当前位置:网站首页>UDP programming
UDP programming
2022-07-06 22:30:00 【Worth the trip -rui】
kehUDP Programming —QQ The chat room
summary :
UDP yes User Datagram Protocol -- User datagram protocol , Is a simple datagram oriented transport layer protocol , It's a connectionless protocol .UDP No reliable transmission , It just passes the application to IP The datagram of the layer is sent out , But there is no guarantee that they will reach their destination . because UDP There is no need to establish a connection between the client and the server before transmitting datagrams , And there is no mechanism such as overtime retransmission , So the transmission speed is very fast .d
characteristic :
- The abstraction of mail system service pattern
- Each group carries a complete destination address
- There is no need to establish a connection before sending data
- Don't check the order of packets , There is no guarantee of the order of the groups
- No recovery and retransmission of packet errors
- The reliability of data transmission is not guaranteed
In the case of poor network quality ,UDP Protocol packet loss will be more serious . But because of UDP Characteristics of :
It is not a connection protocol , Therefore, the consumption of resources is small , The advantage of fast processing speed , So usually audio , Video and ordinary data are used in transmission UDP More , Because even if they occasionally lose one or two packets , It will not have much impact on the acceptance results . For example, we chat with ICQ and QQ Just use UDP agreement
UDP programming C/S framework
[ Failed to transfer the external chain picture , The origin station may have anti-theft chain mechanism , It is suggested to save the pictures and upload them directly (img-KF3AV12z-1656939566349)(D:\ picture \image-20220704180859668.png)]
Compared to the letter model . The client is equivalent to the sender , If you want to succeed in sending a letter , The address of the other party must be written on the envelope
UDP Client program
socket Create socket for communication
#include<sys/socket.h>
int socket(int domain,int type,int protocol);
Parameters :domain Protocol family : agreement AF_INET IPv4 AF_INET6 IPv6
type type :SOCK_DGRAM(UDP Socket ),SOCK_STREAM(TCP Socket ),SOCK_RAW( Raw socket )
protocol Type of agreement :(0,IPPROTO_TCP,IPPROTO_UDP)
Return value :
>0 File descriptor for communication
<0 Create failure
sendto() send out
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/socket.h>
ssize_t sendto(int sockfd,// Socket
const void*buf,// Send data buffer
size_t nbytes,// The size of the send data buffer
int flags,// It's usually 0
const struct sockaddr*to,// Pointer to the destination host address structure
socklen_t addrlen)//to The length of the pointed content
function : towards to Specified in the structure pointer ip, send out UDP data , Can send 0 Of length UDP Data packets
Return value :
success : Length of data sent
Failure :-1
IPv4 Address structure
Deposit IPv4 All address information of protocol communication
#include<netinet/in.h>
struct sockaddr_in {
sa_family_t sin_family;//2 byte agreement AF_INET AF_INET6
in_port_t sin_port;//2 byte port
struct in_addr sin_addr;//4 byte IP Address (32 Bit unsigned integer )
char sin_zero[8]//8 byte Full write 0
};
struct in_addr:
{
in_addr_t s_addr;//4 byte
};
Universal address structure ( Type conversion )
struct sockaddr{
sa_family_t sa_family;//2 byte
char sa_data[14]//14 byte
}
DUP Client programming process , It's a little similar to the process of writing a letter :
Find a postal worker (socket())----- The envelope is addressed and the contents of the letter are posted (sendto())------ The other party accepts (recvform())----- Call it a day (close())
recvfrom() received
ssize_t recvfrom(int sockfd,// Socket
void *buf,// Accept data buffer
size_t nbytes,// Accept the size of the data buffer
int flags,// Socket flag ( Commonly used 0)
struct sockaddr*from,// Pointer to source address structure , The source from which the data is stored
socklen_t*addrlen)//from The length of the content
function : Accept UDP data , And save the source address information in from In the directed structure , By default , If you don't get the data , This function will block , Until the data comes
The client program sends and accepts
#include<stdio.h>
#include<string.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<unistd.h>
#include<sys/socket.h>
#include<netinet/in.h>
#include<arpa/inet.h>
int main()
{
unsigned short port=8080;// Server port
char*server_ip="192.168.1.101";// The server ip Address
int sockfd;
sockfd=socket(AF_INET,SOCK_DGRAM,0);// establish UDP Set word
//udp client Send a message To server
// Define a IPv4 Address structure Store the address information of the server ( Destination host )
struct sockaddr_in ser_addr;
memset(&ser_addr,0,sizeof(ser_addr));
ser_addr.sin_family=AF_INET;
ser_addr.sin_port=htons(port);// Server port
// Server's ip Address
inet_pton(AF_INET,server_ip,&ser_addr.sin_addr.s_addr);
// send data
sendto(sockfd,"hello word",strlen("hello word"),0,(struct sockaddr*)&ser_addr,sizeof(ser_addr));
// receive data
// Define a IPv4 Address structure Store the sender's information
while(1)
{
struct sockaddr_in from_addr;
socklen_t from_len=sizeof(from_addr);
unsigned char buf[1500]="";
int len=recvfrom(sockfd,buf,sizeof(buf),0,(struct sockaddr*)&from_addr,&from_len);
char ip[16]="";
inet_ntop(AF_INET,&from_addr.sin_addr.s_addr,ip,16);
printf(" The news comes from %s %hu---->",ip,ntohs(from_addr.sin_port));
printf("len:%d msg:%s\n",len,buf);
}
// Close socket
close(sockfd);
return 0;
}
UDP matters needing attention :
- Local ip, Local port ( Who am I )
- Purpose ip, Destination port ( To whom )
- In the client's code , We only set the purpose ip, Destination port
- Local of client IP, Local port We call sendto When Linux The bottom layer of the system automatically assigns ; The way to allocate ports is random allocation , And every time the system runs port Dissimilarity
bind to udp Socket binding is fixed port,ip Information
#include<sys/socket.h>
int bind(int socket,const struct sockaddr*address)
socklen_t address_len
Return value :
success :0
Failure is -1
UDP Programming –QQ
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<sys/types.h>
#include<sys/socket.h>
#include<netinet/in.h>
#include<string.h>
#include<pthread.h>
#include<arpa/inet.h>
#include<unistd.h>
void *send_function(void *arg)
{
// Get socket
int sockfd=*(int*)arg;
// Define destination address
struct sockaddr_in dst_addr;
bzero(&dst_addr,sizeof(dst_addr));
dst_addr.sin_family=AF_INET;
while(1)
{
// Get keyboard input
char buf[128]="";
fgets(buf,sizeof(buf),stdin);
buf[strlen(buf)-1]=0;
// Judge whether it is ip port
//sayto ip port
if(strncmp(buf,"sayto",5)==0)
{
char ip[16]="";
unsigned short port=0;
sscanf(buf,"sayto %s %hu",ip,&port);
dst_addr.sin_port=htons(port);
inet_pton(AF_INET,ip,&dst_addr.sin_addr.s_addr);
continue;
}
else
{
sendto(sockfd,buf,strlen(buf),0,(struct sockaddr*)&dst_addr,sizeof(dst_addr));
if(strcmp(buf,"bye")==0)
{
break;
}
}
}
return NULL;
}
void *recv_function(void *arg)
{
int sockfd=*(int*)arg;
while(1)
{
struct sockaddr_in from_addr;
socklen_t from_len=sizeof(from_addr);
unsigned char buf[1500]="";
char ip[16]="";
int len=recvfrom(sockfd,buf,sizeof(buf),0,(struct sockaddr*)&from_addr,&from_len);
printf("%s %hu:%s\n",inet_ntop(AF_INET,&from_addr.sin_addr.s_addr,ip,16),ntohs(from_addr.sin_port),buf);
if(strcmp(buf,"bye")==0)
{
break;
}
}
return NULL;
}
int main(int argc,char const*argv[])
{
// Judgment parameters ,./a.out 8080
if(argc!=2)
{
printf("./a.out 8080\n");
return 0;
}
// establish udp Socket
int sockfd=socket(AF_INET,SOCK_DGRAM,0);
//bind Bind fixed ports ,ip
struct sockaddr_in my_addr;
bzero(&my_addr,sizeof(my_addr));
my_addr.sin_family=AF_INET;
my_addr.sin_port=htons(atoi(argv[1]));
my_addr.sin_addr.s_addr=htonl(INADDR_ANY);
bind(sockfd,(struct sockaddr*)&my_addr,sizeof(my_addr));
// Create the sending thread
pthread_t send_tid;
pthread_create(&send_tid,NULL,send_function,&sockfd);
// Create a receiving thread
pthread_t recv_tid;
pthread_create(&recv_tid,NULL,recv_function,&sockfd);
pthread_join(send_tid,NULL);
pthread_join(recv_tid,NULL);
// Close socket
close(sockfd);
return 0;
}
ead_t send_tid;
pthread_create(&send_tid,NULL,send_function,&sockfd);
// Create a receiving thread
pthread_t recv_tid;
pthread_create(&recv_tid,NULL,recv_function,&sockfd);
pthread_join(send_tid,NULL);
pthread_join(recv_tid,NULL);
// Close socket
close(sockfd);
return 0;
}
边栏推荐
- 0 basic learning C language - digital tube
- Insert sort and Hill sort
- CCNA Cisco network EIGRP protocol
- Lora sync word settings
- Config:invalid signature solution and troubleshooting details
- qt quick项目offscreen模式下崩溃的问题处理
- 空结构体多大?
- void关键字
- 自制J-Flash烧录工具——Qt调用jlinkARM.dll方式
- RESNET rs: Google takes the lead in tuning RESNET, and its performance comprehensively surpasses efficientnet series | 2021 arXiv
猜你喜欢
Installation and use of labelimg
C# 三种方式实现Socket数据接收
2022-07-04 mysql的高性能数据库引擎stonedb在centos7.9编译及运行
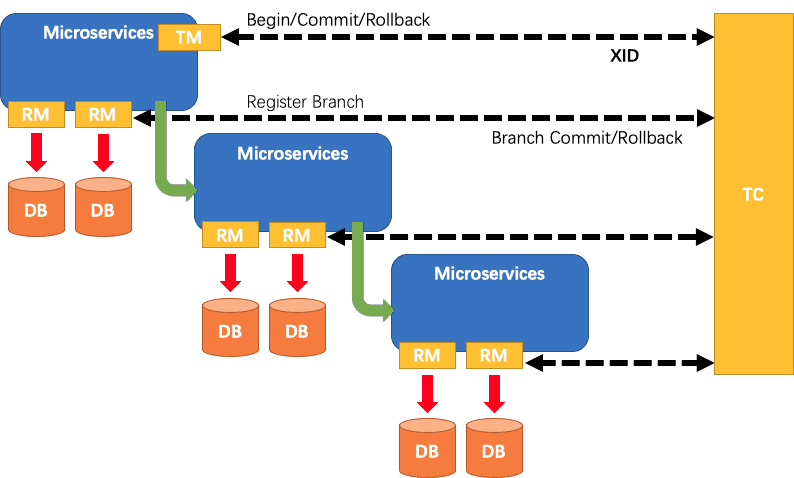
Seata aggregates at, TCC, Saga and XA transaction modes to create a one-stop distributed transaction solution
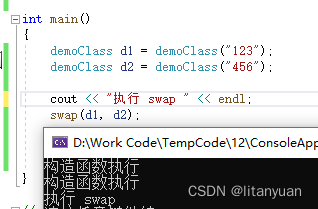
自定义 swap 函数
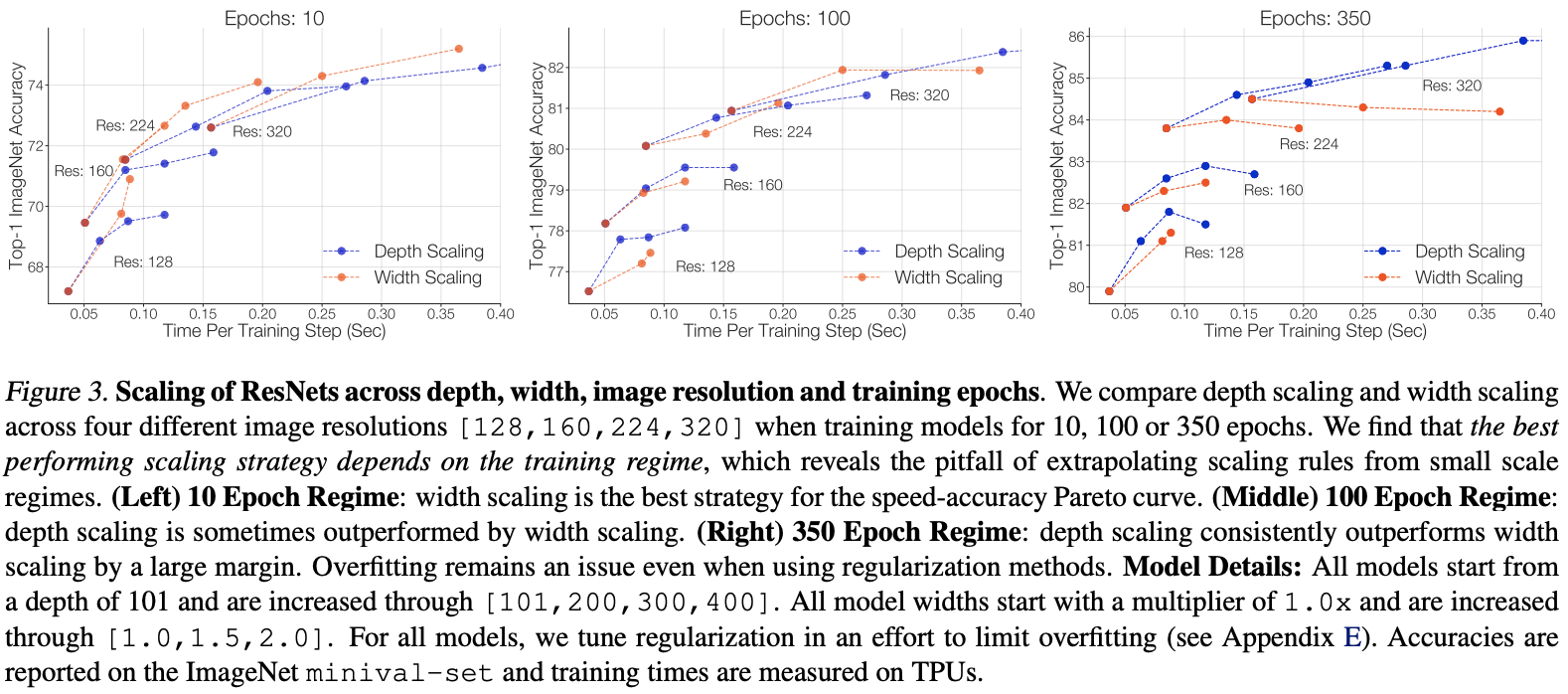
ResNet-RS:谷歌领衔调优ResNet,性能全面超越EfficientNet系列 | 2021 arxiv

重磅新闻 | Softing FG-200获得中国3C防爆认证 为客户现场测试提供安全保障
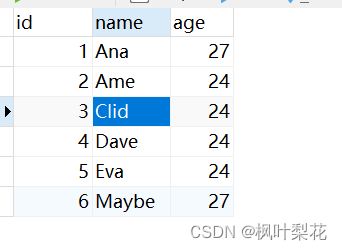
Export MySQL table data in pure mode
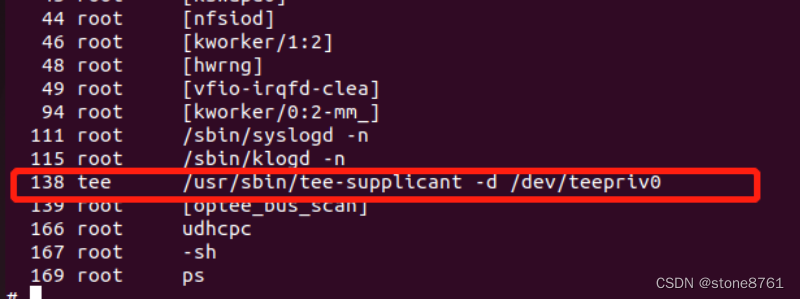
基於 QEMUv8 搭建 OP-TEE 開發環境
Web APIs DOM time object
随机推荐
小程序系统更新提示,并强制小程序重启并使用新版本
0 basic learning C language - digital tube
二分图判定
Advantages of link local address in IPv6
柔性数组到底如何使用呢?
2022-07-05 use TPCC to conduct sub query test on stonedb
软考高级(信息系统项目管理师)高频考点:项目质量管理
MySQL约束的分类、作用及用法
2022-07-05 stonedb sub query processing parsing time analysis
做国外LEAD2022年下半年几点建议
Applet system update prompt, and force the applet to restart and use the new version
Classic sql50 questions
变量与“零值”的比较
Classification, function and usage of MySQL constraints
CocosCreator+TypeScripts自己写一个对象池
AI enterprise multi cloud storage architecture practice | Shenzhen potential technology sharing
【雅思口语】安娜口语学习记录part1
Leetcode: interview question 17.24 Maximum cumulative sum of submatrix (to be studied)
如何实现文字动画效果
ResNet-RS:谷歌领衔调优ResNet,性能全面超越EfficientNet系列 | 2021 arxiv