当前位置:网站首页>[Day5] Soft and hard links File storage, deletion, directory management commands
[Day5] Soft and hard links File storage, deletion, directory management commands
2022-08-05 06:09:00 【Mingli Yui】
目录
Soft connection knowledge summary:
The role of each directory under the root directory:
一、文件存储
文件存储?
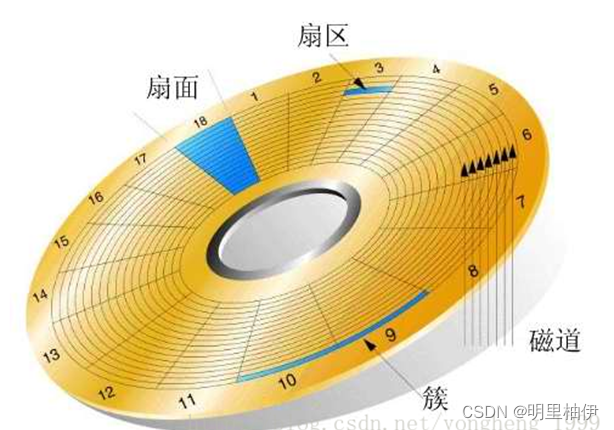
文件储存在硬盘上,硬盘的最小存储单位叫做"扇区"(Sector).每个扇区储存512字节(相当于0.5KB).
操作系统读取硬盘的时候,一次性连续读取多个扇区,即一次性读取一个"块"(block).这种由多个扇区组成的"块",是文件存取的最小单位."块"的大小,最常见的是4KB,即连续八个 sector组成一个 block.
什么是inode?
储存文件的元信息,比如文件的创建者、文件的创建日期、文件的大小等等.这种储存文件元信息的区域就叫做inode,中文译名为"索引节点".
Displays detailed information about files and file systems
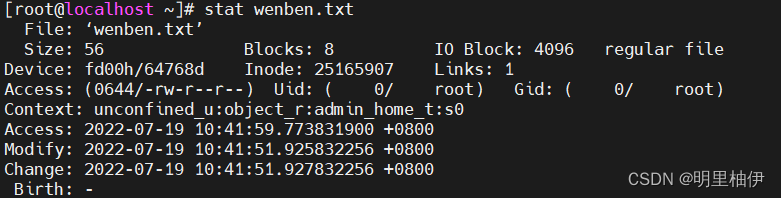
可以用stat命令,查看某个文件的inode信息:
文件的时间戳,共有三个:
ctime显示的是文件的权限、拥有者、所属的组、链接数发生改变时的时间.当然当内容改变时也会随之改变(即inode内容发生改变和Block内容发生改变时)
mtime指文件内容上一次变动的时间,
atimeRefers to the time the file was last accessed.
* 链接数,即有多少文件名指向这个inode
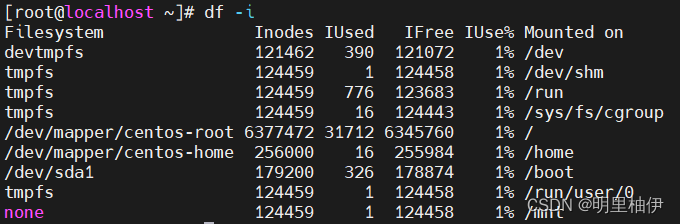
df命令 View the disk space usage of the file system
查看每个硬盘分区的inode信息,可以使用df -i命令.
inode也会消耗硬盘空间,所以硬盘格式化的时候,操作系统自动将硬盘分成两个区域.
一个是数据区,存放文件数据;另一个是inode区(inode table),存放inode所包含的信息.
每个inode节点的大小,一般是128字节或256字节.
inode节点的总数,在格式化时就给定,一般是每1KB或每2KB就设置一个inode.
表面上,用户通过文件名,打开文件.实际上,系统内部这个过程分成三步:
首先,系统找到这个文件名对应的inode号码;
其次,通过inode号码,获取inode信息;
最后,根据inode信息,找到文件数据所在的block,读出数据.
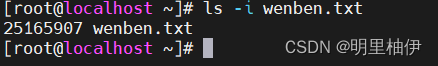
使用ls -i命令,可以看到文件名对应的inode号码:
Unix/Linux系统中,目录(directory)也是一种文件.打开目录,实际上就是打开目录文件.
目录文件的结构非常简单,就是一系列目录项(dirent)的列表.
每个目录项,由两部分组成:所包含文件的文件名,以及该文件名对应的inode号码.
df -h命令 View disk usage in a readable way;
二、硬链接与软链接
硬链接
源文件与硬链接文件的inode是一样的;硬链接文件与原始文件其实是同一个文件,只不过是不同的名字而已.硬连接的作用是允许一个文件拥有多个有效路径名,这样用户就可以建立硬连接到重要文件,以防止“误删”的功能.Deleting just one link has no effect.
如何创建硬链接:
ln 源文件名 硬链接名
If a hard link file is created for a source file,Accidentally delete the source file after moving the hardlink file to another file,然后通过cpAfter the command gets the hardware file to the address of the previous source file,在使用ls -i命令查看inode号,will find himinidenumber changed,通过mvcommand to get the hardware file to the address of the previous source fileinodeNo. has not changed.
Renaming and moving will not affectinode号,cpcommand will be affected.
硬链接知识小结
软连接
The content of the source file of the soft link is the same as that of the link file,inode号不一样;Delete the soft link file,Source files are also accessible,将源文件删除,The linked file cannot be accessed.
如何创建软连接?
ln -s 源文件名 软连接文件名
Soft connection knowledge summary:
The memory will be occupied by the process, Only when the process is freed,内存才会被释放
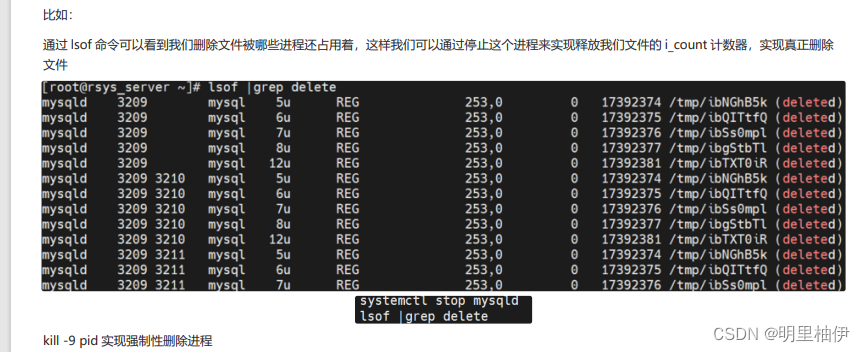
三、文件删除的原理
每个文件都有2各link计数器:i_count(内存引用计数器)和i_nlink(磁盘引用计数器);
Want to delete the file completely,This file must be enabledi_count和i_nlink都为0;
Like a file is being called by a process,而用户却使用rmThe file was deleted,Although this file can't be found at this time,But the process calling the file is still executing,The file's memory was not freed. 因为rm操作只是将i_nlink数减少了,If there are no other linked files then itsi_nlink数为0,But since the file is still being referenced by the process,所以i_count不为0,The system does not actually delete this file,Want to delete the file completely,This file must be enabledi_count和i_nlink都为0.
四、文件目录管理命令
cp命令
copy Implement file or directory copying
copy file1 file2 实现文件 file1 的内容拷贝到文件 file2 上,如果文件 file2 已存在则覆盖,不存在则创建
常用参数:
-R, -r, 递归拷贝
-p same as --preserve=mode,ownership,timestamps Preserve the attribute permissions time of the source file, etc
mv 命令
Moving files or renaming can be achieved
mv After can be a directory or a file,If it is a directory, file movement is implemented,If it is a file, it will be renamed
rm 命令
Implements deleting a file or directory
常见参数有:
-f, Forced deletion is not prompted
-r, -R,Recursively delete subdirectories and files in the containing directory
find命令
find 命令是直接在硬盘中进行搜索的,如果指定的搜索范围过大,find命令就会消耗较大的系统资源,导致服务器压力过大.所以,在使用 find 命令搜索时,不要指定过大的搜索范围.
命令格式:
[[email protected] ~]# find 搜索路径 [选项] 搜索内容
例子: 查找/目录下所有以.log 结尾的文件
[[email protected]_server test]# find / -name "*.log"
cut命令
就是在文件中负责剪切数据用的.cut 是以每一行为一个处理对象的;
常用参数:
-d 自定义分割符,If not defined the default delimiter is used tab 键;
-f By column or field;
-c The parameter specifies the number of characters to be cut from the starting number to the ending number;(cut -c "1-2" wb 切割wbThe first two characters in the file)
sort 命令
sort command to sort,Usually used in conjunction with text processing tools;
常用参数:
-b 忽略每行前面的空格字符. -f 忽略大小写 -M 将前面3个字母依照月份的缩写进行排序. -n 依照数值的大小排序. -o <输出文件> 将排序后的结果存入制定的文件. -r 以相反的顺序来排序. -t <分隔字符> 指定排序时所用的栏位分隔字符. -k 指定需要排序的栏位
-u Only one row of the same data appears 如下:
[[email protected] ~]# sort -k 2 -t "." sort.txt
AA:BB:CC
ee:60:5.1
dd:20:4.2
cc:50:3.3
ee:40:5.3
bb:10:2.4
aa:30:1.9(表示按"."分隔开.Sort the second column from smallest to largest.)
uniq 命令
Mainly used to achieve the removal of duplicate lines The prerequisite is that the text must be sorted first
uniq命令加-cThe option can implement statistics on the number of repetitions.
wc 命令
Statistics such as the number of bytes or lines of the file 常用参数-l -l, --lines print the newline counts
五、文件搜索工具
字符匹配
. 匹配任意单个字符(grep 'r..t' /etc/passwd)
* Match the preceding character any number of times;0,1,多次;例如grep "x*y"
\? matches the character preceding it0次或1次;(Basic regular to add/,No need to add extended regular)
\+ matches the character preceding it1次或多次;
.* 匹配任意多个字符
(使用grepCommands are regular expressions,不适用grep为通配符.)
单词:非特殊字符组成的连续字符(字符串)都称为单词;
\<root 用于单词模式的左侧,Similar to starting with a certain word;
root\> 用于单词模式的左侧,Similar to ending with a certain word
\<apple\> Used to match complete words;
分组及引用

Linux文件搜索命令
which命令
在$PATHThe location to search for a system command in all directories of ,By default, if it is found in the first file, it will not be found in other files;Internal commands are also not found(例如:history)
-a Find system commands in all directories
--skip-alias Only file directories do not have aliases(For command aliases)
whereis命令
Find the location of the help manual for a command or program
-b Find only executable commands
-m 只查找帮助文件
type命令
Used to distinguish whether the command is an external command or an internal command(shell builtin)还是别名
find命令
功能描述:在目录中查找文件.不仅可以按照文件名搜索文件,还可以按照权限、大小、时间、inode 号等来搜索文件.但是 find 命令是直接在硬盘中进行搜索的,如果指定的搜索范围过大,find命令就会消耗较大的系统资源,导致服务器压力过大.所以,在使用 find 命令搜索时,不要指定过大的搜索范围.
命令格式:find 搜索路径 [选项] 搜索内容
常用参数:
-name: 按照文件名搜索;
-iname: 按照文件名搜索,不区分文件名大小;
-inum: 按照 inode 号搜索;
-size[+-]大小:按照指定大小搜索文件(这里的"+"的意思是搜索比指定大小还要大的文件,"-" 的意思是搜索比指定大小还要小的文件.我们来试试:)
-atime [+-]时间: 按照文件访问时间搜索
-mtime [+-]时间: Search by file content time
-ctime [+-]时间: 按照文件状态修改时间搜索
这三个时间的区别我们在 stat 命令中已经解释过了,这里用 mtime 数据修改时间来举例,重点说说 "[+-]"时间的含义.
-5:代表5Files modified every day.
5: 代表前5~6天那一天修改的文件.
+5: 代表5天前修改的文件.



边栏推荐
- 调用TensorFlow Objection Detection API进行目标检测并将检测结果保存至本地
- 错误类型:reflection.ReflectionException: Could not set property ‘xxx‘ of ‘class ‘xxx‘ with value ‘xxx‘
- 网站ICP备案是什么呢?
- [Day8] (Super detailed steps) Use LVM to expand capacity
- 【Day8】Knowledge about disk and disk partition
- vim的三种模式
- 【UiPath2022+C#】UiPath 数据操作
- framebuffer应用编程及文字显示(2)
- 栈区中越界可能造成的死循环可能
- spark算子-coalesce算子
猜你喜欢

(C语言)动态内存管理
【UiPath2022+C#】UiPath Switch

乘云科技受邀出席2022阿里云合作伙伴大会荣获“聚力行远奖”
错误类型:reflection.ReflectionException: Could not set property ‘xxx‘ of ‘class ‘xxx‘ with value ‘xxx‘
链表章6道easy总结(leetcode)
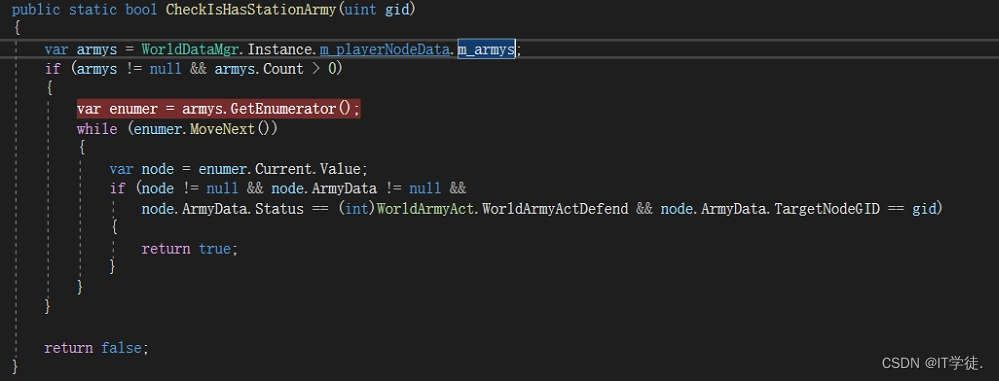
Unity中的GetEnumerator 方法及MoveNext、Reset方法
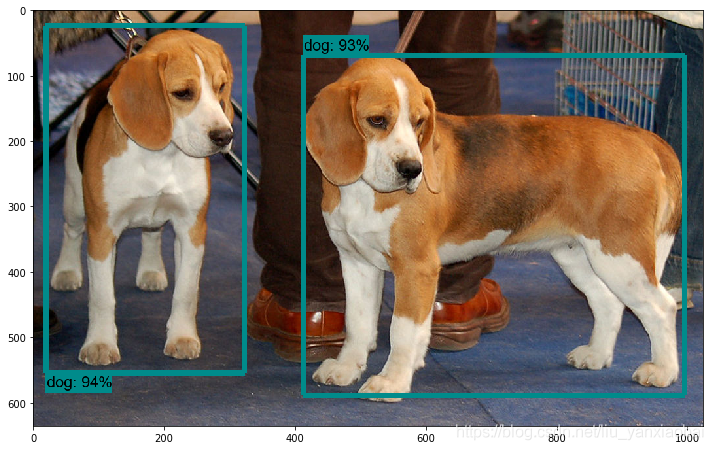

TensorFlow ObjecDetectionAPI在win10系统Anaconda3下的配置
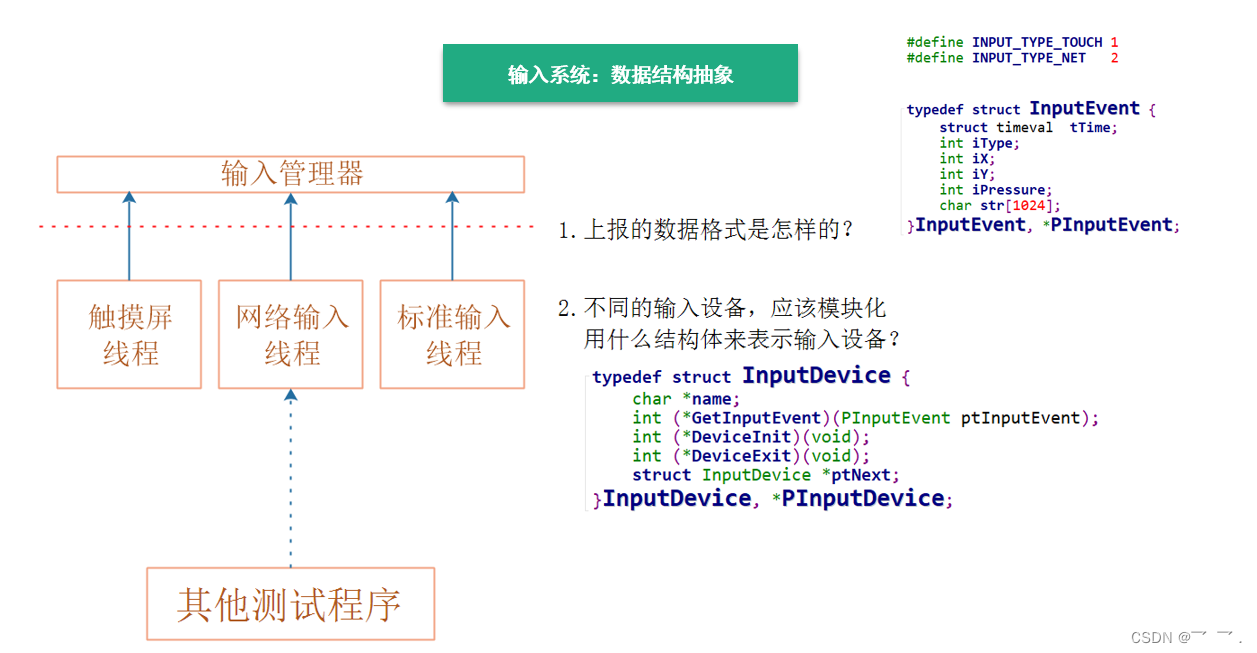
电子产品量产工具(2)- 输入系统实现
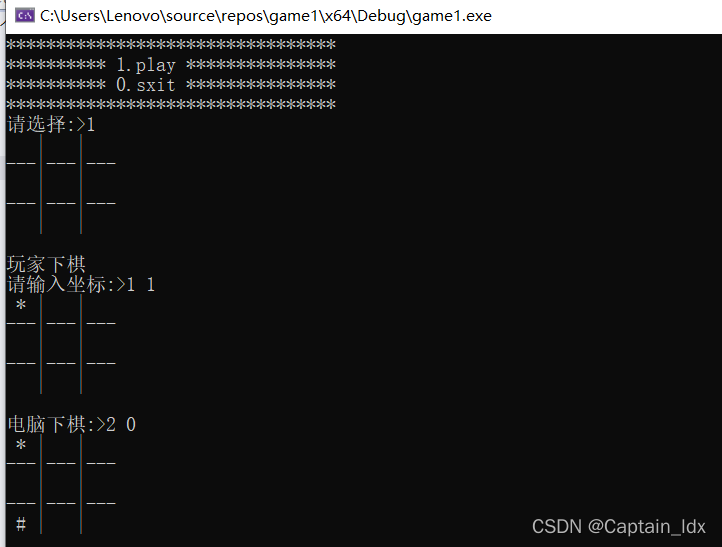
C语言—三子棋的实现
2020,Laya最新中高级面试灵魂32问,你都知道吗?
随机推荐
SSL证书提示过期或者无效,该怎么处理呢?
错误类型:reflection.ReflectionException: Could not set property ‘xxx‘ of ‘class ‘xxx‘ with value ‘xxx‘
Unity中的GetEnumerator 方法及MoveNext、Reset方法
D39_向量
Spark源码-任务提交流程之-6.2-sparkContext初始化-TaskScheduler任务调度器
(oj)原地移除数组中所有的元素val、删除排序数组中的重复项、合并两个有序数组
每日一题-两数相加-0711
lvm逻辑卷及磁盘配额
Getting Started Documentation 12 webserve + Hot Updates
spark源码-任务提交流程之-1-sparkSubmit
Apache配置反向代理
偷题——腾讯游戏开发面试问题及解答
2020年手机上最好的25种免费游戏
图片压缩失效问题
云游戏未来展望
专有宿主机CDH
ACL 和NAT
Autoware中安装Yolo3目标检测模块遇到的问题
Unity物理引擎中的碰撞、角色控制器、Cloth组件(布料)、关节 Joint
Unity huatuo 革命性热更系列1.2 huatuo热更环境安装与示例项目