||
| imp | blocking | uvm_put_imp#(T, IMP) | uvm_blocking_put_imp#(T, IMP) | task put(T t) | |
| nonblocking | uvm_nonblocking_put_imp#(T, IMP) | function bit try_put(T t) And function bit can_put() |
| Data flow | control flow | Obstructive | Composite port class | Single port class | Data flow method |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| get | port | blocking | uvm_get_port#(T) | uvm_blocking_get_port#(T) | task get(output T t) |
| nonblocking | uvm_nonblocking_get_port#(T) | function bit try_get(output T t) And function bit can_get() | |||
| export | blocking | uvm_get_export#(T) | uvm_blocking_get_export#(T) | task get(output T t) | |
| nonblocking | uvm_nonblocking_get_export#(T) | function bit try_get(output T t) And function bit can_get() | |||
| imp | blocking | uvm_get_imp#(T, IMP) | uvm_blocking_get_imp#(T, IMP) | task get(output T t) | |
| nonblocking | uvm_nonblocking_get_imp#(T, IMP) | function bit try_get(output T t) And function bit can_get() |
| Data flow | control flow | Obstructive | Composite port class | Single port class | Data flow method |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| peek | port | blocking | uvm_peek_port#(T) | uvm_blocking_peek_port#(T) | task peek(output T t) |
| nonblocking | uvm_nonblocking_peek_port#(T) | function bit try_peek(output T t) And function bit can_peek() | |||
| export | blocking | uvm_peek_export#(T) | uvm_blocking_peek_export#(T) | task peek(output T t) | |
| nonblocking | uvm_nonblocking_peek_export#(T) | function bit try_peek(output T t) And function bit can_peek() | |||
| imp | blocking | uvm_peek_imp#(T, IMP) | uvm_blocking_peek_imp#(T, IMP) | task peek(output T t) | |
| nonblocking | uvm_nonblocking_peek_imp#(T, IMP) | function bit try_peek(output T t) And function bit can_peek() |
| Data flow | control flow | Obstructive | Composite port class | Single port class | Data flow method |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| get & peek | port | blocking | uvm_get_peek_port#(T) | uvm_blocking_get_peek_port#(T) | task get(output T t) And task peek(output T t) |
| nonblocking | uvm_nonblocking_get_peek_port#(T) | function bit try_get(output T t)、function bit can_get()、function bit try_peek(output T t) And function bit can_peek() | |||
| export | blocking | uvm_get_peek_export#(T) | uvm_blocking_get_peek_export#(T) | task get(output T t) And task peek(output T t) | |
| nonblocking | uvm_nonblocking_get_peek_export#(T) | function bit try_get(output T t)、function bit can_get()、function bit try_peek(output T t) And function bit can_peek() | |||
| imp | blocking | uvm_get_peek_imp#(T, IMP) | uvm_blocking_get_peek_imp#(T, IMP) | task get(output T t) And task peek(output T t) | |
| nonblocking | uvm_nonblocking_get_peek_imp#(T, IMP) | function bit try_get(output T t)、function bit can_get()、function bit try_peek(output T t) And function bit can_peek() |
Note that each composite port class contains all the data flow methods of two single port classes
The above table IMP Indicates where the data flow method is located component type
Source code
//...\questasim64_10.6c\verilog_src\uvm-1.2\src\tlm1\uvm_ports.svh
class uvm_blocking_put_port #(type T=int) extends uvm_port_base #(uvm_tlm_if_base #(T,T));
`UVM_PORT_COMMON(`UVM_TLM_BLOCKING_PUT_MASK,"uvm_blocking_put_port")
`UVM_BLOCKING_PUT_IMP (this.m_if, T, t)
endclass
class uvm_nonblocking_put_port #(type T=int) extends uvm_port_base #(uvm_tlm_if_base #(T,T));
`UVM_PORT_COMMON(`UVM_TLM_NONBLOCKING_PUT_MASK,"uvm_nonblocking_put_port")
`UVM_NONBLOCKING_PUT_IMP (this.m_if, T, t)
endclass
...
//...\questasim64_10.6c\verilog_src\uvm-1.2\src\tlm1\uvm_imps.svh
class uvm_blocking_put_imp #(type T=int, type IMP=int) extends uvm_port_base #(uvm_tlm_if_base #(T,T));
`UVM_IMP_COMMON(`UVM_TLM_BLOCKING_PUT_MASK,"uvm_blocking_put_imp",IMP)
`UVM_BLOCKING_PUT_IMP (m_imp, T, t)
endclass
...
//...\questasim64_10.6c\verilog_src\uvm-1.2\src\tlm1\uvm_exports.svh
class uvm_blocking_put_export #(type T=int) extends uvm_port_base #(uvm_tlm_if_base #(T,T));
`UVM_EXPORT_COMMON(`UVM_TLM_BLOCKING_PUT_MASK,"uvm_blocking_put_export")
`UVM_BLOCKING_PUT_IMP (this.m_if, T, t)
endclass
...
2.1. TLM Establishment and call of communication
The establishment of communication and method invocation have been introduced before , Here's an example .

As shown in the figure above , Components 1 And the component 2 There are two pairs of ports to establish communication , Suppose the first pair of ports are blocked put type 、 The second pair of ports is non blocking get type .
Communication setup and invocation are still : Definition trans、 Create port 、 Implementation method 、 Establishing a connection
Here's the code
class trans1 extends uvm_sequence_item; // Define transaction types
rand int id;
rand int data;
...
endclass
class trans2 extends uvm_sequence_item;
int id;
int data;
...
endclass
class comp1 extends uvm_component;
`uvm_component_utils(comp1)
uvm_blocking_put_port#(trans1) bp_port; //initiator Declaration port
uvm_nonblocking_get_port#(trans2) ng_port; //initiator Declaration port
function void build_phase(uvm_phase phase);
super.build_phase(phase);
bp_port = new("bp_port",this); //initiator Instantiate the port , Be careful not to inherit from uvm_object or uvm_component, Unavailable factory Mechanism instantiation !!!
ng_port = new("ng_port",this); //initiator Instantiate the port , Note that it inherits from uvm_object or uvm_component, Unavailable factory Mechanism instantiation !!!
...
endfunction
task run_phase(uvm_phase phase);
trans1 t1;
trans2 t2;
fork
repeat(5) begin
t1 = trans1::type_id_create("t1");
assert(t1.randomize());
bp_port.put(t1); // Call the port method , The method is defined in comp2
end
forever begin
if(ng_port.try_get(t2)) // Call the port method , The method is defined in comp2
break;
end
join
endtask
endclass
class comp2 extends uvm_component;
`uvm_component_utils(comp2)
uvm_blocking_put_imp#(trans1,comp2) bp_imp; //target Declaration port
uvm_nonblocking_get_imp#(trans2,comp2) ng_imp; //target Declaration port
trans1 tq[$]; //target Data caching
function void build_phase(uvm_phase phase);
super.build_phase(phase);
bp_imp = new("bp_imp",this); //target Instantiate the port
ng_imp = new("ng_imp",this); //target Instantiate the port
...
endfunction
task put(trans1 t);
tq.push_back(t);
endtask
function bit try_get(output trans2 t); // Define port data flow methods
...
endfunction
function bit can_get(); // Define port data flow methods
return (tq.size() > 0);
endfunction
endclass
class env extends uvm_env;
`uvm_component_utils(env);
comp1 c1;
comp2 c2;
function void build_phase(uvm_phase phase);
super.build_phase(phase);
c1 = comp1::type_id::create("c1",this);
c2 = comp2::type_id::create("c2",this);
...
endfunction
function void connect_phase(uvm_phase phase); // The upper component stay connect_phase Realization initiator Port connection target port
super.connect_phase(phase);
c1.bp_port.connect(c2.bp_imp);
c1.ng_port.connect(c2.ng_imp);
...
endfunction
endclass
Note that the instantiation of ports can only be new(string name, uvm_component parent); Out-of-service factory Mechanism instantiation , Compile and report errors !!!
//...\questasim64_10.6c\verilog_src\uvm-1.2\src\base\uvm_port_base.svh
function new (string name,
uvm_component parent,
uvm_port_type_e port_type,
int min_size=0,
int max_size=1);
Data flow method name conflict
When initiator and target There are two pairs of ports of the same type , that target The name of the implemented data flow method is the same , So there is a conflict of data flow methods ,UVM The solution is given .
As shown in the figure above , There are two pairs of blockages put port , The same type , Data flow methods are put.UVM The method given to resolve the conflict is , Register suffixes globally through macros , You can instantiate the new type ports with suffixes , Detailed as follows :
Or to continue the above section of code
class comp1 extends uvm_component;
`uvm_component_utils(comp1)
uvm_blocking_put_port#(trans1) bp_port1;
uvm_blocking_put_port#(trans2) bp_port2;
function void build_phase(uvm_phase phase);
super.build_phase(phase);
bp_port1 = new("bp_port1",this);
bp_port2 = new("bp_port2",this);
...
endfunction
task run_phase(uvm_phase phase);
trans1 t1;
repeat(5) begin
t1 = trans1::type_id_create("t1");
assert(t1.randomize());
bp_port1.put(t1); // Pay attention , Here is still put!! No put1、 Neither put2!!!
bp_port2.put(t1);
end
endtask
endclass
`uvm_blocking_put_imp_decl(1); // Macro registration suffix , After that uvm_blocking_put_imp1#(T, IMP) type , The data flow method also becomes put1
`uvm_blocking_put_imp_decl(2); // The suffix is registered again 2
class comp2 extends uvm_component;
`uvm_component_utils(comp2)
uvm_blocking_put_imp1#(trans1,comp2) bp_imp1; // Look at the suffix
uvm_blocking_put_imp2#(trans1,comp2) bp_imp2;
trans1 tq[$];
function void build_phase(uvm_phase phase);
super.build_phase(phase);
bp_imp1 = new("bp_imp1",this);
bp_imp2 = new("bp_imp2",this);
...
endfunction
task put1(trans1 t); // Look at the suffix
tq.push_back(t);
endtask
task put2(trans1 t);
tq.push_back(t);
endtask
endclass
therefore , Can be in overall situation `uvm_ Obstructive _ Data flow _ control flow _decl( suffix ) To register , can Instantiate an object with a new type that is suffixed but has the same type , The corresponding data flow method name should also be suffixed .
for example uvm_nonblocking_get_peek_imp#(trans,scoreboard) You can register as `uvm_nonblocking_get_peek_imp_decl(_scb)
When it is created uvm_nonblocking_get_peek_imp_scb#(trans,scoreboard) ngp_imp;
The method to be implemented is function bit try_get_scb(output trans t);、function bit can_get_scb();、function bit try_peek_scb(output trans t); and function bit can_peek_scb();
But pay attention to initiator The name of the called data flow method will not change !!!, The statement remains uvm_nonblocking_get_peek_port#(trans) ngp_port;, The method called is still function bit try_get(output trans t);、function bit can_get();、function bit try_peek(output trans t); and function bit can_peek();
3. One (port) For more than (imp) One way data flow Port communication
Just described uvm_ Obstructive _ Data flow _ control flow The type of port can only be connected one-to-one , If you want one to many communication , You can use analysis port .
3.1. Analysis port
You can implement a port With many imp communicate , The data flow approach is based on observer design patterns ,initiator Just broadcast the data .
As shown in the figure below , Arrows indicate the direction of the transaction

Obstructive : nothing
Because it's a broadcast , Just broadcast the data , Don't wait target Response .
Data flow :write
There is only one write Data flow method , Just broadcast the data , therefore target The end needs to implement write Method
● write:initiator Send the data to each of the target
control flow :port、export and imp
Still three , Corresponding uvm_analysis_port、uvm_analysis_export and uvm_analysis_imp Three analysis port
| Data flow | control flow | Single port class | Method prototypes |
|---|---|---|---|
| write | port | uvm_analysis_port#(T) | function void write(T t) |
| export | uvm_analysis_export#(T) | function void write(T t) | |
| imp | uvm_analysis_imp#(T, IMP) | function void write(T t) |
similarly , There are also corresponding macros for class name suffix registration `uvm_analysis_imp_decl(SFX)
Source code is as follows
//...\questasim64_10.6c\verilog_src\uvm-1.2\src\tlm1\uvm_analysis_port.svh
class uvm_analysis_port # (type T = int)
extends uvm_port_base # (uvm_tlm_if_base #(T,T));
function new (string name, uvm_component parent);
super.new (name, parent, UVM_PORT, 0, UVM_UNBOUNDED_CONNECTIONS);
m_if_mask = `UVM_TLM_ANALYSIS_MASK;
endfunction
virtual function string get_type_name();
return "uvm_analysis_port";
endfunction
function void write (input T t);
uvm_tlm_if_base # (T, T) tif;
for (int i = 0; i < this.size(); i++) begin
tif = this.get_if (i);
if ( tif == null )
uvm_report_fatal ("NTCONN", {
"No uvm_tlm interface is connected to ", get_full_name(), " for executing write()"}, UVM_NONE);
tif.write (t);
end
endfunction
endclass
class uvm_analysis_imp #(type T=int, type IMP=int) extends uvm_port_base #(uvm_tlm_if_base #(T,T));
class uvm_analysis_export #(type T=int) extends uvm_port_base #(uvm_tlm_if_base #(T,T));
4. uvm_tlm_analysis_fifo #(T)
Whether it's analysis Port or ordinary port , One of the more troublesome points is that target To implement the data flow method , There must be one in practical application component Be treated as target On the passive side , Obviously, it is difficult for the passive party to actively obtain data according to its own rhythm , You must always judge that you have new data in your cache
Try using a one-to-one port connection scoreboard Of run_phase
Is there anything similar to Systemverilog Medium mailbox Can make two component Can take the initiative to obtain data ?
yes , we have , Namely FIFO.UVM The provided inherits from uvm_component Class uvm_tlm_analysis_fifo Class instantiation is a kind of FIFO, it Can let the two of the communication component All as initiator, It comes from FIFO Numerous on imp Type port .
4.1. Analysis FIFO The port of
As shown in the figure below

You can query the source code :
//...\questasim64_2020.1\verilog_src\uvm-1.2\src\tlm1\uvm_tlm_fifo_base.svh
virtual class uvm_tlm_fifo_base #(type T=int) extends uvm_component; // Inherited from uvm_component
uvm_analysis_port #(T) put_ap;
uvm_analysis_port #(T) get_ap;
uvm_put_imp #(T, this_type) put_export;
uvm_put_imp #(T, this_type) blocking_put_export;
uvm_put_imp #(T, this_type) nonblocking_put_export;
uvm_get_peek_imp #(T, this_type) blocking_get_export;
uvm_get_peek_imp #(T, this_type) nonblocking_get_export;
uvm_get_peek_imp #(T, this_type) get_export;
uvm_get_peek_imp #(T, this_type) blocking_peek_export;
uvm_get_peek_imp #(T, this_type) nonblocking_peek_export;
uvm_get_peek_imp #(T, this_type) peek_export;
uvm_get_peek_imp #(T, this_type) blocking_get_peek_export;
uvm_get_peek_imp #(T, this_type) nonblocking_get_peek_export;
uvm_get_peek_imp #(T, this_type) get_peek_export;
...
endclass
//...\questasim64_2020.1\verilog_src\uvm-1.2\src\tlm1\uvm_tlm_fifos.svh
class uvm_tlm_fifo #(type T=int) extends uvm_tlm_fifo_base #(T);
local mailbox #( T ) m; // The bottom is still SV Medium mailbox
...
endclass
class uvm_tlm_analysis_fifo #(type T = int) extends uvm_tlm_fifo #(T);
uvm_analysis_imp #(T, uvm_tlm_analysis_fifo #(T)) analysis_export;
...
endclass
From the above picture and source code, we can see
● Analysis FIFO contain uvm_analysis_imp Class object analysis_export, Support one to many broadcast communication
● Analysis FIFO contain uvm_analysis_port Class object put_ap and get_ap, explain Anylsis FIFO Can also be used as initiator To the other target Broadcast .
And Analysis FIFO Connected initiator Every time you call put or get Data flow method ,FIFO Will call write radio broadcast , Look at the source code
//...\questasim64_2020.1\verilog_src\uvm-1.2\src\tlm1\uvm_tlm_fifos.svh
class uvm_tlm_fifo #(type T=int) extends uvm_tlm_fifo_base #(T);
...
virtual task put( input T t );
m.put( t );
put_ap.write( t ); // radio broadcast
endtask
virtual task get( output T t );
m_pending_blocked_gets++;
m.get( t );
m_pending_blocked_gets--;
get_ap.write( t ); // radio broadcast
endtask
...
endclass
class uvm_tlm_analysis_fifo #(type T = int) extends uvm_tlm_fifo #(T);
● except put_ap and get_ap, Other ports are _export ending , But actually it's all imp Type of .
Establish communication and call
It's easy , Need to send trans Of component Internal creation put_port port , Need to accept trans Of component Internal creation get_port port , And then on the upper floor component Create a Anylsis FIFO, Connect the three .
for example monitor Broadcast data to scoreboard
class monitor extends uvm_monitor;
`uvm_component_utils(monitor)
virtual reg_intf vif;
uvm_analysis_port#(trans) a_port;
...
function void build_phase(uvm_phase phase);
super.build_phase(phase);
ap = new("ap",this);
if(!uvm_config_db#(virtual reg_intf)::get(this,"","vif",vif))
uvm_report_error("INTF",$sformatf("%s gets interface failed",get_full_name()),UVM_NONE);
endfunction
task run_phase(uvm_phase phase);
forever begin
trans t;
t = trans::type_id::create("t");
@(posedge vif.clk iff(vif.mon_ck.cmd != IDLE))
t.cmd = vif.mon_ck.cmd;
t.cmd_addr = vif.mon_ck.cmd_addr;
a_port.write(t);
end
endtask
endclass
class scoreboard extends uvm_scoreboard;
`uvm_component_utils(scoreboard)
uvm_blocking_get_port#(trans) bg_port;
...
function void build_phase(uvm_phase phase);
super.build_phase(phase);
bg_port = new("bg_port",this);
endfunction
task run_phase(uvm_phase phase);
forever begin
trans t;
bg_port.get(t);
...
end
endtask
endclass
class env extends uvm_env;
`uvm_component_utils(env)
uvm_tlm_analysis_fifo#(trans) agt_scb_fifo;
agent agt;
scoreboard scb;
...
function void build_phase(uvm_phase phase);
super.build_phase(phase);
agt_scb_fifo = uvm_tlm_analysis_fifo#(trans)::type_id::create("agt_scb_fifo",this);
...
endfunction
function void connect_phase(uvm_phase phase);
agt.mon.a_port.connect(agt_scb_fifo.analysis_export); // And FIFO Connect
scb.bg_port.connect(agt_scb_fifo.blocking_get_export);
...
endfunction
endclass
4.2. Analysis FIFO Methods
You can call some methods to view FIFO internal data
//...\questasim64_2020.1\verilog_src\uvm-1.2\src\tlm1\uvm_tlm_fifos.svh
class uvm_tlm_fifo #(type T=int) extends uvm_tlm_fifo_base #(T);
function new(string name, uvm_component parent = null, int size = 1); // Create a function ,size Can be specified FIFO Capacity ,0 Is infinite size
virtual function int used(); // return FIFO Stored in the trans The number of
virtual function bit is_empty(); //FIFO Is it empty
virtual function bit is_full(); //FIFO Full or not
virtual function void flush(); // Empty FIFO
endfunction
边栏推荐
- Node version control tool NVM
- Procédures d'introduction et d'installation de sonarqube
- How to optimize plantuml flow diagram (sequence diagram)
- 2022 618笔记本选购指北
- 自定义JSP标签->概念->生命周期
- [JUC series] overview of executor framework
- Balanced binary tree (AVL tree)
- Gin integrated graphic verification code
- Introduction and installation steps of sonarqube
- 愉快无负担的跨进程通信方式
猜你喜欢
Pad printing process flow and application precautions

SAP SD create / modify price list

环境搭建2

点云库pcl从入门到精通学习记录 第八章

In order to stimulate inspiration and creativity, Shanghai daoning united with XMIND to bring you full-featured mind mapping and brainstorming software

二叉排序树

I2C read / write process

Ar helps brand stores achieve global data growth

Here we go! Dragon lizard community enters PKU classroom

Lake Shore - supervaritemp low temperature thermostat
随机推荐
Mingdeyang ADC series development board-ad9653 daughter board multi-channel high resolution and high sampling rate
Notes on knowledge points of dynamic planning
Integrate工具之Jenkins
Lake shore vnf series low temperature thermostat system - sample in flowing steam
Class. Getresource() and class Getresourceasstream() method
(linear DP | monotone queue) acwing 895 Longest ascending subsequence
Shell (32): configure SSH privacy free
DPT-FSNET: DUAL-PATH TRANSFORMER BASED FULL-BAND AND SUB-BAND FUSION NETWORK FOR SPEECH ENHANCEMENT
MySQL some simple commands
Jenkins基本配置
[industry application] an article on power digital transformation
Wechat applet Bluetooth development
DOM知識點總結
Gin solves cross domain problems
使用 select 切换协程
Here we go! Dragon lizard community enters PKU classroom
loading
m-way search trees
I2C read / write process
Flex flexible layout tutorial and understanding of the main axis cross axis: Grammar