当前位置:网站首页>Basic structure of PostgreSQL - table
Basic structure of PostgreSQL - table
2022-07-04 21:52:00 【Hua Weiyun】
How to be in PostgreSQL Is equivalent to Oracle DESCRIBE TABLE The order of ( Use psql command )?
#1 floor
DESCRIBE TABLE Of psql The equivalent term is \\d table .
For more details , Please see the PostgreSQL Manual psql part .
#2 floor
You can use psql The slash command performs this operation :
\d myTable describe tableIt also applies to other objects :
\d myView describe view \d myIndex describe index \d mySequence describe sequencesource : faqs.org
#3 floor
Give it a try ( stay psql In command line tools ):
\d+ tablenameFor more information , Please see the manual .
#4 floor
except PostgreSQL The way (\\ d'something' or \\ dt'table' or \\ ds'sequence' etc. )
SQL Standard way , As shown in the figure ad locum :
select column_name, data_type, character_maximum_lengthfrom INFORMATION_SCHEMA.COLUMNS where table_name = '<name of table>';Many database engines support it .
#5 floor
If you want to query from instead of psql Get it , Then you can query the directory schema . This is a complex query that performs this operation :
SELECT f.attnum AS number, f.attname AS name, f.attnum, f.attnotnull AS notnull, pg_catalog.format_type(f.atttypid,f.atttypmod) AS type, CASE WHEN p.contype = 'p' THEN 't' ELSE 'f' END AS primarykey, CASE WHEN p.contype = 'u' THEN 't' ELSE 'f' END AS uniquekey, CASE WHEN p.contype = 'f' THEN g.relname END AS foreignkey, CASE WHEN p.contype = 'f' THEN p.confkey END AS foreignkey_fieldnum, CASE WHEN p.contype = 'f' THEN g.relname END AS foreignkey, CASE WHEN p.contype = 'f' THEN p.conkey END AS foreignkey_connnum, CASE WHEN f.atthasdef = 't' THEN d.adsrc END AS defaultFROM pg_attribute f JOIN pg_class c ON c.oid = f.attrelid JOIN pg_type t ON t.oid = f.atttypid LEFT JOIN pg_attrdef d ON d.adrelid = c.oid AND d.adnum = f.attnum LEFT JOIN pg_namespace n ON n.oid = c.relnamespace LEFT JOIN pg_constraint p ON p.conrelid = c.oid AND f.attnum = ANY (p.conkey) LEFT JOIN pg_class AS g ON p.confrelid = g.oid WHERE c.relkind = 'r'::char AND n.nspname = '%s' -- Replace with Schema name AND c.relname = '%s' -- Replace with table name AND f.attnum > 0 ORDER BY number;It's very complicated , But it does show you PostgreSQL Function and flexibility of system directory , And you should gradually master pg_catalog ;-). Make sure to change %s. The first is mode , The second is the table name .
#6 floor
You can Use the asterisk \\d *search pattern * To find the table that matches the search pattern you are interested in .
#7 floor
You can use :
SELECT attname FROM pg_attribute,pg_class WHERE attrelid=pg_class.oid AND relname='TableName' AND attstattarget <>0; #8 floor
Except for the command line that has been found \\d+ <table_name> , You can also use it info -schema adopt info_schema.columns find information .
SELECT *FROM info_schema.columnsWHERE table_schema = 'your_schema'AND table_name = 'your_table'#9 floor
Use the following SQL sentence
SELECT DATA_TYPE FROM INFORMATION_SCHEMA.COLUMNS WHERE table_name = 'tbl_name' AND COLUMN_NAME = 'col_name'If you replace tbl_name and col_name, It will show the data type of the specific column you are looking for .
#10 floor
You can also use the following query to check
Select * from schema_name.table_name limit 0;Example : My watch has 2 Column name and password . Provide the following screenshots .
* Use PG admin3
#11 floor
Use this command \d table namelike \d queuerecords Table "public.queuerecords" Column | Type | Modifiers-----------+-----------------------------+----------- id | uuid | not null endtime | timestamp without time zone | payload | text | queueid | text | starttime | timestamp without time zone | status | text |#12 floor
The best way to describe a table , For example, columns , type , Column modifier, etc .
\d+ tablename or \d tablename#13 floor
/ dt It's a comma , It lists all the tables that exist in the database . Use
/ d Command and / d + We can get the details of the table . The system will look like
* / d table_name( or )\\ d + table_name
#14 floor
This change of query ( As stated in other answers ) It works for me .
SELECT COLUMN_NAMEFROM information_schema.COLUMNSWHERE TABLE_NAME = 'city';Here is a detailed introduction : http : //www.postgresqltutorial.com/postgresql-describe-table/
#15 floor
I made the following script for getting the table schema .
'CREATE TABLE ' || 'yourschema.yourtable' || E'\n(\n' ||array_to_string(array_agg(' ' || column_expr), E',\n') || E'\n);\n'from(SELECT ' ' || column_name || ' ' || data_type || coalesce('(' || character_maximum_length || ')', '') || case when is_nullable = 'YES' then ' NULL' else ' NOT NULL' end as column_exprFROM information_schema.columnsWHERE table_schema || '.' || table_name = 'yourschema.yourtable'ORDER BY ordinal_position) column_list;#16 floor
stay MySQL in ,DESCRIBE table_name
stay PostgreSQL in ,\\ d table_name
perhaps , You can use the following long commands :
SELECT a.attname AS Field, t.typname || '(' || a.atttypmod || ')' AS Type, CASE WHEN a.attnotnull = 't' THEN 'YES' ELSE 'NO' END AS Null, CASE WHEN r.contype = 'p' THEN 'PRI' ELSE '' END AS Key, (SELECT substring(pg_catalog.pg_get_expr(d.adbin, d.adrelid), '\'(.*)\'') FROM pg_catalog.pg_attrdef d WHERE d.adrelid = a.attrelid AND d.adnum = a.attnum AND a.atthasdef) AS Default, '' as ExtrasFROM pg_class c JOIN pg_attribute a ON a.attrelid = c.oid JOIN pg_type t ON a.atttypid = t.oid LEFT JOIN pg_catalog.pg_constraint r ON c.oid = r.conrelid AND r.conname = a.attnameWHERE c.relname = 'tablename' AND a.attnum > 0ORDER BY a.attnum#17 floor
In postgres \d is used to describe the table structure.e.g. \d schema_name.table_name;this command will provide you the basic info of table such as, columns, type and modifiers.If you want more info about table use\d+ schema_name.table_name;this will give you extra info such as, storage, stats target and description#18 floor
To improve another answer SQL Inquire about ( great !), This is a modified query . It also includes constraint names , Inherit information and data types decomposed into components ( type , length , precision , Decimal digit ). It also filters out deleted columns ( The database still exists ).
SELECT n.nspname as schema, c.relname as table, f.attname as column, f.attnum as column_id, f.attnotnull as not_null, f.attislocal not_inherited, f.attinhcount inheritance_count, pg_catalog.format_type(f.atttypid,f.atttypmod) AS data_type_full, t.typname AS data_type_name, CASE WHEN f.atttypmod >= 0 AND t.typname <> 'numeric'THEN (f.atttypmod - 4) --first 4 bytes are for storing actual length of data END AS data_type_length, CASE WHEN t.typname = 'numeric' THEN (((f.atttypmod - 4) >> 16) & 65535) END AS numeric_precision, CASE WHEN t.typname = 'numeric' THEN ((f.atttypmod - 4)& 65535 ) END AS numeric_scale, CASE WHEN p.contype = 'p' THEN 't' ELSE 'f' END AS is_primary_key, CASE WHEN p.contype = 'p' THEN p.conname END AS primary_key_name, CASE WHEN p.contype = 'u' THEN 't' ELSE 'f' END AS is_unique_key, CASE WHEN p.contype = 'u' THEN p.conname END AS unique_key_name, CASE WHEN p.contype = 'f' THEN 't' ELSE 'f' END AS is_foreign_key, CASE WHEN p.contype = 'f' THEN p.conname END AS foreignkey_name, CASE WHEN p.contype = 'f' THEN p.confkey END AS foreign_key_columnid, CASE WHEN p.contype = 'f' THEN g.relname END AS foreign_key_table, CASE WHEN p.contype = 'f' THEN p.conkey END AS foreign_key_local_column_id, CASE WHEN f.atthasdef = 't' THEN d.adsrc END AS default_valueFROM pg_attribute f JOIN pg_class c ON c.oid = f.attrelid JOIN pg_type t ON t.oid = f.atttypid LEFT JOIN pg_attrdef d ON d.adrelid = c.oid AND d.adnum = f.attnum LEFT JOIN pg_namespace n ON n.oid = c.relnamespace LEFT JOIN pg_constraint p ON p.conrelid = c.oid AND f.attnum = ANY (p.conkey) LEFT JOIN pg_class AS g ON p.confrelid = g.oid WHERE c.relkind = 'r'::char AND f.attisdropped = false AND n.nspname = '%s' -- Replace with Schema name AND c.relname = '%s' -- Replace with table name AND f.attnum > 0 ORDER BY f.attnum;#19 floor
This should be the solution :
SELECT * FROM information_schema.columnsWHERE table_schema = 'your_schema' AND table_name = 'your_table'边栏推荐
- Cadeus has never stopped innovating. Decentralized edge rendering technology makes the metauniverse no longer far away
- 2022 version of stronger jsonpath compatibility and performance test (snack3, fastjson2, jayway.jsonpath)
- MongoDB中的索引操作总结
- Jerry added the process of turning off the touch module before turning it off [chapter]
- 应用实践 | 蜀海供应链基于 Apache Doris 的数据中台建设
- Application practice | Shuhai supply chain construction of data center based on Apache Doris
- 迈动互联中标北京人寿保险
- 文件读取写入
- Jerry's ad series MIDI function description [chapter]
- QT—绘制其他问题
猜你喜欢
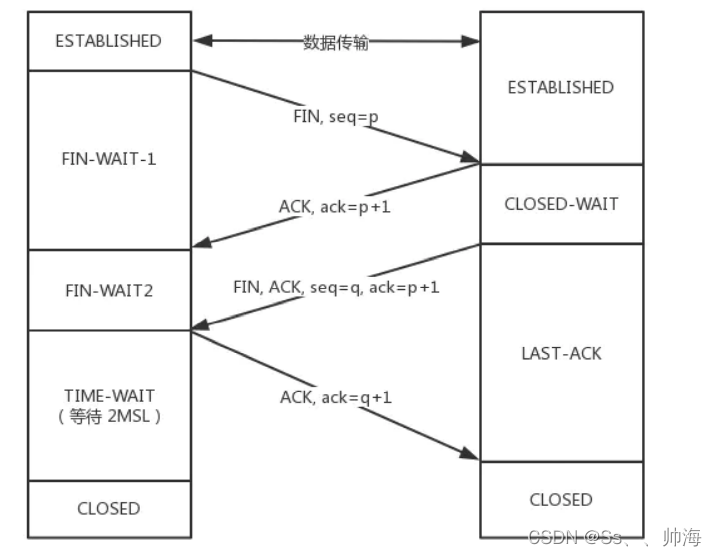
TCP三次握手,四次挥手,你真的了解吗?
![Compréhension approfondie du symbole [langue C]](/img/4b/26cf10baa29eeff08101dcbbb673a2.png)
Compréhension approfondie du symbole [langue C]
![[optimtool.unconstrained] unconstrained optimization toolbox](/img/ef/65379499df205c068ee9bc9df797ac.png)
[optimtool.unconstrained] unconstrained optimization toolbox

Exclusive interview of open source summer | new committer Xie Qijun of Apache iotdb community

创客思维在高等教育中的启迪作用
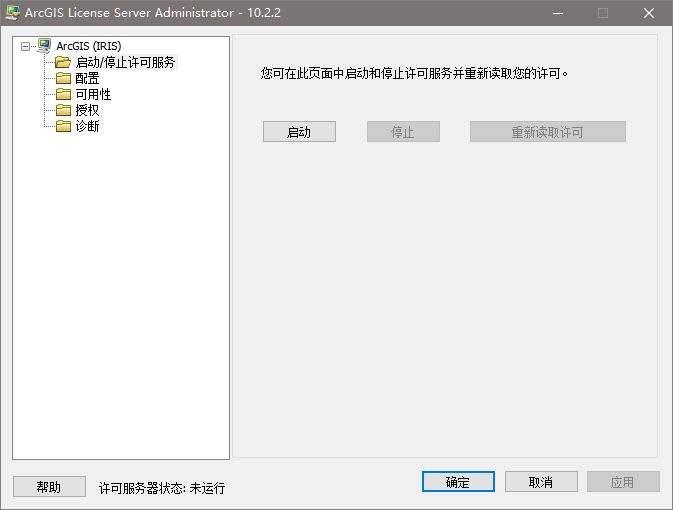
Arcgis 10.2.2 | arcgis license server无法启动的解决办法
Sorting and sharing of selected papers, systems and applications related to the most comprehensive mixed expert (MOE) model in history

解析steam教育中蕴含的众创空间
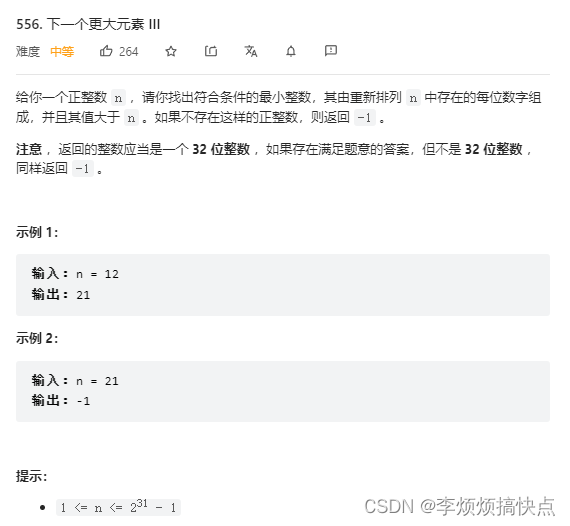
Daily question-leetcode556-next larger element iii-string-double pointer-next_ permutation
QT - plot other problems
随机推荐
From repvgg to mobileone, including mobileone code
Jerry's ad series MIDI function description [chapter]
flink1.13 sql基础语法(一)DDL、DML
GTEST from ignorance to proficiency (4) how to write unit tests with GTEST
Analyzing the maker space contained in steam Education
How to remove the black dot in front of the title in word document
vim 从嫌弃到依赖(23)——最后的闲扯
Go language loop statement (3 in Lesson 10)
EhLib 数据库记录的下拉选择
奋斗正当时,城链科技战略峰会广州站圆满召开
minidom 模块写入和解析 XML
Super detailed tutorial, an introduction to istio Architecture Principle and practical application
Jerry's ad series MIDI function description [chapter]
AcWing 2022 每日一题
CloudCompare&Open3D DBSCAN聚类(非插件式)
什么是商业智能(BI),就看这篇文章足够了
Analysis of maker education technology in the Internet Era
MongoDB聚合操作总结
TCP shakes hands three times and waves four times. Do you really understand?
bizchart+slider实现分组柱状图
