当前位置:网站首页>Go array and slice
Go array and slice
2022-07-05 13:12:00 【UPythonFish】
List of articles
go Arrays and slices
Array
An array is a collection of elements of the same type , Be similar to python Collection types in . however Go Mixing different types of elements is not allowed in a language , For example, an array of strings and integers .( Of course , If it is interface{} Type array , Can contain any type )
Declaration of arrays
The representation of an array is [n]T.n Represents the number of elements in an array ,T Represents the type of each element . Number of elements n It's also part of the type , In definition , The size of the array is fixed , And can't modify
func main() {
// How to define an array
var a [3]int // Define only without assignment
var a [3]int = [3]int{
4, 5, 6} // [3]int Is the data type of the array
a := [3]int{
4} // [3] 3 The size of the index group , The length of the array cannot be greater than the size of the array
a := [30]int{
28:1} // The array size is 30, The index is 28 Insert data at the location of 1, The remaining values are of value type 0 Value padding
var a = [...]int{
3, 4, 5} // Although the use of ... initialization , But the length is also fixed , Determine the length according to the value
var a =[...]int{
50:99}
fmt.Printf("%T",a) // [51]int
// Use [...] Only this writing method is supported
}
Add :
Numbers , character string , Boolean , Array ----》 Value type ( It's worth having your own 0 value , The number is 0, character string :"" Boolean :false Array : Zero value of element type )
Slicing and map ----> Reference type Zero is nil (None:python All types of null values in are None)
go Value type and reference type
Array modification and looping
func main() {
// Array through the index value and modify the value , But it cannot exceed the index value range
var a [3]int = [3]int{
4, 5, 6}
fmt.Println(a)
a[0] = 99
fmt.Println(a[0]) // 99
// Index based loop
for i:=0;i<len(a);i++{
fmt.Println(a[i])
}
for i:=len(a)-1;i>=0;i--{
fmt.Println(a[i])
}
// Iteration based loop range It's a keyword , Can return a value , One value is the index , You can return two values , The two values are index and value
for i:=range a{
fmt.Println(a[i])
}
for i,value:=range a{
fmt.Println(i,value)
}
}
Multidimensional data
Multidimensional data , Simply put, it is data set data , Follow python The list type in is the same , You can nest... Infinitely , Here is just 2 Layer as an example
var a [3][4]int=[3][4]int{
{
3,3,3,3},{
4,4,4},{
5}}
fmt.Println(a)
// loop ( Two layers of circulation )
for _,value:=range a{
for _,v:=range value{
fmt.Println(v)
}
}
section
Slicing is a convenience created by arrays 、 Flexible and powerful packaging , The slice itself doesn't have any data , They are just applications of existing arrays ( Pointer to array )
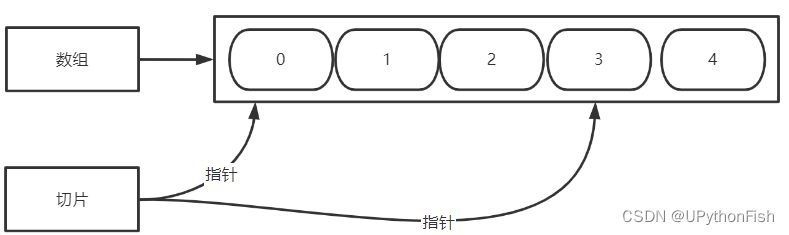
Definition of slice
1. Define an empty slice
var s []int // If there is nothing in the brackets, it is the slice endotype
2. Based on the array , Reference assignment
a:=[10]int{
1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10}
var s []int
// Reference the array from beginning to end to s Two ways of writing
s=a[0:len(a)] // Front closing back opening section
s=[:]
fmt.Printf("s The type is :%T, The value is :%v",s,s) // s The type is :[]int, The value is :[1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10]
3. Define slices and initialize
var s []int=[]int{
2,3,4}
fmt.Println(s)
fmt.Println(len(s)) // The length is 3
fmt.Println(cap(s)) // Capacity is 3
Use of slices
Use is to get and change values through index
a:=[10]int{
1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10}
var s []int
s=[:]
fmt.Println(s[0]) // 1
s[0]=999
fmt.Println(s[100]) // Compile without error , But the executive meeting , Because it exceeds the length of the slice
fmt.Println(s) // [999 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10]
fmt.Println(a) // [999 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10]
You will find that when the slice changes the value , The value of the underlying array will also change accordingly , Always consistent with slice preservation
Conclusion 1: Changes in slices , It will affect the underlying array to change , Empathy , Changes in the underlying array will also affect slice changes
Length and capacity of slices
Arrays have lengths , And the length cannot be changed , Slices also have length , But the length can be changed , And the slice has capacity
a:=[10]int{
1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10}
var s []int=a[0:3] // Front closing back opening section
fmt.Println(s) // [1,2,3]
// The length of the slice , Refers to how long the current slice is
fmt.Println(len(s)) // 3
// The volume of the slice : How much value can this slice save at most , Based on the underlying array
fmt.Println(cap(s)) //cap Built in functions , Calculate the capacity of the slice 10
But here's the thing , The capacity of the slice is not necessarily equal to the length of the underlying array
a:=[10]int{
1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10}
var s []int=a[3:6] // Front closing back opening section
fmt.Println(s) // [4,5,6]
fmt.Println(len(s)) // 3
fmt.Println(cap(s)) // 7
Believe in this , You can also see , The slice capacity is determined by the underlying array , The size of the capacity depends on where the slice starts cutting the array , Capacity = The length of the array - Cut the starting point ( Index value )
make function
Can pass make Function to create a slice ,make The function has three arguments
- The first is type It can also be used to create other types of data
- The second is the length of the slice
- The third is the capacity of slices
var s []int=make([]int,3,4) // Create and assign , But there is no value in it , Default 0 value ,
fmt.Println(s) // [0 0 0]
fmt.Println(len(s)) // The length is 3
fmt.Println(cap(s)) // Capacity is 4
Additional slice
Slicing can be done through append Built in functions add values
var s =make([]int,3,4)
fmt.Println(s) // [0 0 0]
fmt.Println(len(s)) //3
fmt.Println(cap(s)) //4
s=append(s,99)
fmt.Println(s) // [0 0 0 99]
fmt.Println(len(s)) //4
fmt.Println(cap(s)) //4
// When the slice has reached the maximum capacity , If you add , length +1, The capacity is doubled based on the original capacity , Automatic expansion
s=append(s,88)
fmt.Println(s)
fmt.Println(len(s)) // 5
fmt.Println(cap(s)) // 8
So here comes the question , We know from the previous study that , Slicing is based on the reference of the underlying array , How does the underlying array change after adding slices ?
a:=[10]int{
1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10}
s:=a[2:9]
fmt.Println(s)
// Slicing change , The underlying array will change
s[0]=666
fmt.Println(s) //[666 4 5 6 7 8 9]
fmt.Println(a) //[1 2 666 4 5 6 7 8 9 10]
// Array changes , The slice will also change
a[8]=999
fmt.Println(a) //[1 2 666 4 5 6 7 8 999 10]
fmt.Println(s) //[666 4 5 6 7 8 999]
The slice is appended to the critical state , Additional , Arrays are not enough , What changes will happen ( Code on )?
s=append(s,222)
fmt.Println(s) // [666 4 5 6 7 8 999 222]
// The underlying array ? It's going to change
fmt.Println(a) // [1 2 666 4 5 6 7 8 999 222]
You can see , If the underlying array is not enough , Slice and add , It will no longer affect the original array .
go The language will automatically apply for a new array , Size of the original slice capacity 2 times , And the value of the original slice , Copy to the new array , At this point, the slice is separated from the original array , The pointer points to the new array
s=append(s,333)
fmt.Println(s) //[666 4 5 6 7 8 999 222 333]
fmt.Println(len(s)) //9
fmt.Println(cap(s)) //16
Multi slice
There are multidimensional arrays in the array , Slice based on array , There are also multidimensional slices
var s [][]int
// Define and initialize
var s [][]int=[][]int{
{
1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1},{
2,2,},{
3,3,3,3}}
fmt.Println(s)
fmt.Println(len(s)) // 3 A slice in the inner layer counts as a value
fmt.Println(cap(s)) // 3
// adopt make initialization
var s [][]int=make([][]int,3,4)
// Slice the inner layer , Not initialized , Just use the inner slice , All slices in the inner layer should be initialized
fmt.Println(s[0]) // [] section , This slice is not initialized
// fmt.Println(s[0][0]) // Report errors
s[0]=make([]int,5,6) // Initialize the inner slice
s[0][0]=99
fmt.Println(s[0])
fmt.Println(s[0][5]) // Slice out of bounds , Although the capacity is 6, But it hasn't been used yet , You can't take
// Circular multidimensional slice ( Based on Index , Based on iteration )
var s [][]int=[][]int{
{
1,1},{
2,2},{
3,3,3,3}}
for i:=0;i<len(s);i++{
for j:=0;j<len(s[i]);j++{
fmt.Println(s[i][j])
}
}
for _,v:=range s{
for _,v1:=range v{
fmt.Println(v1)
}
}
copy section
Take a slice , Copy to another slice , The usage scenarios are as follows ( Memory optimization scheme )
var a [10000]int=[10000]int{
3,4,5}
fmt.Println(a)
s:=a[:3]
fmt.Println(s)
// Just use s, The bottom layer is based on a large array , Memory usage is very high
// When , You can put the s copy To another slice based on a small array
s1:=make([]int,3,3)
fmt.Println(s1) // [0 0 0]
copy(s1,s)
fmt.Println(s1) //[3 4 5] , I'll use it later s1 operation , Save memory
But there is also a problem , The two slices are the same length , Sure copy, What if it's not the same length ?
s1:=make([]int,5,5)
s2:=make([]int,2,2)
copy(s1,s)
copy(s2,s)
fmt.Println(s1) // [3 4 5 0 0]
fmt.Println(s2) // [3 4]
It's obvious that , If the capacity is not enough, just copy part , If the capacity exceeds, it will be zero Type data filling
边栏推荐
猜你喜欢
MSTP and eth trunk
初次使用腾讯云,解决只能使用webshell连接,不能使用ssh连接。
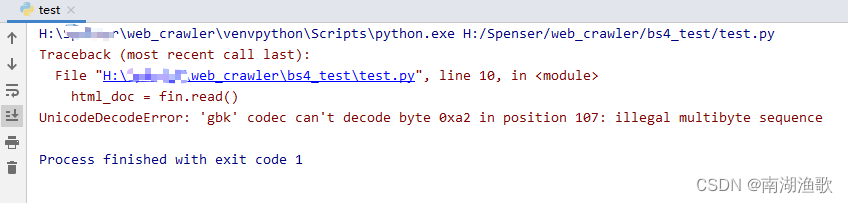
Solve Unicode decodeerror: 'GBK' codec can't decode byte 0xa2 in position 107
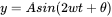
Flutter 绘制波浪移动动画效果,曲线和折线图

国际自动机工程师学会(SAE International)战略投资几何伙伴
leetcode:221. 最大正方形【dp状态转移的精髓】
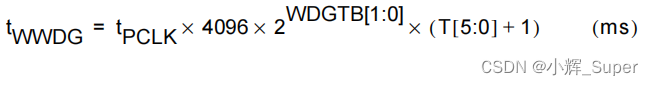
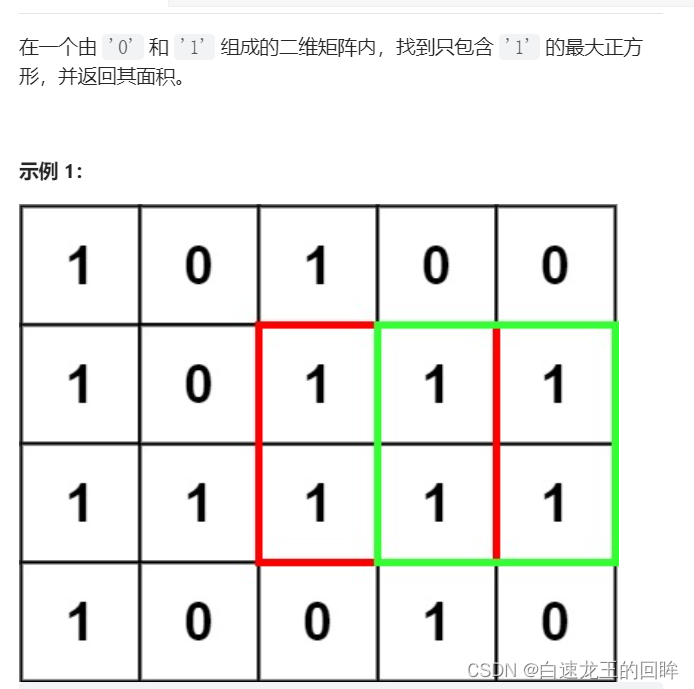
Pandora IOT development board learning (HAL Library) - Experiment 7 window watchdog experiment (learning notes)

Asemi rectifier bridge hd06 parameters, hd06 pictures, hd06 applications
SAP SEGW 事物码里的 ABAP Editor
Overflow toolbar control in SAP ui5 view
随机推荐
Overflow toolbar control in SAP ui5 view
阿里云SLB负载均衡产品基本概念与购买流程
Write macro with word
AVC1与H264的区别
Principle and configuration of RSTP protocol
Reflection and imagination on the notation like tool
SAP SEGW 事物码里的 ABAP Editor
LeetCode20.有效的括号
函数传递参数小案例
DataPipeline双料入选中国信通院2022数智化图谱、数据库发展报告
Get to know linkerd project for the first time
山东大学暑期实训一20220620
A deep long article on the simplification and acceleration of join operation
About the single step debugging of whether SAP ui5 floating footer is displayed or not and the benefits of using SAP ui5
The solution of outputting 64 bits from printf format%lld of cross platform (32bit and 64bit)
【Hot100】33. 搜索旋转排序数组
JXL notes
uni-app开发语音识别app,讲究的就是简单快速。
Developers, is cloud native database the future?
Rocky basics 1