当前位置:网站首页>递归:一维链表和数组
递归:一维链表和数组
2022-07-03 03:28:00 【我家大宝最可爱】
反转字符串
编写一个函数,其作用是将输入的字符串反转过来。输入字符串以字符数组 s 的形式给出。
递归是将一个大问题转化成同样的小问题,原始问题与小问题是一样的,只不过问题的规模给缩小了。再反转字符串的时候,其实就是头尾两端的字符进行交换,然后依次向中间走即可。
| l —> | <— r | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| h | e | l | l | o |
| l —> | l | <— r | ||
| o | e | l | l | h |
可以看到,就是重复操作左右两侧的字符串进行交换,然后字符串不断缩小(问题规模缩小),但是操作一直是重复不变的。
反转字符串的时候由于不需要递归之后再进行操作,因此操作再递归之前
class Solution:
def reverseString(self, s: List[str]) -> None:
""" Do not return anything, modify s in-place instead. """
def dfs(arr, l, r):
if l >= r: # 递归的终止条件
return
arr[l],arr[r] = arr[r],arr[l] # 重复操作部分。交换左右的两个字符
dfs(arr,l+1,r-1) # 缩减问题的规模,重复操作
dfs(s,0,len(s)-1)
return s
反转链表
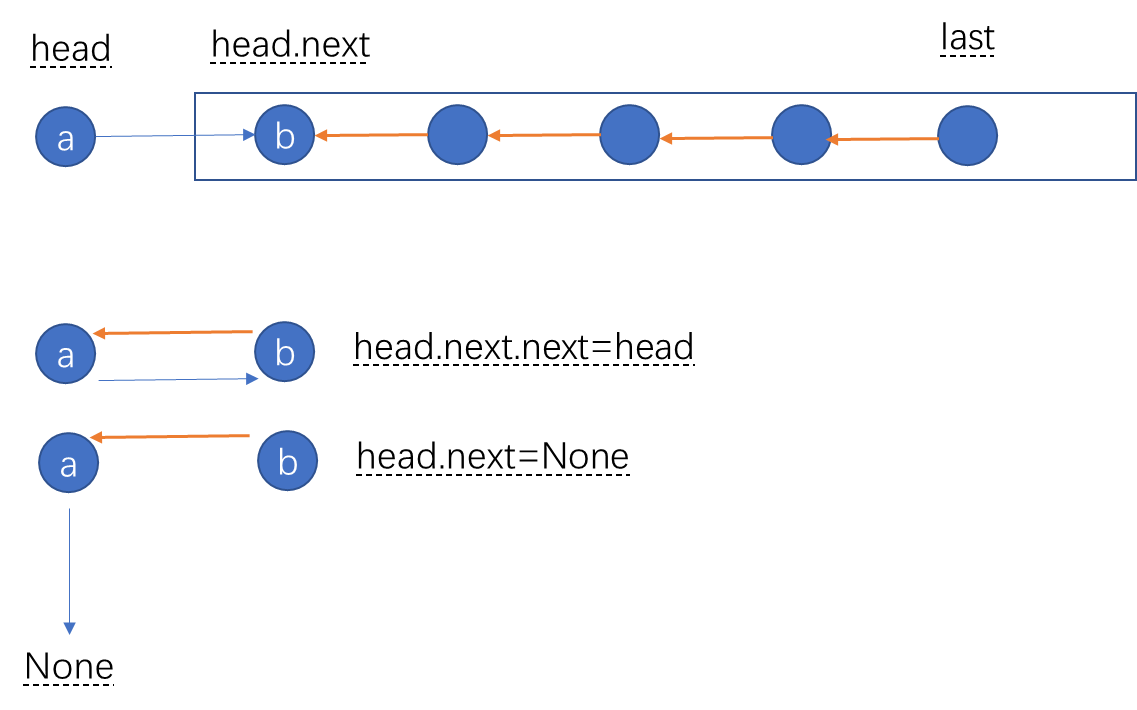
链表的反转也可以使用递归的,首先是我们要找到最末尾的元素,然后这个元素就是反转后的头节点,因此我们进行返回。然后我们就可以对元素进行反转,假设后续已经反转好了(递归会逐个反转的),现在a这个节点该如何反转呢?a的next是b,现在的目的是让b的next指向a,其实就很简单了
b=a.next # 目标
b.next=a # 目标是让b.next指向a
a.next.next=a # 由于a.next=b,所以可以直接写成
# Definition for singly-linked list.
# class ListNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, next=None):
# self.val = val
# self.next = next
class Solution:
def reverseList(self, head: ListNode) -> ListNode:
if head is None or head.next is None:
return head
last = self.reverseList(head.next)
head.next.next = head
head.next = None
return last
从尾到头打印链表
输入一个链表的头节点,从尾到头反过来返回每个节点的值(用数组返回)。
在递归函数后面还有操作,也就说这个递归函数一直往后找,最终找到了停止条件,这个时候就会返回了,在返回之后再进行一些操作,这里是把数据保存下来。
而且发现了一个问题,就是我们输入的参数是head,然后再递归函数中还有一个head.next,也就是说此时我们其实是由cur和next的。
一开始递归不是不断的从上往下走的,并不需要什么操作,一直走到最后找到了停止条件,然后开始逐步返回,这个时候就是从下往上走(逆向了),我们把每一步的head存储下来即可。
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | None | |
| head | ||||||
| head | ||||||
| head | ||||||
| 此时head是4 | head | |||||
| 此时head是5,传入head.next | head | |||||
| 停止条件,head is None | head |
# Definition for singly-linked list.
# class ListNode:
# def __init__(self, x):
# self.val = x
# self.next = None
class Solution:
def reversePrint(self, head: ListNode) -> List[int]:
res = []
def dfs(head):
if head is None:
return
dfs(head.next) # head.next is None,此时找到了停止条件
res.append(head.val) # head的值并不是None,所以将值添加进来,并且此时开始逐步返回递归的head,也就是上一步的head
dfs(head)
return res
删除链表的倒数第 N 个结点
链表的递归我感觉更像是递归遍历,不通过for循环操作进行遍历,直接使用递归的原理进行遍历,再删除倒数第N个节点的时候,通过递归会顺向遍历到尾部,然后再从下往上返回,这个时候我们就可以计数了,记到第N+1个的时候,我们可以进行操作。
这其中有两个小技巧,一个是定义一个dummy的节点放到head的前面,这样如果要删除head的结点依然可以返回dummy.next,第二个是使用nonlocal这个关键字,这个关键字定义了内部函数可以操作函数以外的变量。
# Definition for singly-linked list.
# class ListNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, next=None):
# self.val = val
# self.next = next
class Solution:
def removeNthFromEnd(self, head: ListNode, n: int) -> ListNode:
dummy = ListNode(0,head)
def dfs(head):
nonlocal n
if head is None:
return
dfs(head.next)
n -= 1
if n == -1:
head.next = head.next.next
dfs(dummy)
return dummy.next
两两交换链表中的节点

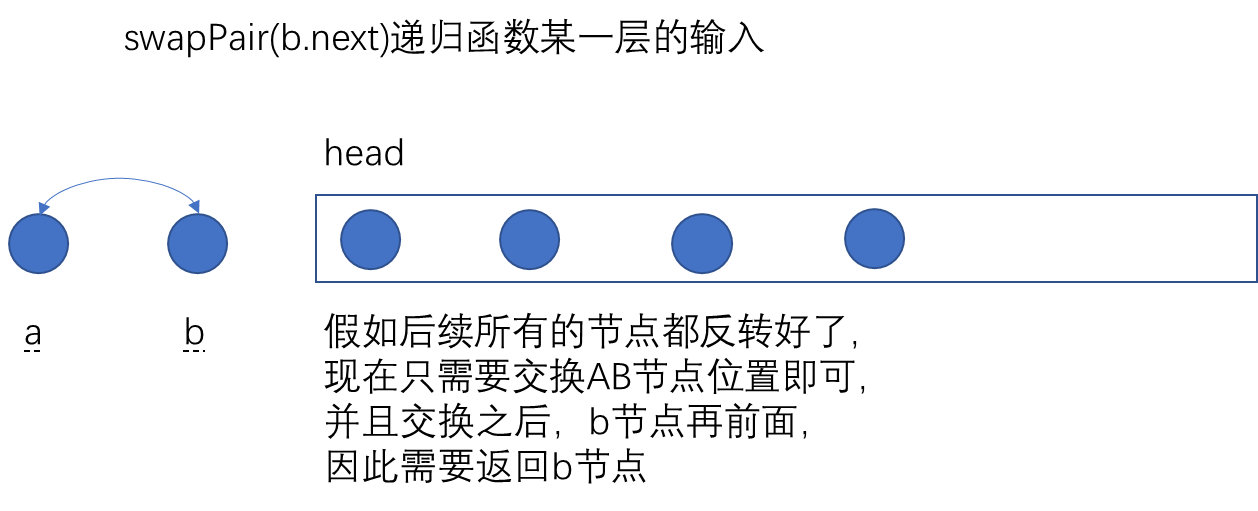
这个同样可以考虑递归,我们首先交换两个节点,后面的节点都是重复的操作,所以,这个问题可以用循环,也可以使用递归,不过这个问题需要思考返回的是什么。
我们怎么知道这个迭代公式的?怎么判断这个问题就是可以用递归呢?万一大问题并不能拆解成小问题呢?
# Definition for singly-linked list.
# class ListNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, next=None):
# self.val = val
# self.next = next
class Solution:
def swapPairs(self, head: ListNode) -> ListNode:
if head is None or head.next is None:
return head
a = head
b = head.next
a.next = self.swapPairs(b.next)
b.next = a
return b
2的幂
给你一个整数 n,请你判断该整数是否是 2 的幂次方
这个问题同样可以考虑使用递归,大问题是判断一个数是否是2的幂次方,这个数除以2之后得到的新数同样会判断是否是2的幂次方,即大问题可以一步一步拆解成小问题,并且每一步都是再重复操作,重复去判断是否可以被2整除
可以看到这个问题是直接返回了递归函数,而且没有任何其他操作,这就意味着递归到最后一层的结果是直接层层返回去了,没有任何中间商,所以直接最后一步能否整除就是最后的结果。
我不知道n是否是2的幂次方,但是如果可以通过求解n%2来判断,如果我知道了n%21,那么n肯定不是2的幂次方,如果n%20,我依然不知道,但是我可以缩减问题的规模,如果我知道了(n//2)%==1,那么n肯定不是2的幂次方。
class Solution:
def isPowerOfTwo(self, n: int) -> bool:
if n == 1:
return True
elif n % 2 > 0 or n < 1:
return False
return self.isPowerOfTwo(n // 2)
汉诺塔

汉诺塔也是用递归的方式来做。假如我们有N个圆盘,我们先通过C把前N-1个圆盘移动到B上面,然后把A上面的圆盘给移动到C上面,然后我们再通过A,把B上上面的N-1个圆盘移动到C上面。
为什么会想到用递归呢?因为原始问题与缩减后的问题是一样的,我们可以把N转化成N-1,N-1转化成N-2,一直转化到2,1等等。使用的都是同样的方式,递归其实非常像是高中学习的递推公式,首先增明N=1的时候符合规律,然后证明N+1的时候也是符合规律的。也就是说不管问题规模有多大,都是符合同一个规律的,因此我们可以通过迭代的方式计算出来。
汉诺塔还有一个很有意思的地方,我们的输入是move(n,A,B,C),要得到这个结果,所以我们函数中递归了一个move(n-1.A,C,B),问题是我们该如何把n-1个圆盘进行移动呢?不知道,所以这就是递归让人疑惑的地方,就这么不断的递归下去问题就能解决了吗?是的,就这么解决了。反正我现在还没有想明白,通过move(n-1.A,C,B)之后,A上面就只有一个圆盘了,此时我们直接把这个圆盘移动到C上面即可。问题是,我现在都不知道C上面是否还有圆盘,问什么就可以直接移动,很神奇。
class Solution:
def hanota(self, A: List[int], B: List[int], C: List[int]) -> None:
""" Do not return anything, modify C in-place instead. """
def move(n,A,B,C):
if n == 1: # 剩下一个圆盘的时候,直接将A的圆盘移动到C上
C.append(A.pop())
return
move(n-1, A, C, B) # 将A上面的n-1个圆盘通过C,移动到B上面
C.append(A.pop()) # 此时把A上面最后一个圆盘移动到C上面即可
move(n-1, B, A, C) # 此时B上面有n-1个圆盘,B再通过A把n-1个圆盘移动到C上面即可
n = len(A)
move(n,A,B,C)
50. Pow(x, n)
这个递归也非常有意思,同样是有点难以理解,我们求 x n x^n xn其实可以递归成两种情况
x n = { ( x n 2 ) 2 n%2==0 x ∗ ( x n 2 ) 2 n%2==1 x^n= \begin{cases} (x^{\frac{n}{2}})^2 & \text{n\%2==0} \\ x*(x^{\frac{n}{2}})^2 & \text{n\%2==1} \\ \end{cases} xn={ (x2n)2x∗(x2n)2n%2==0n%2==1
转化成递归函数的形式就是
p o w ( x , n ) = { p o w ( x , n / / 2 ) 2 n%2==0 x ∗ p o w ( x , n / / 2 ) 2 n%2==1 pow(x,n)= \begin{cases} pow(x,n//2)^2& \text{n\%2==0} \\ x*pow(x,n//2)^2 & \text{n\%2==1} \\ \end{cases} pow(x,n)={ pow(x,n//2)2x∗pow(x,n//2)2n%2==0n%2==1
你问我怎么求解 p o w ( x , n / / 2 ) pow(x,n//2) pow(x,n//2)我也不知道,反正就是根据这个递归公式不断递归就可以求解出来了。我也不知道怎么求 p o w ( x , n ) pow(x,n) pow(x,n),但是如果我求出了 p o w ( x , n / / 2 ) pow(x,n//2) pow(x,n//2)我就可以求出 p o w ( x , n ) pow(x,n) pow(x,n)了,如和求求解 p o w ( x , n / / 2 ) pow(x,n//2) pow(x,n//2)呢?我只要求解出 p o w ( x , n / / 4 ) pow(x,n//4) pow(x,n//4)就可以了,这样问题最后就会缩减到n=1也就是停止条件上,然后递归再进行返回,我们操作这个返回结果即可。
这个跟汉诺塔的问题非常的相像, 我不知道如何把n个圆盘从A移到C,但是如果我把n-1一个圆盘能移动到B,那么就可以完成。
class Solution:
def myPow(self, x: float, n: int) -> float:
def dfs(x,n):
if n == 0:
return 1
y = dfs(x, n//2)
if n % 2 == 0:
return y * y
else:
return x * y * y
if n < 0:
x = 1 / x
n = -n
r = dfs(x,n)
return r
边栏推荐
- What happens between entering the URL and displaying the page?
- 递归:快速排序,归并排序和堆排序
- Pytoch lightweight visualization tool wandb (local)
- MySQL practice 45 lecture [row lock]
- 用Three.js做一个简单的3D场景
- Node start server
- Agile certification (professional scrum Master) simulation exercise-2
- PAT乙级常用函数用法总结
- Mongodb master profile
- 渤、黄海的潮汐特征
猜你喜欢
![Ansible introduction [unfinished (semi-finished products)]](/img/2a/0003daf761ba02d8837c4657fc3f29.png)
Ansible introduction [unfinished (semi-finished products)]

900w+ data, from 17s to 300ms, how to operate
![[Chongqing Guangdong education] cultural and natural heritage reference materials of China University of Geosciences (Wuhan)](/img/19/815e7cba81f6eb52db5ef0db556dfd.jpg)
[Chongqing Guangdong education] cultural and natural heritage reference materials of China University of Geosciences (Wuhan)

Applet get user avatar and nickname

MongoDB简介

ffmpeg录制屏幕和截屏
Gavin teacher's perception of transformer live class - rasa project's actual banking financial BOT Intelligent Business Dialogue robot architecture, process and phenomenon decryption through rasa inte

The idea setting code is in UTF-8 idea Properties configuration file Chinese garbled

Hutool动态添加定时任务
VS code配置虚拟环境
随机推荐
Converts a timestamp to a time in the specified format
Pat class B "1104 forever" DFS optimization idea
node 开启服务器
900w+ data, from 17s to 300ms, how to operate
VS code配置虚拟环境
为什么线程崩溃不会导致 JVM 崩溃
Agile certification (professional scrum Master) simulation exercise-2
float与0比较
Model transformation onnx2engine
MongoDB基本操作【增、删、改、查】
MySQL practice 45 lecture [row lock]
文件重命名
递归:深度优先搜索
小程序获取用户头像和昵称
Idea format code idea set shortcut key format code
简易版 微信小程序开发之页面跳转、数据绑定、获取用户信息、获取用户位置信息
[AI practice] Application xgboost Xgbregressor builds air quality prediction model (I)
基于QT的tensorRT加速的yolov5
Vs Code configure virtual environment
The calculation of stripe, kernel and padding in CNN