当前位置:网站首页>吴恩达机器学习课后习题——线性回归
吴恩达机器学习课后习题——线性回归
2022-07-26 04:10:00 【一舟yz】
单变量线性回归
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
path = "ex1data1.txt"
data = pd.read_csv(path, header=None, names=['Population', 'Profit'])
# pandas.read_csv默认情况下会把数据内容的第一行默认为字段名标题,header=None指明读取的原始文件数据没有列索引
data.head() # 方法用于返回数据帧或序列的前n行(默认值为5)。返回类型:DataFrame,可理解为一个表格,或者说矩阵
# DataFrame本质上是二维矩阵,跟常规二维矩阵的差别在于前者额外指定了每一行和每一列的名称。
| Population | Profit | |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | 6.1101 | 17.5920 |
| 1 | 5.5277 | 9.1302 |
| 2 | 8.5186 | 13.6620 |
| 3 | 7.0032 | 11.8540 |
| 4 | 5.8598 | 6.8233 |
data.describe()
# describe() 函数可以查看数据的基本情况,
# 包括:count 非空值数、mean 平均值、std 标准差、max 最大值、min 最小值、(25%、50%、75%)分位数等。
| Population | Profit | |
|---|---|---|
| count | 97.000000 | 97.000000 |
| mean | 8.159800 | 5.839135 |
| std | 3.869884 | 5.510262 |
| min | 5.026900 | -2.680700 |
| 25% | 5.707700 | 1.986900 |
| 50% | 6.589400 | 4.562300 |
| 75% | 8.578100 | 7.046700 |
| max | 22.203000 | 24.147000 |
# 画出图形
data.plot(kind='scatter',x='Population',y='Profit',figsize=(12,8))
# scatter表示散点图,figsize表示图片大小,单位:英寸
plt.show()

使用梯度下降来最小化代价函数,
创建一个以参数θ为特征函数的代价函数
J ( θ ) = 1 2 m ∑ i = 1 m ( h θ ( x ( i ) ) − y ( i ) ) 2 J\left( \theta \right)=\frac{1}{2m}\sum\limits_{i=1}^{m}{ { {\left( { {h}_{\theta }}\left( { {x}^{(i)}} \right)-{ {y}^{(i)}} \right)}^{2}}} J(θ)=2m1i=1∑m(hθ(x(i))−y(i))2
其中:
h θ ( x ) = θ T X = θ 0 x 0 + θ 1 x 1 + θ 2 x 2 + . . . + θ n x n { {h}_{\theta }}\left( x \right)={ {\theta }^{T}}X={ {\theta }_{0}}{ {x}_{0}}+{ {\theta }_{1}}{ {x}_{1}}+{ {\theta }_{2}}{ {x}_{2}}+...+{ {\theta }_{n}}{ {x}_{n}}\\ hθ(x)=θTX=θ0x0+θ1x1+θ2x2+...+θnxn
def computeCost(X,y,theta): # 输入X是列向量,y也是列向量,theta是行向量
inner = np.power(((X*theta.T)-y),2) # x*θ的转置就是假设函数 power函数计算numpy数组中每个数值的指定幂次
return np.sum(inner/(2*len(X))) # 将数组/矩阵中的元素全部加起来 len(X)矩阵行数
data.insert(0,'Ones',1)
# 插入一列为1是为了更好的向量化,需要在训练集中添加一列x_0,以便我们可以使用向量化的解决方案来计算代价和梯度,见视频p18
# 变量的初始化
cols = data.shape[1] # shape[0]是行数 shape[1]是列数
X = data.iloc[:,0:cols-1] # 数据集 行全要 列从0到cols-1(不包括) 左闭右开
y = data.iloc[:,cols-1:cols] # 目标值
X.head()
| Ones | Population | |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | 1 | 6.1101 |
| 1 | 1 | 5.5277 |
| 2 | 1 | 8.5186 |
| 3 | 1 | 7.0032 |
| 4 | 1 | 5.8598 |
获取的数据类型是DataFrame类型,所以需要进行类型转换。同时还需要初始化theta,即theta所有元素都设置为0
X = np.matrix(X.values)
y = np.matrix(y.values)
theta = np.matrix(np.array([0,0]))
维度
X.shape, theta.shape, y.shape
((97, 2), (1, 2), (97, 1))
computeCost(X,y,theta) #计算代价函数
32.072733877455676
batch gradient decent(批量梯度下降)
θ j : = θ j − α ∂ ∂ θ j J ( θ ) { {\theta }_{j}}:={ {\theta }_{j}}-\alpha \frac{\partial }{\partial { {\theta }_{j}}}J\left( \theta \right) θj:=θj−α∂θj∂J(θ)
梯度下降
def gradientDescent(X,y,theta,alpha,iters): # iters是迭代次数 alpha是学习率 即步长
temp_theta = np.matrix(np.zeros(theta.shape)) # 零值矩阵 暂存theta
parameters = int(theta.ravel().shape[1]) # ravel计算需要求解的参数个数 功能将多维数组降至一维 这里值为2
cost = np.zeros(iters) #构建iters个0的数组
#迭代:
for i in range(iters):
difference = (X*theta.T) - y # 差值
for j in range(parameters):
term = np.multiply(difference,X[:,j]) #乘以x_i X[:,j]表示所有行 j列,简言之就是抽出第j列
# 注意这里就不是矩阵乘法了 这里是求导后要求乘的 multiply是两个相同大小矩阵对应位置的数直接相乘
temp_theta[0,j] = theta[0,j] - (alpha/len(X))*np.sum(term) # 更新theta_j
theta = temp_theta # 更新全部theta值
cost[i] = computeCost(X,y,theta) # 更新代价值
return theta,cost
初始化一些附加变量 - 学习速率α和要执行的迭代次数。
alpha = 0.01
iters = 1000
获取theta值,代价最小值
g,cost = gradientDescent(X,y,theta,alpha,iters)
g
matrix([[-3.24140214, 1.1272942 ]])
cost[-1] # 获取数组的最后一个值
4.515955503078913
最后,用我们拟合过的theta值计算训练模型的代价函数
computeCost(X, y, g)
4.515955503078913
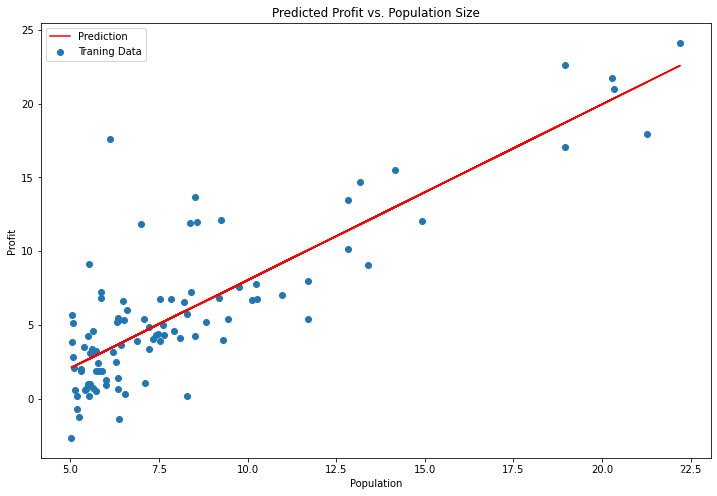
绘制线性模型以及数据,直观地看出它的拟合
x = np.linspace(data.Population.min(), data.Population.max(), 100) # 生成指定范围内指定个数的一维数组
f = g[0, 0] + (g[0, 1] * x) # x1=1 g[0, 0]表示theta_0 g[0, 1]表示theta_1
fig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(12,8)) # plt.subplot()函数用于直接指定划分方式和位置进行绘图。
# fig代表绘图窗口(Figure);ax代表这个绘图窗口上的坐标系(axis),一般会继续对ax进行操作。
# 设置横纵坐标的函数,并设置颜色为红色,在图标上标上'Prediction'标签 横坐标x 纵坐标f
ax.plot(x, f, 'r', label='Prediction')
# 定义散点图的横纵坐标,并给出散点图点的'Traning Data'标签名
ax.scatter(data.Population, data.Profit, label='Traning Data')
ax.legend(loc=2) # 2表示在左上角
ax.set_xlabel('Population')
ax.set_ylabel('Profit')
ax.set_title('Predicted Profit vs. Population Size')
plt.show()

由于梯度方程式函数也在每个训练迭代中输出一个代价的向量,所以我们也可以绘制。 注意,代价总是降低
fig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(12,8))
ax.plot(np.arange(iters), cost, 'r')
ax.set_xlabel('Iterations')
ax.set_ylabel('Cost')
ax.set_title('Error vs. Training Epoch')
plt.show()

多变量的线性回归
该练习包括一个房屋价格数据集,其中包含两个变量(房屋大小、卧室数量)和目标(房子价格)。
path = 'ex1data2.txt'
data2 = pd.read_csv(path, header=None, names=['Size', 'Bedrooms', 'Price'])
data2.head()
| Size | Bedrooms | Price | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 2104 | 3 | 399900 |
| 1 | 1600 | 3 | 329900 |
| 2 | 2400 | 3 | 369000 |
| 3 | 1416 | 2 | 232000 |
| 4 | 3000 | 4 | 539900 |
data2.describe()
| Size | Bedrooms | Price | |
|---|---|---|---|
| count | 47.000000 | 47.000000 | 47.000000 |
| mean | 2000.680851 | 3.170213 | 340412.659574 |
| std | 794.702354 | 0.760982 | 125039.899586 |
| min | 852.000000 | 1.000000 | 169900.000000 |
| 25% | 1432.000000 | 3.000000 | 249900.000000 |
| 50% | 1888.000000 | 3.000000 | 299900.000000 |
| 75% | 2269.000000 | 4.000000 | 384450.000000 |
| max | 4478.000000 | 5.000000 | 699900.000000 |
房屋大小约为卧室数量的1000倍。当特征相差几个数量级时,首先执行特征缩放(均值归一化)可以使梯度下降更快地收敛。
data2 = (data2 - data2.mean()) / data2.std() # 解决的方法是尝试将所有特征尺度都尽量缩放到 -1 ~ 1
data2.head()
| Size | Bedrooms | Price | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0.130010 | -0.223675 | 0.475747 |
| 1 | -0.504190 | -0.223675 | -0.084074 |
| 2 | 0.502476 | -0.223675 | 0.228626 |
| 3 | -0.735723 | -1.537767 | -0.867025 |
| 4 | 1.257476 | 1.090417 | 1.595389 |
data2.insert(0, 'Ones', 1)
cols = data2.shape[1]
X2 = data2.iloc[:,0:cols-1]
y2 = data2.iloc[:,cols-1:cols]
X2 = np.matrix(X2.values)
y2 = np.matrix(y2.values)
theta2 = np.matrix(np.array([0,0,0]))
g2, cost2 = gradientDescent(X2, y2, theta2, alpha, iters)
computeCost(X2, y2, g2) # 计算代价
0.1307033696077189
代价函数收敛图
fig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(12,8))
ax.plot(np.arange(iters), cost2, 'r')
ax.set_xlabel('Iterations')
ax.set_ylabel('Cost')
ax.set_title('Error vs. Training Epoch')
plt.show()

使用sklearn线性回归函数简化过程
from sklearn import linear_model
model = linear_model.LinearRegression() #基于最小二乘法的线性回归。
model.fit(X, y)
x = np.array(X[:, 1].A1)
f = model.predict(X).flatten()
fig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(12,8))
ax.plot(x, f, 'r', label='Prediction')
ax.scatter(data.Population, data.Profit, label='Traning Data')
ax.legend(loc=2)
ax.set_xlabel('Population')
ax.set_ylabel('Profit')
ax.set_title('Predicted Profit vs. Population Size')
plt.show()
normal equation(正规方程)
思路
正规方程是通过求解下面的方程来找出使得代价函数最小的参数的: ∂ ∂ θ j J ( θ j ) = 0 \frac{\partial }{\partial { {\theta }_{j}}}J\left( { {\theta }_{j}} \right)=0 ∂θj∂J(θj)=0 。
假设我们的训练集特征矩阵为 X(包含了 x 0 = 1 { {x}_{0}}=1 x0=1)并且我们的训练集结果为向量 y,则利用正规方程解出向量 θ = ( X T X ) − 1 X T y \theta ={ {\left( { {X}^{T}}X \right)}^{-1}}{ {X}^{T}}y θ=(XTX)−1XTy 。
上标T代表矩阵转置,上标-1 代表矩阵的逆。设矩阵 A = X T X A={ {X}^{T}}X A=XTX,则: ( X T X ) − 1 = A − 1 { {\left( { {X}^{T}}X \right)}^{-1}}={ {A}^{-1}} (XTX)−1=A−1
梯度下降与正规方程的比较:
梯度下降:需要选择学习率α,需要多次迭代,当特征数量n大时也能较好适用,适用于各种类型的模型
正规方程:不需要选择学习率α,一次计算得出,需要计算 ( X T X ) − 1 { {\left( { {X}^{T}}X \right)}^{-1}} (XTX)−1,如果特征数量n较大则运算代价大,因为矩阵逆的计算时间复杂度为 O ( n 3 ) O(n3) O(n3),通常来说当 n n n小于10000 时还是可以接受的,只适用于线性模型,不适合逻辑回归模型等其他模型
# 正规方程函数
def normalEqn(X, y):
theta = np.linalg.inv(X.[email protected])@X.[email protected]#[email protected]等价于X.T.dot(X) np.linalg.inv():矩阵求逆
return theta
final_theta2=normalEqn(X, y)
final_theta2 # 梯度matrix([[-3.24140214, 1.1272942 ]])
matrix([[-3.89578088],
[ 1.19303364]])
边栏推荐
- What model is good for the analysis of influencing factors?
- Constructing verb sources for relation extraction
- Worked overtime for a week to develop a reporting system. This low code free it reporting artifact is very easy to use
- Chinese database oceanbase was selected into the Forrester translational data platform report
- PHP implements the algorithm of adding from 1 to 100
- Laravel8 implements interface authentication encapsulation using JWT
- Dynamic planning for stair climbing
- `Oi problem solving ` ` leetcode '2040. The k-th minor product of two ordered arrays
- Overview of wavelet packet transform methods
- sorting and searching 二分查找法
猜你喜欢
STM32状态机编程实例——全自动洗衣机(下)

荐书丨《教育心理学》:送给明日教师的一本书~

Apple removed the last Intel chip from its products

在 Istio 服务网格内连接外部 MySQL 数据库

2021 CIKM |GF-VAE: A Flow-based Variational Autoencoder for Molecule Generation

STM32 state machine programming example - full automatic washing machine (Part 2)
![Matrix and Gauss elimination [matrix multiplication, Gauss elimination, solving linear equations, solving determinants] the most detailed in the whole network, with examples and sister chapters of 130](/img/84/e5cb5199fe4602440b50dfc4afe963.gif)
Matrix and Gauss elimination [matrix multiplication, Gauss elimination, solving linear equations, solving determinants] the most detailed in the whole network, with examples and sister chapters of 130

荐书|《DBT技巧训练手册》:宝贝,你就是你活着的原因

How to build an enterprise level OLAP data engine for massive data and high real-time requirements?

2021 CIKM |GF-VAE: A Flow-based Variational Autoencoder for Molecule Generation
随机推荐
基于移位寄存器的同步FIFO
php 保存数组到文件 var_export、serialize
软考 系统架构设计师 简明教程 | 案例分析解题技巧
Operator new, operator delete supplementary handouts
Can't the container run? The Internet doesn't have to carry the blame
Where does international crude oil open an account, a formal, safe and secure platform
华为再发“天才少年”全球召集令,有人曾放弃360万年薪加入
荐书 |《学者的术与道》:写论文是门手艺
Find my technology | the Internet of things asset tracking market has reached US $6.6 billion, and find my helps the market develop
《opencv学习笔记》-- 边缘检测和canny算子、sobel算子、LapIacian 算子、scharr滤波器
Basic line chart: the most intuitive presentation of data trends and changes
2021 CIKM |GF-VAE: A Flow-based Variational Autoencoder for Molecule Generation
Worked overtime for a week to develop a reporting system. This low code free it reporting artifact is very easy to use
php eval() 函数可以将一个字符串当做 php 代码来运行
Write a paper for help, how to write the discussion part?
Educational Codeforces Round 132 (Rated for Div. 2) E. XOR Tree
规则引擎Drools的使用
How engineers treat open source -- the heartfelt words of an old engineer
Basic principles of iptables
座椅/安全配置升级 新款沃尔沃S90行政体验到位了吗