当前位置:网站首页>HTTP cache, forced cache, negotiated cache
HTTP cache, forced cache, negotiated cache
2022-07-06 07:33:00 【Let the code fly 1926】
What is caching ?
When the browser loads a web page , You need to load some resources ,html,css,js,img..., All requests are required for the first time , When the second time , The third time I visited this page , In fact, you can not send the request repeatedly , You can use http Cache policy , Make the web page load faster .
Mandatory cache
The browser sends a request to the server , The server should return to the client resource , But the client wants to cache these resources , You need to set the response header cache-control:max-age=31536000, In this way, the browser will cache resources , Check it the next time you ask max-age Has it expired , If it doesn't expire , Just take resources directly , If it's out of date , Just send a request , If you don't use caching, use no-cache
Negotiate the cache
Using negotiation cache , The browser makes a request for the first time , The server will return resources and resources identification , Then put the resources locally , At the next request , Send the request together with the resource ID to the server , The server determines the ID sent and the latest resource ID on the server , If it's the latest , The server returns 304 Status code , Get resources directly from the cache , If it's not the latest , Just go back to 200 Status code and the latest resource and resource identification
Resource identification :
There are two kinds of , One is last-Modified: Last modification time of resource , It's only accurate to seconds , The key name when sending the request is :if-Modified-Since
One is ETag: The unique string corresponding to the resource , The key name when sending the request is :if-None-Match, priority of use ETag
边栏推荐
- GET/POST/PUT/PATCH/DELETE含义
- TypeScript void 基础类型
- Relevant introduction of clip image
- [dictionary tree] [trie] p3879 [tjoi2010] reading comprehension
- Pre knowledge reserve of TS type gymnastics to become an excellent TS gymnastics master
- word怎么只删除英语保留汉语或删除汉语保留英文
- Multithreading and concurrent programming (2)
- Fundamentals of C language 9: Functions
- Twelve rules for naming variables
- TypeScript 函数定义
猜你喜欢
(4) Web security | penetration testing | network security web site source code and related analysis
The way to learn go (I) the basic introduction of go to the first HelloWorld

Compliance and efficiency, accelerate the digital transformation of pharmaceutical enterprises, and create a new document resource center for pharmaceutical enterprises

学go之路(一)go的基本介绍到第一个helloworld
TS 类型体操 之 循环中的键值判断,as 关键字使用
杰理之开发板上电开机,就可以手机打开 NRF 的 APP【篇】

Google可能在春节后回归中国市场。

Week6 weekly report

Force buckle day31
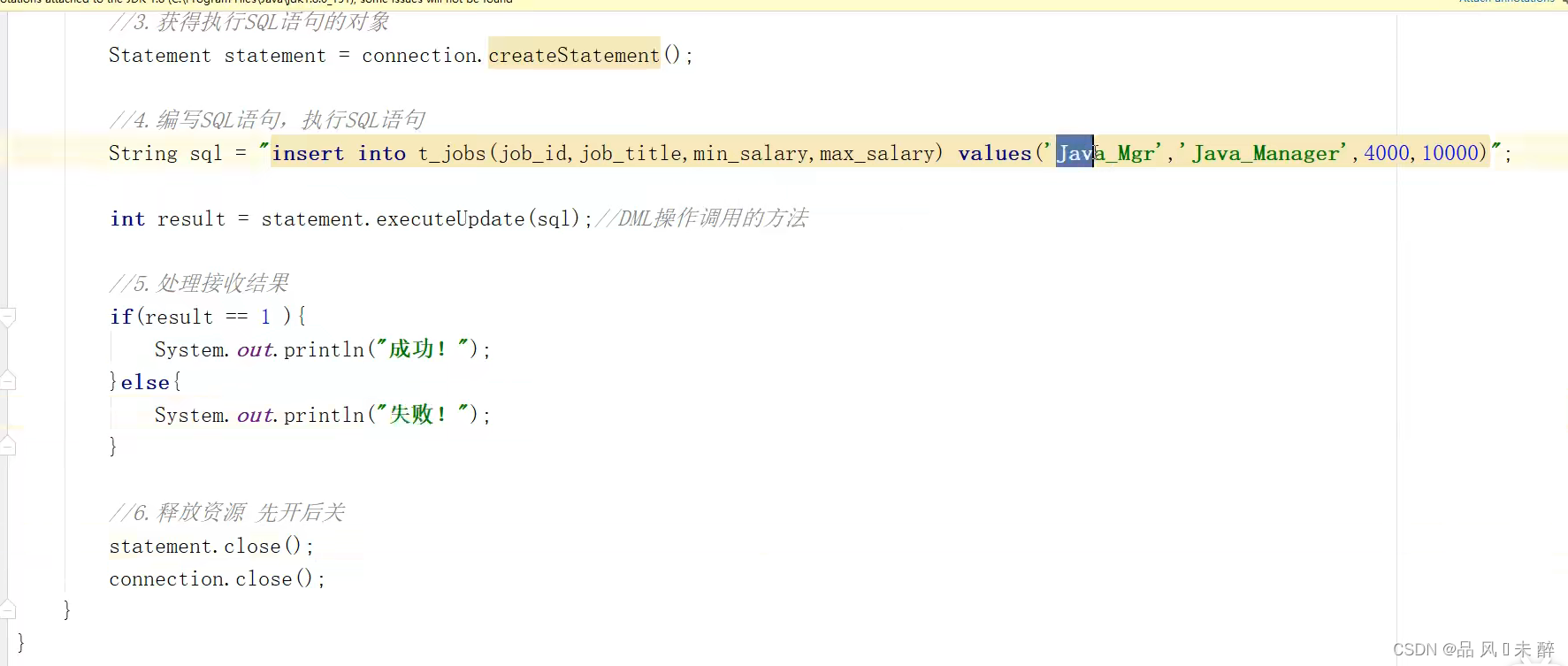
JDBC learning notes
随机推荐
How to configure GUI guide development environment
Introduction to the basics of network security
杰理之需要修改 gatt 的 profile 定义【篇】
Compliance and efficiency, accelerate the digital transformation of pharmaceutical enterprises, and create a new document resource center for pharmaceutical enterprises
TS类型体操 之 字符串的妙用
How MySQL merges data
opencv学习笔记八--答题卡识别
学go之路(二)基本类型及变量、常量
GET/POST/PUT/PATCH/DELETE含义
Games101 Lesson 7 shading 1 Notes
Chrome view page FPS
TypeScript 函数定义
TypeScript 可索引类型
洛谷P4127 [AHOI2009]同类分布 题解
Crawling exercise: Notice of crawling Henan Agricultural University
Force buckle day31
Wonderful use of TS type gymnastics string
After the hot update of uniapp, "mismatched versions may cause application exceptions" causes and Solutions
TypeScript 变量作用域
How to delete all the words before or after a symbol in word