当前位置:网站首页>【数据库】事务的四大特性<详解>
【数据库】事务的四大特性<详解>
2022-08-02 03:33:00 【Money、坤】
数据库事务
1.概念
事务是应用程序中一些列严密的操作,所有操作要么全部成功执行,要么全部执行失败。
2.事务的四大特性
- 原子性(Atomicity)
业务动作对应的SQL应该是一个整体,不可以再拆分,针对数据的修改是能是要么全部成功执行们要么全部执行失败。 - 一致性(Consistency)
数据的一致性体现在两个方面:
①利用数据库的一些特性来保证部分一致性需求:比如声明某个列为NOT NULL 来拒绝NULL值得插入等。
②绝大部分还是需要我们程序员在编写业务代码的时候来保证。 - 隔离性(Isolation)
当有多个DBMS的用户,同时对数据进行增删查改时,用户之间的操作是相对独立的,一个用户的操作对其他用户而言是不可见的。 - 持久性(Durability)
一个事务一旦提交成功,对数据库中的数据的改变是持久性的。
3.如何使用事务
- 方式一 数据库使用事务
--开启事务
START TRANSACTION;
--执行sql的语句
INSERT INTO records(rid,bid) VALUES(1,2);
UPDATE books SET count=count-1 WHERE bid=2;
--rollback; //手动回滚
--提交事务
COMMIT; //代表一个事务的结束
注意点:
1.事务开启后,一旦执行SQL语句出现错误,事务中所有的操作都将回滚到数据操作前;
2.数据没有提交前,对数据库中的所有操作都不会写进磁盘,一旦发生某些错误,数据将恢复到操作前的状态;
3.数据库使用事务时,提交事务后,如果发生某些SQL的执行错误,系统将自动回滚;
- 方式二 通过JDBC使用事务
1.创建连接数据库的工具类
package com.qk.utils;
import com.mysql.jdbc.jdbc2.optional.MysqlDataSource;
import javax.sql.DataSource;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.SQLException;
public class DbUtils {
private static final DataSource DATA_SOURCE;
static {
MysqlDataSource db=new MysqlDataSource();
String url="jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/beta?useSSL=false&characterEncodiing=utf-8&severTimezone=Asia/Shanghai";
db.setUrl(url);
db.setUser("root");
db.setPassword("787426");
DATA_SOURCE =db;
}
public static Connection getConnection() throws SQLException {
return DATA_SOURCE.getConnection();
}
}
2.测试事务提交
package com.qk;
import com.qk.utils.DbUtils;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.PreparedStatement;
import java.sql.SQLException;
public class Demo1 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws SQLException {
String sql1="insert into records(rid,bid) values(1,2)";
String sql2="update books set count=count-1 where bid =2";
//同一个事务中,执行sql1和sql2,意味着必须在同一个Connection中完成
try(Connection connection = DbUtils.getConnection()) {
//connection中有一个autocommit属性,默认情况下是开启(true)
//开启状态下,意味着每一条sql都被视作一个事务
//要让sql1和sql2看作一个整体,就需关闭自动提交,手动提交事务
connection.setAutoCommit(false);
try(PreparedStatement ps=connection.prepareStatement(sql1)) {
ps.executeUpdate();
}
try(PreparedStatement ps=connection.prepareStatement(sql2)) {
ps.executeUpdate();
}
//手动提交事务,以上数据操作才算真正执行,数据写入磁盘
connection.commit();
}
}
}
3.JDBC事务使用的四个场景
- 有事务,commit成功
demo1,事务成功提交。 - 没有事务,被动失败(重启服务器)
demo2,没有执行事务,重启服务器后,sql2执行失败,数据库数据未成功更新
package com.qk;
import com.qk.utils.DbUtils;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.PreparedStatement;
import java.sql.SQLException;
public class Demo2 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws SQLException {
String sql1="insert into records(rid,bid) values(1,2)";
String sql2="update books set count=count-1 where bid =2";
try(Connection connection = DbUtils.getConnection()) {
try(PreparedStatement ps=connection.prepareStatement(sql1)) {
ps.executeUpdate();
}
//执行完第一天sql1后,第二天sql2执行失败
try(PreparedStatement ps=connection.prepareStatement(sql2)) {
ps.executeUpdate();
}
}
}
}
- 有事务,被动失败(重启服务器)程序出错
demo3,开启事务,重启服务器或程序出现错误后,数据会发生回滚
package com.qk;
import com.qk.utils.DbUtils;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.PreparedStatement;
import java.sql.SQLException;
public class Demo3 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws SQLException {
String sql1="insert into records(rid,bid) values(1,2)";
String sql2="update books set count=count-1 where bid =2";
try(Connection connection = DbUtils.getConnection()) {
//开启事务
connection.setAutoCommit(false);
try(PreparedStatement ps=connection.prepareStatement(sql1)) {
ps.executeUpdate();
}
//执行完第一天sql1后,第二天sql2执行失败
try(PreparedStatement ps=connection.prepareStatement(sql2)) {
ps.executeUpdate();
}
connection.commit();
}
}
}
- 有事务,主动失败(rollback)
demo4,开启事务,执行完sql语句后,主动回滚事务,所有数据操作都将回滚到操作前
package com.qk;
import com.qk.utils.DbUtils;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.PreparedStatement;
import java.sql.SQLException;
public class Demo4 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws SQLException {
String sql1="insert into records(rid,bid) values(1,2)";
String sql2="update books set count=count-1 where bid =2";
try(Connection connection = DbUtils.getConnection()) {
//开启事务
connection.setAutoCommit(false);
try(PreparedStatement ps=connection.prepareStatement(sql1)) {
ps.executeUpdate();
}
try(PreparedStatement ps=connection.prepareStatement(sql2)) {
ps.executeUpdate();
}
connection.rollback(); //主动回滚
}
}
}
边栏推荐
猜你喜欢
MC1496乘法器
AD8307对数检波器

ICN6211:MIPI DSI转RGB视频转换芯片方案介绍 看完涨知识了呢
MPU6050 accelerometer and gyroscope sensor is connected with the Arduino

C语言教程 - 制作单位转换器
为什么D类音频功放可以免输出滤波器
![[Arduino connects the clock module to display the time on LCD1602]](/img/88/5baac76a24924d1cfd675ff5da830e.png)
[Arduino connects the clock module to display the time on LCD1602]
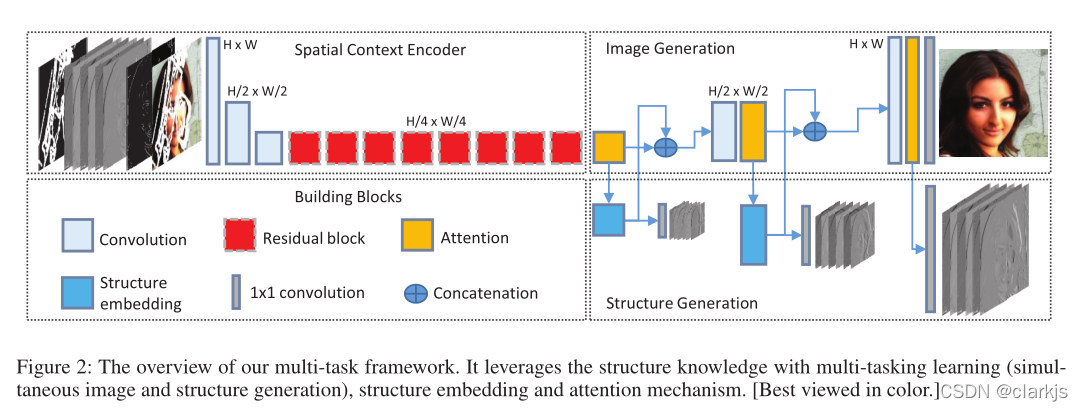
2020 - AAAI - Image Inpainting论文导读《Learning to Incorporate Structure Knowledge for Image Inpainting》
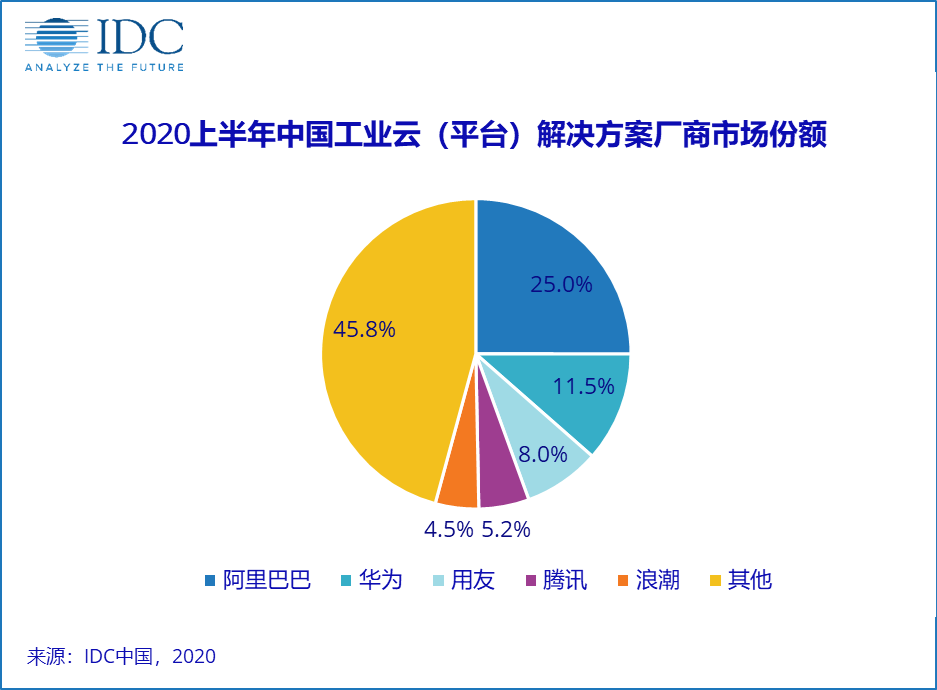
阿里云华为云对比分析
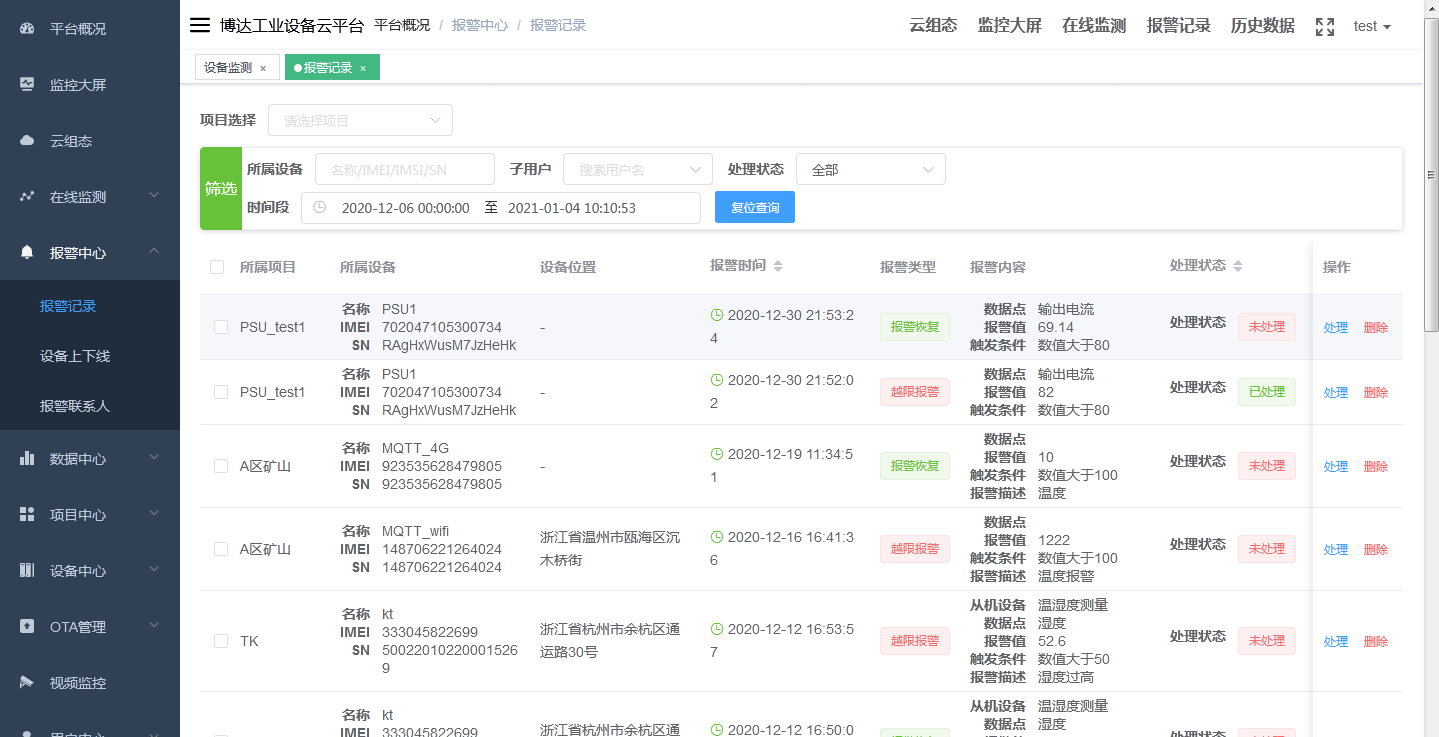
Comparison between Boda Industrial Cloud and Alibaba Cloud
随机推荐
LT8918L LVDS转MIPI芯片技术支持资料
基于阿里云OSS+PicGo的个人图床搭建
Comparison between Boda Industrial Cloud and Alibaba Cloud
进程(下):进程控制、终止、等待、替换
【plang 1.4.5】编写坦克(双人)游戏脚本
【科普贴】SPI接口详解
R语言 —— 多元线性回归
USB3.0一致性测试方法
网站开发方案研究
蛮力法求解凸包问题
增量编译技术在Lightly中的实践
【科普贴】MDIO接口详解
同时求最大值与最小值(看似简单却值得思考~)
LL(1)文法 :解决 if-else/if-else 产生式二义性问题
Industry where edge gateway strong?
Chrome 里的小恐龙游戏是怎么做出来的?
2020 - AAAI - 图像修复 Image Inpainting论文导读 -《Region Normalization for Image Inpainting》
阿里云华为云对比分析
【科普贴】I2C接口详解——偏硬件解析
字符串匹配(蛮力法+KMP)