当前位置:网站首页>spark算子-coalesce算子
spark算子-coalesce算子
2022-08-05 05:18:00 【zdaiqing】
完整代码
/** * 返回一个新的RDD,它被缩减为numPartitions分区。 * Return a new RDD that is reduced into `numPartitions` partitions. * * 这就导致了一个狭窄的依赖,例如,如果你从1000个分区到100个分区,不会有一个转移, * 而是每100个新分区将占用10个当前分区。如果请求的分区数量更大,则会保持当前的分 * 区数量。 * This results in a narrow dependency, e.g. if you go from 1000 partitions * to 100 partitions, there will not be a shuffle, instead each of the 100 * new partitions will claim 10 of the current partitions. If a larger number * of partitions is requested, it will stay at the current number of partitions. * * 然而,如果你正在做一个激烈的合并,例如numPartitions = 1,这可能会导致你的计算发生 * 在比你希望的更少的节点上(例如,在numPartitions = 1的情况下只有一个节点)。为了避免 * 这种情况,你可以传递shuffle = true。这将增加一个shuffle步骤,但意味着当前上游分区 * 将并行执行(无论当前分区是什么)。 * However, if you're doing a drastic coalesce, e.g. to numPartitions = 1, * this may result in your computation taking place on fewer nodes than * you like (e.g. one node in the case of numPartitions = 1). To avoid this, * you can pass shuffle = true. This will add a shuffle step, but means the * current upstream partitions will be executed in parallel (per whatever * the current partitioning is). * * 注意: * 使用shuffle = true,实际上可以合并到更多的分区。如果您有少量的分区(比如100个),并 * 且可能有几个分区异常大,那么这很有用。调用coalesce(1000, shuffle = true)将产生 * 1000个分区,数据使用散列分区器分布。传入的可选分区合并器必须是可序列化的。 * @note With shuffle = true, you can actually coalesce to a larger number * of partitions. This is useful if you have a small number of partitions, * say 100, potentially with a few partitions being abnormally large. Calling * coalesce(1000, shuffle = true) will result in 1000 partitions with the * data distributed using a hash partitioner. The optional partition coalescer * passed in must be serializable. */
def coalesce(numPartitions: Int, shuffle: Boolean = false,
partitionCoalescer: Option[PartitionCoalescer] = Option.empty)
(implicit ord: Ordering[T] = null)
: RDD[T] = withScope {
require(numPartitions > 0, s"Number of partitions ($numPartitions) must be positive.")
if (shuffle) {
/** Distributes elements evenly across output partitions, starting from a random partition. */
val distributePartition = (index: Int, items: Iterator[T]) => {
var position = new Random(hashing.byteswap32(index)).nextInt(numPartitions)
items.map {
t =>
// Note that the hash code of the key will just be the key itself. The HashPartitioner
// will mod it with the number of total partitions.
position = position + 1
(position, t)
}
} : Iterator[(Int, T)]
// include a shuffle step so that our upstream tasks are still distributed
new CoalescedRDD(
new ShuffledRDD[Int, T, T](
mapPartitionsWithIndexInternal(distributePartition, isOrderSensitive = true),
new HashPartitioner(numPartitions)),
numPartitions,
partitionCoalescer).values
} else {
new CoalescedRDD(this, numPartitions, partitionCoalescer)
}
}
shuffle
默认情况
默认shuffle为false,默认不进行shuffle
def coalesce(numPartitions: Int, shuffle: Boolean = false,
partitionCoalescer: Option[PartitionCoalescer] = Option.empty)
shuffle处理流程
shuffle后数据分布
- 从一个随机分区开始,在输出分区中均匀分布元素
- HashPartitioner:数据落地分区数 = position%总的分区数
- index:上游分区索引;numPartitions:当前shuffle后的rdd的分区数
val distributePartition = (index: Int, items: Iterator[T]) => {
var position = new Random(hashing.byteswap32(index)).nextInt(numPartitions)
items.map {
t =>
// Note that the hash code of the key will just be the key itself. The HashPartitioner
// will mod it with the number of total partitions.
position = position + 1
(position, t)
}
} : Iterator[(Int, T)]
shuffle逻辑
- new ShuffledRDD() 构建shuffle RDD
- 构建shuffle RDD时,调用distributePartition函数调整数据分布的分区
- 将shuffle RDD转为 CoalescedRDD,分区数根据numPartitions这个新分区数确定
new CoalescedRDD(
new ShuffledRDD[Int, T, T](
mapPartitionsWithIndexInternal(distributePartition, isOrderSensitive = true),
new HashPartitioner(numPartitions)),
numPartitions,
partitionCoalescer).values
非shuffle处理流程
- 直接将RDD转为CoalescedRDD,分区数根据numPartitions这个新分区数确定
new CoalescedRDD(this, numPartitions, partitionCoalescer)
参考资料
边栏推荐
猜你喜欢
随机推荐
C语言查看大小端(纯代码)
每日一题-合并两个有序链表-0720
LeetCode刷题之第54题
每日一题-正则表达式匹配-0715
Redis设计与实现(第三部分):多机数据库的实现
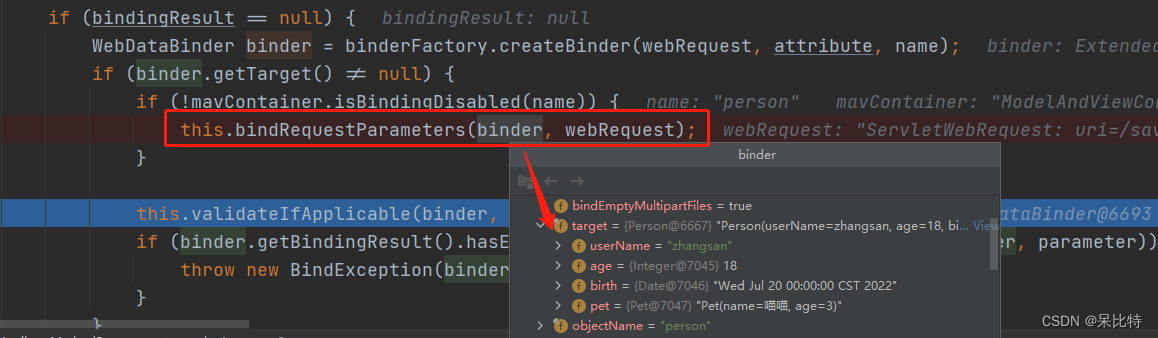
八、请求处理之自定义类型参数绑定原理
网络通信及相关函数介绍
HuiFer 带你读懂 BeanFactory getBean 方法
Redis设计与实现(第二部分):单机数据库的实现
每日一题-合并K个升序链表-0722
腾讯内部技术:《轩辕传奇》服务器架构演变
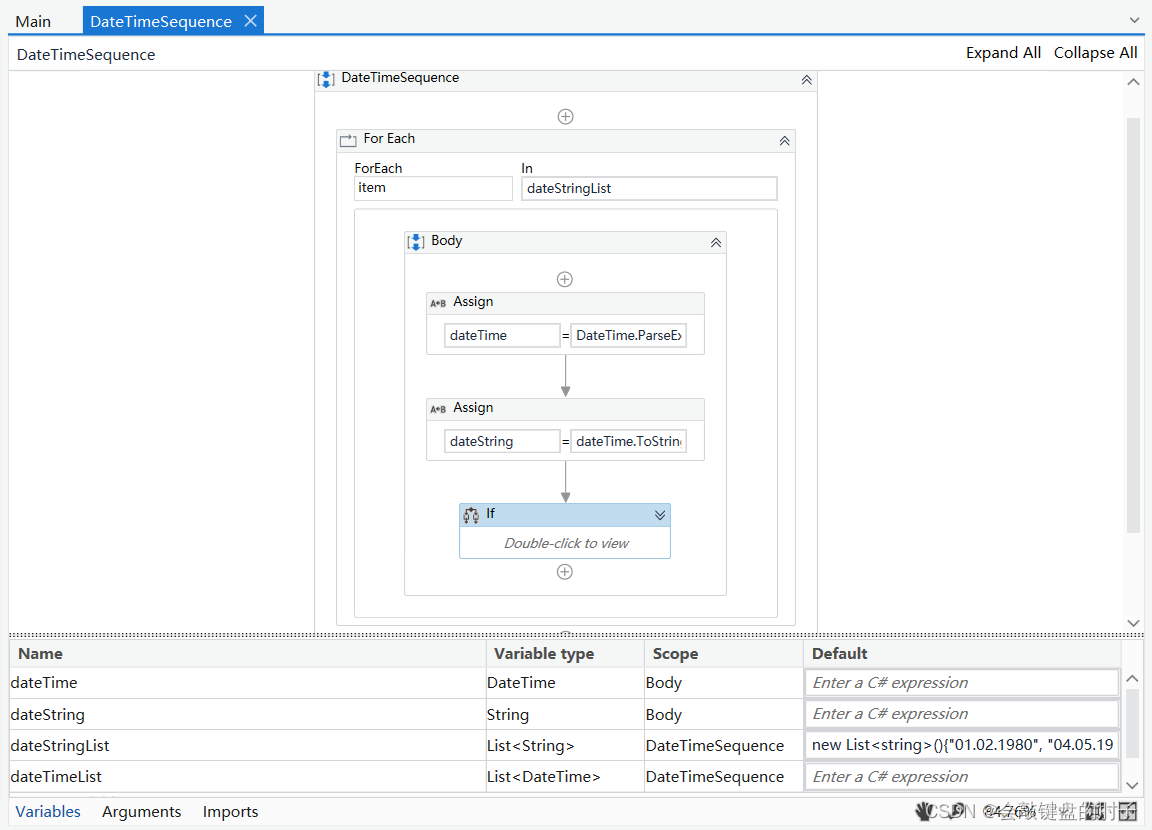
【UiPath2022+C#】UiPath 循环
UE5再次更新!扫描或手动建模面部模型可直接转为绑定好的Metahuman
LeetCode刷题之第74题
【nodejs】第一章:nodejs架构
OpenCV3.0 兼容VS2010与VS2013的问题
LeetCode刷题之第55题
专有宿主机CDH
spark源码-任务提交流程之-5-CoarseGrainedExecutorBackend
TCP/IP四层模型