当前位置:网站首页>Finally, I understand the event loop, synchronous / asynchronous, micro task / macro task, and operation mechanism in JS (with test questions attached)
Finally, I understand the event loop, synchronous / asynchronous, micro task / macro task, and operation mechanism in JS (with test questions attached)
2022-07-02 15:38:00 【Mr. fingertip dancer】
Catalog
js It's a single-threaded language
Synchronization task (synchronous)
Asynchronous task (asynchronous)
js It's a single-threaded language
process , The smallest unit of resource allocation , It has independent stack space and data storage space
Threads , The smallest unit of program execution , A process can include multiple threads
If there are multiple processes , Simultaneous operation DOM, Then the consequences are out of control
for example : For the same button , Different processes give different colors , How to show
Single thread means , All tasks are queued , The previous task is over , Will perform the latter task . If the previous task took a long time , The latter task had to wait
JavaScript The language designers realized , The main thread can be completely ignored IO equipment , Suspended pending tasks , Run the next task first . wait until IO The device returned the result , back , Carry on with the suspended task .
therefore , All tasks can be divided into two kinds , One is synchronous tasks (synchronous), The other is asynchronous tasks (asynchronous).
Synchronization task (synchronous)
Synchronous task refers to , Tasks queued for execution on the main thread , Only the previous task was completed , To perform the next task
Asynchronous task (asynchronous)
Asynchronous task means , Do not enter the main thread , And enter ” Task queue ”(task queue) The task of , Only ” Task queue ” Notification thread , Some asynchronous task is ready to execute , This task is then executed on the main thread .
The event loop (Event Loop)
- Synchronous and asynchronous tasks are executed differently " place ", Enter the main thread synchronously , Enter asynchronously Event Table And register functions .
- When the appointed thing is done ,Event Table Will move this function into Event Queue.
- The task in the main thread is empty after execution , Will go to Event Queue Read the corresponding function , Enter the main thread execution .
- The above process will be repeated , That's what they say Event Loop( The event loop ).
Macro task (macrotask)
The code currently executed in the call stack becomes a macro task. . Include :script In the code 、setTimeout、setInterval、I/O、UI render
Micro task (microtask)
At present ( In this cycle of events ) The macro task is finished , Tasks to be executed before the next macro task starts , It can be understood as a callback event
Include :process.nextTick、MutationObserver、Promise.then
promise
Promise Asynchrony in then and catch in , So it's written in Promise The code in is executed immediately as a synchronization task
new Promise(function(resolve) {
console.log('promise'); // Execute now here
resolve();
}).then(res=>{
console.log('rosolve') // Join the micro task (microtask in ) in
})
Async/await
And in the async/await in , stay await Before appearance , The code is also executed immediately . Many people think await We will wait until the expression is executed before continuing to execute the following code , actually await It's a sign to let the thread go . await The following expression will be executed first , take await The following code is added to the micro task microtask in , And then it will jump out of the whole async Function to execute the following code . because async await Itself is promise+generator The grammar sugar of . therefore await The following code is microtask
async function async1() {
console.log('async1 start'); // Execute now
await async2(); // Execute now await The following expression
console.log('async1 end'); // take await The following code is added to the micro task (microtask in ) in
}
Topic 1
async function async1() {
console.log('async1 start');
await async2();
console.log('async1 end');
}
async function async2() {
console.log('async2');
}
console.log('script start');
setTimeout(function() {
console.log('setTimeout');
}, 0)
async1();
new Promise(function(resolve) {
console.log('promise1');
resolve();
}).then(function() {
console.log('promise2');
});
console.log('script end');
/*
script start
async1 start
async2
promise1
script end
async1 end
promise2
setTimeout
*/
analysis :
1. Event loop from macro task (macrotask) The queue begins , Macro task queue , only one script( The overall code ) Mission , Execute the entire code block
2. encounter 2 A defined async function , Keep going down , encounter console sentence , Direct output 'script start'
3.script The task continues down , encounter async1() function ,async Function in await The previous code was executed immediately , So the output 'async1 start', And then execute async2() function , Output 'async2', take ‘console.log('async1 end')’ Assigned to microtask In line
4.script The mission goes on , encounter Promise,Promise The code in is executed immediately as a synchronization task , So the output 'promise1', And then execute resolve, take 'promise2' Assigned to microtask In line
5.script The mission goes on , Finally, only one sentence is output 'script end', thus , The global task is finished
6. After each macro task , I'll check to see if it exists microtask; If there is , execute microtask Until emptied microtask Queue. So in script After task execution , Start searching, clear the micro task queue
7.microtask In line ,Promise There are two tasks in the queue async1 end and promise2, So output in sequence async1 end 、promise2, be-all microtask After execution , Means that the first round of the loop is over
8. The second loop still starts with the macro task queue . At this point, there is only one macro task setTimeout, Take out the direct output , So far the whole process is over
Topic two
Different from question 1 async2() The function is also written inside Promise,Promise The code in is executed immediately as a synchronization task , All will output 'promise1','promise2' Is assigned to microtask In line , So the output is finished 'script end' after , Will be output successively promise2, async1 end ,promise4,setTimeout
async function async1() {
console.log('async1 start');
await async2();
console.log('async1 end');
}
async function async2() {
//async2 Make the following changes :
new Promise(function(resolve) {
console.log('promise1');
resolve();
}).then(function() {
console.log('promise2');
});
}
console.log('script start');
setTimeout(function() {
console.log('setTimeout');
}, 0)
async1();
new Promise(function(resolve) {
console.log('promise3');
resolve();
}).then(function() {
console.log('promise4');
});
console.log('script end');
/*
script start
async1 start
promise1
promise3
script end
promise2
async1 end
promise4
setTimeout
*/
Question three
analysis :
When output is promise2 after , Next, we will join setTimeout Queue in order to output , Through the code, we can see that the order of adding is 3 2 1, So I'll press 3,2,1 In order to output .
sync function async1() {
console.log('async1 start');
await async2();
// Change it as follows :
setTimeout(function() {
console.log('setTimeout1')
},0)
}
async function async2() {
// Change it as follows :
setTimeout(function() {
console.log('setTimeout2')
},0)
}
console.log('script start');
setTimeout(function() {
console.log('setTimeout3');
}, 0)
async1();
new Promise(function(resolve) {
console.log('promise1');
resolve();
}).then(function() {
console.log('promise2');
});
console.log('script end');
/*
script start
async1 start
promise1
script end
promise2
setTimeout3
setTimeout2
setTimeout1
*/
Question 4
async function a1 () {
console.log('a1 start')
await a2()
console.log('a1 end')
}
async function a2 () {
console.log('a2')
}
console.log('script start')
setTimeout(() => {
console.log('setTimeout')
}, 0)
Promise.resolve().then(() => {
console.log('promise1')
})
a1()
let promise2 = new Promise((resolve) => {
resolve('promise2.then')
console.log('promise2')
})
promise2.then((res) => {
console.log(res)
Promise.resolve().then(() => {
console.log('promise3')
})
})
console.log('script end')
/*
script start
a1 start
a2
promise2
script end
promise1
a1 end
promise2.then
promise3
setTimeout
*/
analysis :
1. Promise.resolve().then(() => {
console.log("promise1");
});
a1();
'promise1' Is also assigned to microtask Queue , And it is in a1() Before function execution , Allocated first , So in 'script end' After output , Output first 'promise1' Then output in turn
2. let promise2 = new Promise((resolve) => {
resolve("promise2.then");
console.log("promise2");
});
This will output directly "promise2", 'resolve' differ 'await', Will not prevent subsequent execution
ending
If this article helps your little friend , Guys, manually like it
We will continue to update the front-end related articles in the future , Thank you for your support
reference :
边栏推荐
- Redux——详解
- [leetcode] 1162 map analysis
- Loss function and positive and negative sample allocation: Yolo series
- 13_Redis_事务
- Case introduction and problem analysis of microservice
- Infra11199 database system
- 百变大7座,五菱佳辰产品力出众,人性化大空间,关键价格真香
- 【网络安全】网络资产收集
- LeetCode刷题——奇偶链表#328#Medium
- [leetcode] 167 - sum of two numbers II - enter an ordered array
猜你喜欢
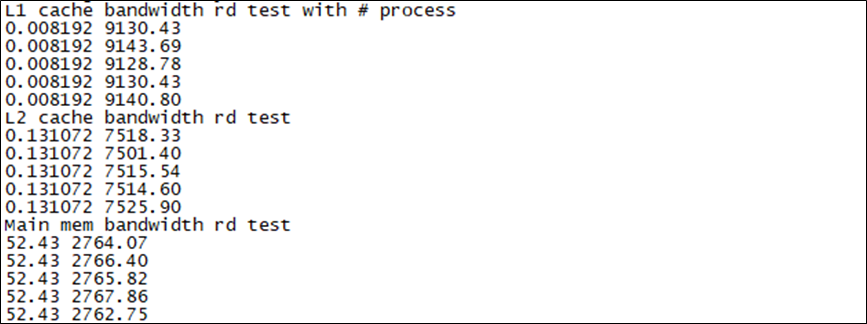
Storage read-write speed and network measurement based on rz/g2l | ok-g2ld-c development board

Leetcode skimming - remove duplicate letters 316 medium

Basic knowledge of cryptography

Yolov5 code reproduction and server operation

Leetcode skimming -- incremental ternary subsequence 334 medium
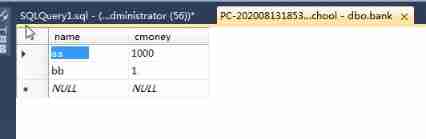
SQL transaction

LeetCode刷题——统计各位数字都不同的数字个数#357#Medium
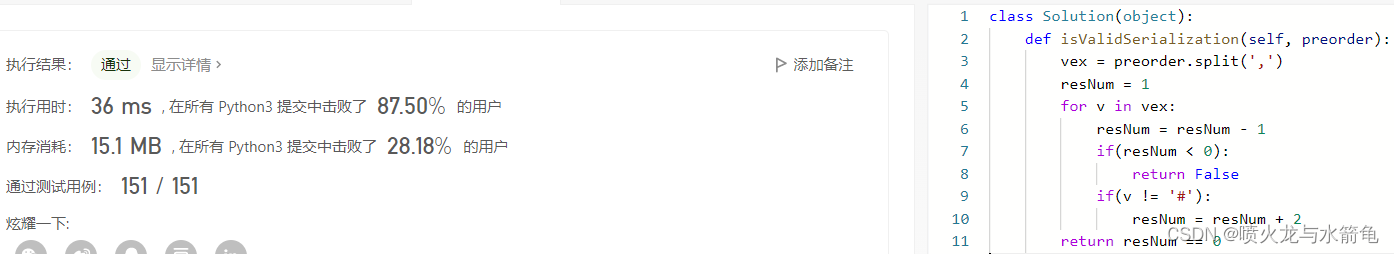
LeetCode刷题——验证二叉树的前序序列化#331#Medium

There are 7 seats with great variety, Wuling Jiachen has outstanding product power, large humanized space, and the key price is really fragrant

FPGA - 7系列 FPGA内部结构之Clocking -03- 时钟管理模块(CMT)
随机推荐
[leetcode] 417 - Pacific Atlantic current problem
(4) Flink's table API and SQL table schema
MD5加密
怎样从微信返回的json字符串中截取某个key的值?
【LeetCode】977-有序数组的平方
Markdown tutorial
【LeetCode】877-石子游戏
17_ Redis_ Redis publish subscription
【LeetCode】344-反转字符串
【LeetCode】577-反转字符串中的单词 III
工程师评测 | RK3568开发板上手测试
19_ Redis_ Manually configure the host after downtime
【LeetCode】19-删除链表的倒数第N个结点
【LeetCode】1020-飞地的数量
Beijing rental data analysis
[leetcode] 283 move zero
终于搞懂了JS中的事件循环,同步/异步,微任务/宏任务,运行机制(附笔试题)
Bing. Com website
【LeetCode】695-岛屿的最大面积
Yolov5 code reproduction and server operation

 https://blog.csdn.net/qq_56989560/article/details/125032315?spm=1001.2014.3001.5501
https://blog.csdn.net/qq_56989560/article/details/125032315?spm=1001.2014.3001.5501