当前位置:网站首页>Slist of linked list
Slist of linked list
2022-07-05 08:06:00 【Car chezi】
List of articles
background
about C Language , When you need to use linked lists in programming , Programmers usually need to redesign the structure of linked lists . This is not only troublesome , And need to verify the correctness of the code , For everyone who reads the code , Need to re understand .
If there is a unified interface , Wouldn't it be better ?
stay FreeBSD There is queue.h Such a header file (Linux Also have , The file path is /usr/include/x86_64-linux-gnu/sys/queue.h, You can refer to manual Manual queue(3) ).
The header file queue.h by C The linked list in the language provides a more standard programming interface . Today's versions are mostly University of California, Berkeley 1994 year 8 Of the month 8.5 edition (8.5 (Berkeley) 8/20/94).
queue It is divided into SLIST、LIST、STAILQ、TAILQ、CIRCLEQ , Different linked lists have different function support .queue All source codes of are macro definitions , Therefore, it is completely included in queue.h among , No need to compile into library files .
I got queue.h altogether 500 Multiple lines , The code will be attached at the end of this article , Different versions may be different .
Suggest : If you want to use it in your project , The best choice is to copy your favorite one into your project and use it . Don't rely on the operating system . It's just a header file with a bunch of macros , You don't need a library or any dependencies to work .
SLIST brief introduction
SLIST yes Singly-linked List Abbreviation , It means one-way tailless linked list .
[ Failed to transfer the external chain picture , The origin station may have anti-theft chain mechanism , It is suggested to save the pictures and upload them directly (img-WuRai1gC-1644726064142)(pics/image-20220101164926598.png)]
SLIST Is the simplest structure , It is suitable for occasions with a large amount of data and almost no need to delete data , Or as a stack .
Interface and implementation
/* * Singly-linked List declarations. */
#define SLIST_HEAD(name, type) \ struct name {
\ struct type *slh_first; /* first element */ \ }
#define SLIST_HEAD_INITIALIZER(head) \ {
NULL }
#define SLIST_ENTRY(type) \ struct {
\ struct type *sle_next; /* next element */ \ }
/* * Singly-linked List functions. */
#define SLIST_EMPTY(head) ((head)->slh_first == NULL)
#define SLIST_FIRST(head) ((head)->slh_first)
#define SLIST_FOREACH(var, head, field) \ for ((var) = SLIST_FIRST((head)); \ (var); \ (var) = SLIST_NEXT((var), field))
#define SLIST_INIT(head) do {
\ SLIST_FIRST((head)) = NULL; \ } while (0)
#define SLIST_INSERT_AFTER(slistelm, elm, field) do {
\ SLIST_NEXT((elm), field) = SLIST_NEXT((slistelm), field); \ SLIST_NEXT((slistelm), field) = (elm); \ } while (0)
#define SLIST_INSERT_HEAD(head, elm, field) do {
\ SLIST_NEXT((elm), field) = SLIST_FIRST((head)); \ SLIST_FIRST((head)) = (elm); \ } while (0)
#define SLIST_NEXT(elm, field) ((elm)->field.sle_next)
#define SLIST_REMOVE(head, elm, type, field) do {
\ if (SLIST_FIRST((head)) == (elm)) {
\ SLIST_REMOVE_HEAD((head), field); \ } \ else {
\ struct type *curelm = SLIST_FIRST((head)); \ while (SLIST_NEXT(curelm, field) != (elm)) \ curelm = SLIST_NEXT(curelm, field); \ SLIST_NEXT(curelm, field) = \ SLIST_NEXT(SLIST_NEXT(curelm, field), field); \ } \ } while (0)
#define SLIST_REMOVE_HEAD(head, field) do {
\ SLIST_FIRST((head)) = SLIST_NEXT(SLIST_FIRST((head)), field); \ } while (0)
give an example
Just looking at the code may make you dizzy , Let's illustrate with examples .
Examples come from https://man7.org/linux/man-pages/man3/SLIST_ENTRY.3.html
#include <stddef.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <sys/queue.h>
struct entry {
int data;
SLIST_ENTRY(entry) entries;
};
SLIST_HEAD(slisthead, entry);
int main(void)
{
struct entry *n1, *n2, *n3, *np;
struct slisthead head; /* Singly linked list head */
SLIST_INIT(&head); /* Initialize the queue */
n1 = malloc(sizeof(struct entry)); /* Insert at the head */
SLIST_INSERT_HEAD(&head, n1, entries);
n2 = malloc(sizeof(struct entry)); /* Insert after */
SLIST_INSERT_AFTER(n1, n2, entries);
SLIST_REMOVE(&head, n2, entry, entries);/* Deletion */
free(n2);
// Delete the first node
n3 = SLIST_FIRST(&head);
SLIST_REMOVE_HEAD(&head, entries); /* Deletion from the head */
free(n3);
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
n1 = malloc(sizeof(struct entry));
SLIST_INSERT_HEAD(&head, n1, entries);
n1->data = i;
}
/* Forward traversal */
SLIST_FOREACH(np, &head, entries)
printf("%i\n", np->data);
while (!SLIST_EMPTY(&head)) {
/* List deletion */
n1 = SLIST_FIRST(&head);
SLIST_REMOVE_HEAD(&head, entries);
free(n1);
}
SLIST_INIT(&head);
exit(EXIT_SUCCESS);
}
The code analysis
Let's analyze it bit by bit .
SLIST_ENTRY and SLIST_HEAD
Let's first look at the definition of structure
struct entry {
int data;
SLIST_ENTRY(entry) entries;
};
SLIST_HEAD(slisthead, entry);
We need to pay attention to , It has 3 individual entry, Whatever the name is , It has to be consistent ;
int data; It's user data , Add as needed ;
entries yes
struct { struct entry *sle_next; }
Members of type ( notes : This structure has no label ),entries You can also change it to another name ;
slisthead Is the tag name of the chain header structure .
After macro replacement
struct entry {
int data;
struct {
struct entry *sle_next;
} entries;
};
struct slisthead {
struct entry *slh_first;
};
You can see , It's different from what we defined when we first learned , Beginners are unlikely to put the first 4、9 Lines are wrapped in structures .
SLIST_INIT
Let's keep looking .
struct entry *n1, *n2, *n3, *np;
struct slisthead head; /* Singly linked list head */
SLIST_INIT(&head); /* Initialize the queue */
1: Defined 3 A pointer to a node ;
2: Define structural variables that represent headers head,slisthead Be consistent with the previous ;
3: The macro is replaced by (&head)->slh_first = NULL; It means initializing to an empty linked list , The head pointer points to NULL
SLIST_INSERT_HEAD
n1 = malloc(sizeof(struct entry)); /* Insert at the head */
SLIST_INSERT_HEAD(&head, n1, entries);
1: Allocate memory for nodes , The check of the return finger is omitted here ;
2: The macro is replaced by
(n1)->entries.sle_next = (&head)->slh_first;
(&head)->slh_first = (n1);
Typical head insert .SLIST_INSERT_HEAD(&head, n1, entries) It means : hold n1 Insert the node into the linked list head The head of ; The first parameter is the address of the header , The second parameter is the address of the node to be inserted , The third parameter is the member name of the unlabeled structure , Be consistent with the previous .
SLIST_INSERT_AFTER
n2 = malloc(sizeof(struct entry)); /* Insert after */
SLIST_INSERT_AFTER(n1, n2, entries);
2: The macro is replaced by
(n2)->entries.sle_next = (n1)->entries.sle_next;
(n1)->entries.sle_next = (n2);
In vernacular, it means n1 The latter node is connected to n2 Back , And then n2 Receive n1 Back , therefore :
SLIST_INSERT_AFTER(n1, n2, entries) It means to put nodes n2 Insert into n1 Behind .n1、n2 Are the addresses of nodes ,entries Is the member name of the unlabeled structure , Be consistent with the previous .
SLIST_REMOVE
SLIST_REMOVE(&head, n2, entry, entries);/* Deletion */
free(n2);
This macro replacement is a little complicated :
if ((&head)->slh_first == (n2)) {
((&head))->slh_first = ((&head))->slh_first->entries.sle_next;
}
else {
struct entry *curelm = (&head)->slh_first;
while(curelm->entries.sle_next != (n2))
curelm = curelm->entries.sle_next;
curelm->entries.sle_next = curelm->entries.sle_next->entries.sle_next;
}
1: See if the node to be deleted is the first node , If it is , Just delete ; If not , go else Branch
5: Take the first node as the current node
6: Judge whether the next node of the current node is the node to be deleted , If it is ,while End of sentence , Execution section 8 That's ok , Delete .
summary ,SLIST_REMOVE(&head, n2, entry, entries) It means :
The first parameter is the address of the header , The second parameter is the address of the node to be deleted , The third and fourth parameters should be consistent with the first definition of the structure , such as SLIST_ENTRY(entry) entries Medium entry、entries
SLIST_FIRST and SLIST_REMOVE_HEAD
n3 = SLIST_FIRST(&head);
SLIST_REMOVE_HEAD(&head, entries); /* Deletion from the head */
free(n3);
Macro replacement is :
n3 = ((&head)->slh_first);
(&head)->slh_first = (&head)->slh_first->entries.sle_next;
SLIST_FIRST (&head) This macro is to take the address of the first node , The parameter is the address of the header ;
2: Delete the first node
Why is there a second 1 Line? ? If you don't save the address of the first node at this time , Then delete , You can't get its address , It is impossible to carry out the second 3 OK, free up space . therefore , This example provides us with a standard header deletion operation .
SLIST_REMOVE_HEAD(&head, entries) This macro means to delete the first node , The first parameter is the address of the header ,entries Is the member name of the unlabeled structure , Be consistent with the previous .
SLIST_FOREACH
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
n1 = malloc(sizeof(struct entry));
SLIST_INSERT_HEAD(&head, n1, entries);
n1->data = i;
}
/* Forward traversal */
SLIST_FOREACH(np, &head, entries)
printf("%i\n", np->data);
3:SLIST_INSERT_HEAD This was mentioned earlier , It's a head plug
4: After macro replacement , yes
for((np) = (&head)->slh_first; (np); (np) = (np)->entries.sle_next)
printf("%i\n", np->data);
Typical traversal . Be careful , This traversal cannot be deleted , Because if you put np The node pointed to is deleted ,
(np)->entries.sle_next This sentence is wrong .
SLIST_FOREACH(np, &head, entries) Used to traverse each node of the linked list . The first parameter is a temporary variable , Point to the current node , The second parameter is the address of the header , Third entries Is the member name of the unlabeled structure , Same as before .
In this example, there is printing in this place , The result of printing is :
4
3
2
1
0
Because it's the head , So the first one inserted will be at the end of the linked list . The order of traversal is from beginning to end , So the order is 4,3,2,1,0
SLIST_EMPTY and SLIST_INIT
while (!SLIST_EMPTY(&head)) {
/* List deletion */
n1 = SLIST_FIRST(&head);
SLIST_REMOVE_HEAD(&head, entries);
free(n1);
}
2-4 OK, I won't explain , As I said before .
SLIST_EMPTY(&head) Macro expansion yes :
(&head)->slh_first == NULL, Is to judge whether the linked list is empty .
appendix queue.h
/* * Copyright (c) 1991, 1993 * The Regents of the University of California. All rights reserved. * * Redistribution and use in source and binary forms, with or without * modification, are permitted provided that the following conditions * are met: * 1. Redistributions of source code must retain the above copyright * notice, this list of conditions and the following disclaimer. * 2. Redistributions in binary form must reproduce the above copyright * notice, this list of conditions and the following disclaimer in the * documentation and/or other materials provided with the distribution. * 4. Neither the name of the University nor the names of its contributors * may be used to endorse or promote products derived from this software * without specific prior written permission. * * THIS SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED BY THE REGENTS AND CONTRIBUTORS ``AS IS'' AND * ANY EXPRESS OR IMPLIED WARRANTIES, INCLUDING, BUT NOT LIMITED TO, THE * IMPLIED WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY AND FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE * ARE DISCLAIMED. IN NO EVENT SHALL THE REGENTS OR CONTRIBUTORS BE LIABLE * FOR ANY DIRECT, INDIRECT, INCIDENTAL, SPECIAL, EXEMPLARY, OR CONSEQUENTIAL * DAMAGES (INCLUDING, BUT NOT LIMITED TO, PROCUREMENT OF SUBSTITUTE GOODS * OR SERVICES; LOSS OF USE, DATA, OR PROFITS; OR BUSINESS INTERRUPTION) * HOWEVER CAUSED AND ON ANY THEORY OF LIABILITY, WHETHER IN CONTRACT, STRICT * LIABILITY, OR TORT (INCLUDING NEGLIGENCE OR OTHERWISE) ARISING IN ANY WAY * OUT OF THE USE OF THIS SOFTWARE, EVEN IF ADVISED OF THE POSSIBILITY OF * SUCH DAMAGE. * * @(#)queue.h 8.5 (Berkeley) 8/20/94 * $FreeBSD: src/sys/sys/queue.h,v 1.32.2.7 2002/04/17 14:21:02 des Exp $ */
#ifndef _QUEUE_H_
#define _QUEUE_H_
#ifdef __cplusplus
extern "C" {
#endif
/* * This file defines five types of data structures: singly-linked lists, * singly-linked tail queues, lists, tail queues, and circular queues. * * A singly-linked list is headed by a single forward pointer. The elements * are singly linked for minimum space and pointer manipulation overhead at * the expense of O(n) removal for arbitrary elements. New elements can be * added to the list after an existing element or at the head of the list. * Elements being removed from the head of the list should use the explicit * macro for this purpose for optimum efficiency. A singly-linked list may * only be traversed in the forward direction. Singly-linked lists are ideal * for applications with large datasets and few or no removals or for * implementing a LIFO queue. * * A singly-linked tail queue is headed by a pair of pointers, one to the * head of the list and the other to the tail of the list. The elements are * singly linked for minimum space and pointer manipulation overhead at the * expense of O(n) removal for arbitrary elements. New elements can be added * to the list after an existing element, at the head of the list, or at the * end of the list. Elements being removed from the head of the tail queue * should use the explicit macro for this purpose for optimum efficiency. * A singly-linked tail queue may only be traversed in the forward direction. * Singly-linked tail queues are ideal for applications with large datasets * and few or no removals or for implementing a FIFO queue. * * A list is headed by a single forward pointer (or an array of forward * pointers for a hash table header). The elements are doubly linked * so that an arbitrary element can be removed without a need to * traverse the list. New elements can be added to the list before * or after an existing element or at the head of the list. A list * may only be traversed in the forward direction. * * A tail queue is headed by a pair of pointers, one to the head of the * list and the other to the tail of the list. The elements are doubly * linked so that an arbitrary element can be removed without a need to * traverse the list. New elements can be added to the list before or * after an existing element, at the head of the list, or at the end of * the list. A tail queue may be traversed in either direction. * * A circle queue is headed by a pair of pointers, one to the head of the * list and the other to the tail of the list. The elements are doubly * linked so that an arbitrary element can be removed without a need to * traverse the list. New elements can be added to the list before or after * an existing element, at the head of the list, or at the end of the list. * A circle queue may be traversed in either direction, but has a more * complex end of list detection. * * For details on the use of these macros, see the queue(3) manual page. * * * SLIST LIST STAILQ TAILQ CIRCLEQ * _HEAD + + + + + * _HEAD_INITIALIZER + + + + + * _ENTRY + + + + + * _INIT + + + + + * _EMPTY + + + + + * _FIRST + + + + + * _NEXT + + + + + * _PREV - - - + + * _LAST - - + + + * _FOREACH + + + + + * _FOREACH_REVERSE - - - + + * _INSERT_HEAD + + + + + * _INSERT_BEFORE - + - + + * _INSERT_AFTER + + + + + * _INSERT_TAIL - - + + + * _REMOVE_HEAD + - + - - * _REMOVE + + + + + * */
/* * Singly-linked List declarations. */
#define SLIST_HEAD(name, type) \ struct name {
\ struct type *slh_first; /* first element */ \ }
#define SLIST_HEAD_INITIALIZER(head) \ {
NULL }
#define SLIST_ENTRY(type) \ struct {
\ struct type *sle_next; /* next element */ \ }
/* * Singly-linked List functions. */
#define SLIST_EMPTY(head) ((head)->slh_first == NULL)
#define SLIST_FIRST(head) ((head)->slh_first)
#define SLIST_FOREACH(var, head, field) \ for ((var) = SLIST_FIRST((head)); \ (var); \ (var) = SLIST_NEXT((var), field))
#define SLIST_INIT(head) do {
\ SLIST_FIRST((head)) = NULL; \ } while (0)
#define SLIST_INSERT_AFTER(slistelm, elm, field) do {
\ SLIST_NEXT((elm), field) = SLIST_NEXT((slistelm), field); \ SLIST_NEXT((slistelm), field) = (elm); \ } while (0)
#define SLIST_INSERT_HEAD(head, elm, field) do {
\ SLIST_NEXT((elm), field) = SLIST_FIRST((head)); \ SLIST_FIRST((head)) = (elm); \ } while (0)
#define SLIST_NEXT(elm, field) ((elm)->field.sle_next)
#define SLIST_REMOVE(head, elm, type, field) do {
\ if (SLIST_FIRST((head)) == (elm)) {
\ SLIST_REMOVE_HEAD((head), field); \ } \ else {
\ struct type *curelm = SLIST_FIRST((head)); \ while (SLIST_NEXT(curelm, field) != (elm)) \ curelm = SLIST_NEXT(curelm, field); \ SLIST_NEXT(curelm, field) = \ SLIST_NEXT(SLIST_NEXT(curelm, field), field); \ } \ } while (0)
#define SLIST_REMOVE_HEAD(head, field) do {
\ SLIST_FIRST((head)) = SLIST_NEXT(SLIST_FIRST((head)), field); \ } while (0)
/* * Singly-linked Tail queue declarations. */
#define STAILQ_HEAD(name, type) \ struct name {
\ struct type *stqh_first;/* first element */ \ struct type **stqh_last;/* addr of last next element */ \ }
#define STAILQ_HEAD_INITIALIZER(head) \ {
NULL, &(head).stqh_first }
#define STAILQ_ENTRY(type) \ struct {
\ struct type *stqe_next; /* next element */ \ }
/* * Singly-linked Tail queue functions. */
#define STAILQ_EMPTY(head) ((head)->stqh_first == NULL)
#define STAILQ_FIRST(head) ((head)->stqh_first)
#define STAILQ_FOREACH(var, head, field) \ for((var) = STAILQ_FIRST((head)); \ (var); \ (var) = STAILQ_NEXT((var), field))
#define STAILQ_INIT(head) do {
\ STAILQ_FIRST((head)) = NULL; \ (head)->stqh_last = &STAILQ_FIRST((head)); \ } while (0)
#define STAILQ_INSERT_AFTER(head, tqelm, elm, field) do {
\ if ((STAILQ_NEXT((elm), field) = STAILQ_NEXT((tqelm), field)) == NULL)\ (head)->stqh_last = &STAILQ_NEXT((elm), field); \ STAILQ_NEXT((tqelm), field) = (elm); \ } while (0)
#define STAILQ_INSERT_HEAD(head, elm, field) do {
\ if ((STAILQ_NEXT((elm), field) = STAILQ_FIRST((head))) == NULL) \ (head)->stqh_last = &STAILQ_NEXT((elm), field); \ STAILQ_FIRST((head)) = (elm); \ } while (0)
#define STAILQ_INSERT_TAIL(head, elm, field) do {
\ STAILQ_NEXT((elm), field) = NULL; \ *(head)->stqh_last = (elm); \ (head)->stqh_last = &STAILQ_NEXT((elm), field); \ } while (0)
#define STAILQ_LAST(head, type, field) \ (STAILQ_EMPTY(head) ? \ NULL : \ ((struct type *) \ ((char *)((head)->stqh_last) - offsetof(struct type, field))))
#define STAILQ_NEXT(elm, field) ((elm)->field.stqe_next)
#define STAILQ_REMOVE(head, elm, type, field) do {
\ if (STAILQ_FIRST((head)) == (elm)) {
\ STAILQ_REMOVE_HEAD(head, field); \ } \ else {
\ struct type *curelm = STAILQ_FIRST((head)); \ while (STAILQ_NEXT(curelm, field) != (elm)) \ curelm = STAILQ_NEXT(curelm, field); \ if ((STAILQ_NEXT(curelm, field) = \ STAILQ_NEXT(STAILQ_NEXT(curelm, field), field)) == NULL)\ (head)->stqh_last = &STAILQ_NEXT((curelm), field);\ } \ } while (0)
#define STAILQ_REMOVE_HEAD(head, field) do {
\ if ((STAILQ_FIRST((head)) = \ STAILQ_NEXT(STAILQ_FIRST((head)), field)) == NULL) \ (head)->stqh_last = &STAILQ_FIRST((head)); \ } while (0)
#define STAILQ_REMOVE_HEAD_UNTIL(head, elm, field) do {
\ if ((STAILQ_FIRST((head)) = STAILQ_NEXT((elm), field)) == NULL) \ (head)->stqh_last = &STAILQ_FIRST((head)); \ } while (0)
#define STAILQ_REMOVE_AFTER(head, elm, field) do {
\ if ((STAILQ_NEXT(elm, field) = \ STAILQ_NEXT(STAILQ_NEXT(elm, field), field)) == NULL) \ (head)->stqh_last = &STAILQ_NEXT((elm), field); \ } while (0)
/* * List declarations. */
#define LIST_HEAD(name, type) \ struct name {
\ struct type *lh_first; /* first element */ \ }
#define LIST_HEAD_INITIALIZER(head) \ {
NULL }
#define LIST_ENTRY(type) \ struct {
\ struct type *le_next; /* next element */ \ struct type **le_prev; /* address of previous next element */ \ }
/* * List functions. */
#define LIST_EMPTY(head) ((head)->lh_first == NULL)
#define LIST_FIRST(head) ((head)->lh_first)
#define LIST_FOREACH(var, head, field) \ for ((var) = LIST_FIRST((head)); \ (var); \ (var) = LIST_NEXT((var), field))
#define LIST_INIT(head) do {
\ LIST_FIRST((head)) = NULL; \ } while (0)
#define LIST_INSERT_AFTER(listelm, elm, field) do {
\ if ((LIST_NEXT((elm), field) = LIST_NEXT((listelm), field)) != NULL)\ LIST_NEXT((listelm), field)->field.le_prev = \ &LIST_NEXT((elm), field); \ LIST_NEXT((listelm), field) = (elm); \ (elm)->field.le_prev = &LIST_NEXT((listelm), field); \ } while (0)
#define LIST_INSERT_BEFORE(listelm, elm, field) do {
\ (elm)->field.le_prev = (listelm)->field.le_prev; \ LIST_NEXT((elm), field) = (listelm); \ *(listelm)->field.le_prev = (elm); \ (listelm)->field.le_prev = &LIST_NEXT((elm), field); \ } while (0)
#define LIST_INSERT_HEAD(head, elm, field) do {
\ if ((LIST_NEXT((elm), field) = LIST_FIRST((head))) != NULL) \ LIST_FIRST((head))->field.le_prev = &LIST_NEXT((elm), field);\ LIST_FIRST((head)) = (elm); \ (elm)->field.le_prev = &LIST_FIRST((head)); \ } while (0)
#define LIST_NEXT(elm, field) ((elm)->field.le_next)
#define LIST_REMOVE(elm, field) do {
\ if (LIST_NEXT((elm), field) != NULL) \ LIST_NEXT((elm), field)->field.le_prev = \ (elm)->field.le_prev; \ *(elm)->field.le_prev = LIST_NEXT((elm), field); \ } while (0)
/* * Tail queue declarations. */
#define TAILQ_HEAD(name, type) \ struct name {
\ struct type *tqh_first; /* first element */ \ struct type **tqh_last; /* addr of last next element */ \ }
#define TAILQ_HEAD_INITIALIZER(head) \ {
NULL, &(head).tqh_first }
#define TAILQ_ENTRY(type) \ struct {
\ struct type *tqe_next; /* next element */ \ struct type **tqe_prev; /* address of previous next element */ \ }
/* * Tail queue functions. */
#define TAILQ_EMPTY(head) ((head)->tqh_first == NULL)
#define TAILQ_FIRST(head) ((head)->tqh_first)
#define TAILQ_FOREACH(var, head, field) \ for ((var) = TAILQ_FIRST((head)); \ (var); \ (var) = TAILQ_NEXT((var), field))
#define TAILQ_FOREACH_REVERSE(var, head, headname, field) \ for ((var) = TAILQ_LAST((head), headname); \ (var); \ (var) = TAILQ_PREV((var), headname, field))
#define TAILQ_INIT(head) do {
\ TAILQ_FIRST((head)) = NULL; \ (head)->tqh_last = &TAILQ_FIRST((head)); \ } while (0)
#define TAILQ_INSERT_AFTER(head, listelm, elm, field) do {
\ if ((TAILQ_NEXT((elm), field) = TAILQ_NEXT((listelm), field)) != NULL)\ TAILQ_NEXT((elm), field)->field.tqe_prev = \ &TAILQ_NEXT((elm), field); \ else \ (head)->tqh_last = &TAILQ_NEXT((elm), field); \ TAILQ_NEXT((listelm), field) = (elm); \ (elm)->field.tqe_prev = &TAILQ_NEXT((listelm), field); \ } while (0)
#define TAILQ_INSERT_BEFORE(listelm, elm, field) do {
\ (elm)->field.tqe_prev = (listelm)->field.tqe_prev; \ TAILQ_NEXT((elm), field) = (listelm); \ *(listelm)->field.tqe_prev = (elm); \ (listelm)->field.tqe_prev = &TAILQ_NEXT((elm), field); \ } while (0)
#define TAILQ_INSERT_HEAD(head, elm, field) do {
\ if ((TAILQ_NEXT((elm), field) = TAILQ_FIRST((head))) != NULL) \ TAILQ_FIRST((head))->field.tqe_prev = \ &TAILQ_NEXT((elm), field); \ else \ (head)->tqh_last = &TAILQ_NEXT((elm), field); \ TAILQ_FIRST((head)) = (elm); \ (elm)->field.tqe_prev = &TAILQ_FIRST((head)); \ } while (0)
#define TAILQ_INSERT_TAIL(head, elm, field) do {
\ TAILQ_NEXT((elm), field) = NULL; \ (elm)->field.tqe_prev = (head)->tqh_last; \ *(head)->tqh_last = (elm); \ (head)->tqh_last = &TAILQ_NEXT((elm), field); \ } while (0)
#define TAILQ_LAST(head, headname) \ (*(((struct headname *)((head)->tqh_last))->tqh_last))
#define TAILQ_NEXT(elm, field) ((elm)->field.tqe_next)
#define TAILQ_PREV(elm, headname, field) \ (*(((struct headname *)((elm)->field.tqe_prev))->tqh_last))
#define TAILQ_REMOVE(head, elm, field) do {
\ if ((TAILQ_NEXT((elm), field)) != NULL) \ TAILQ_NEXT((elm), field)->field.tqe_prev = \ (elm)->field.tqe_prev; \ else \ (head)->tqh_last = (elm)->field.tqe_prev; \ *(elm)->field.tqe_prev = TAILQ_NEXT((elm), field); \ } while (0)
/* * Circular queue declarations. */
#define CIRCLEQ_HEAD(name, type) \ struct name {
\ struct type *cqh_first; /* first element */ \ struct type *cqh_last; /* last element */ \ }
#define CIRCLEQ_HEAD_INITIALIZER(head) \ {
(void *)&(head), (void *)&(head) }
#define CIRCLEQ_ENTRY(type) \ struct {
\ struct type *cqe_next; /* next element */ \ struct type *cqe_prev; /* previous element */ \ }
/* * Circular queue functions. */
#define CIRCLEQ_EMPTY(head) ((head)->cqh_first == (void *)(head))
#define CIRCLEQ_FIRST(head) ((head)->cqh_first)
#define CIRCLEQ_FOREACH(var, head, field) \ for ((var) = CIRCLEQ_FIRST((head)); \ (var) != (void *)(head) || ((var) = NULL); \ (var) = CIRCLEQ_NEXT((var), field))
#define CIRCLEQ_FOREACH_REVERSE(var, head, field) \ for ((var) = CIRCLEQ_LAST((head)); \ (var) != (void *)(head) || ((var) = NULL); \ (var) = CIRCLEQ_PREV((var), field))
#define CIRCLEQ_INIT(head) do {
\ CIRCLEQ_FIRST((head)) = (void *)(head); \ CIRCLEQ_LAST((head)) = (void *)(head); \ } while (0)
#define CIRCLEQ_INSERT_AFTER(head, listelm, elm, field) do {
\ CIRCLEQ_NEXT((elm), field) = CIRCLEQ_NEXT((listelm), field); \ CIRCLEQ_PREV((elm), field) = (listelm); \ if (CIRCLEQ_NEXT((listelm), field) == (void *)(head)) \ CIRCLEQ_LAST((head)) = (elm); \ else \ CIRCLEQ_PREV(CIRCLEQ_NEXT((listelm), field), field) = (elm);\ CIRCLEQ_NEXT((listelm), field) = (elm); \ } while (0)
#define CIRCLEQ_INSERT_BEFORE(head, listelm, elm, field) do {
\ CIRCLEQ_NEXT((elm), field) = (listelm); \ CIRCLEQ_PREV((elm), field) = CIRCLEQ_PREV((listelm), field); \ if (CIRCLEQ_PREV((listelm), field) == (void *)(head)) \ CIRCLEQ_FIRST((head)) = (elm); \ else \ CIRCLEQ_NEXT(CIRCLEQ_PREV((listelm), field), field) = (elm);\ CIRCLEQ_PREV((listelm), field) = (elm); \ } while (0)
#define CIRCLEQ_INSERT_HEAD(head, elm, field) do {
\ CIRCLEQ_NEXT((elm), field) = CIRCLEQ_FIRST((head)); \ CIRCLEQ_PREV((elm), field) = (void *)(head); \ if (CIRCLEQ_LAST((head)) == (void *)(head)) \ CIRCLEQ_LAST((head)) = (elm); \ else \ CIRCLEQ_PREV(CIRCLEQ_FIRST((head)), field) = (elm); \ CIRCLEQ_FIRST((head)) = (elm); \ } while (0)
#define CIRCLEQ_INSERT_TAIL(head, elm, field) do {
\ CIRCLEQ_NEXT((elm), field) = (void *)(head); \ CIRCLEQ_PREV((elm), field) = CIRCLEQ_LAST((head)); \ if (CIRCLEQ_FIRST((head)) == (void *)(head)) \ CIRCLEQ_FIRST((head)) = (elm); \ else \ CIRCLEQ_NEXT(CIRCLEQ_LAST((head)), field) = (elm); \ CIRCLEQ_LAST((head)) = (elm); \ } while (0)
#define CIRCLEQ_LAST(head) ((head)->cqh_last)
#define CIRCLEQ_NEXT(elm,field) ((elm)->field.cqe_next)
#define CIRCLEQ_PREV(elm,field) ((elm)->field.cqe_prev)
#define CIRCLEQ_REMOVE(head, elm, field) do {
\ if (CIRCLEQ_NEXT((elm), field) == (void *)(head)) \ CIRCLEQ_LAST((head)) = CIRCLEQ_PREV((elm), field); \ else \ CIRCLEQ_PREV(CIRCLEQ_NEXT((elm), field), field) = \ CIRCLEQ_PREV((elm), field); \ if (CIRCLEQ_PREV((elm), field) == (void *)(head)) \ CIRCLEQ_FIRST((head)) = CIRCLEQ_NEXT((elm), field); \ else \ CIRCLEQ_NEXT(CIRCLEQ_PREV((elm), field), field) = \ CIRCLEQ_NEXT((elm), field); \ } while (0)
#ifdef __cplusplus
}
#endif
#endif /* !_SYS_QUEUE_H_ */
Reference material
【1】https://blog.csdn.net/tissar/article/details/86978743
【2】http://manpages.courier-mta.org/htmlman3/slist.3.html
【3】https://wizardforcel.gitbooks.io/100-gcc-tips/content/inhibit-linemarkers.html
【4】where to find Linux version sys/queue.h header file? - Stack Overflow
边栏推荐
- 导电滑环磨损快的原因
- UEFI development learning 5 - simple use of protocol
- 1089 insert or merge, including test point 5
- Step motor generates S-curve upper computer
- 找不到实时聊天软件?给你推荐电商企业都在用的!
- Basic embedded concepts
- Consul installation
- String judgment
- [trio basic tutorial 18 from introduction to proficiency] trio motion controller UDP fast exchange data communication
- 如何进行导电滑环选型
猜你喜欢

C language enhancement -- pointer
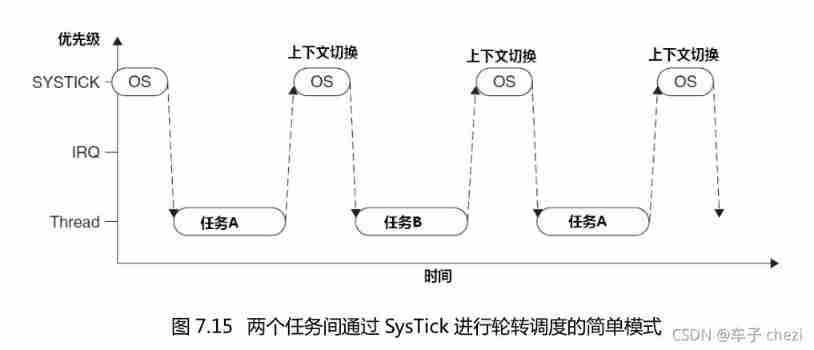
Explain task scheduling based on Cortex-M3 in detail (Part 1)
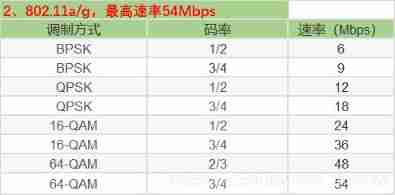
Wifi-802.11 negotiation rate table

生产中影响滑环质量的因素
![Shape template matching based on Halcon learning [viii] PM_ multiple_ models. Hdev routine](/img/13/22a1915329f58acd54c40176f6f301.jpg)
Shape template matching based on Halcon learning [viii] PM_ multiple_ models. Hdev routine
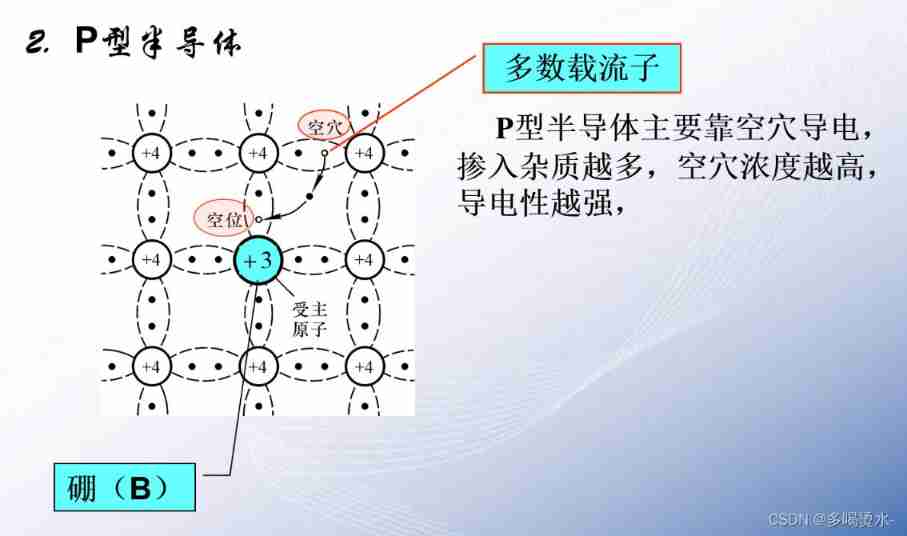
Semiconductor devices (I) PN junction
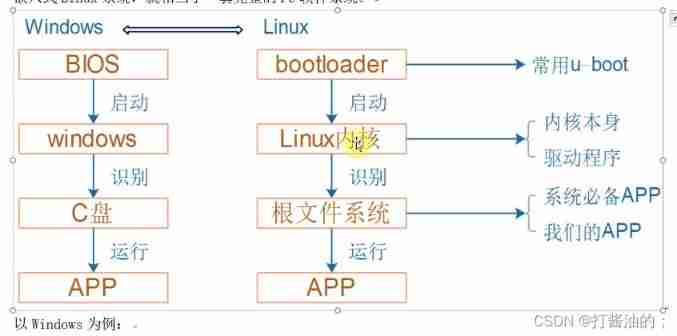
Embedded composition and route
Matlab2018b problem solving when installing embedded coder support package for stmicroelectronic
![C WinForm [get file path -- traverse folder pictures] - practical exercise 6](/img/8b/1e470de4e4ecd4fd1bb8e5cf23f466.jpg)
C WinForm [get file path -- traverse folder pictures] - practical exercise 6

Ads learning record (lna_atf54143)
随机推荐
Semiconductor devices (I) PN junction
Bootloader implementation of PIC MCU
A simple method to prove 1/t Fourier transform
Create inf module in AMI code
How to migrate the device data accessed by the RTSP of the easycvr platform to easynvr?
Carrier period, electrical speed, carrier period variation
DokuWiki deployment notes
Measurement fitting based on Halcon learning [II] meaure_ pin. Hdev routine
Explication de la procédure stockée pour SQL Server
找不到实时聊天软件?给你推荐电商企业都在用的!
UEFI development learning 6 - creation of protocol
IEEE access personal contribution experience record
Pointnet++ classification practice
[professional literacy] core conferences and periodicals in the field of integrated circuits
After installing the new version of keil5 or upgrading the JLINK firmware, you will always be prompted about the firmware update
Global and Chinese market of core pallets 2022-2028: Research Report on technology, participants, trends, market size and share
1-stm32 operation environment construction
matlab timeserise
Record the visual shock of the Winter Olympics and the introduction of the screen 2
Screen record of the opening ceremony of the Beijing winter olympics 2