当前位置:网站首页>[SOC FPGA] custom IP PWM breathing lamp
[SOC FPGA] custom IP PWM breathing lamp
2022-07-07 06:15:00 【EPCCcc】
List of articles
One 、 Basic preparation
Two 、Verilog Code section
Because we are custom ip, So we need to know avalon bus protocol , because SoC FPGA yes AXI Bus and avalon Bus automatic conversion , So we need to interface up avalon The interface of 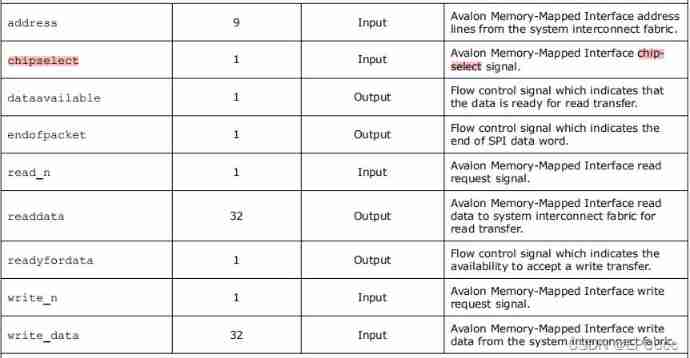
1.pwm_avalon_port.v
module pwm_avalon_port(
input clk,
input rst_n,
// avalon mm slave
input as_chipselect,
input [1:0] as_address,
input as_write,
input [31:0] as_writedata,
output reg [31:0] as_readdata,
// o_pwm
output o_pwm
);
reg [31:0] counter_arr;// Pre loaded value control frequency
reg [31:0] counter_ccr;// The pre comparison value controls the duty cycle
reg control;// Control register
// Preload value
always @(posedge clk or negedge rst_n)begin
if(!rst_n)begin
counter_arr <= 32'b0;
end
else if(as_chipselect && as_write && (as_address == 0))begin
counter_arr <= as_writedata;
end
else begin
counter_arr <= counter_arr;
end
end
// Pre comparison value
always @(posedge clk or negedge rst_n)begin
if(!rst_n)begin
counter_ccr <= 32'b0;
end
else if(as_chipselect && as_write && (as_address == 1))begin
counter_ccr <= as_writedata;
end
else begin
counter_ccr <= counter_ccr;
end
end
// control Control register
always @(posedge clk or negedge rst_n)begin
if(!rst_n)begin
control <= 0;
end
else if(as_chipselect && as_write && (as_address == 2))begin
control <= as_writedata[0];
end
else begin
control <= control;
end
end
// as_readdata Read register
always @(posedge clk or negedge rst_n)begin
if(!rst_n)begin
as_readdata <= 0;
end
else if(as_chipselect)begin
case (as_address)
0 : as_readdata <= counter_arr;
1 : as_readdata <= counter_ccr;
2 : as_readdata <= control;
default : as_readdata <= 0;
endcase
end
end
pwm_logic u_pwm_logic(
/* input */.clk (clk ),
/* input */.rst_n (rst_n ),
/* input */.cnt_en (control ),// Counter enable
/* input [31:0] */.counter_arr (counter_arr),// Preload value
/* input [31:0] */.counter_ccr (counter_ccr),// Pre comparison value
/* output reg */.o_pwm (o_pwm )
);
endmodule
2.pwm_logic.v
module pwm_logic(
input clk ,
input rst_n ,
input cnt_en ,// Counter enable
input [31:0] counter_arr ,// Preload value
input [31:0] counter_ccr ,// Pre comparison value
output reg o_pwm
);
reg [31:0] cnt;
wire add_cnt;
wire end_cnt;
reg [31:0] counter_ccr_r;
always @(posedge clk or negedge rst_n)begin
if(!rst_n)begin
cnt <= 0;
end
else if(add_cnt)begin
if(end_cnt)begin
cnt <= 0;
end
else begin
cnt <= cnt + 1;
end
end
else begin
cnt <= cnt;
end
end
assign add_cnt = cnt_en;
assign end_cnt = add_cnt && cnt == counter_arr - 1;
// Register save value
always @(posedge clk)begin
if(!cnt)begin
counter_ccr_r <= counter_ccr;
end
else begin
counter_ccr_r <= counter_ccr_r;
end
end
// Output
always @(posedge clk or negedge rst_n)begin
if(!rst_n)begin
o_pwm <= 1'b0;
end
else if(counter_ccr_r >= cnt)begin
o_pwm <= 1'b0;
end
else if(counter_ccr_r < cnt)begin
o_pwm <= 1'b1;
end
else begin
o_pwm <= o_pwm;
end
end
endmodule
3、 ... and 、 Customize ip Set up
1. Create a new one ip
take Verilog Put the file in ip Nuclear 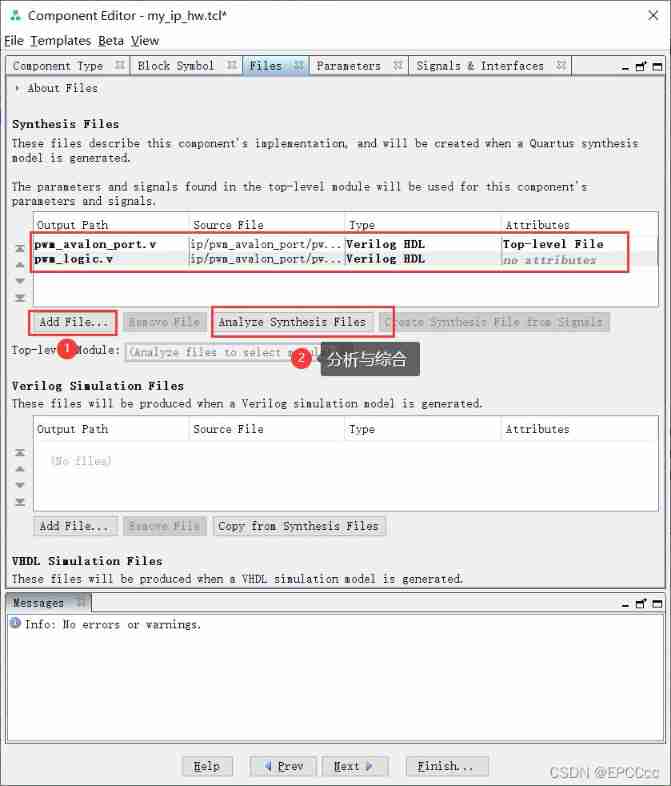
Modify the signal and interface ,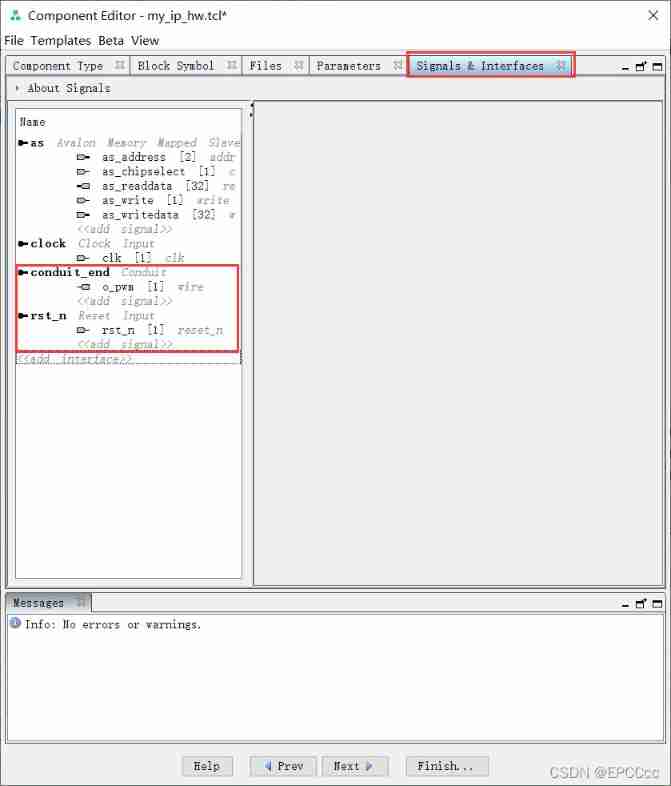
Pipeline output pwm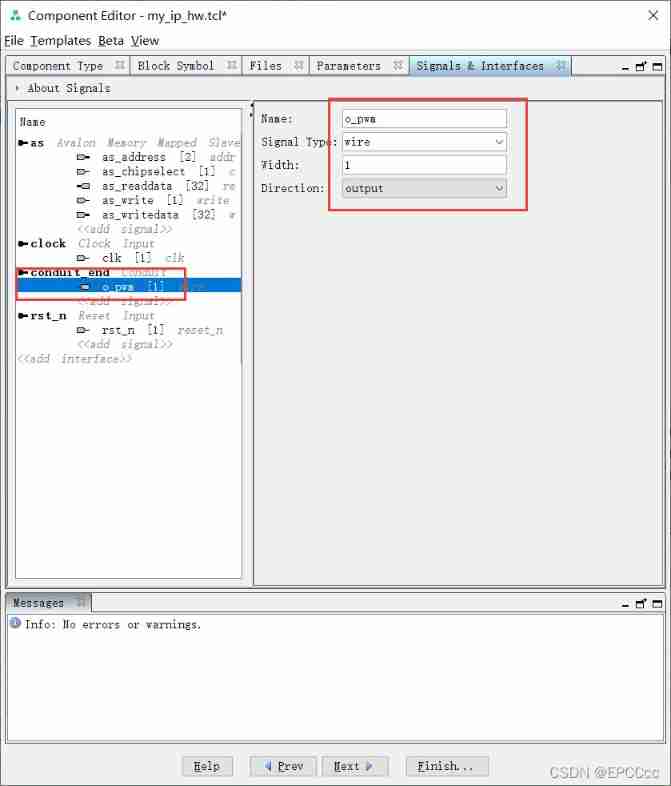
Reset signal 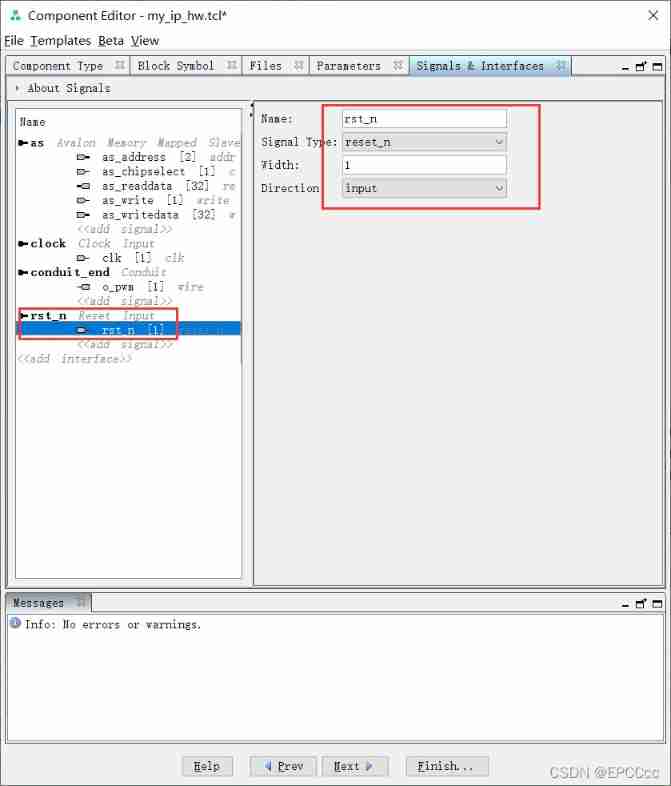

Four 、 Gold project code modification
wire pwm;
assign LED = {4{pwm}};
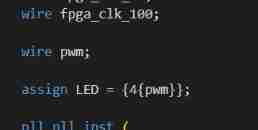
// pwm
.pwm_conduit_wire (pwm) // pwm_conduit.wire

Complete code
module C5MB_top(
/ FPGA /
input FPGA_CLK1_50,
/ HPS /
output [14: 0] HPS_DDR3_ADDR,
output [ 2: 0] HPS_DDR3_BA,
output HPS_DDR3_CAS_n,
output [ 0: 0] HPS_DDR3_CKE,
output HPS_DDR3_CK_n,
output HPS_DDR3_CK_p,
output [ 0: 0] HPS_DDR3_CS_n,
output [ 3: 0] HPS_DDR3_DM,
inout [31: 0] HPS_DDR3_DQ,
inout [ 3: 0] HPS_DDR3_DQS_n,
inout [ 3: 0] HPS_DDR3_DQS_p,
output [ 0: 0] HPS_DDR3_ODT,
output HPS_DDR3_RAS_n,
output HPS_DDR3_RESET_n,
input HPS_DDR3_RZQ,
output HPS_DDR3_WE_n,
output HPS_ENET_GTX_CLK,
inout HPS_ENET_INT_n, //hps_gpio_GPIO35
output HPS_ENET_MDC,
inout HPS_ENET_MDIO,
input HPS_ENET_RX_CLK,
input [ 3: 0] HPS_ENET_RX_DATA,
input HPS_ENET_RX_DV,
output [ 3: 0] HPS_ENET_TX_DATA,
output HPS_ENET_TX_EN,
inout HPS_EMMC_SEL, //hps_io_gpio_inst_GPIO44
output HPS_SDMMC_CLK,
inout HPS_SDMMC_CMD,
inout [ 7: 0] HPS_SDMMC_DATA,
output HPS_EMMC_RST_n,
input HPS_UART_RX,
output HPS_UART_TX,
//## HPS_USB ##
input HPS_USB_CLKOUT,
inout [ 7: 0] HPS_USB_DATA,
input HPS_USB_DIR,
input HPS_USB_NXT,
output HPS_USB_STP,
output [ 3: 0] LED
// input [ 1: 0] KEY
);
//=======================================================
// REG/WIRE declarations
//=======================================================
wire hps_fpga_reset_n;
wire fpga_clk_50;
wire fpga_clk_100;
wire pwm;
assign LED = {4{pwm}};
pll pll_inst (
.refclk (FPGA_CLK1_50), // refclk.clk
.rst (~hps_fpga_reset_n), // reset.reset
.outclk_0 (fpga_clk_50), // outclk0.clk
.outclk_1 (fpga_clk_100)
);
//=======================================================
// Structural coding
//=======================================================
soc_system u0 (
.clk_clk (fpga_clk_50), // clk.clk
.reset_reset_n (hps_fpga_reset_n), // reset.reset_n
//HPS ddr3
.memory_mem_a (HPS_DDR3_ADDR), // memory.mem_a
.memory_mem_ba (HPS_DDR3_BA), // .mem_ba
.memory_mem_ck (HPS_DDR3_CK_p), // .mem_ck
.memory_mem_ck_n (HPS_DDR3_CK_n), // .mem_ck_n
.memory_mem_cke (HPS_DDR3_CKE), // .mem_cke
.memory_mem_cs_n (HPS_DDR3_CS_n), // .mem_cs_n
.memory_mem_ras_n (HPS_DDR3_RAS_n), // .mem_ras_n
.memory_mem_cas_n (HPS_DDR3_CAS_n), // .mem_cas_n
.memory_mem_we_n (HPS_DDR3_WE_n), // .mem_we_n
.memory_mem_reset_n (HPS_DDR3_RESET_n), // .mem_reset_n
.memory_mem_dq (HPS_DDR3_DQ), // .mem_dq
.memory_mem_dqs (HPS_DDR3_DQS_p), // .mem_dqs
.memory_mem_dqs_n (HPS_DDR3_DQS_n), // .mem_dqs_n
.memory_mem_odt (HPS_DDR3_ODT), // .mem_odt
.memory_mem_dm (HPS_DDR3_DM), // .mem_dm
.memory_oct_rzqin (HPS_DDR3_RZQ), // .oct_rzqin
//HPS ethernet
.hps_0_hps_io_hps_io_emac1_inst_TX_CLK (HPS_ENET_GTX_CLK), // hps_0_hps_io.hps_io_emac1_inst_TX_CLK
.hps_0_hps_io_hps_io_emac1_inst_TXD0 (HPS_ENET_TX_DATA[0]), // .hps_io_emac1_inst_TXD0
.hps_0_hps_io_hps_io_emac1_inst_TXD1 (HPS_ENET_TX_DATA[1]), // .hps_io_emac1_inst_TXD1
.hps_0_hps_io_hps_io_emac1_inst_TXD2 (HPS_ENET_TX_DATA[2]), // .hps_io_emac1_inst_TXD2
.hps_0_hps_io_hps_io_emac1_inst_TXD3 (HPS_ENET_TX_DATA[3]), // .hps_io_emac1_inst_TXD3
.hps_0_hps_io_hps_io_emac1_inst_RXD0 (HPS_ENET_RX_DATA[0]), // .hps_io_emac1_inst_RXD0
.hps_0_hps_io_hps_io_emac1_inst_MDIO (HPS_ENET_MDIO), // .hps_io_emac1_inst_MDIO
.hps_0_hps_io_hps_io_emac1_inst_MDC (HPS_ENET_MDC), // .hps_io_emac1_inst_MDC
.hps_0_hps_io_hps_io_emac1_inst_RX_CTL (HPS_ENET_RX_DV), // .hps_io_emac1_inst_RX_CTL
.hps_0_hps_io_hps_io_emac1_inst_TX_CTL (HPS_ENET_TX_EN), // .hps_io_emac1_inst_TX_CTL
.hps_0_hps_io_hps_io_emac1_inst_RX_CLK (HPS_ENET_RX_CLK), // .hps_io_emac1_inst_RX_CLK
.hps_0_hps_io_hps_io_emac1_inst_RXD1 (HPS_ENET_RX_DATA[1]), // .hps_io_emac1_inst_RXD1
.hps_0_hps_io_hps_io_emac1_inst_RXD2 (HPS_ENET_RX_DATA[2]), // .hps_io_emac1_inst_RXD2
.hps_0_hps_io_hps_io_emac1_inst_RXD3 (HPS_ENET_RX_DATA[3]), // .hps_io_emac1_inst_RXD3
//HPS SD card
.hps_0_hps_io_hps_io_sdio_inst_CMD (HPS_SDMMC_CMD), // .hps_io_sdio_inst_CMD
.hps_0_hps_io_hps_io_sdio_inst_D0 (HPS_SDMMC_DATA[0]), // .hps_io_sdio_inst_D0
.hps_0_hps_io_hps_io_sdio_inst_D1 (HPS_SDMMC_DATA[1]), // .hps_io_sdio_inst_D1
.hps_0_hps_io_hps_io_sdio_inst_CLK (HPS_SDMMC_CLK), // .hps_io_sdio_inst_CLK
.hps_0_hps_io_hps_io_sdio_inst_D2 (HPS_SDMMC_DATA[2]), // .hps_io_sdio_inst_D2
.hps_0_hps_io_hps_io_sdio_inst_D3 (HPS_SDMMC_DATA[3]), // .hps_io_sdio_inst_D3
.hps_0_hps_io_hps_io_sdio_inst_D4 (HPS_SDMMC_DATA[4]), // .hps_io_sdio_inst_D4
.hps_0_hps_io_hps_io_sdio_inst_D5 (HPS_SDMMC_DATA[5]), // .hps_io_sdio_inst_D5
.hps_0_hps_io_hps_io_sdio_inst_D6 (HPS_SDMMC_DATA[6]), // .hps_io_sdio_inst_D6
.hps_0_hps_io_hps_io_sdio_inst_D7 (HPS_SDMMC_DATA[7]), // .hps_io_sdio_inst_D7
.hps_0_hps_io_hps_io_sdio_inst_PWREN (HPS_EMMC_RST_n), // .hps_io_sdio_inst_PWREN
//HPS USB
.hps_0_hps_io_hps_io_usb1_inst_D0 (HPS_USB_DATA[0]), // .hps_io_usb1_inst_D0
.hps_0_hps_io_hps_io_usb1_inst_D1 (HPS_USB_DATA[1]), // .hps_io_usb1_inst_D1
.hps_0_hps_io_hps_io_usb1_inst_D2 (HPS_USB_DATA[2]), // .hps_io_usb1_inst_D2
.hps_0_hps_io_hps_io_usb1_inst_D3 (HPS_USB_DATA[3]), // .hps_io_usb1_inst_D3
.hps_0_hps_io_hps_io_usb1_inst_D4 (HPS_USB_DATA[4]), // .hps_io_usb1_inst_D4
.hps_0_hps_io_hps_io_usb1_inst_D5 (HPS_USB_DATA[5]), // .hps_io_usb1_inst_D5
.hps_0_hps_io_hps_io_usb1_inst_D6 (HPS_USB_DATA[6]), // .hps_io_usb1_inst_D6
.hps_0_hps_io_hps_io_usb1_inst_D7 (HPS_USB_DATA[7]), // .hps_io_usb1_inst_D7
.hps_0_hps_io_hps_io_usb1_inst_CLK (HPS_USB_CLKOUT), // .hps_io_usb1_inst_CLK
.hps_0_hps_io_hps_io_usb1_inst_STP (HPS_USB_STP), // .hps_io_usb1_inst_STP
.hps_0_hps_io_hps_io_usb1_inst_DIR (HPS_USB_DIR), // .hps_io_usb1_inst_DIR
.hps_0_hps_io_hps_io_usb1_inst_NXT (HPS_USB_NXT), // .hps_io_usb1_inst_NXT
//HPS UART
.hps_0_hps_io_hps_io_uart0_inst_RX (HPS_UART_RX), // .hps_io_uart0_inst_RX
.hps_0_hps_io_hps_io_uart0_inst_TX (HPS_UART_TX), // .hps_io_uart0_inst_TX
.hps_0_hps_io_hps_io_gpio_inst_GPIO35 (HPS_ENET_INT_n), // .hps_io_gpio_inst_GPIO35
.hps_0_hps_io_hps_io_gpio_inst_GPIO44 (HPS_EMMC_SEL), // .hps_io_gpio_inst_GPIO44
.hps_0_h2f_reset_reset_n (hps_fpga_reset_n), // hps_0_h2f_reset.reset_n
.hps_0_f2h_cold_reset_req_reset_n (1'b1), // hps_0_f2h_cold_reset_req.reset_n
.hps_0_f2h_debug_reset_req_reset_n (1'b1), // hps_0_f2h_debug_reset_req.reset_n
.hps_0_f2h_warm_reset_req_reset_n (1'b1), // hps_0_f2h_warm_reset_req.reset_n
// pio_led
// .pio_led_external_connection_export (LED), // pio_led_external_connection.export
// pio_key
// .pio_key_external_connection_export (KEY) // pio_key_external_connection.export
// pwm
.pwm_conduit_wire (pwm) // pwm_conduit.wire
);
endmodule
5、 ... and 、C Language implementation
To write C The language code
//gcc Standard header file
#include <stdio.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <sys/mman.h>
//HPS The underlying definition header file provided by the manufacturer
#define soc_cv_av // Development platform Cyclone V series
#include "hwlib.h"
#include "socal/socal.h"
#include "socal/hps.h"
// Specific to the user HPS Hardware description header file related to the application system
#include "hps_0.h"
#define HW_REGS_BASE (ALT_STM_OFST) //HPS Peripheral address segment base address
#define HW_REGS_SPAN (0x04000000) //HPS Peripheral address segment address space 64MB size
#define HW_REGS_MASK (HW_REGS_SPAN - 1) //HPS Peripheral address field address mask
static volatile unsigned long *my_pwm = NULL;
//fpga initialization
int fpga_init(int *virtual_base)
{
int fd;
void *perph_virtual_base;
//1.open open mmu
fd = open("/dev/mem",(O_RDWR | O_SYNC));
if(fd == -1)
{
printf("open failed..\n");
exit(1);
}
//mmap Mapping virtual addresses
perph_virtual_base = mmap(NULL,HW_REGS_SPAN, ( PROT_READ | PROT_WRITE ),MAP_SHARED,fd,HW_REGS_BASE);
if(perph_virtual_base == MAP_SHARED)
{
printf("mmap() is failed..\n");
return 1;
}
// Interface
my_pwm = perph_virtual_base + ((unsigned long)(ALT_LWFPGASLVS_OFST + PWM_BASE) & (unsigned long)(HW_REGS_MASK));
// Save virtual address
*virtual_base = perph_virtual_base;
return fd;
}
int main()
{
int virtual_base;
int fd;
fd = fpga_init(&virtual_base);
int tmp = -0xffff;
// Open enable
*(my_pwm + 2) = 0x1;
*(my_pwm + 0) = 65536;// 65536
while(1)
{
tmp = tmp + 10;
if(tmp > 65536)
{
tmp = -65536;
}
else if(tmp > 0)
{
*(my_pwm + 1) = tmp;
}
else
{
*(my_pwm + 1) = -tmp;
}
usleep(150);
}
// Unmapping address
if(munmap(virtual_base,HW_REGS_SPAN) != 0)
{
printf("munmap() is failed..\n");
close(fd);
return 1;
}
close(fd);
return 0;
}
6、 ... and 、 Execution effect
It's not convenient to shoot here , It's the effect of breathing lamp
7、 ... and 、 summary
Follow the teacher step by step , Some don't quite understand
边栏推荐
- Qtthread, one of many methods of QT multithreading
- 每秒10W次分词搜索,产品经理又提了一个需求!!!(收藏)
- Go语学习笔记 - gorm使用 - 原生sql、命名参数、Rows、ToSQL | Web框架Gin(九)
- Find duplicate email addresses
- 外设驱动库开发笔记43:GPIO模拟SPI驱动
- Cloud acceleration helps you effectively solve attack problems!
- 360织语发布7.0新品 为党政军、央国企打造专属“统一数字工作空间”
- The boss always asks me about my progress. Don't you trust me? (what do you think)
- @Detailed differences between pathvariable and @requestparam
- 980. Different path III DFS
猜你喜欢
一名普通学生的大一总结【不知我等是愚是狂,唯知一路向前奔驰】
Find duplicate email addresses
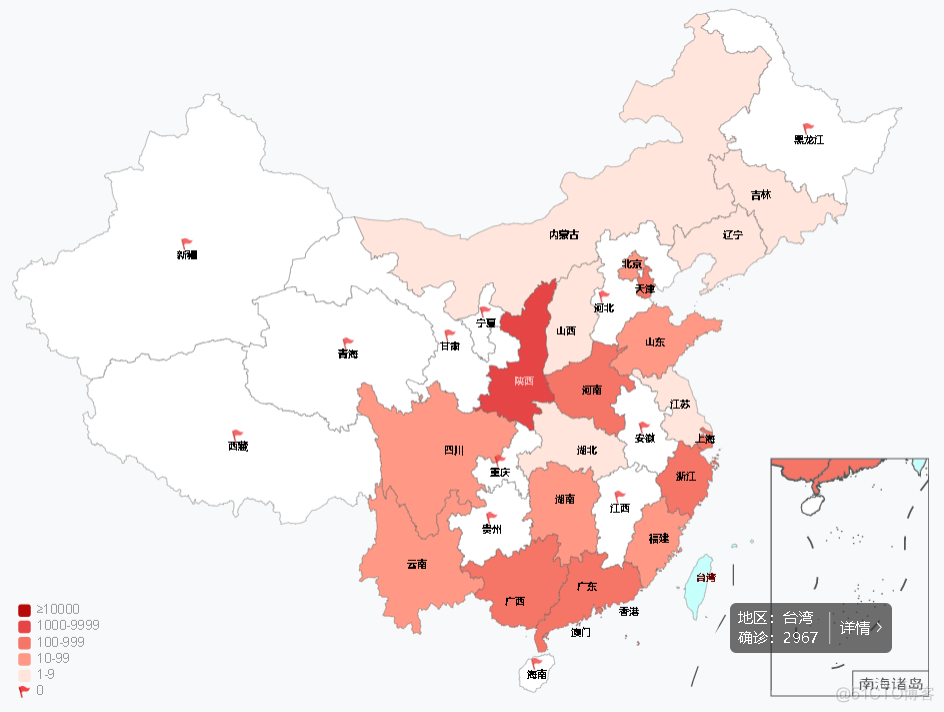
【SQL实战】一条SQL统计全国各地疫情分布情况

JVM命令之 jstack:打印JVM中线程快照
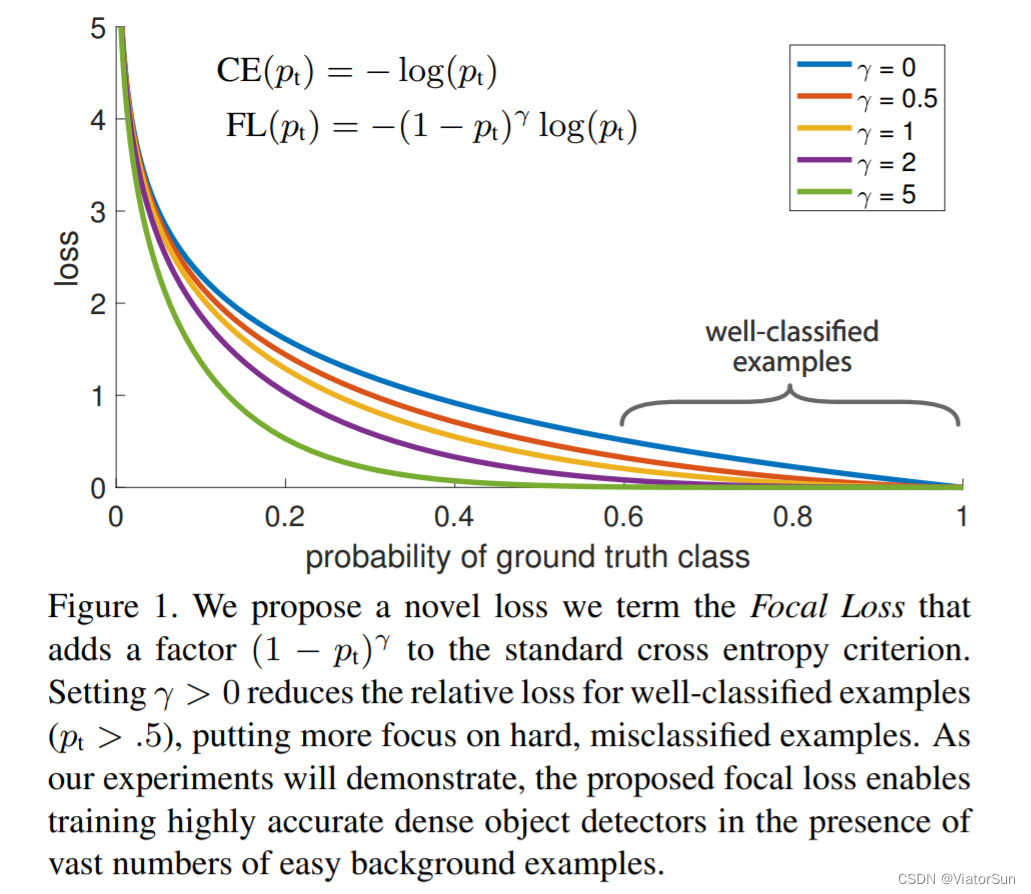
「解析」FocalLoss 解决数据不平衡问题
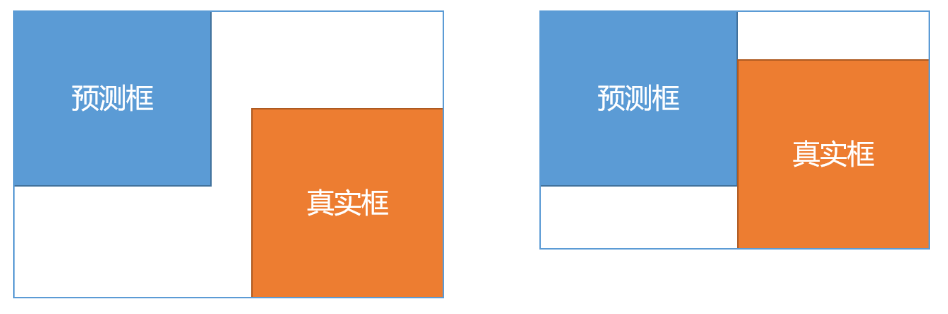
Bbox regression loss function in target detection -l2, smooth L1, IOU, giou, Diou, ciou, focal eiou, alpha IOU, Siou
JVM命令之 jinfo:实时查看和修改JVM配置参数
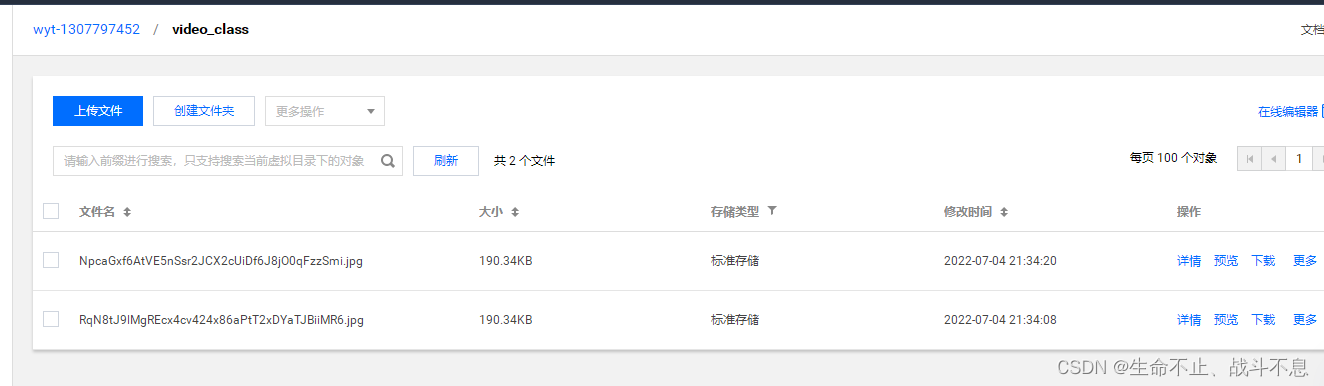
Laravel uses Tencent cloud cos5 full tutorial
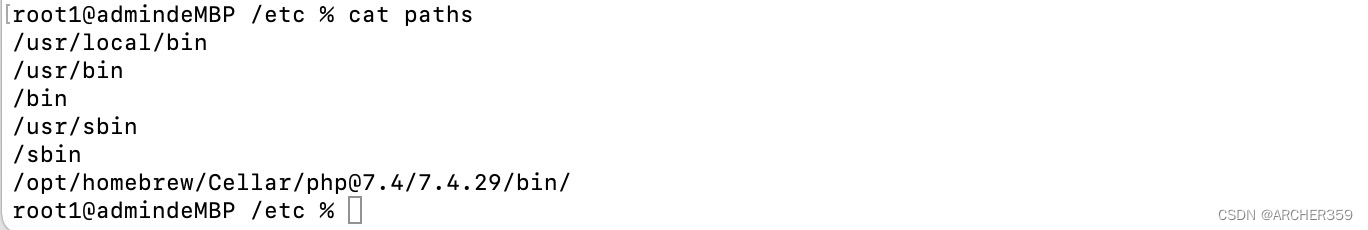
Mac version PHP installed Xdebug environment (M1 version)
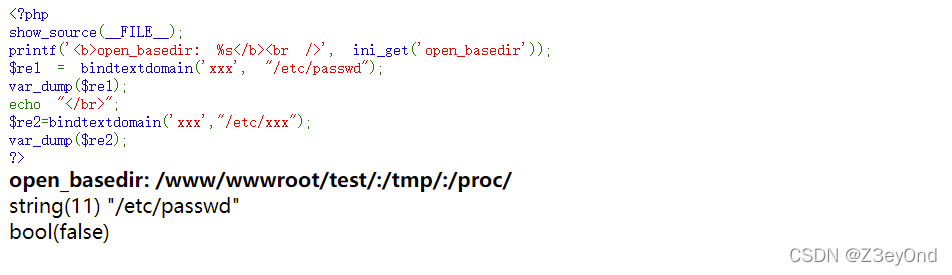
Bypass open_ basedir
随机推荐
Rk3399 platform development series explanation (WiFi) 5.53, hostapd (WiFi AP mode) configuration file description
How much do you know about clothing ERP?
苹果cms V10模板/MXone Pro自适应影视电影网站模板
Data storage 3
每秒10W次分词搜索,产品经理又提了一个需求!!!(收藏)
Laravel uses Tencent cloud cos5 full tutorial
Rk3399 platform development series explanation (WiFi) 5.52. Introduction to WiFi framework composition
C. colonne Swapping [tri + Simulation]
[SQL practice] a SQL statistics of epidemic distribution across the country
Redisl garbled code and expiration time configuration
PowerPivot - DAX (function)
Classic questions about data storage
3531. Huffman tree
绕过open_basedir
window下面如何安装swoole
k8s运行oracle
Qt多线程的多种方法之一 QThread
PTA 天梯赛练习题集 L2-003 月饼 测试点2,测试点3分析
Chain storage of stack
yarn入门(一篇就够了)